Immune Netw.
2014 Apr;14(2):73-80. 10.4110/in.2014.14.2.73.
Advances in Systems Biology Approaches for Autoimmune Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul 143-729, Korea. ho0919@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul 143-729, Korea.
- KMID: 2168017
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2014.14.2.73
Abstract
- Because autoimmune diseases (AIDs) result from a complex combination of genetic and epigenetic factors, as well as an altered immune response to endogenous or exogenous antigens, systems biology approaches have been widely applied. The use of multi-omics approaches, including blood transcriptomics, genomics, epigenetics, proteomics, and metabolomics, not only allow for the discovery of a number of biomarkers but also will provide new directions for further translational AIDs applications. Systems biology approaches rely on high-throughput techniques with data analysis platforms that leverage the assessment of genes, proteins, metabolites, and network analysis of complex biologic or pathways implicated in specific AID conditions. To facilitate the discovery of validated and qualified biomarkers, better-coordinated multi-omics approaches and standardized translational research, in combination with the skills of biologists, clinicians, engineers, and bioinformaticians, are required.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
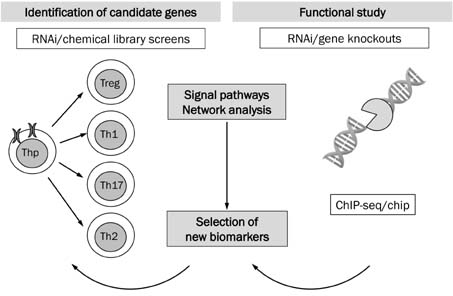
Figure
Reference
-
1. Whitacre CC. Sex differences in autoimmune disease. Nat Immunol. 2001; 2:777–780.
Article2. Blumberg RS, Dittel B, Hafler D, von Herrath M, Nestle FO. Unraveling the autoimmune translational research process layer by layer. Nat Med. 2012; 18:35–41.
Article3. Goldblatt F, O'Neill SG. Clinical aspects of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Lancet. 2013; 382:797–808.
Article4. Trowsdale J. The MHC, disease and selection. Immunol Lett. 2011; 137:1–8.
Article5. Nocturne G, Mariette X. Advances in understanding the pathogenesis of primary Sjogrens syndrome. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013; 9:544–556.
Article6. Harley JB, Sestak AL, Willis LG, Fu SM, Hansen JA, Reichlin M. A model for disease heterogeneity in systemic lupus erythematosus Relationships between histocompatibility antigens, autoantibodies, and lymphopenia or renal disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1989; 32:826–836.7. Lessard CJ, Li H, Adrianto I, Ice JA, Rasmussen A, Grundahl KM, Kelly JA, Dozmorov MG, Miceli-Richard C, Bowman S, Lester S, Eriksson P, Eloranta ML, Brun JG, Gøransson LG, Harboe E, Guthridge JM, Kaufman KM, Kvarnström M, Jazebi H, CunninghameGraham DS, Grandits ME, Nazmul-Hossain AN, Patel K, Adler AJ, Maier-Moore JS, Farris AD, Brennan MT, Lessard JA, Chodosh J, Gopalakrishnan R, Hefner KS, Houston GD, Huang AJ, Hughes PJ, Lewis DM, Radfar L, Rohrer MD, Stone DU, Wren JD, Vyse TJ, Gaffney PM, James JA, Omdal R, Wahren-Herlenius M, Illei GG, Witte T, Jonsson R, Rischmueller M, Rönnblom L, Nordmark G, Ng WF; UK Primary Sjögren's Syndrome Registry, Mariette X, Anaya JM, Rhodus NL, Segal BM, Scofield RH, Montgomery CG, Harley JB, Sivils KL. Variants at multiple loci implicated in both innate and adaptive immune responses are associated with Sjogren's syndrome. Nat Genet. 2013; 45:1284–1292.
Article8. Viatte S, Plant D, Raychaudhuri S. Genetics and epigenetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013; 9:141–153.
Article9. Zhebrun D, Kudryashova Y, Babenko A, Maslyansky A, Kunitskaya N, Popcova D, Klushina A, Grineva E, Kostareva A, Shlyakhto E. Association of PTPN22 1858T/T genotype with type 1 diabetes, Graves' disease but not with rheumatoid arthritis in Russian population. Aging. 2011; 3:368–373.
Article10. Hewagama A, Richardson B. The genetics and epigenetics of autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun. 2009; 33:3–11.
