Diabetes Metab J.
2012 Dec;36(6):404-411. 10.4093/dmj.2012.36.6.404.
Periodontitis and Insulin Resistance: Casual or Causal Relationship?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontics, Tatyasaheb Kore Dental College & Research Centre, Kolhapur, India. drabhijitgurav@gmail.com
- KMID: 2174362
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.6.404
Abstract
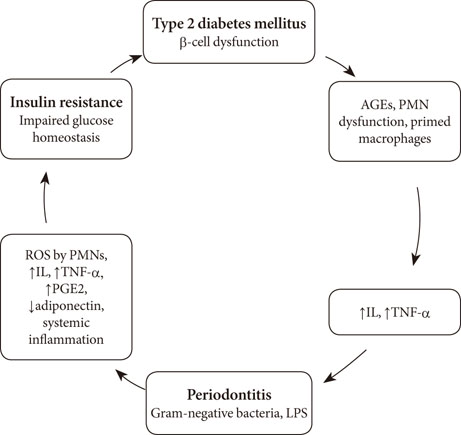
- Insulin resistance (IR) is now considered as a chronic and low level inflammatory condition. It is closely related to altered glucose tolerance, hypertriglyceridemia, abdominal obesity, and coronary heart disease. IR is accompanied by the increase in the levels of inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-1 and 6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha. These inflammatory cytokines also play a crucial part in pathogenesis and progression of insulin resistance. Periodontitis is the commonest of oral diseases, affecting tooth investing tissues. Pro-inflammatory cytokines are released in the disease process of periodontitis. Periodontitis can be attributed with exacerbation of IR. Data in the literature supports a "two way relationship" between diabetes and periodontitis. Periodontitis is asymptomatic in the initial stages of disease process and it often escapes diagnosis. This review presents the blurred nexus between periodontitis and IR, underlining the pathophysiology of the insidious link. The knowledge of the association between periodontitis and IR can be valuable in planning effectual treatment modalities for subjects with altered glucose homeostasis and diabetics. Presently, the studies supporting this association are miniscule. Further studies are mandatory to substantiate the role of periodontitis in the deterioration of IR.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aluminum Hydroxide
Carbonates
Coronary Disease
Cytokines
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2
Glucose
Homeostasis
Hypertriglyceridemia
Insulin
Insulin Resistance
Interleukin-1
Obesity, Abdominal
Periodontitis
Resin Cements
Tooth
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
United Nations
Aluminum Hydroxide
Carbonates
Cytokines
Glucose
Insulin
Interleukin-1
Resin Cements
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of scaling and root planing combined with systemic doxycycline therapy on glycemic control in diabetes mellitus subjects with chronic generalized periodontitis: a clinical study
Subodh P. Gaikwad, Abhijit N. Gurav, Abhijeet R. Shete, Hitesh M. Desarda
J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013;43(2):79-86. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.79.
Reference
-
1. Lam DW, LeRoith D. The worldwide diabetes epidemic. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012. 19:93–96.2. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985. 28:412–419.3. Samuel VT, Shulman GI. Mechanisms for insulin resistance: common threads and missing links. Cell. 2012. 148:852–871.4. Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS, Johnson NW. Periodontal diseases. Lancet. 2005. 366:1809–1820.5. Williams RC, Barnett AH, Claffey N, Davis M, Gadsby R, Kellett M, Lip GY, Thackray S. The potential impact of periodontal disease on general health: a consensus view. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008. 24:1635–1643.6. Grossi SG, Genco RJ. Periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus: a two-way relationship. Ann Periodontol. 1998. 3:51–61.7. Benakanakere M, Kinane DF. Innate cellular responses to the periodontal biofilm. Front Oral Biol. 2012. 15:41–55.8. Preshaw PM, Taylor JJ. How has research into cytokine interactions and their role in driving immune responses impacted our understanding of periodontitis? J Clin Periodontol. 2011. 38:Suppl 11. 60–84.9. Ebersole JL, Stevens J, Steffen MJ, Dawson Iii D, Novak MJ. Systemic endotoxin levels in chronic indolent periodontal infections. J Periodontal Res. 2010. 45:1–7.10. Loos BG. Systemic markers of inflammation in periodontitis. J Periodontol. 2005. 76:11 Suppl. 2106–2115.11. Nesse W, Abbas F, van der Ploeg I, Spijkervet FK, Dijkstra PU, Vissink A. Periodontal inflamed surface area: quantifying inflammatory burden. J Clin Periodontol. 2008. 35:668–673.12. Wu T, Trevisan M, Genco RJ, Falkner KL, Dorn JP, Sempos CT. Examination of the relation between periodontal health status and cardiovascular risk factors: serum total and high density lipoprotein cholesterol, C-reactive protein, and plasma fibrinogen. Am J Epidemiol. 2000. 151:273–282.13. Jin LJ, Wang CY. An update on periodontal infections, systemic inflammatory biomarkers, and cardiovascular disease. Chin J Dent Res. 2007. 