Endocrinol Metab.
2020 Sep;35(3):507-514. 10.3803/EnM.2020.303.
Systems Biology: A Multi-Omics Integration Approach to Metabolism and the Microbiome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea
- 2Centre for Host-Microbiome Interactions, Faculty of Dentistry, Oral & Craniofacial Sciences, King’s College London, London, UK
- 3Science for Life Laboratory, KTH-Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden
- KMID: 2507999
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.303
Abstract
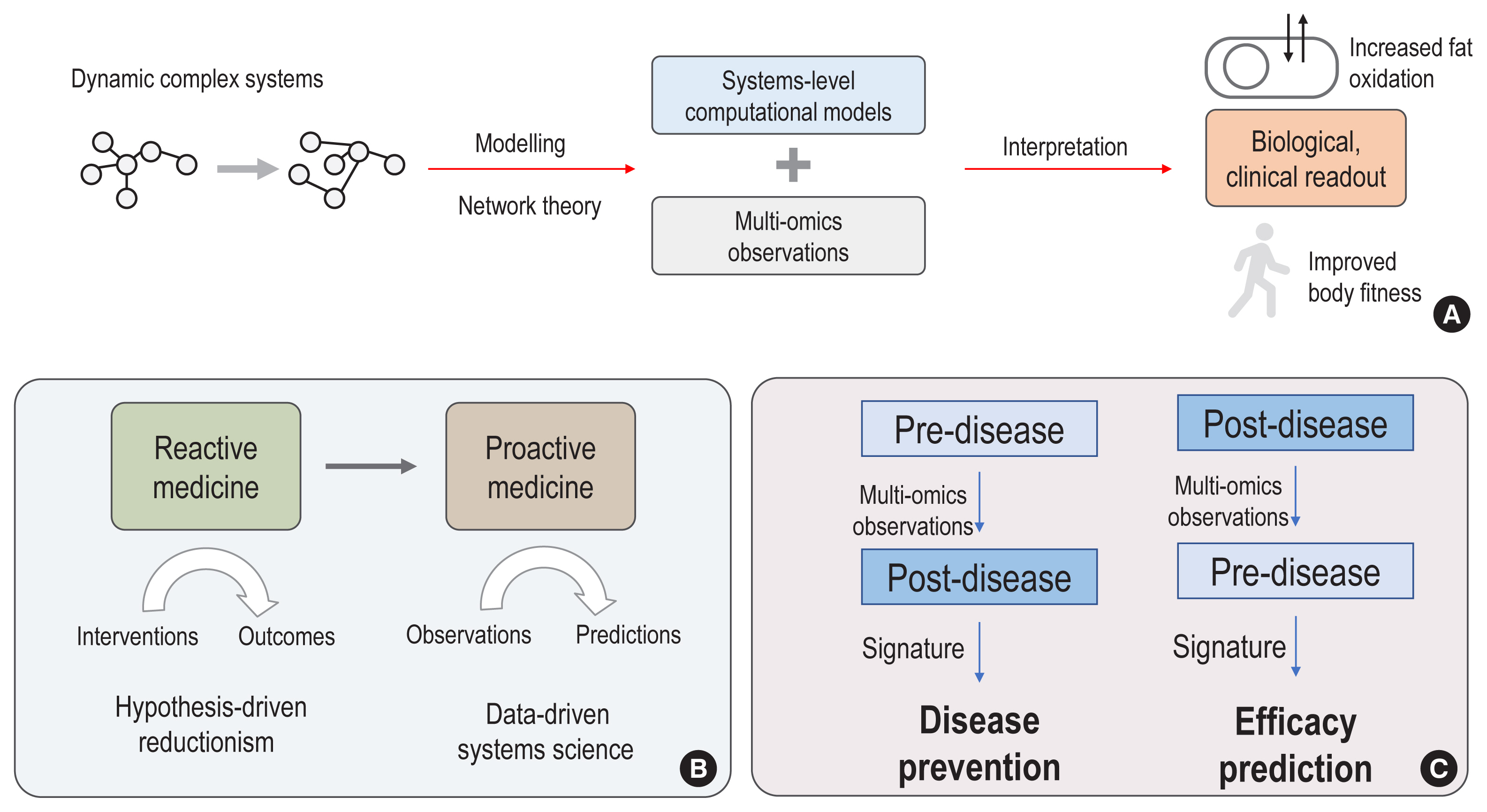
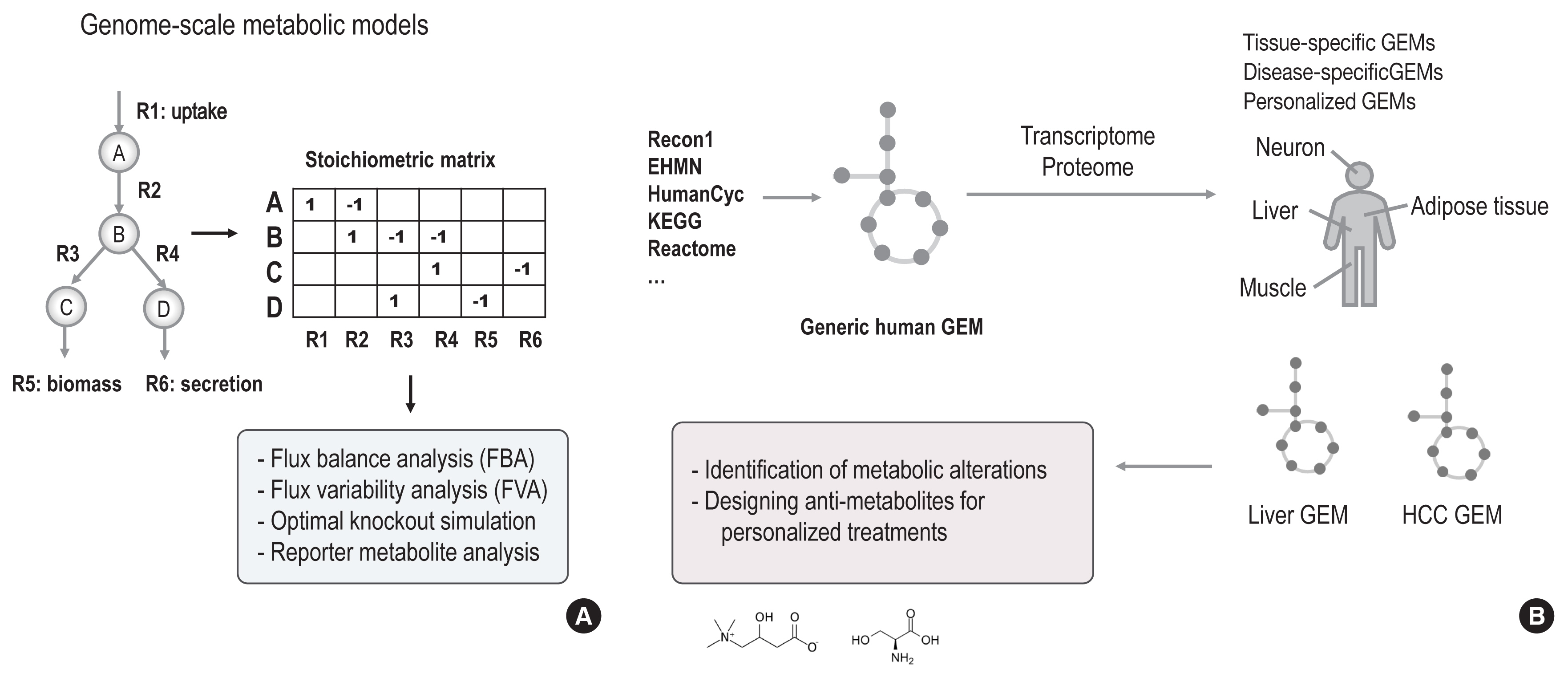
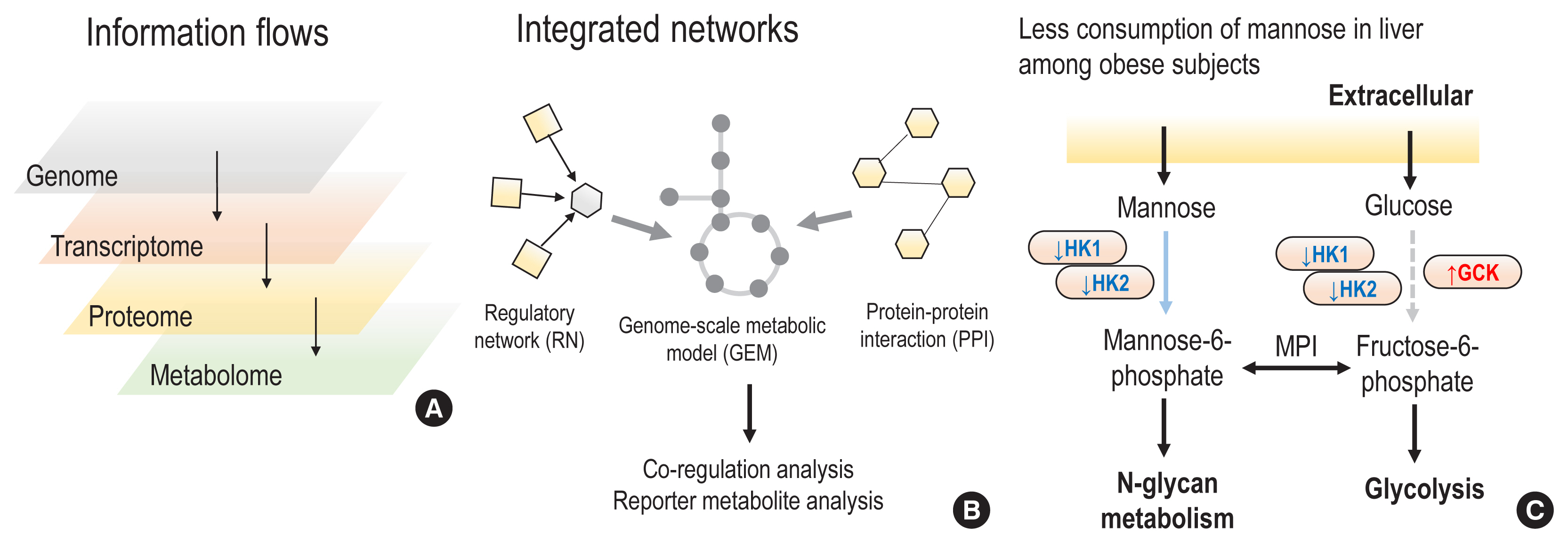
- The complex and dynamic nature of human physiology, as exemplified by metabolism, has often been overlooked due to the lack of quantitative and systems approaches. Recently, systems biology approaches have pushed the boundaries of our current understanding of complex biochemical, physiological, and environmental interactions, enabling proactive medicine in the near future. From this perspective, we review how state-of-the-art computational modelling of human metabolism, i.e., genome-scale metabolic modelling, could be used to