Article11. Franke A, McGovern DP, Barrett JC, Wang K, Radford-Smith GL, Ahmad T, Lees CW, Balschun T, Lee J, Roberts R, Anderson CA, Bis JC, Bumpstead S, Ellinghaus D, Festen EM, Georges M, Green T, Haritunians T, Jostins L, Latiano A, Mathew CG, Montgomery GW, Prescott NJ, Raychaudhuri S, Rotter JI, Schumm P, Sharma Y, Simms LA, Taylor KD, Whiteman D, Wijmenga C, Baldassano RN, Barclay M, Bayless TM, Brand S, Büning C, Cohen A, Colombel JF, Cottone M, Stronati L, Denson T, De Vos M, D'Inca R, Dubinsky M, Edwards C, Florin T, Franchimont D, Gearry R, Glas J, Van Gossum A, Guthery SL, Halfvarson J, Verspaget HW, Hugot JP, Karban A, Laukens D, Lawrance I, Lemann M, Levine A, Libioulle C, Louis E, Mowat C, Newman W, Panés J, Phillips A, Proctor DD, Regueiro M, Russell R, Rutgeerts P, Sanderson J, Sans M, Seibold F, Steinhart AH, Stokkers PC, Torkvist L, Kullak-Ublick G, Wilson D, Walters T, Targan SR, Brant SR, Rioux JD, D'Amato M, Weersma RK, Kugathasan S, Griffiths AM, Mansfield JC, Vermeire S, Duerr RH, Silverberg MS, Satsangi J, Schreiber S, Cho JH, Annese V, Hakonarson H, Daly MJ, Parkes M. Genome-wide meta-analysis increases to 71 the number of confirmed Crohn's disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:1118–1125.
Article12. Oksenberg JR, Baranzini SE, Sawcer S, Hauser SL. The genetics of multiple sclerosis: SNPs to pathways to pathogenesis. Nat Rev Genet. 2008; 9:516–526.
Article13. Duffin KC, Chandran V, Gladman DD, Krueger GG, Elder JT, Rahman P. Genetics of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: update and future direction. J Rheumatol. 2008; 35:1449–1453.14. Stahl EA, Raychaudhuri S, Remmers EF, Xie G, Eyre S, Thomson BP, Li Y, Kurreeman FA, Zhernakova A, Hinks A, Guiducci C, Chen R, Alfredsson L, Amos CI, Ardlie KG; BIRAC Consortium, Barton A, Bowes J, Brouwer E, Burtt NP, Catanese JJ, Coblyn J, Coenen MJ, Costenbader KH, Criswell LA, Crusius JB, Cui J, de Bakker PI, De Jager PL, Ding B, Emery P, Flynn E, Harrison P, Hocking LJ, Huizinga TW, Kastner DL, Ke X, Lee AT, Liu X, Martin P, Morgan AW, Padyukov L, Posthumus MD, Radstake TR, Reid DM, Seielstad M, Seldin MF, Shadick NA, Steer S, Tak PP, Thomson W, van der Helm-van Mil AH, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, van der Schoot CE, van Riel PL, Weinblatt ME, Wilson AG, Wolbink GJ, Wordsworth BP; YEAR Consortium, Wijmenga C, Karlson EW, Toes RE, de Vries N, Begovich AB, Worthington J, Siminovitch KA, Gregersen PK, Klareskog L, Plenge RM. Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies seven new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:508–514.
Article15. Zhernakova A, Stahl EA, Trynka G, Raychaudhuri S, Festen EA, Franke L, Westra HJ, Fehrmann RS, Kurreeman FA, Thomson B, Gupta N, Romanos J, McManus R, Ryan AW, Turner G, Brouwer E, Posthumus MD, Remmers EF, Tucci F, Toes R, Grandone E, Mazzilli MC, Rybak A, Cukrowska B, Coenen MJ, Radstake TR, van Riel PL, Li Y, de Bakker PI, Gregersen PK, Worthington J, Siminovitch KA, Klareskog L, Huizinga TW, Wijmenga C, Plenge RM. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in celiac disease and rheumatoid arthritis identifies fourteen non-HLA shared loci. PLoS Genet. 2011; 7:e1002004.
Article16. Han JW, Zheng HF, Cui Y, Sun LD, Ye DQ, Hu Z, Xu JH, Cai ZM, Huang W, Zhao GP, Xie HF, Fang H, Lu QJ, Xu JH, Li XP, Pan YF, Deng DQ, Zeng FQ, Ye ZZ, Zhang XY, Wang QW, Hao F, Ma L, Zuo XB, Zhou FS, Du WH, Cheng YL, Yang JQ, Shen SK, Li J, Sheng YJ, Zuo XX, Zhu WF, Gao F, Zhang PL, Guo Q, Li B, Gao M, Xiao FL, Quan C, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Zhu KJ, Li Y, Hu DY, Lu WS, Huang JL, Liu SX, Li H, Ren YQ, Wang ZX, Yang CJ, Wang PG, Zhou WM, Lv YM, Zhang AP, Zhang SQ, Lin D, Li Y, Low HQ, Shen M, Zhai ZF, Wang Y, Zhang FY, Yang S, Liu JJ, Zhang XJ. Genome-wide association study in a Chinese Han population identifies nine new susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2009; 41:1234–1237.
