J Korean Soc Transplant.
2010 Mar;24(1):35-39. 10.4285/jkstn.2010.24.1.35.
A Case of Successful Treatment of Cutaneous Aspergillosis with Voriconazole at the Low Cyclosporine Trough Level in a Renal Transplant
- Affiliations
-
- 1Organ Transplantation Center, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. medipark@inje.ac.kr
- KMID: 2202222
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2010.24.1.35
Abstract
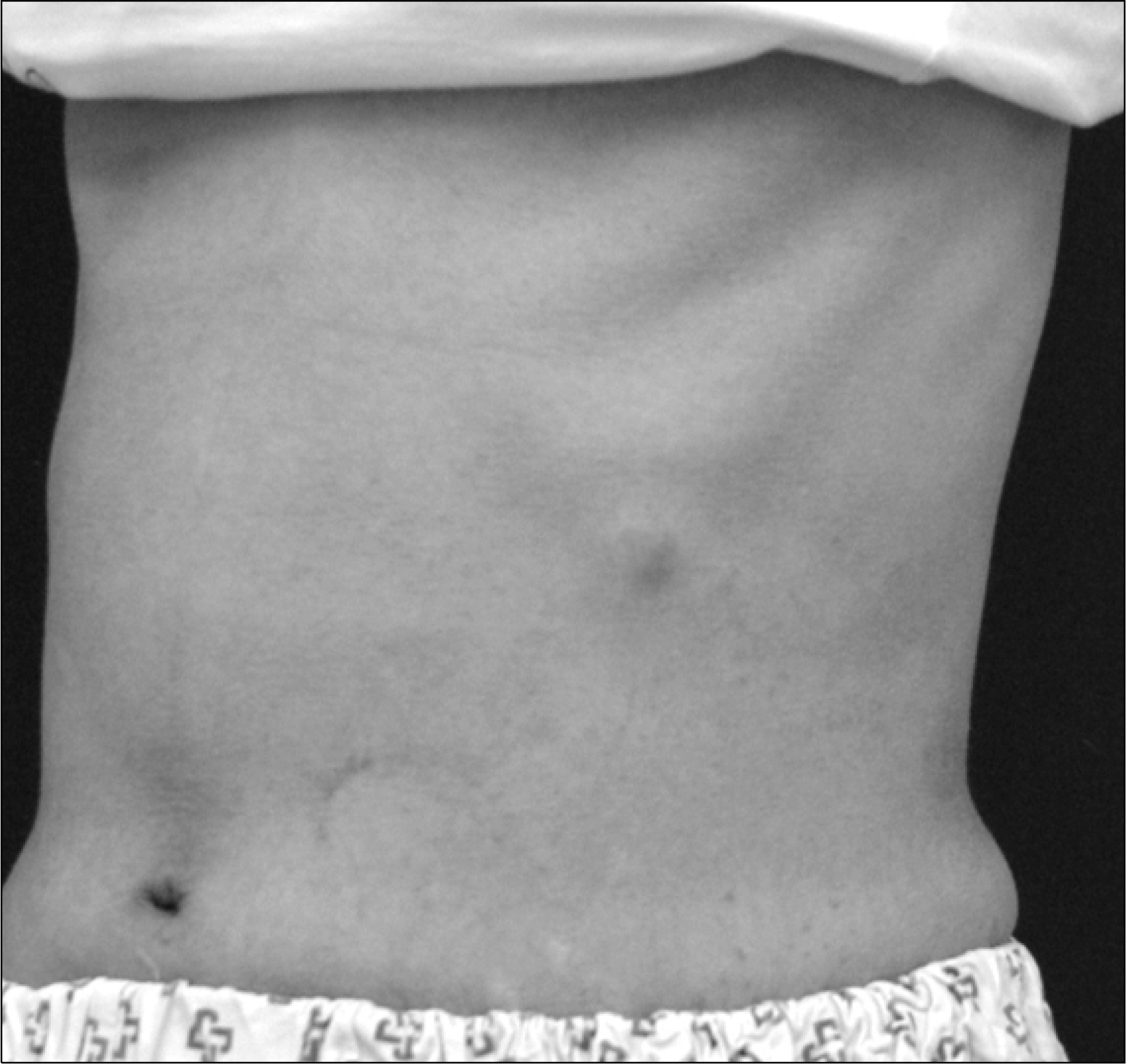
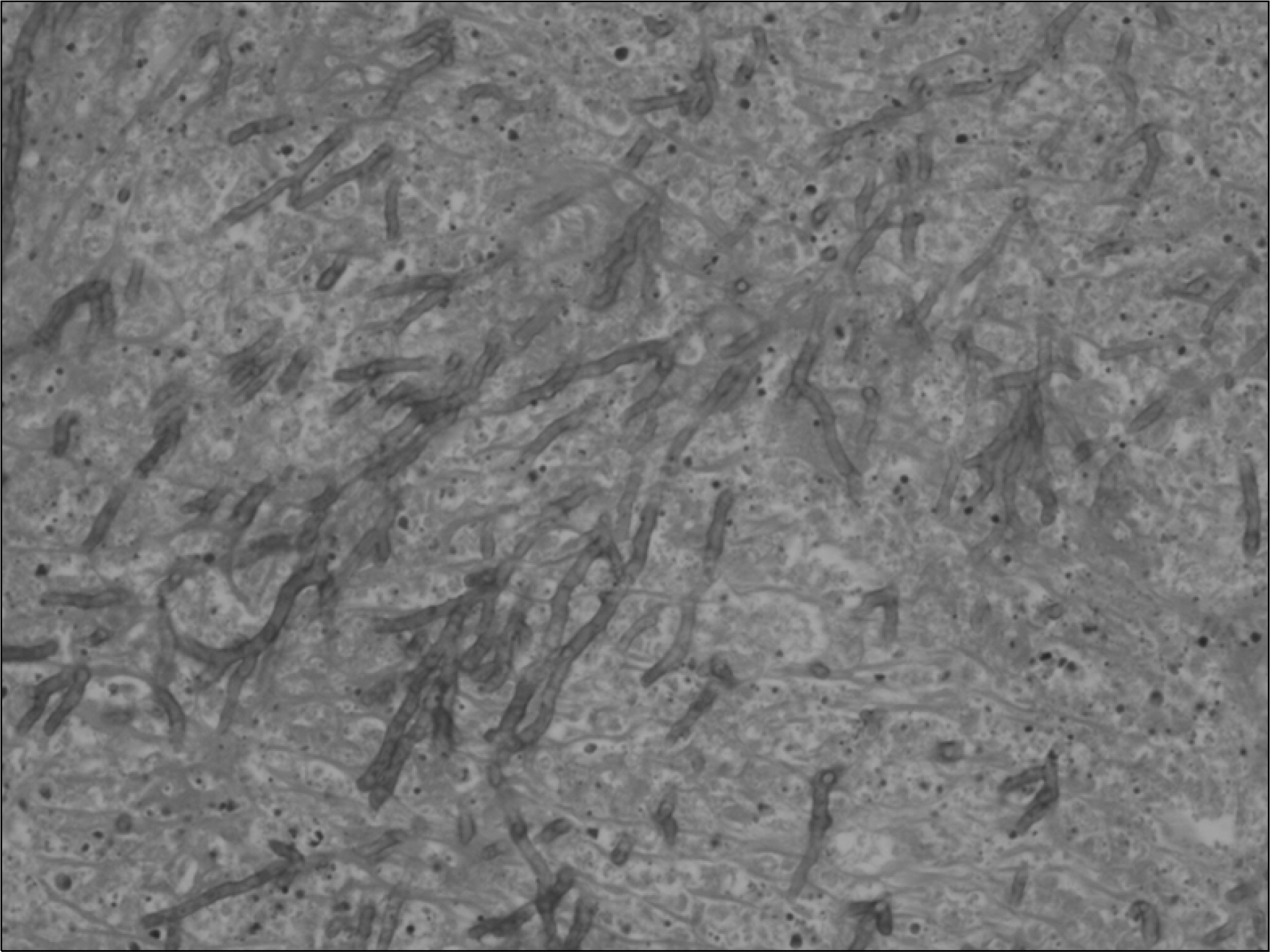
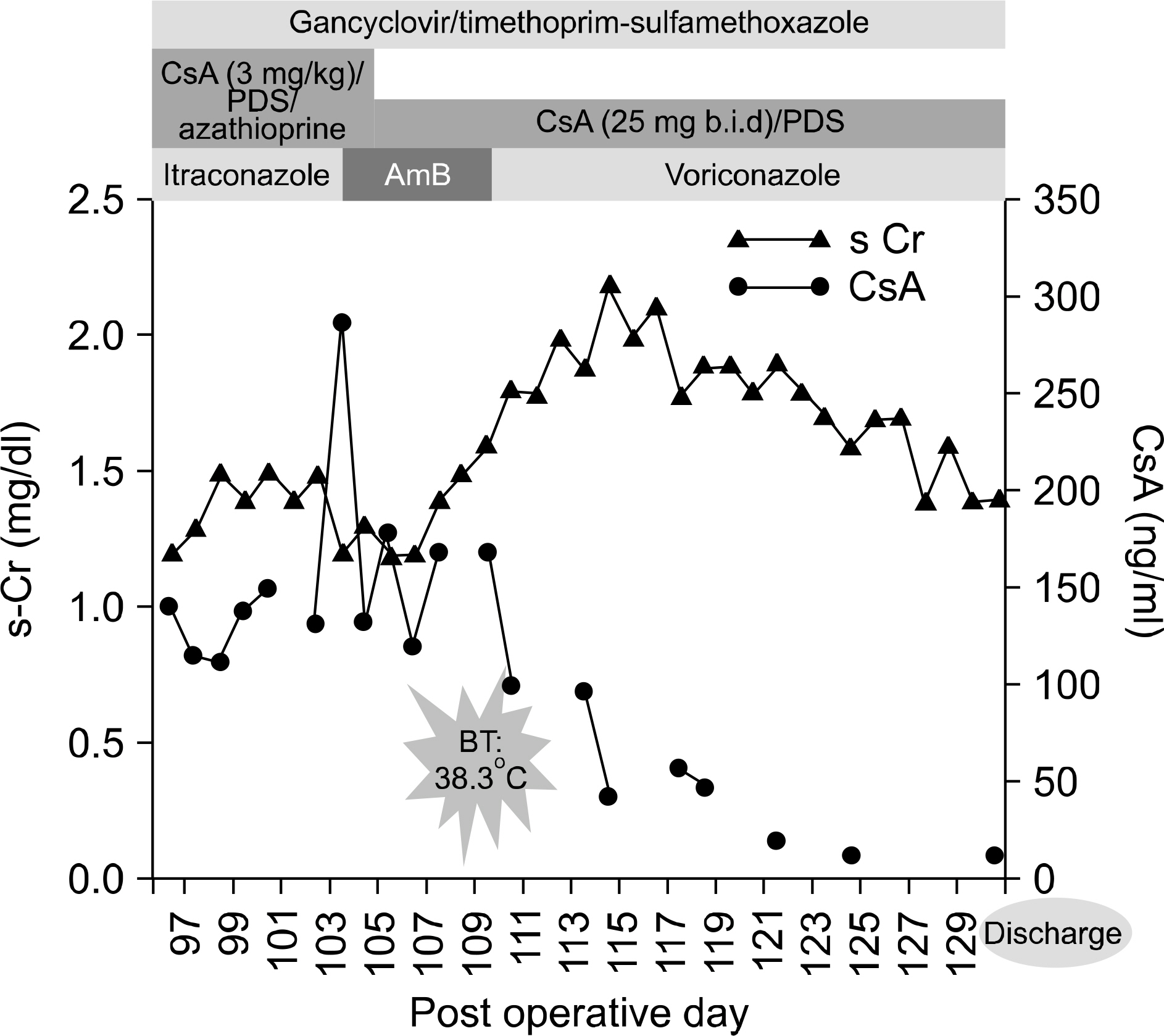
- Aspergillosis is a serious infectious complication with high mortality in transplant recipients. Voriconazole is a broad spectrum triazole antifungal agent, but it has a drug-drug interaction with immunosuppressants. Herein we report a case of the use of a small dose of cyclosporine (CsA) with coadministration of voriconazole. A 23 year old woman received a kidney transplant from a deceased donor. The initial immunosuppressant was tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, steroids, and basiliximab. Thirty-two days after kidney transplantation, because of hemolytic uremic syndrome, she received Rabbit anti-human thymocyte immunoglobulin and plasmapheresis. Cyclosporine was used instead of tacrolimus. Three months after transplantation, she was admitted to the hospital because of an erythematous nodule on her trunk and a dry cough. Skin biopsy revealed an Aspergillus species and tissue culture showed that it was A. fumigatus. We treated her with itraconazole and subsequently with amphotericin B. Afterwards, her condition got worse. So we changed amphotericin B to voriconazole and a minimum dose of CsA (25 mg bid) at the peril of graft failure. Eventually, she recovered and maintained good graft function. The trough level of CsA ranged from 3.2 to 27.9 ng/mL.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Amphotericin B
Antibodies, Monoclonal
Aspergillosis
Aspergillus
Biopsy
Cough
Cyclosporine
Female
Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome
Humans
Immunoglobulins
Immunosuppressive Agents
Itraconazole
Kidney
Kidney Transplantation
Mycophenolic Acid
P-Glycoprotein
Plasmapheresis
Pyrimidines
Recombinant Fusion Proteins
Skin
Steroids
Tacrolimus
Thymocytes
Tissue Donors
Transplants
Triazoles
Amphotericin B
Antibodies, Monoclonal
Cyclosporine
Immunoglobulins
Immunosuppressive Agents
Itraconazole
Mycophenolic Acid
P-Glycoprotein
Pyrimidines
Recombinant Fusion Proteins
Steroids
Tacrolimus
Triazoles
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Fatal Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis after Combined Induction with Rituximab and Antithymocyte Globulin for Kidney Transplantation in a Sensitized Recipient, and Early Rejection Therapy with Plasmapheresis and Low-dose Immunoglobulin
Da Wun Jeong, Sang-Ho Lee, Ju-Young Moon, Yang-Gyun Kim, Yu Ho Lee, Kipyo Kim, Hochul Park, Sun Hyung Joo
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2017;31(1):52-57. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2017.31.1.52.