identify the metabolic footprints of diseases, to guide the design of personalized treatments, and to estimate the microbiome contributions to host metabolism. These state-of-the-art models can serve as a scaffold for integrating multi-omics data, thereby enabling the identification of signatures of dysregulated metabolism by systems approaches. For example, increased plasma mannose levels due to decreased uptake in the liver have been identified as a potential biomarker of early insulin resistance by multi-omics approaches. In addition, we also review the emerging axis of human physiology and the human microbiome, discussing its contribution to host metabolism and quantitative approaches to study its variations in individuals.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Betts JG, Desaix P, Johnson E, Johnson JE, Korol O, Kruse D, et al. Anatomy and physiology: part 2. Houston: 12th Media Services;2016.2. Lavrik IN, Zhivotovsky B. Systems biology: a way to make complex problems more understandable. Cell Death Dis. 2014; 5:e1256.
Article3. Barabasi AL, Gulbahce N, Loscalzo J. Network medicine: a network-based approach to human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2011; 12:56–68.
Article4. Agren R, Bordel S, Mardinoglu A, Pornputtapong N, Nookaew I, Nielsen J. Reconstruction of genome-scale active metabolic networks for 69 human cell types and 16 cancer types using INIT. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012; 8:e1002518.
Article5. Mardinoglu A, Nielsen J. New paradigms for metabolic modeling of human cells. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2015; 34:91–7.
Article6. Shoaie S, Karlsson F, Mardinoglu A, Nookaew I, Bordel S, Nielsen J. Understanding the interactions between bacteria in the human gut through metabolic modeling. Sci Rep. 2013; 3:2532.
Article7. Shoaie S, Ghaffari P, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Mardinoglu A, Sen P, Pujos-Guillot E, et al. Quantifying diet-induced metabolic changes of the human gut microbiome. Cell Metab. 2015; 22:320–31.
Article8. Bidkhori G, Benfeitas R, Klevstig M, Zhang C, Nielsen J, Uhlen M, et al. Metabolic network-based stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma reveals three distinct tumor subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018; 115:E11874–83.