Article17. Barrett JC, Clayton DG, Concannon P, Akolkar B, Cooper JD, Erlich HA, Julier C, Morahan G, Nerup J, Nierras C, Plagnol V, Pociot F, Schuilenburg H, Smyth DJ, Stevens H, Todd JA, Walker NM, Rich SS. Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis find that over 40 loci affect risk of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2009; 41:703–707.
Article18. Hu X, Kim H, Stahl E, Plenge R, Daly M, Raychaudhuri S. Integrating autoimmune risk loci with gene-expression data identifies specific pathogenic immune cell subsets. Am J Hum Genet. 2011; 89:496–506.
Article19. Ermann J, Fathman CG. Autoimmune diseases: genes, bugs and failed regulation. Nat Immunol. 2001; 2:759–761.
Article20. Jaenisch R, Bird A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Genet. 2003; 33:Suppl. 245–254.
Article21. Jirtle RL, Skinner MK. Environmental epigenomics and disease susceptibility. Nat Rev Genet. 2007; 8:253–262.
Article22. Portela A, Esteller M. Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nat Biotechnol. 2010; 28:1057–1068.
Article23. Sekigawa I, Kawasaki M, Ogasawara H, Kaneda K, Kaneko H, Takasaki Y, Ogawa H. DNA methylation: its contribution to systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Med. 2006; 6:99–106.
Article24. Quintero-Ronderos P, Montoya-Ortiz G. Epigenetics and autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune Dis. 2012; 2012:593720.
Article25. Pauley KM, Cha S, Chan EK. MicroRNA in autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun. 2009; 32:189–194.
Article26. Pascual V, Chaussabel D, Banchereau J. A genomic approach to human autoimmune diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 2010; 28:535–571.
Article27. Blanco P, Palucka AK, Gill M, Pascual V, Banchereau J. Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science. 2001; 294:1540–1543.
Article28. Shodell M, Shah K, Siegal FP. Circulating human plasmacytoid dendritic cells are highly sensitive to corticosteroid administration. Lupus. 2003; 12:222–230.
Article29. Bennett L, Palucka AK, Arce E, Cantrell V, Borvak J, Banchereau J, Pascual V. Interferon and granulopoiesis signatures in systemic lupus erythematosus blood. J Exp Med. 2003; 197:711–723.
Article30. Vincent FB, Northcott M, Hoi A, Mackay F, Morand EF. Clinical associations of serum interleukin-17 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013; 15:R97.
Article31. Krausgruber T, Blazek K, Smallie T, Alzabin S, Lockstone H, Sahgal N, Hussell T, Feldmann M, Udalova IA. IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and TH1-TH17 responses. Nat Iimmunol. 2011; 12:231–238.
Article32. Banchereau J, Pascual V. Type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Immunity. 2006; 25:383–392.
Article33. Nikula T, Mykkanen J, Simell O, Lahesmaa R. Genome-wide comparison of two RNA-stabilizing reagents for transcriptional profiling of peripheral blood. Transl Res. 2013; 161:181–188.
Article34. Chiche L, Jourde-Chiche N, Pascual V, Chaussabel D. Current perspectives on systems immunology approaches to rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65:1407–1417.
Article35. Croze E. Differential gene expression and translational approaches to identify biomarkers of interferon beta activity in multiple sclerosis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010; 30:743–749.
Article36. Mohr S, Liew CC. The peripheral-blood transcriptome: new insights into disease and risk assessment. Trends Mol Med. 2007; 13:422–432.
Article37. Robinson WH, Steinman L, Utz PJ. Proteomics technologies for the study of autoimmune disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46:885–893.
Article38. Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Karypis G, Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ, Shark KB, Grande WJ, Hughes KM, Kapur V, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003; 100:2610–2615.
