J Gynecol Oncol.
2008 Sep;19(3):185-190. 10.3802/jgo.2008.19.3.185.
Expression profile of histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 in ovarian cancer tissues
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. jhnam@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Asan Institute for Life Sciences, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2173400
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3802/jgo.2008.19.3.185
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
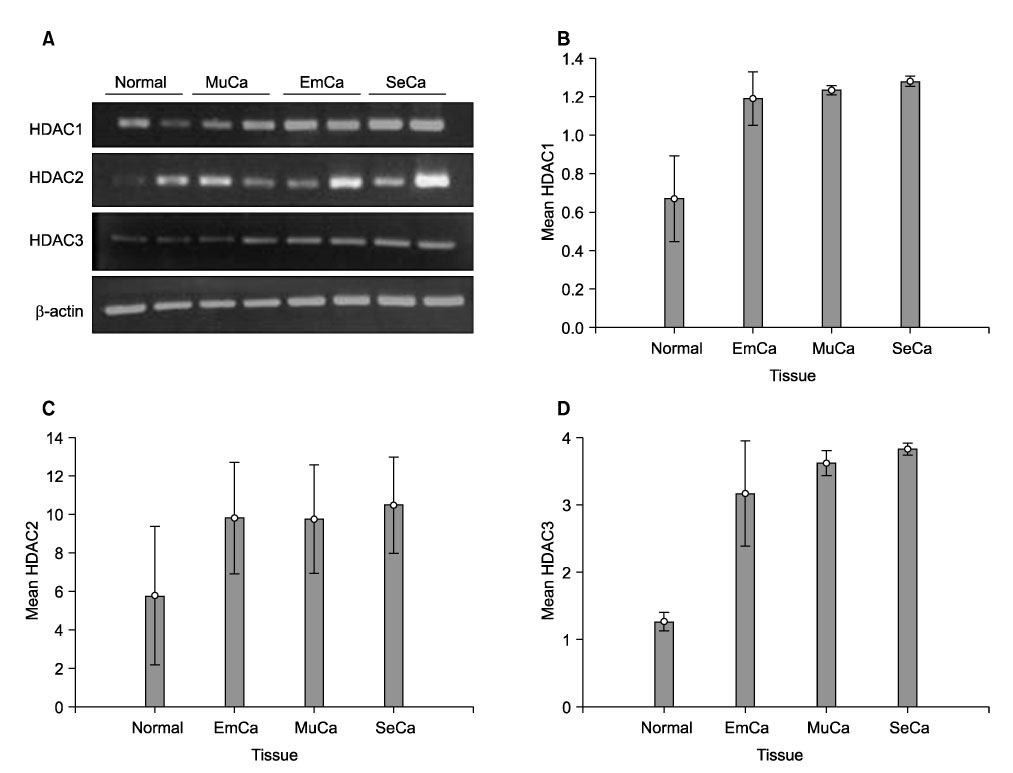
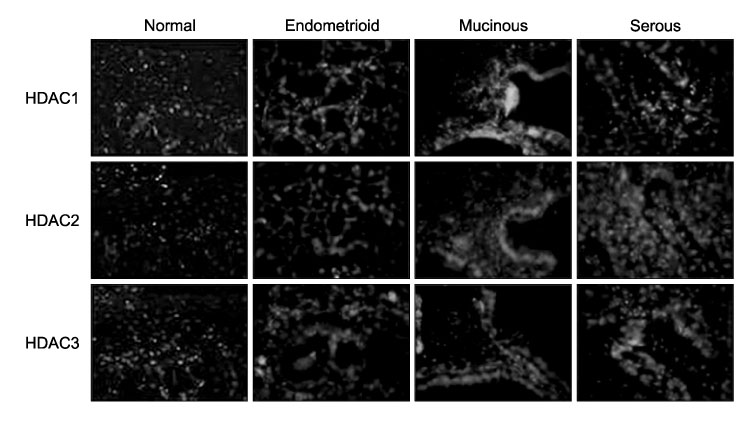
To investigate the expression levels of histone deacetylase (HDAC) 1, 2, and 3 in ovarian cancer tissues and normal ovarian tissues. METHODS: Randomly assigned each of six patients with serous, mucinous and endometrioid ovarian cancer were included. Another six patients with normal ovarian tissue were included for comparison. RT-PCR was performed to quantify the levels of HDACs1-3 mRNA in the cancer and normal tissues. Western blot analysis was performed to measure the expression levels of HDACs1-3 protein. The HDACs1-3 expression pattern was also topologically examined by immunohistochemistry. RESULTS: Increased mRNA expressions of HDCA1, HDAC 2 and HDAC 3 were detected in 83%, 67% and 83% of 18 cancer tissue samples, compared to normal tissue samples. The relative densities of HDAC1 mRNA and HDAC3 mRNA in the serous, mucinous and endometrioid cancer tissues, and HDAC2 mRNA in serous cancer tissues were significantly higher than those of the normal tissues, respectively (p<0.05). Overexpression of HDAC1, HDAC2 and HDAC3 proteins were detected in 94%, 72% and 83% of 18 cancer samples, respectively. The relative densities of HDAC1 protein and HDAC3 protein in serous, mucinous and endometrioid cancer, and HDAC2 protein in serous and mucinous cancer tissues were significantly higher than those of normal tissues, respectively (p<0.05). Most cancer tissues expressed moderate to strong staining of HDACs1, 2 and 3 in immunohistochemistry. Staining of HDAC2 was weak in only one endometrioid cancer tissue. CONCLUSION: HDACs1-3 are over expressed in ovarian cancer tissues and probably play a significant role in ovarian carcinogenesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Peterson CL, Laniel M. Histone and histone modification. Curr Biol. 2004. 14:R546–R551.2. Gu W, Roeder RG. Activation of p53 sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 c-terminal domain. Cell. 1997. 90:595–606.3. Marizio G, Wagener C, Gutierrez MI, Cartwright P, Helin K, Giacca M. E2F family members are differentially regulated by reversible acetylation. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:10887–10892.4. Ammanamanchi S, Freeman JW, Brattain MG. Acetylated Sp3 is a transcriptional activator. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:35775–35780.5. Mariadason JM, Barkla DH, Gibson PR. Effect of short-chain fatty acids on paracellular permeability in Caco-2 intestinal epithelium model. Am J Physiol. 1997. 272:G705–G712.6. Mariadason JM, Rickard KL, Barkla DH, Augenlicht LH, Gibson PR. Divergent phenotypic patterns and commitment to apoptosis of Caco-2 cells during spontaneous and butyrate-induced differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2000. 183:347–354.7. Mariadason JM, Velcich A, Wison AJ, Augenlicht LH, Gibson PR. Resistance to butyrate-induced cell differentiation and apoptosis during spontaneous Caco-2 cell differentiation. Gastroenterology. 2001. 120:889–899.8. Takai N, Kawamata N, Gui D, Said JW, Miyakawa I, Koeffler HP. Human ovarian carcinoma cell: Histone deacetylase inhibitors exhibit antiproliferative activity and potently induce apoptosis. Cancer. 2004. 101:2760–2770.9. Kim MS, Kwon HJ, Lee YM, Baek JH, Jang JE, Lee SW, et al. Histone deacetylases induce angiogenesis by negative regulation of tumor suppressor genes. Nat Med. 2001. 7:437–443.10. de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN, Kemp S, van Kuilenburg AB. Histone deacelytase (HDACs): Characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J. 2003. 370:737–749.11. Gregoretti IV, Lee YM, Goodson HV. Molecular evolution of the histone deacetylase family: Functional implications of phylogenetic analysis. J Mol Biol. 2004. 338:17–31.12. Takami Y, Nakayama T. N-terminal region, C-terminal region, nuclear export signal, and deacetylation activity of histone deacetylase-3 are essential for the viability of the DT40 chicken B cell line. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:16191–16201.13. Thiagalingam S, Cheng KH, Lee HJ, Mineva N, Thiagalingam A, Ponte JF. Histone deacetylases: Unique players in shaping the epigenetic code. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. 983:84–100.14. Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Saito H, Yatabe Y, Mitsudomi T, Takahashi T. Reduced expression of class II histone deacetylase genes is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2004. 112:26–32.15. Zhu P, Martin E, Mengwasser J, Schlag P, Janssen KP, Gottlicher M. Induction of HDAC2 expression upon loss of APC in colorectal tumogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2004. 5:455–463.16. Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev. 2000. 14:121–141.17. Ayer DE. Histone deacetylases: Transcriptional repression with SINers and NuRDs. Trends Cell Biol. 1999. 9:193–198.18. Wilson AJ, Byun DS, Popova N, Murray LB, L'Italien K, Sowa Y, et al. Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) and other class I HDACs regulate colon cell maturation and p21 expression and are deregulated in human colon cancer. J Biol Chem. 2006. 281:13548–13558.19. Rampalli S, Pavithra L, Bhatt A, Jundu TK, Chattopadhyay S. Tumor suppressor SMAR1 mediates cyclinD1 repression by recruitment of the SIN3/histone deacetylase 1 complex. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. 25:8415–8429.20. Kawai H, Li H, Avraham S, Jiang S, Acraham HK. Overexpression of histone deacetylase HDAC1 modulates breast cancer progression by negative regulation of estrogen receptor α. Int J Cancer. 2003. 107:353–358.21. Terao Y, Nishida J, Horiuchi S, Rong F, Ueoka Y, Matsuda T, et al. Sodium butyrate induces growth arrest and senescence-like phenotypes in gynecologic cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2001. 94:257–267.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Histone Deacetylases and Their Regulatory MicroRNAs in Hepatocarcinogenesis
- HDAC and HDAC Inhibitor: From Cancer to Cardiovascular Diseases
- Dual Inhibitors Against Topoisomerases and Histone Deacetylases
- Epigenetic Modifications: Novel Therapeutic Approach for Thyroid Cancer
- The relationship between cisplatin resistance and histone deacetylase isoform overexpression in epithelial ovarian cancer cell lines