Immune Netw.
2011 Dec;11(6):383-389. 10.4110/in.2011.11.6.383.
Cellular Mechanism of Newly Synthesized Indoledione Derivative-induced Immunological Death of Tumor Cell
- Affiliations
-
- 1Office of Biomedical Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea. andyjosh@skku.edu
- 2College of Pharmacy & Division of Life and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ewha Womans University, Seoul 120-750, Korea.
- KMID: 2150724
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2011.11.6.383
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
EY-6 is one of the newly synthesized indoledione derivatives to induce tumor cell-specific cell death. In this study, we investigated the mechanism of immunological death induced by EY-6 at mouse colon cancer cell as well as at the normal immune cell represented by dendritic cell.
METHODS
C57BL/6 mouse syngeneic colon cancer cell MC38 was treated with EY-6, and analyzed by MTT for viability test, flow cytometry for confirming surface expressing molecules and ELISA for detection of cytokine secretion. Normal myeloid-dendritic cell (DC) was ex vivo cultured from bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells of C57BL/6 mice with GM-CSF and IL-4 to analyze the DC uptake of dead tumor cells and to observe the effect of EY-6 on the normal DC.
RESULTS
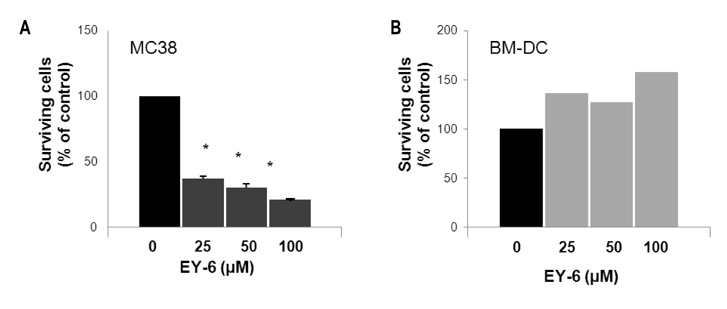
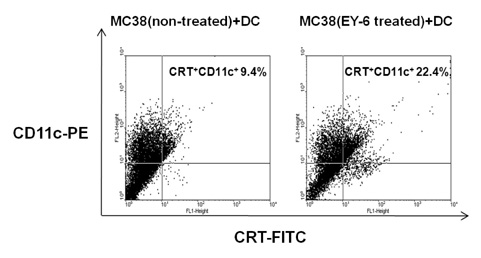
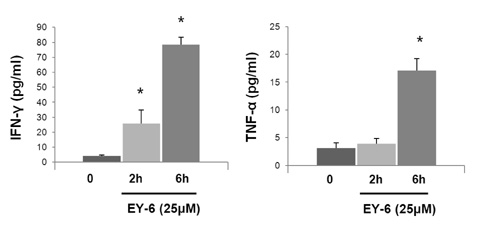
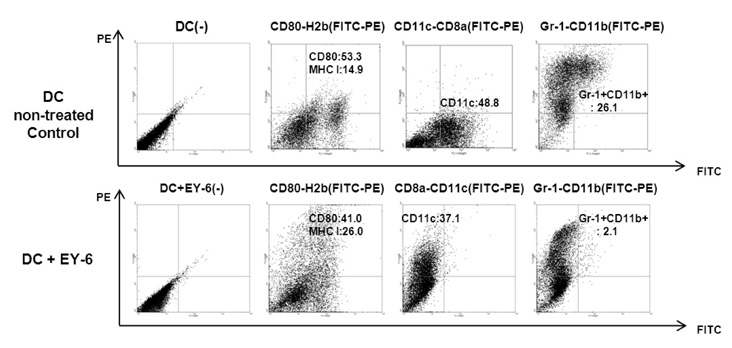
EY-6 killed the MC38 tumor cells in a dose dependent manner (25, 50 and 100 microM) with carleticulin induction. And EY-6 induced the secretion of IFN-gamma but not of TNF-alpha from the MC38 tumor cells. EY-6 did not kill the ex-vivo cultured DCs at the dose killing tumor cells and did slightly but not significantly induced the DC maturation. The OVA-specific cross-presentation ability of DC was not induced by chemical treatment (both MHC II and MHC I-restricted antigen presentation).
CONCLUSION
Data indicate that the EY-6 induced tumor cell specific and immunological cell death by modulation of tumor cell phenotype and cytokine secretion favoring induction of specific immunity eliminating tumor cells.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Bone Marrow
Cell Death
Colonic Neoplasms
Cross-Priming
Dendritic Cells
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Flow Cytometry
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Homicide
Interleukin-4
Mice
Phenotype
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Interleukin-4
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Chemotherapeutic Candidate Inducing Immunological Death of Human Tumor Cell Lines
Su-Jin Oh, Chung-Kyu Ryu, Inhak Choi, So-Young Baek, Hyunah Lee
Immune Netw. 2012;12(2):66-69. doi: 10.4110/in.2012.12.2.66.Immunogenic Cell Death Induced by Ginsenoside Rg3: Significance in Dendritic Cell-based Anti-tumor Immunotherapy
Keum-joo Son, Ki ryung Choi, Seog Jae Lee, Hyunah Lee
Immune Netw. 2016;16(1):75-84. doi: 10.4110/in.2016.16.1.75.