Reference
-
References
1). Singh N, Paterson DL. Aspergillus infections in transplant recipients. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005; 18:44–69.2). Hoffer FA, Gow K, Flynn PM, Davidoff A. Accuracy of percutaneous lung biopsy for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Pediatr Radiol. 2001; 31:144–52.
Article3). Husain S, Kwak EJ, Obman A, Wagener MM, Kusne S, Stout JE, et al. Prospective assessment of Platelia Aspergillus galactomannan antigen for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in lung transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2004; 4:796–802.4). Lin SJ, Schranz J, Teutsch SM. Aspergillosis case-fatality rate: systematic review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis. 2001; 32:358–66.
Article5). Segal BH, Walsh TJ. Current approaches to diagnosis and treatment of invasive aspergillosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006; 173:707–17.
Article6). Denning DW, Ribaud P, Milpied N, Caillot D, Herbrecht R, Thiel E, et al. Efficacy and safety of voriconazole in the treatment of acute invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2002; 34:563–71.
Article7). Cantarovich M, Besner JG, Barkun JS, Elstein E, Loertscher R. Two-hour cyclosporine level determination is the appropriate tool to monitor Neoral therapy. Clin Transplant. 1998; 12:243–9.8). Knight SR, Morris PJ. The clinical benefits of cyclosporine C2-level monitoring: a systematic review. Transplantation. 2007; 83:1525–35.
Article9). Coto E, Tavira B. Pharmacogenetics of calcineurin inhibitors in renal transplantation. Transplantation. 2009; 88(3S):62–7.
Article10). Ford J, Hoggard PG, Owen A, Khoo SH, Back DJ. A simplified approach to determining P-glycoprotein expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cell subsets. J Immunol Methods. 2003; 274:129–37.
Article11). Goto M, Masuda S, Kiuchi T, Ogura Y, Oike F, Tanaka K, et al. Relation between mRNA expression level of multidrug resistance 1/ABCB1 in blood cells and required level of tacrolimus in pediatric living-donor liver transplantation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008; 325:610–6.
Article12). Crettol S, Venetz JP, Fontana M, Aubert JD, Ansermot N, Fathi M, et al. Influence of ABCB1 genetic polymorphisms on cyclosporine intracellular concentration in transplant recipients. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008; 18:307–15.
Article13). Cattaneo D, Ruggenenti P, Baldelli S, Motterlini N, Gotti E, Sandrini S, et al. ABCB1 genotypes predict cyclosporine-related adverse events and kidney allograft outcome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 20:1404–15.14). Barbari AG, Masri MA, Stephan AG, El Ghoul B, Rizk S, Mourad N, et al. Cyclosporine lymphocyte maximum level monitoring in de novo kidney transplant patients: a prospective study. Exp Clin Transplant. 2006; 4:400–5.15). Falck P, Asberg A, Guldseth H, Bremer S, Akhlaghi F, Reubsaet JL, et al. Declining intracellular T-lymphocyte concentration of cyclosporine a precedes acute rejection in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2008; 85.
Article16). de Jonge H, Naesens M, Kuypers DR. New insights into the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the calcineurin inhibitors and mycophenolic acid: possible consequences for therapeutic drug monitoring in solid organ transplantation. Ther Drug Monit. 2009; 31:416–35.17). Saad AH, DePestel DD, Carver PL. Factors influencing the magnitude and clinical significance of drug interactions between azole antifungals and select immunosuppressants. Pharmacotherapy. 2006; 26:1730–44.
Article18). Levêque D, Nivoix Y, Jehl F, Herbrecht R. Clinical pharmacokinetics of voriconazole. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006; 27:274–84.19). Romero AJ, Le Pogamp P, Nilsson LG, Wood N. Effect of voriconazole on the pharmacokinetics of cyclosporine in renal transplant patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002; 71:226–34.
Article20). Anglicheau D, Pallet N, Rabant M, Marquet P, Cassinat B, Méria P, et al. Role of P-glycoprotein in cyclosporine cytotoxicity in the cyclosporine-sirolimus interaction. Kidney Int. 2006; 70:1019–25.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Disseminated aspergillosis with cutaneous aspergillosis and aspergergillus thyroiditis in a renal allograft recipient
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Cutaneous Aspergillosis
- A Case of Visual and Auditory Hallucinations during Intravenous Voriconazole Therapy
- Comparison of Cyclosporine in Soft Gelatine Capsule and Microemulsion Cyclosporine in Renal Transplant Recipients
- Invasive Aspergillosis Complicated by Occlusion of Internal Carotid Artery and Cerebral Infarction