Article9. Benfeitas R, Bidkhori G, Mukhopadhyay B, Klevstig M, Arif M, Zhang C, et al. Characterization of heterogeneous redox responses in hepatocellular carcinoma patients using network analysis. EBioMedicine. 2019; 40:471–87.
Article10. Nilsson A, Mardinoglu A, Nielsen J. Predicting growth of the healthy infant using a genome scale metabolic model. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2017; 3:3.
Article11. Omenetti S, Bussi C, Metidji A, Iseppon A, Lee S, Tolaini M, et al. The intestine harbors functionally distinct homeostatic tissue-resident and inflammatory Th17 cells. Immunity. 2019; 51:77–89.
Article12. Liu L, Agren R, Bordel S, Nielsen J. Use of genome-scale metabolic models for understanding microbial physiology. FEBS Lett. 2010; 584:2556–64.
Article13. Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y, Morishima K. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017; 45:D353–61.
Article14. Robinson JL, Kocabas P, Wang H, Cholley PE, Cook D, Nilsson A, et al. An atlas of human metabolism. Sci Signal. 2020; 13:eaaz1482.
Article15. Jassal B, Matthews L, Viteri G, Gong C, Lorente P, Fabregat A, et al. The reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020; 48:D498–503.
Article16. Lee S, Zhang C, Arif M, Liu Z, Benfeitas R, Bidkhori G, et al. TCSBN: a database of tissue and cancer specific biological networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018; 46:D595–600.
Article17. Price ND, Magis AT, Earls JC, Glusman G, Levy R, Lausted C, et al. A wellness study of 108 individuals using personal, dense, dynamic data clouds. Nat Biotechnol. 2017; 35:747–56.
Article18. Mardinoglu A, Wu H, Bjornson E, Zhang C, Hakkarainen A, Rasanen SM, et al. An integrated understanding of the rapid metabolic benefits of a carbohydrate-restricted diet on hepatic steatosis in humans. Cell Metab. 2018; 27:559–71.
Article19. Kirschner M, Bauch A, Agusti A, Hilke S, Merk S, Pison C, et al. Implementing systems medicine within healthcare. Genome Med. 2015; 7:102.
Article20. Auffray C. Interview with a thought leader on systems medicine. Syst Med. 2018; 1:11–2.21. Gomez-Cabrero D, Marabita F, Tarazona S, Cano I, Roca J, Conesa A, et al. Guidelines for developing successful short advanced courses in systems medicine and systems biology. Cell Syst. 2017; 5:168–75.
Article22. Nielsen J. Systems biology of metabolism: a driver for developing personalized and precision medicine. Cell Metab. 2017; 25:572–9.
Article23. Nielsen J. Systems biology of metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 2017; 86:245–75.
Article24. O’Brien EJ, Monk JM, Palsson BO. Using genome-scale models to predict biological capabilities. Cell. 2015; 161:971–87.
Article25. Agren R, Mardinoglu A, Asplund A, Kampf C, Uhlen M, Nielsen J. Identification of anticancer drugs for hepatocellular carcinoma through personalized genome-scale metabolic modeling. Mol Syst Biol. 2014; 10:721.
Article26. Mardinoglu A, Agren R, Kampf C, Asplund A, Nookaew I, Jacobson P, et al. Integration of clinical data with a genome-scale metabolic model of the human adipocyte. Mol Syst Biol. 2013; 9:649.
Article27. Mardinoglu A, Agren R, Kampf C, Asplund A, Uhlen M, Nielsen J. Genome-scale metabolic modelling of hepatocytes reveals serine deficiency in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Commun. 2014; 5:3083.
Article28. Varemo L, Scheele C, Broholm C, Mardinoglu A, Kampf C, Asplund A, et al. Proteome- and transcriptome-driven reconstruction of the human myocyte metabolic network and its use for identification of markers for diabetes. Cell Rep. 2015; 11:921–33.
Article29. Mardinoglu A, Kampf C, Asplund A, Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM, Edlund K, et al. Defining the human adipose tissue proteome to reveal metabolic alterations in obesity. J Proteome Res. 2014; 13:5106–19.
Article30. Mardinoglu A, Bjornson E, Zhang C, Klevstig M, Soderlund S, Stahlman M, et al. Personal model-assisted identification of NAD + and glutathione metabolism as intervention target in NAFLD. Mol Syst Biol. 2017; 13:916.
Article31. Mardinoglu A, Boren J, Smith U, Uhlen M, Nielsen J. Systems biology in hepatology: approaches and applications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 15:365–77.
Article32. Zhang C, Bjornson E, Arif M, Tebani A, Lovric A, Benfeitas R, et al. The acute effect of metabolic cofactor supplementation: a potential therapeutic strategy against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Syst Biol. 2020; 16:e9495.
Article33. Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Backhed F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell. 2016; 165:1332–45.
Article34. Karczewski KJ, Snyder MP. Integrative omics for health and disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2018; 19:299–310.
Article35. Lee S, Zhang C, Kilicarslan M, Piening BD, Bjornson E, Hallstrom BM, et al. Integrated network analysis reveals an association between plasma mannose levels and insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2016; 24:172–84.
Article36. Patil KR, Nielsen J. Uncovering transcriptional regulation of metabolism by using metabolic network topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:2685–9.
Article37. Sharma V, Smolin J, Nayak J, Ayala JE, Scott DA, Peterson SN, et al. Mannose alters gut microbiome, prevents diet-induced obesity, and improves host metabolism. Cell Rep. 2018; 24:3087–98.
Article38. Kao D, Roach B, Silva M, Beck P, Rioux K, Kaplan GG, et al. Effect of oral capsule- vs colonoscopy-delivered fecal microbiota transplantation on recurrent clostridium difficile infection: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017; 318:1985–93.
Article39. Khoruts A, Sadowsky MJ. Understanding the mechanisms of faecal microbiota transplantation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 13:508–16.
Article40. Depommier C, Everard A, Druart C, Plovier H, Van Hul M, Vieira-Silva S, et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: a proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat Med. 2019; 25:1096–103.
Article41. Gopalakrishnan V, Spencer CN, Nezi L, Reuben A, Andrews MC, Karpinets TV, et al. Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science. 2018; 359:97–103.42. Koppel N, Maini Rekdal V, Balskus EP. Chemical transformation of xenobiotics by the human gut microbiota. Science. 2017; 356:eaag2770.
Article43. Dance A. The search for microbial dark matter. Nature. 2020; 582:301–3.
Article44. Lagier JC, Dubourg G, Million M, Cadoret F, Bilen M, Fenollar F, et al. Culturing the human microbiota and culturomics. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018; 16:540–50.
Article45. Lok C. Mining the microbial dark matter. Nature. 2015; 522:270–3.
Article46. Milanese A, Mende DR, Paoli L, Salazar G, Ruscheweyh HJ, Cuenca M, et al. Microbial abundance, activity and population genomic profiling with mOTUs2. Nat Commun. 2019; 10:1014.
Article47. Hillmann B, Al-Ghalith GA, Shields-Cutler RR, Zhu Q, Gohl DM, Beckman KB, et al. Evaluating the information content of shallow shotgun metagenomics. mSystems. 2018; 3:e00069–18.
Article48. Nayfach S, Shi ZJ, Seshadri R, Pollard KS, Kyrpides NC. New insights from uncultivated genomes of the global human gut microbiome. Nature. 2019; 568:505–10.
Article49. Kang DD, Li F, Kirton E, Thomas A, Egan R, An H, et al. MetaBAT 2: an adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ. 2019; 7:e7359.
Article50. Nielsen HB, Almeida M, Juncker AS, Rasmussen S, Li J, Sunagawa S, et al. Identification and assembly of genomes and genetic elements in complex metagenomic samples without using reference genomes. Nat Biotechnol. 2014; 32:822–8.
Article51. Plaza Onate F, Le Chatelier E, Almeida M, Cervino ACL, Gauthier F, Magoules F, et al. MSPminer: abundance-based reconstitution of microbial pan-genomes from shotgun metagenomic data. Bioinformatics. 2019; 35:1544–52.
Article52. Wang J, Jia H. Metagenome-wide association studies: fine-mining the microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016; 14:508–22.
Article53. Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F, et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2012; 490:55–60.
Article54. Arumugam M, Raes J, Pelletier E, Le Paslier D, Yamada T, Mende DR, et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature. 2011; 473:174–80.
Article55. Chiu CY, Miller SA. Clinical metagenomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2019; 20:341–55.
Article56. Zeevi D, Korem T, Zmora N, Israeli D, Rothschild D, Weinberger A, et al. Personalized nutrition by prediction of glycemic responses. Cell. 2015; 163:1079–94.
Article