Article39. Pascual V, Banchereau J, Palucka AK. The central role of dendritic cells and interferon-alpha in SLE. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003; 15:548–556.40. Sigurdsson S, Nordmark G, Garnier S, Grundberg E, Kwan T, Nilsson O, Eloranta ML, Gunnarsson I, Svenungsson E, Sturfelt G, Bengtsson AA, Jönsen A, Truedsson L, Rantapää-Dahlqvist S, Eriksson C, Alm G, Göring HH, Pastinen T, Syvänen AC, Rönnblom L. A risk haplotype of STAT4 for systemic lupus erythematosus is over-expressed, correlates with anti-dsDNA and shows additive effects with two risk alleles of IRF5. Hum Mol Genet. 2008; 17:2868–2876.
Article41. Remmers EF, Plenge RM, Lee AT, Graham RR, Hom G, Behrens TW, de Bakker PI, Le JM, Lee HS, Batliwalla F, Li W, Masters SL, Booty MG, Carulli JP, Padyukov L, Alfredsson L, Klareskog L, Chen WV, Amos CI, Criswell LA, Seldin MF, Kastner DL, Gregersen PK. STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:977–986.
Article42. Elkon KB, Stone VV. Type I interferon and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011; 31:803–812.
Article43. Stetson DB, Ko JS, Heidmann T, Medzhitov R. Trex1 prevents cell-intrinsic initiation of autoimmunity. Cell. 2008; 134:587–598.
Article44. Bauer JW, Petri M, Batliwalla FM, Koeuth T, Wilson J, Slattery C, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW, Baechler EC. Interferon-regulated chemokines as biomarkers of systemic lupus erythematosus disease a validation study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60:3098–3107.
Article45. Tektonidou MG, Ward MM. Validity of clinical associations of biomarkers in translational research studies: the case of systemic autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010; 12:R179.
Article46. Kussmann M, Raymond F, Affolter M. OMICS-driven biomarker discovery in nutrition and health. J Biotechnol. 2006; 124:758–787.
Article47. Plebani M, Pittoni M, Celadin M, Bernardi D, Mion MM. Recent advances in diagnostic technologies for autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2009; 8:238–243.
Article48. Kussmann M, Blum S. OMICS-derived targets for inflammatory gut disorders: opportunities for the development of nutrition related biomarkers. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2007; 7:271–287.
Article49. Delaleu N, Immervoll H, Cornelius J, Jonsson R. Biomarker profiles in serum and saliva of experimental Sjogren's syndrome: associations with specific autoimmune manifestations. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008; 10:R22.50. Schweitzer B, Predki P, Snyder M. Microarrays to characterize protein interactions on a whole-proteome scale. Proteomics. 2003; 3:2190–2199.
Article51. Ciofani M, Madar A, Galan C, Sellars M, Mace K, Pauli F, Agarwal A, Huang W, Parkurst CN, Muratet M, Newberry KM, Meadows S, Greenfield A, Yang Y, Jain P, Kirigin FK, Birchmeier C, Wagner EF, Murphy KM, Myers RM, Bonneau R, Littman DR. A validated regulatory network for Th17 cell specification. Cell. 2012; 151:289–303.
Article52. Ivanov II, Zhou L, Littman DR. Transcriptional regulation of Th17 cell differentiation. Semin Immunol. 2007; 19:409–417.
Article53. Yosef N, Shalek AK, Gaublomme JT, Jin H, Lee Y, Awasthi A, Wu C, Karwacz K, Xiao S, Jorgolli M, Gennert D, Satija R, Shakya A, Lu DY, Trombetta JJ, Pillai MR, Ratcliffe PJ, Coleman ML, Bix M, Tantin D, Park H, Kuchroo VK, Regev A. Dynamic regulatory network controlling TH17 cell differentiation. Nature. 2013; 496:461–468.
Article54. Solt LA, Kumar N, Nuhant P, Wang Y, Lauer JL, Liu J, Istrate MA, Kamenecka TM, Roush WR, Vidović D, Schürer SC, Xu J, Wagoner G, Drew PD, Griffin PR, Burris TP. Suppression of TH17 differentiation and autoimmunity by a synthetic ROR ligand. Nature. 2011; 472:491–494.
Article55. Kitteringham NR, Jenkins RE, Lane CS, Elliott VL, Park BK. Multiple reaction monitoring for quantitative biomarker analysis in proteomics and metabolomics. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009; 877:1229–1239.
Article56. Ghosh D, Poisson LM. "Omics" data and levels of evidence for biomarker discovery. Genomics. 2009; 93:13–16.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Systems Biology-Based Platforms to Accelerate Research of Emerging Infectious Diseases
- Current advances in the treatment of autoimmune-associated interstitial lung diseases
- Applications of systems approaches in the study of rheumatic diseases
- Systems Biology: A Multi-Omics Integration Approach to Metabolism and the Microbiome
- Recent Advances in Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases