Immune Netw.
2011 Feb;11(1):59-67. 10.4110/in.2011.11.1.59.
Dietary Aloe Improves Insulin Sensitivity via the Suppression of Obesity-induced Inflammation in Obese Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Pharmacy, Sahmyook University, Seoul 139-742, Korea. kimkj@syu.ac.kr
- 2Univera Inc., Seoul 133-120, Korea.
- 3School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Korea University, Seoul 136-701, Korea.
- 4College of Pharmacy, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju 361-763, Korea.
- KMID: 2150693
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2011.11.1.59
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Insulin resistance is an integral feature of metabolic syndromes, including obesity, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia. In this study, we evaluated whether the aloe component could reduce obesity-induced inflammation and the occurrence of metabolic disorders such as blood glucose and insulin resistance.
METHODS
Male C57BL/6 obese mice fed a high-fat diet for 54 days received a supplement of aloe formula (PAG, ALS, Aloe QDM, and Aloe QDM complex) or pioglitazone (PGZ) and were compared with unsupplemented controls (high-fat diet; HFD) or mice fed a regular diet (RD). RT-PCR and western blot analysis were used to quantify the expression of obesity-induced inflammation.
RESULTS
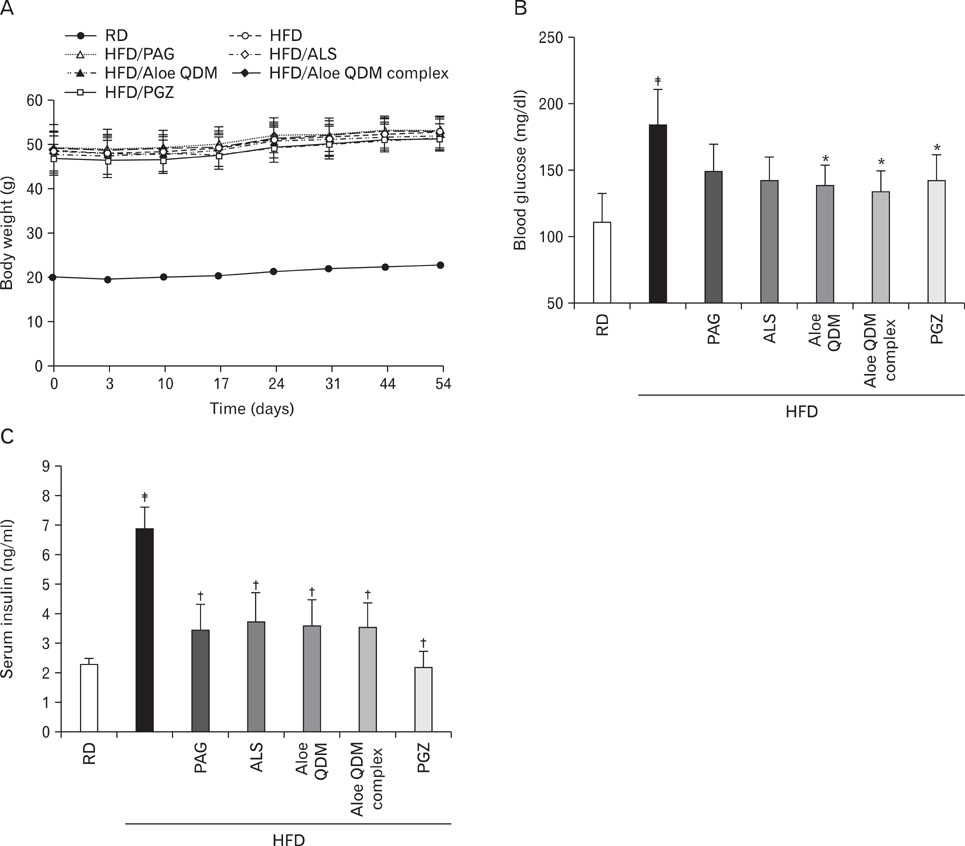
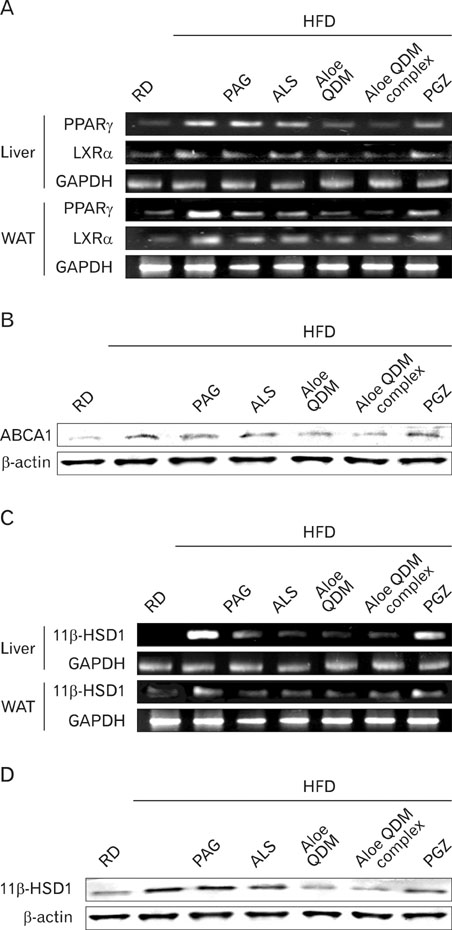
Aloe QDM lowered fasting blood glucose and plasma insulin compared with HFD. Obesity-induced inflammatory cytokine (IL-1beta, -6, -12, TNF-alpha) and chemokine (CX3CL1, CCL5) mRNA and protein were decreased markedly, as was macrophage infiltration and hepatic triglycerides by Aloe QDM. At the same time, Aloe QDM decreased the mRNA and protein of PPARgamma/LXRalpha and 11beta-HSD1 both in the liver and WAT.
CONCLUSION
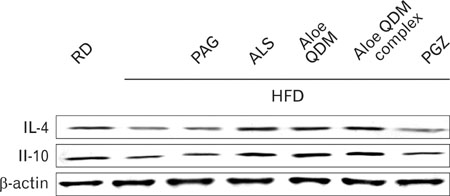
Dietary aloe formula reduces obesity-induced glucose tolerance not only by suppressing inflammatory responses but also by inducing anti-inflammatory cytokines in the WAT and liver, both of which are important peripheral tissues affecting insulin resistance. The effect of Aloe QDM complex in the WAT and liver are related to its dual action on PPARgamma and 11beta-HSD1 expression and its use as a nutritional intervention against T2D and obesity-related inflammation is suggested.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
11-beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1
Aloe
Animals
Blood Glucose
Blotting, Western
Cytokines
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2
Diet
Diet, High-Fat
Fasting
Glucose
Humans
Hyperglycemia
Hyperlipidemias
Inflammation
Insulin
Insulin Resistance
Liver
Macrophages
Male
Mice
Mice, Obese
Obesity
Plasma
PPAR gamma
RNA, Messenger
Thiazolidinediones
Triglycerides
11-beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1
Blood Glucose
Cytokines
Glucose
Insulin
PPAR gamma
RNA, Messenger
Thiazolidinediones
Triglycerides
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Dietary Aloe Reduces Adipogenesis via the Activation of AMPK and Suppresses Obesity-related Inflammation in Obese Mice
Eunju Shin, Seulmee Shin, Hyunseok Kong, Sungwon Lee, Seon-Gil Do, Tae Hyung Jo, Young-In Park, Chong-Kil Lee, In-Kyeong Hwang, Kyungjae Kim
Immune Netw. 2011;11(2):107-113. doi: 10.4110/in.2011.11.2.107.The Synergy Effect of Weight‐Bearing Circuit Training and Aloe QDM Complex on Obese Middle Aged Women: a Randomized Double‐Blind Controlled Trial
Mi Jung Choi, Yong An Kim, Eunju Shin, Seon-Gil Do, Wook Song
Korean J Health Promot. 2014;14(2):59-66. doi: 10.15384/kjhp.2014.14.2.59.
Reference
-
1. Pickup JC, Crook MA. Is type II diabetes mellitus a disease of the innate immune system? Diabetologia. 1998. 41:1241–1248.
Article2. Grimble RF. Inflammatory status and insulin resistance. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2002. 5:551–559.
Article3. Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA, Chen H. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2003. 112:1821–1830.
Article4. Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 2003. 112:1796–1808.
Article5. Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Marino MW, Hotamisligil GS. Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature. 1997. 389:610–614.
Article6. Browning JD, Horton JD. Molecular mediators of hepatic steatosis and liver injury. J Clin Invest. 2004. 114:147–152.
Article7. Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM, Patel HR, Ahima RS, Lazar MA. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature. 2001. 409:307–312.
Article8. Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, Kotani K, Quadro L, Kahn BB. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2005. 436:356–362.
Article9. Olefsky JM, Glass CK. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2010. 72:219–246.
Article10. Matsuzawa Y, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Shimomura I. Adiponectin and metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004. 24:29–33.
Article11. Hausman DB, DiGirolamo M, Bartness TJ, Hausman GJ, Martin RJ. The biology of white adipocyte proliferation. Obes Rev. 2001. 2:239–254.
Article12. Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993. 259:87–91.
Article13. Wang P, Mariman E, Renes J, Keijer J. The secretory function of adipocytes in the physiology of white adipose tissue. J Cell Physiol. 2008. 216:3–13.
Article14. Josep BR, Amir G, Jennifer K, Raquel H. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: the nutritionally controlled molecular networks that integrate inflammation, immunity and metabolism. Curr Nutr Food Sci. 2005. 1:179–187.
Article15. Capasso F, Borrelli F, Capasso R, Di Carlo G, Izzo A, Pinto L, Mascolo N, Castaldo S, Longo R. Aloe and its therapeutic use. Phytother Res. 1998. 12:S124–S127.
Article16. Heggers JP, Kucukcelebi A, Stabenau CJ, Ko F, Broemeling LD, Robson MC, Winters WD. Wound healing effects of Aloe gel and other topical antibacterial agents on rat skin. Phytother Res. 1995. 9:455–457.
Article17. Koo MWL. Aloe vera: Antiulcer and antidiabetic effects. Phytother Res. 1994. 8:461–464.
Article18. Winters WD, Benavides R, Clouse WJ. Effects of aloe extracts on human normal and tumor cells in vitro. Econ Bot. 1981. 35:89–95.
Article19. Yongchaiyudha S, Rungpitarangsi V, Bunyapraphatsara N, Chokechaijaroenporn O. Antidiabetic activity of Aloe vera L. juice: I. Clinical trial in new cases of diabetes mellitus. Phytomedicine. 1996. 3:241–243.
Article20. Bunyapraphatsara N, Yongchaiyudha S, Rungpitarangsi V, Chokechaijaroenporn O. Antidiabetic activity of Aloe vera L. juice. II. Clinical trial in diabetes mellitus patients in combination with glibenclamide. Phytomedicine. 1996. 3:245–248.
Article21. Schwarz K, Mertz W. Chromium(III) and the glucose tolerance factor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959. 85:292–295.
Article22. Anderson RA. Chromium, glucose intolerance and diabetes. J Am Coll Nutr. 1998. 17:548–555.
Article23. Kim K, Kim H, Kwon J, Lee S, Kong H, Im SA, Lee YH, Lee YR, Oh ST, Jo TH, Park YI, Lee CK, Kim K. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of processed Aloe vera gel in a mouse model of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Phytomedicine. 2009. 16:856–863.
Article24. Kong H, Lee S, Shin S, Kwon J, Jo TH, Shin E, Shim KS, Park YI, Lee CK, Kim K. Down-regulation of adipogenesis and hyperglycemia in diet-induced obesity mouse model by Aloe QDM. Biomolecules Therapeutics. 2010. 18:336–342.
Article25. Odegaard JI, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Red Eagle A, Vats D, Morel CR, Goforth MH, Subramanian V, Mukundan L, Ferrante AW, Chawla A. Alternative M2 activation of Kupffer cells by PPARdelta ameliorates obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2008. 7:496–507.
Article26. Kim J, Temple KA, Jones SA, Meredith KN, Basko JL, Brady MJ. Differential modulation of 3T3-L1 adipogenesis mediated by 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1 levels. J Biol Chem. 2007. 282:11038–11046.
Article27. Kim JO, Kim KS, Lee GD, Kwon JH. Antihyperglycemic and antioxidative effects of new herbal formula in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Med Food. 2009. 12:728–735.
Article28. Stienstra R, Mandard S, Tan NS, Wahli W, Trautwein C, Richardson TA, Lichtenauer-Kaligis E, Kersten S, Müller M. The Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist is a direct target gene of PPARalpha in liver. J Hepatol. 2007. 46:869–877.
Article29. Costet P, Luo Y, Wang N, Tall AR. Sterol-dependent transactivation of the ABC1 promoter by the liver X receptor/retinoid X receptor. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:28240–28245.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dietary Aloe QDM Complex Reduces Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance and Adipogenesis in Obese Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
- Dietary Aloe Reduces Adipogenesis via the Activation of AMPK and Suppresses Obesity-related Inflammation in Obese Mice
- The Role of T Cells in Obesity-Associated Inflammation and Metabolic Disease
- Metformin Down-regulates TNF-alpha Secretion via Suppression of Scavenger Receptors in Macrophages
- Effects of Functional Food Components in Reducing Obesity-induced Inflammation and Metabolic Diseases