Korean Circ J.
2016 Jan;46(1):93-98. 10.4070/kcj.2016.46.1.93.
Isoproterenol Enhances Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand-Induced Apoptosis in Human Embryonic Kidney Cells through Death Receptor 5 up-Regulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cell Therapy and Tissue Engineering Center, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea.
- 2Cardiology Division, Department of Internal Medicine, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea. yubs@yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2223774
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2016.46.1.93
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Chronic impairment of beta-adrenergic receptor signaling increases cardiac apoptosis, hypertrophy and fibrosis. The aim of this study was to investigate whether isoproterenol (ISO), an agonist of the adrenergic receptor, can enhance tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
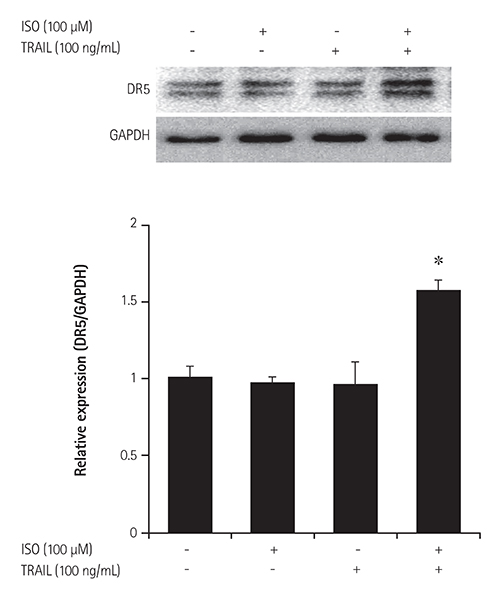
HEK 293 cells were treated with ISO and/or TRAIL for 24 hours. Cell viability was evaluated by microscopy and an established viability assay, and apoptotic cell death was analyzed by staining with fluorescein isothiocynate-annexin-V/propidium iodide (PI) and caspase activation. To confirm the mechanism of cell death induced by co-treatment with ISO and TRAIL, expression of TRAIL receptor 2 (death receptor 5, DR5) was evaluated by immunoblotting.
RESULTS
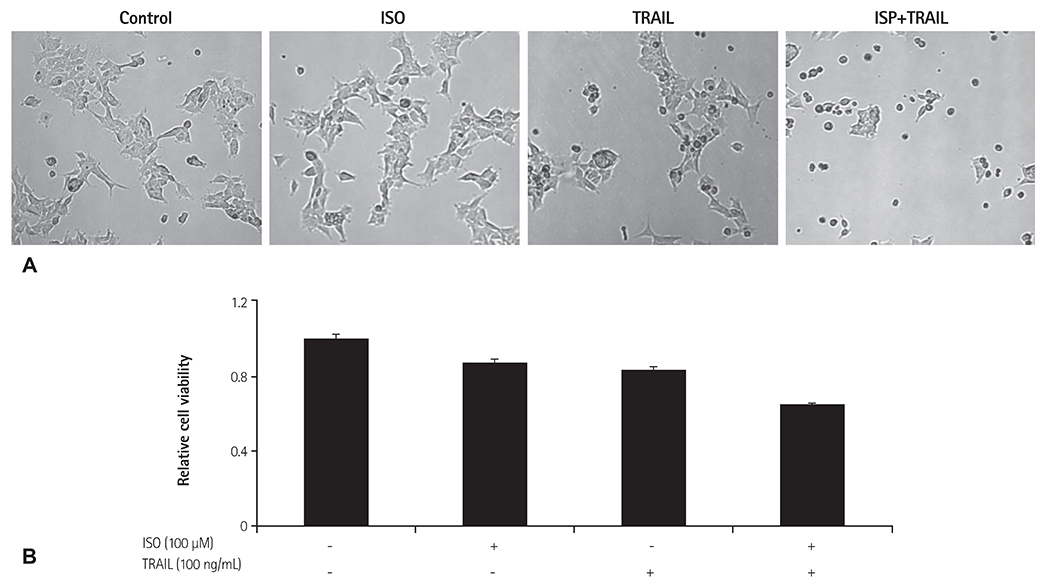
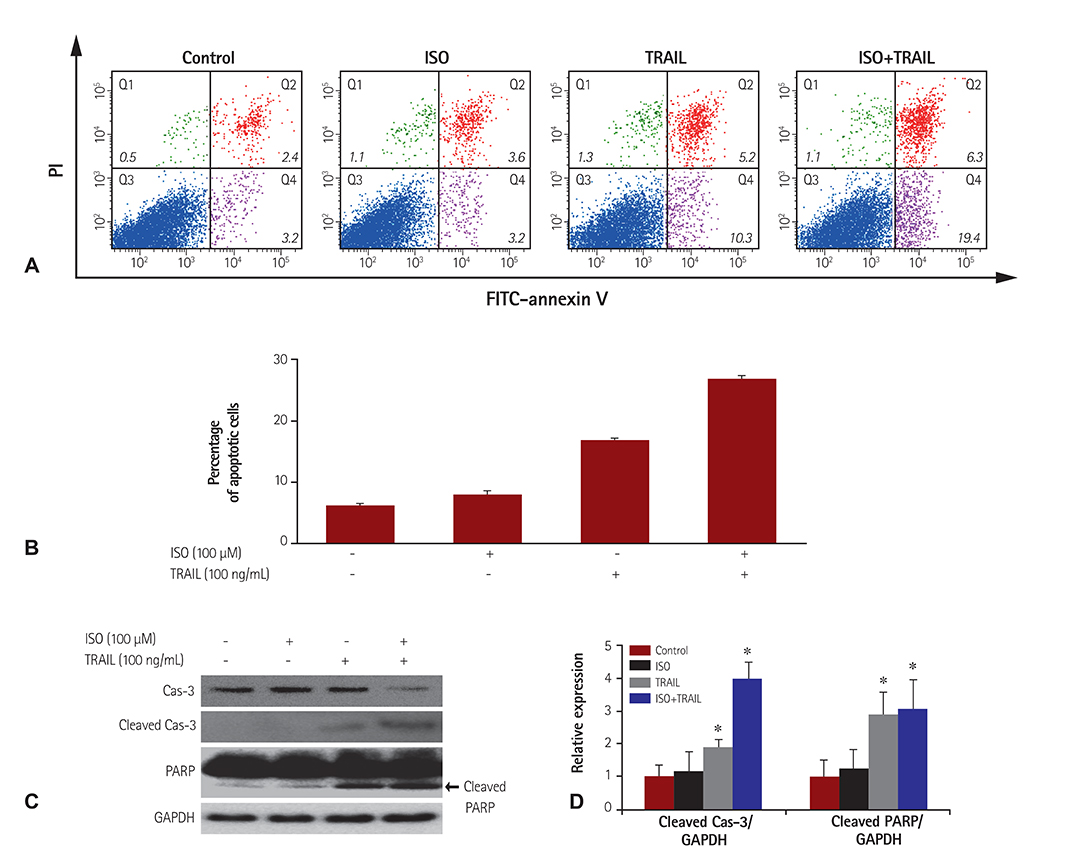
Although ISO or TRAIL treatment decreased HEK 293 cell viability by 13% and 17%, respectively, co-treatment with ISO and TRAIL resulted in a markedly higher death rate of 35% after 24 hours. Increases were evident in early apoptotic cells (i.e., annexin-V positive/PI negative; 19.4%), late apoptotic cells (i.e., annexin-V positive/PI positive; 6.3%) and dead cells (i.e., annexin-V negative/PI positive; 1.1%) when cells were co-treated with ISO and TRAIL, compared to cells treated with either ISO or TRAIL. In addition, marked increases of cleaved cas-3, cleaved poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase and DR5 were observed in HEK 293 cells co-treated with ISO and TRAIL.
CONCLUSION
Treatments combining ISO with TRAIL may be responsible for death of HEK 293 cells through DR5 up-regulation. Activation of adrenergic receptors is responsible for the synergistic cell death observed with TRAIL.
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis*
Cell Death
Cell Survival
Fibrosis
Fluorescein
HEK293 Cells
Humans*
Hypertrophy
Immunoblotting
Isoproterenol*
Kidney*
Microscopy
Mortality
Necrosis*
Receptors, Adrenergic
Receptors, TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand*
TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand
Up-Regulation*
Fluorescein
Isoproterenol
Receptors, Adrenergic
Receptors, TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand
TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand
Figure
Reference
-
1. Whelan RS, Kaplinskiy V, Kitsis RN. Cell death in the pathogenesis of heart disease: mechanisms and significance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2010; 72:19–44.2. Zauli G, Secchiero P. The role of the TRAIL/TRAIL receptors system in hematopoiesis and endothelial cell biology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006; 17:245–257.3. Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Apoptosis control by death and decoy receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999; 11:255–260.4. Galligan L, Longley DB, McEwan M, Wilson TR, McLaughlin K, Johnston PG. Chemotherapy and TRAIL-mediated colon cancer cell death: the roles of p53, TRAIL receptors, and c-FLIP. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005; 4:2026–2036.5. Kim Y, Seol DW. TRAIL, a mighty apoptosis inducer. Mol Cells. 2003; 15:283–293.6. Ashkenazi A. Targeting death and decoy receptors of the tumour-necrosis factor superfamily. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002; 2:420–430.7. Wilson NS, Dixit V, Ashkenazi A. Death receptor signal transducers: nodes of coordination in immune signaling networks. Nat Immunol. 2009; 10:348–355.8. Yamaguchi H, Wang HG. CHOP is involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by enhancing DR5 expression in human carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:45495–45502.9. Naga Prasad SV, Nienaber J, Rockman HA. Beta-adrenergic axis and heart disease. Trends Genet. 2001; 17:S44–S49.10. Engelhardt S, Hein L, Wiesmann F, Lohse MJ. Progressive hypertrophy and heart failure in beta1-adrenergic receptor transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:7059–7064.11. Houser SR, Margulies KB, Murphy AM, et al. Animal models of heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Res. 2012; 111:131–150.12. Communal C, Singh K, Pimentel DR, Colucci WS. Norepinephrine stimulates apoptosis in adult rat ventricular myocytes by activation of the beta-adrenergic pathway. Circulation. 1998; 98:1329–1334.13. Zaugg M, Xu W, Lucchinetti E, Shafiq SA, Jamali NZ, Siddiqui MA. Beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes differentially affect apoptosis in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Circulation. 2000; 102:344–350.14. Liu JJ, Li DL, Zhou J, et al. Acetylcholine prevents angiotensin IIinduced oxidative stress and apoptosis in H9c2 cells. Apoptosis. 2011; 16:94–103.15. Groenning BA, Nilsson JC, Sondergaard L, Fritz-Hansen T, Larsson HB, Hildebrandt PR. Antiremodeling effects on the left ventricle during beta-blockade with metoprolol in the treatment of chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000; 36:2072–2080.16. Park JB, Lee JS, Cho BP, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured at high cell density express brain-derived neurotrophic factor and exert neuroprotective effects in a 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson's disease. Genes Genom. 2015; 37:213–221.17. Shetty S, Gladden JB, Henson ES, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) up-regulates death receptor 5 (DR5) mediated by NFkappaB activation in epithelial derived cell lines. Apoptosis. 