Reference
-
1. Obeid M, Panaretakis T, Tesniere A, Joza N, Tufi R, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Leveraging the immune system during chemotherapy: moving calreticulin to the cell surface converts apoptotic death from "silent" to immunogenic. Cancer Res. 2007. 67:7941–7944.
Article2. Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pagès C, Tosolini M, Camus M, Berger A, Wind P, Zinzindohoué F, Bruneval P, Cugnenc PH, Trajanoski Z, Fridman WH, Pagès F. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. 2006. 313:1960–1964.
Article3. Apetoh L, Mignot G, Panaretakis T, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L. Immunogenicity of anthracyclines: moving towards more personalized medicine. Trends Mol Med. 2008. 14:141–151.
Article4. Zitvogel L, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Kroemer G. Immunological aspects of cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008. 8:59–73.
Article5. Chan OT, Yang LX. The immunological effects of taxanes. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2000. 49:181–185.
Article6. Spreafico F, Vecchi A, Colotta F, Montovani A. Cancer chemotherapeutics as immunomodulators. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1985. 8:361–374.
Article7. North RJ. Cyclophosphamide-facilitated adoptive immunotherapy of an established tumor depends on elimination of tumor-induced suppressor T cells. J Exp Med. 1982. 155:1063–1074.
Article8. Nowak AK, Robinson BW, Lake RA. Gemcitabine exerts a selective effect on the humoral immune response: implications for combination chemo-immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2002. 62:2353–2358.9. Suzuki E, Kapoor V, Jassar AS, Kaiser LR, Albelda SM. Gemcitabine selectively eliminates splenic Gr-1+/CD11b+ myeloid suppressor cells in tumor-bearing animals and enhances antitumor immune activity. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. 11:6713–6721.
Article10. Machiels JP, Reilly RT, Emens LA, Ercolini AM, Lei RY, Weintraub D, Okoye FI, Jaffee EM. Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and paclitaxel enhance the antitumor immune response of granulocyte/macrophage-colony stimulating factor-secreting whole-cell vaccines in HER-2/neu tolerized mice. Cancer Res. 2001. 61:3689–3697.11. Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Senovilla L, Menger L, Chaput N, Kroemer G. Immunogenic tumor cell death for optimal anticancer therapy: the calreticulin exposure pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. 16:3100–3104.
Article12. Panaretakis T, Kepp O, Brockmeier U, Tesniere A, Bjorklund AC, Chapman DC, Durchschlag M, Joza N, Pierron G, van Endert P, Yuan J, Zitvogel L, Madeo F, Williams DB, Kroemer G. Mechanisms of pre-apoptotic calreticulin exposure in immunogenic cell death. EMBO J. 2009. 28:578–590.
Article13. Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Fimia GM, Apetoh L, Perfettini JL, Castedo M, Mignot G, Panaretakis T, Casares N, Métivier D, Larochette N, van Endert P, Ciccosanti F, Piacentini M, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death. Nat Med. 2007. 13:54–61.
Article14. Ko JH, Yeon SW, Ryu JS, Kim TY, Song EH, You HJ, Park RE, Ryu CK. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 5-arylamino-6-chloro-1H-indazole-4,7-diones as inhibitors of protein kinase B/Akt. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006. 16:6001–6005.
Article15. Chung KH, Hong SY, You HJ, Park RE, Ryu CK. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 5-arylamino-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-4,7-diones as inhibitor of endothelial cell proliferation. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006. 14:5795–5801.
Article16. Kim JS, Rhee HK, Park HJ, Lee IK, Lee SK, Suh ME, Lee HJ, Ryu CK, Choo HY. Synthesis of 6-chloroisoquinoline-5,8-diones and pyrido[3,4-b]phenazine-5,12-diones and evaluation of their cytotoxicity and DNA topoisomerase II inhibitory activity. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007. 15:451–457.
Article17. Seo JM, Jin YR, Ryu CK, Kim TJ, Han XH, Hong JT, Yoo HS, Lee CK, Yun YP. JM91, a newly synthesized indoledione derivative, inhibits rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and cell cycle progression through inhibition of ERK1/2 and Akt activations. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. 75:1331–1340.
Article18. Esumi N, Hunt B, Itaya T, Frost P. Reduced tumorigenicity of murine tumor cells secreting gamma-interferon is due to nonspecific host responses and is unrelated to class I major histocompatibility complex expression. Cancer Res. 1991. 51:1185–1189.19. Janelidze S, Bexell D, Badn W, Darabi A, Smith KE, Fritzell S, Gunnarsson S, Milos P, Bengzon J, Salford LG, Siesjö P, Visse E. Immunizations with IFNgamma secreting tumor cells can eliminate fully established and invasive rat gliomas. J Immunother. 2009. 32:593–601.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chemotherapeutic Candidate Inducing Immunological Death of Human Tumor Cell Lines
- The role of autophagy in the placenta as a regulator of cell death
- Protective Effects of K6PC-5, A Sphingosine Kinase Activator, Against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced Dopaminergic Neuronal Cell Death
- Mechanism of Neuronal Damage in Epilepsy
- Sonication Induces Apoptosis in HL-60 Cells