10:7–13.14. Boura-Halfon S, Zick Y. Phosphorylation of IRS proteins, insulin action, and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. 296:E581–E591.15. Schultze SM, Hemmings BA, Niessen M, Tschopp O. PI3K/AKT, MAPK and AMPK signalling: protein kinases in glucose homeostasis. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2012. 14:e1.16. Bhattacharya S, Dey D, Roy SS. Molecular mechanism of insulin resistance. J Biosci. 2007. 32:405–413.17. Palmada M, Boehmer C, Akel A, Rajamanickam J, Jeyaraj S, Keller K, Lang F. SGK1 kinase upregulates GLUT1 activity and plasma membrane expression. Diabetes. 2006. 55:421–427.18. Lenz JC, Reusch HP, Albrecht N, Schultz G, Schaefer M. Ca2+-controlled competitive diacylglycerol binding of protein kinase C isoenzymes in living cells. J Cell Biol. 2002. 159:291–302.19. Farese RV. Function and dysfunction of aPKC isoforms for glucose transport in insulin-sensitive and insulin-resistant states. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 283:E1–E11.20. Kellerer M, Mushack J, Seffer E, Mischak H, Ullrich A, Haring HU. Protein kinase C isoforms alpha, delta and theta require insulin receptor substrate-1 to inhibit the tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor in human kidney embryonic cells (HEK 293 cells). Diabetologia. 1998. 41:833–838.21. Tarantino G, Caputi A. JNKs, insulin resistance and inflammation: a possible link between NAFLD and coronary artery disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. 17:3785–3794.22. Wang T, Villegas S, Huang Y, White SK, Ahlem C, Lu M, Olefsky JM, Reading C, Frincke JM, Alleva D, Flores-Riveros J. Amelioration of glucose intolerance by the synthetic androstene HE3286: link to inflammatory pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. 333:70–80.23. Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2006. 116:1793–1801.24. Nishimura F, Iwamoto Y, Mineshiba J, Shimizu A, Soga Y, Murayama Y. Periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus: the role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in a 2-way relationship. J Periodontol. 2003. 74:97–102.25. Kim J, Amar S. Periodontal disease and systemic conditions: a bidirectional relationship. Odontology. 2006. 94:10–21.26. Janket SJ, Jones JA, Meurman JH, Baird AE, Van Dyke TE. Oral infection, hyperglycemia, and endothelial dysfunction. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008. 105:173–179.27. Lehr S, Hartwig S, Sell H. Adipokines: a treasure trove for the discovery of biomarkers for metabolic disorders. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2012. 6:91–101.28. Hillenbrand A, Weiss M, Knippschild U, Wolf AM, Huber-Lang M. Sepsis-induced adipokine change with regard to insulin resistance. Int J Inflam. 2012. 2012:972368.29. Maeda N, Takahashi M, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Nishizawa H, Kishida K, Nagaretani H, Matsuda M, Komuro R, Ouchi N, Kuriyama H, Hotta K, Nakamura T, Shimomura I, Matsuzawa Y. PPARgamma ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, an adipose-derived protein. Diabetes. 2001. 50:2094–2099.30. Park PH, Huang H, McMullen MR, Mandal P, Sun L, Nagy LE. Suppression of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by adiponectin is mediated by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 2008. 283:26850–26858.31. Hotamisligil GS, Murray DL, Choy LN, Spiegelman BM. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits signaling from the insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. 91:4854–4858.32. Popa C, Netea MG, van Riel PL, van der Meer JW, Stalenhoef AF. The role of TNF-alpha in chronic inflammatory conditions, intermediary metabolism, and cardiovascular risk. J Lipid Res. 2007. 48:751–762.33. Grunfeld C, Feingold KR. The metabolic effects of tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines. Biotherapy. 1991. 3:143–158.34. Petersen KF, Shulman GI. Etiology of insulin resistance. Am J Med. 2006. 119:5 Suppl 1. S10–S16.35. Kern PA, Di Gregorio GB, Lu T, Rassouli N, Ranganathan G. Adiponectin expression from human adipose tissue: relation to obesity, insulin resistance, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. Diabetes. 2003. 52:1779–1785.36. Hajri T, Tao H, Wattacheril J, Marks-Shulman P, Abumrad NN. Regulation of adiponectin production by insulin: interactions with tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011. 300:E350–E360.37. Long SD, Pekala PH. Regulation of GLUT4 mRNA stability by tumor necrosis factor-alpha: alterations in both protein binding to the 3' untranslated region and initiation of translation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996. 220:949–953.38. Hansen LL, Ikeda Y, Olsen GS, Busch AK, Mosthaf L. Insulin signaling is inhibited by micromolar concentrations of H(2) O(2). Evidence for a role of H(2)O(2) in tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:25078–25084.39. Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA. Point: Interleukin-6 does have a beneficial role in insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis. J Appl Physiol. 2007. 102:814–816.40. Mooney RA. Counterpoint: interleukin-6 does not have a beneficial role in insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis. J Appl Physiol. 2007. 102:816–818.41. Rabe K, Lehrke M, Parhofer KG, Broedl UC. Adipokines and insulin resistance. Mol Med. 2008. 14:741–751.42. Nishimura F, Soga Y, Iwamoto Y, Kudo C, Murayama Y. Periodontal disease as part of the insulin resistance syndrome in diabetic patients. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2005. 7:16–20.43. Watanabe K, Petro BJ, Shlimon AE, Unterman TG. Effect of periodontitis on insulin resistance and the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Periodontol. 2008. 79:1208–1216.44. Ekuni D, Tomofuji T, Irie K, Kasuyama K, Umakoshi M, Azuma T, Tamaki N, Sanbe T, Endo Y, Yamamoto T, Nishida T, Morita M. Effects of periodontitis on aortic insulin resistance in an obese rat model. Lab Invest. 2010. 90:348–359.45. Pontes Andersen CC, Flyvbjerg A, Buschard K, Holmstrup P. Periodontitis is associated with aggravation of prediabetes in Zucker fatty rats. J Periodontol. 2007. 78:559–565.46. Genco RJ, Grossi SG, Ho A, Nishimura F, Murayama Y. A proposed model linking inflammation to obesity, diabetes, and periodontal infections. J Periodontol. 2005. 76:11 Suppl. 2075–2084.47. Benguigui C, Bongard V, Ruidavets JB, Chamontin B, Sixou M, Ferrieres J, Amar J. Metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and periodontitis: a cross-sectional study in a middle-aged French population. J Clin Periodontol. 2010. 37:601–608.48. Timonen P, Suominen-Taipale L, Jula A, Niskanen M, Knuuttila M, Ylostalo P. Insulin sensitivity and periodontal infection in a non-diabetic, non-smoking adult population. J Clin Periodontol. 2011. 38:17–24.49. Allen EM, Matthews JB, DJ OH, Griffiths HR, Chapple IL. Oxidative and inflammatory status in type 2 diabetes patients with periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2011. 38:894–901.50. Karima M, Kantarci A, Ohira T, Hasturk H, Jones VL, Nam BH, Malabanan A, Trackman PC, Badwey JA, Van Dyke TE. Enhanced superoxide release and elevated protein kinase C activity in neutrophils from diabetic patients: association with periodontitis. J Leukoc Biol. 2005. 78:862–870.51. Saxlin T, Suominen-Taipale L, Leiviska J, Jula A, Knuuttila M, Ylostalo P. Role of serum cytokines tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in the association between body weight and periodontal infection. J Clin Periodontol. 2009. 36:100–105.52. Gorman A, Kaye EK, Apovian C, Fung TT, Nunn M, Garcia RI. Overweight and obesity predict time to periodontal disease progression in men. J Clin Periodontol. 2012. 39:107–114.53. Mealey BL, Rose LF. Diabetes mellitus and inflammatory periodontal diseases. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2008. 15:135–141.54. Gurav A, Jadhav V. Periodontitis and risk of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes. 2011. 3:21–28.55. Fernandez-Real JM, Ricart W. Insulin resistance and chronic cardiovascular inflammatory syndrome. Endocr Rev. 2003. 24:278–301.56. Humphrey LL, Fu R, Buckley DI, Freeman M, Helfand M. Periodontal disease and coronary heart disease incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med. 2008. 23:2079–2086.57. Friedewald VE, Kornman KS, Beck JD, Genco R, Goldfine A, Libby P, Offenbacher S, Ridker PM, Van Dyke TE, Roberts WC. American Journal of Cardiology. Journal of Periodontology. The American Journal of Cardiology and Journal of Periodontology editors' consensus: periodontitis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. J Periodontol. 2009. 80:1021–1032.58. Cornier MA, Dabelea D, Hernandez TL, Lindstrom RC, Steig AJ, Stob NR, Van Pelt RE, Wang H, Eckel RH. The metabolic syndrome. Endocr Rev. 2008. 29:777–822.59. Nesse W, Linde A, Abbas F, Spijkervet FK, Dijkstra PU, de Brabander EC, Gerstenbluth I, Vissink A. Dose-response relationship between periodontal inflamed surface area and HbA1c in type 2 diabetics. J Clin Periodontol. 2009. 36:295–300.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diabetes and Periodontal Disease
- Testosterone and metabolic syndrome in men
- An Inquiry to the Casual Perceptions and Health seeking Behaviors of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- Risk Assessment of Periodontitis according to Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance in Korean Population: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2013–2015)
- Link between Periodontal Disease and Diabetes