2002; 7:413–420.18. Fanger NA, Maliszewski CR, Schooley K, Griffith TS. Human dendritic cells mediate cellular apoptosis via tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). J Exp Med. 1999; 190:1155–1164.19. Griffith TS, Wiley SR, Kubin MZ, Sedger LM, Maliszewski CR, Fanger NA. Monocyte-mediated tumoricidal activity via the tumor necrosis factor-related cytokine, TRAIL. J Exp Med. 1999; 189:1343–1354.20. Kemp TJ, Moore JM, Griffith TS. Human B cells express functional TRAIL/Apo-2 ligand after CpG-containing oligodeoxynucleotide stimulation. J Immunol. 2004; 173:892–899.21. Zamai L, Ahmad M, Bennett IM, Azzoni L, Alnemri ES, Perussia B. Natural killer (NK) cell-mediated cytotoxicity: differential use of TRAIL and Fas ligand by immature and mature primary human NK cells. J Exp Med. 1998; 188:2375–2380.22. Cassatella MA, Huber V, Calzetti F, et al. Interferon-activated neutrophils store a TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL/Apo-2 ligand) intracellular pool that is readily mobilizable following exposure to proinflammatory mediators. J Leukoc Biol. 2006; 79:123–132.23. Koga Y, Matsuzaki A, Suminoe A, Hattori H, Hara T. Neutrophil-derived TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL): a novel mechanism of antitumor effect by neutrophils. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:1037–1043.24. Kemp TJ, Ludwig AT, Earel JK, et al. Neutrophil stimulation with Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) results in the release of functional soluble TRAIL/Apo-2L. Blood. 2005; 106:3474–3482.25. Simons MP, Leidal KG, Nauseef WM, Griffith TS. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is expressed throughout myeloid development, resulting in a broad distribution among neutrophil granules. J Leukoc Biol. 2008; 83:621–629.26. Murray DR, Prabhu SD, Chandrasekar B. Chronic beta-adrenergic stimulation induces myocardial proinflammatory cytokine expression. Circulation. 2000; 101:2338–2341.27. Liao X, Wang X, Gu Y, Chen Q, Chen LY. Involvement of death receptor signaling in mechanical stretch-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Life Sci. 2005; 77:160–174.28. Prasad S, Kim JH, Gupta SC, Aggarwal BB. Targeting death receptors for TRAIL by agents designed by Mother Nature. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014; 35:520–536.29. Lee MW, Park SC, Kim JH, et al. The involvement of oxidative stress in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells. Cancer Lett. 2002; 182:75–82.30. Chandel NS, Schumacker PT, Arch RH. Reactive oxygen species are downstream products of TRAF-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:42728–42736.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Involvement of Up-regulation of Death Receptors and Bim in Hispolon-mediated TNF-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand Sensitization in Human Renal Carcinoma
- Cytotoxic Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand (TRAIL)and its Molecular Mechanism in Human Gastric Cancer Cells
- Apoptosis and upregulation of TNF-alpha and TRAIL receptor 1 (DR4) in the pathogenesis of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome
- Bisphosphonate enhances TRAIL sensitivity to human osteosarcoma cells via death receptor 5 upregulation
- Up-regulation of the DR5 Expression by Proteasome Inhibitor MG132 Augments TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Soft Tissue Sarcoma Cell Lines