J Lung Cancer.
2010 Dec;9(2):77-84. 10.6058/jlc.2010.9.2.77.
Combination Therapy of Bortezomib (PS-341) and SAHA (Vorinostat) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Respiratory Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine and Lung Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2199908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6058/jlc.2010.9.2.77
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The recent introduction of targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has changed the paradigm of lung cancer chemotherapy. However, only a small portion of NSCLC patients received the benefit of these new drugs. A proteasome inhibitor (bortezomib) and a histone deacetylase inhibitor (SAHA) were approved for clinical use for treating some hematologic malignancies. In this study, we investigated the combination treatment of bortezomib and SAHA in NSCLC cell lines.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
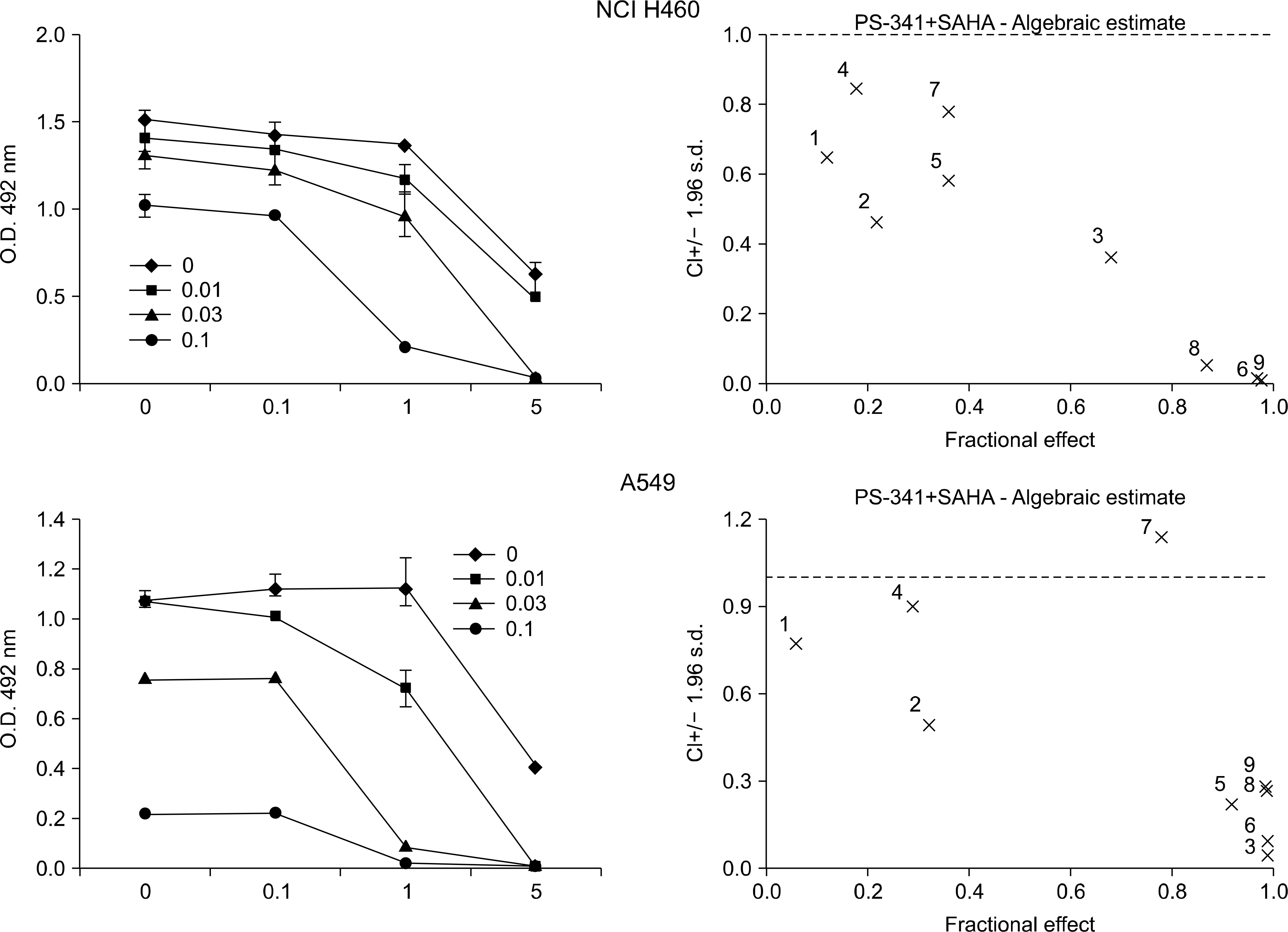
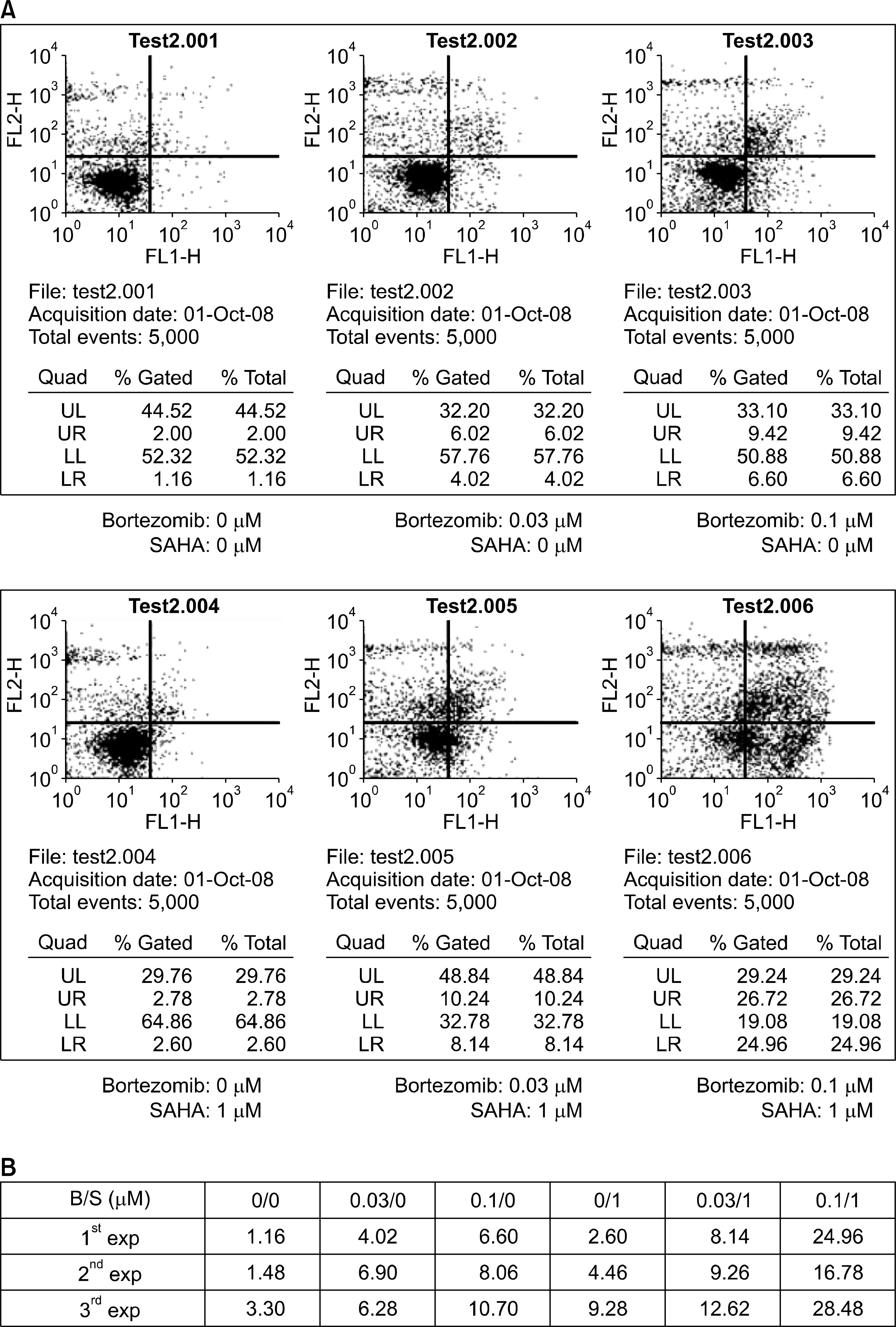
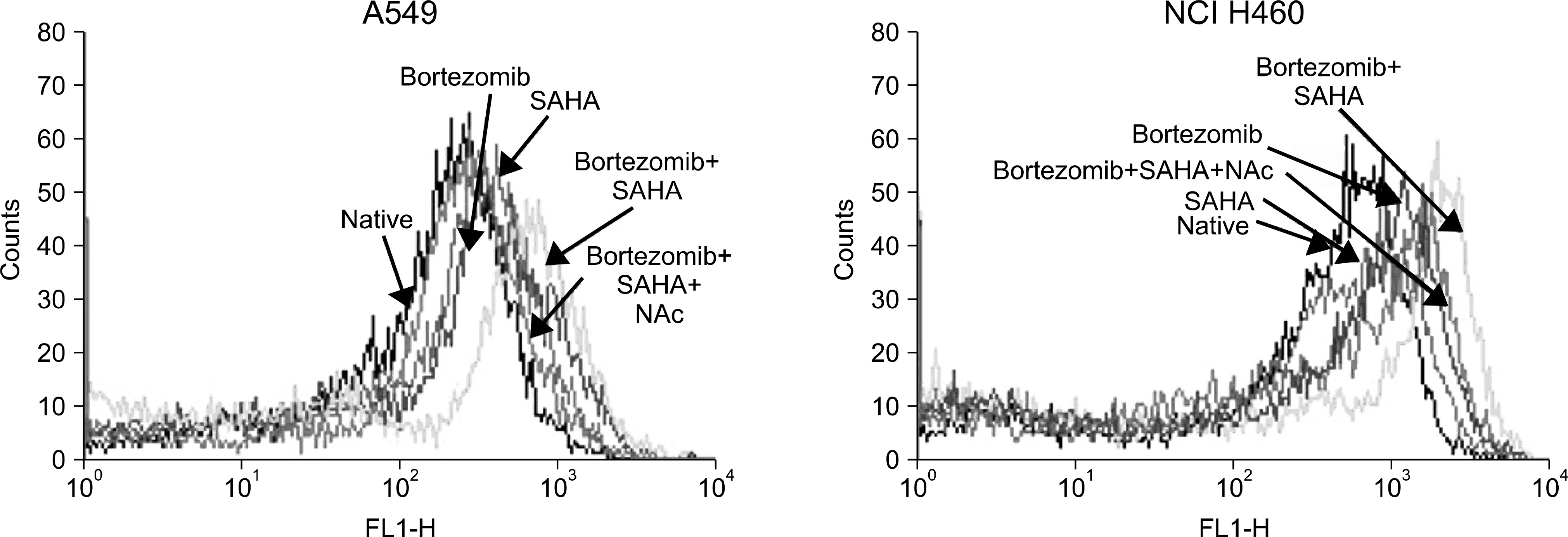
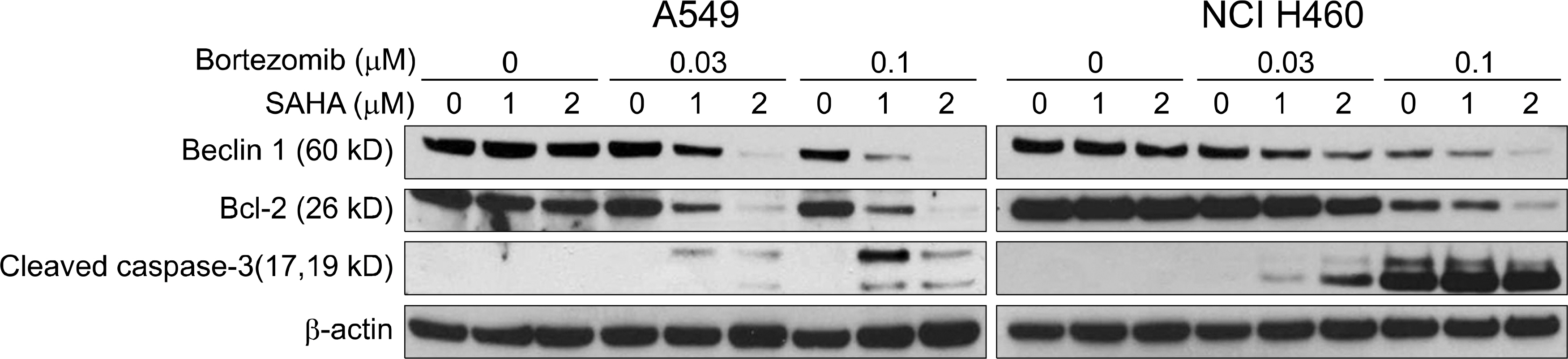
The combined effects of bortezomib and SAHA on lung cancer cell lines were measured by Calcusyn software. Induction of apoptosis was examined by performing an Annexin V assay. Generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protection by N-acetylcysteine were measured by flow cytometry after staining with DCFH-DA. The effect of the combination of drugs on apoptosis and autophagy was investigated by Western blot assay.
RESULTS
Strong synergism was found for the combination of bortezomib and SAHA. The synergistic interaction was mediated by strong apoptosis. Increased ROS generation was partly responsible for the induction of apoptosis, and this was suppressed by the ROS scavenger N-acetylcysteine. Combined treatment induced the strong activation of caspase-3 and the breakdown of the antiapoptotic molecule Bcl-2. Furthermore, increased breakdown of beclin-1, which is known to be an autophagic molecule, was also found.
CONCLUSION
Combination therapy with bortezomib and SAHA showed a strong synergistic antitumor effect on human lung cancer cell lines. Enhanced induction of apoptosis was a responsible mechanism, and this was partly mediated by ROS generation. Further studies are warranted for determining the role of apoptosis and autophagy for this combination therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acetylcysteine
Annexin A5
Apoptosis
Autophagy
Blotting, Western
Boronic Acids
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung
Caspase 3
Cell Line
Flow Cytometry
Fluoresceins
Hematologic Neoplasms
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors
Humans
Lung Neoplasms
Proteasome Inhibitors
Pyrazines
Reactive Oxygen Species
Bortezomib
Acetylcysteine
Annexin A5
Boronic Acids
Caspase 3
Fluoresceins
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors
Proteasome Inhibitors
Pyrazines
Reactive Oxygen Species
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ludwig H, Khayat D, Giaccone G, et al. Proteasome inhibition and its clinical prospects in the treatment of hematologic and solid malignancies. Cancer. 2005; 104:1794–1807.
Article2. Genin E, Reboud-Ravaux M, Vidal J. Proteasome inhibitors: recent advances and new perspectives in medicinal chemistry. Curr Top Med Chem. 2010; 10:232–256.
Article3. Fanucchi MP, Fossella FV, Belt R, et al. Randomized phase II study of bortezomib alone and bortezomib in combination with docetaxel in previously treated advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:5025–5033.
Article4. Somech R, Izraeli S, J Simon A. Histone deacetylase inhibitors–a new tool to treat cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004; 30:461–472.5. Duvic M, Talpur R, Ni X, et al. Phase 2 trial of oral vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood. 2007; 109:31–39.
Article6. Komatsu N, Kawamata N, Takeuchi S, et al. SAHA, a HDAC inhibitor, has profound anti-growth activity against nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2006; 15:187–191.
Article7. Imre G, Gekeler V, Leja A, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress the inducibility of nuclear factor-kappaB by tumor necrosis factoralpha receptor-1 down-regulation. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:5409–5418.8. Yu C, Rahmani M, Conrad D, et al. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib interacts synergistically with histone deacetylase inhibitors to induce apoptosis in Bcr/Abl+ cells sensitive and resistant to STI571. Blood. 2003; 102:3765–3774.
Article9. Emanuele S, Lauricella M, Carlisi D, et al. SAHA induces apoptosis in hepatoma cells and synergistically interacts with the proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib. Apoptosis. 2007; 12:1327–1338.
Article10. Heider U, von Metzler I, Kaiser M, et al. Synergistic interaction of the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in mantle cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol. 2008; 80:133–142.
Article11. Zhang QL, Wang L, Zhang YW, et al. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib interacts synergistically with the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid to induce T-leukemia/lymphoma cells apoptosis. Leukemia. 2009; 23:1507–1514.
Article12. Heider U, Rademacher J, Lamottke B, et al. Synergistic interaction of the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol. 2009; 82:440–449.
Article13. Alva AS, Gultekin SH, Baehrecke EH. Autophagy in human tumors: cell survival or death? Cell Death Differ. 2004; 11:1046–1048.
Article14. Baehrecke EH. Autophagy: dual roles in life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005; 6:505–510.
Article15. Debnath J, Baehrecke EH, Kroemer G. Does autophagy contribute to cell death? Autophagy. 2005; 1:66–74.
Article16. Li J, Liu R, Lei Y, et al. Proteomic analysis revealed association of aberrant ROS signaling with suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid-induced autophagy in Jurkat T-leukemia cells. Autophagy. 2010; 6:711–7124.
Article17. Belloni D, Veschini L, Foglieni C, et al. Bortezomib induces autophagic death in proliferating human endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 2010; 316:1010–1018.
Article18. Zhu K, Dunner K Jr, McConkey DJ. Proteasome inhibitors activate autophagy as a cytoprotective response in human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 2010; 29:451–462.
Article19. Yu L, Lenardo MJ, Baehrecke EH. Autophagy and caspases: a new cell death program. Cell Cycle. 2004; 3:1124–1126.
Article20. Martin DN, Baehrecke EH. Caspases function in autophagic programmed cell death in Drosophila. Development. 2004; 131:275–284.
Article21. Cho DH, Jo YK, Hwang JJ, et al. Caspase-mediated cleavage of ATG6/Beclin-1 links apoptosis to autophagy in HeLa cells. Cancer Lett. 2009; 274:95–100.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High VPP combination chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- PS-341-Induced Apoptosis is Related to JNK-Dependent Caspase 3 Activation and It is Negatively Regulated by PI3K/Akt-Mediated Inactivation of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3beta in Lung Cancer Cells
- Total necrosis of small cell lung carcinoma after combination chemotherapy and radiotherapy: one case report-
- The effects of transferring tumor suppressor gene p16INK4A to p16INK4A-deleted cancer cells
- Clinical Significant of S-Phase Fraction in Small Lung Cancer