Immune Netw.
2010 Jun;10(3):104-108. 10.4110/in.2010.10.3.104.
Agonistic Anti-CD137 Monoclonal Antibody Treatment Induces CD11b+Gr-1+ Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Immunology, Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. cykang@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Science, Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2150667
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2010.10.3.104
Abstract
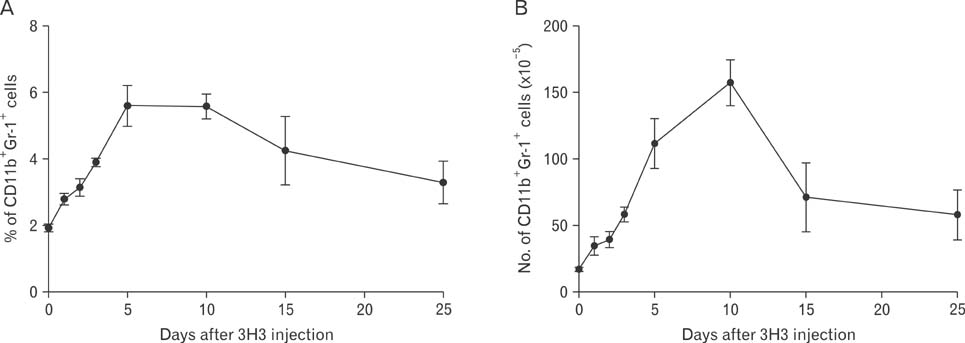
- CD137 (4-1BB/tnfrsf9) has been shown to co-stimulate T cells. However, agonistic anti-CD137 monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatment can suppress CD4+ T cells, ameliorating autoimmune diseases, whereas it induces activation of CD8+ T cells, resulting in diverse therapeutic activity in cancer, viral infection. To investigate the CD137-mediated T cell suppression mechanism, we examined whether anti-CD137 mAb treatment could affect CD11b+Gr-1+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Intriguingly, anti-CD137 mAb injection significantly increased CD11b+Gr-1+ cells, peaking at days 5 to 10 and continuing for at least 25 days. Furthermore, this cell population could suppress both CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells. Thus, this study demonstrated that, for the first time, anti-CD137 mAb treatment could induce CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSCs under normal conditions, suggesting a possible relationship between myeloid cell induction and CD137-mediated immune suppression.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vinay DS, Cha K, Kwon BS. Dual immunoregulatory pathways of 4-1BB signaling. J Mol Med. 2006. 84:726–736.
Article2. Miller RE, Jones J, Le T, Whitmore J, Boiani N, Gliniak B, Lynch DH. 4-1BB-specific monoclonal antibody promotes the generation of tumor-specific immune responses by direct activation of CD8 T cells in a CD40-dependent manner. J Immunol. 2002. 169:1792–1800.
Article3. Xu D, Gu P, Pan PY, Li Q, Sato AI, Chen SH. NK and CD8+ T cell-mediated eradication of poorly immunogenic B16-F10 melanoma by the combined action of IL-12 gene therapy and 4-1BB costimulation. Int J Cancer. 2004. 109:499–506.
Article4. Halstead ES, Mueller YM, Altman JD, Katsikis PD. In vivo stimulation of CD137 broadens primary antiviral CD8+ T cell responses. Nat Immunol. 2002. 3:536–541.
Article5. Hong HJ, Lee JW, Park SS, Kang YJ, Chang SY, Kim KM, Kim JO, Murthy KK, Payne JS, Yoon SK, Park MJ, Kim IC, Kim JG, Kang CY. A humanized anti--4-1BB monoclonal antibody suppresses antigen-induced humoral immune response in nonhuman primates. J Immunother. 2000. 23:613–621.
Article6. Sun Y, Chen HM, Subudhi SK, Chen J, Koka R, Chen L, Fu YX. Costimulatory molecule-targeted antibody therapy of a spontaneous autoimmune disease. Nat Med. 2002. 8:1405–1413.
Article7. Sun Y, Lin X, Chen HM, Wu Q, Subudhi SK, Chen L, Fu YX. Administration of agonistic anti-4-1BB monoclonal antibody leads to the amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2002. 168:1457–1465.
Article8. Foell J, Strahotin S, O'Neil SP, McCausland MM, Suwyn C, Haber M, Chander PN, Bapat AS, Yan XJ, Chiorazzi N, Hoffmann MK, Mittler RS. CD137 costimulatory T cell receptor engagement reverses acute disease in lupus-prone NZB x NZW F1 mice. J Clin Invest. 2003. 111:1505–1518.
Article9. Seo SK, Choi JH, Kim YH, Kang WJ, Park HY, Suh JH, Choi BK, Vinay DS, Kwon BS. 4-1BB-mediated immunotherapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 2004. 10:1088–1094.
Article10. Foell JL, Diez-Mendiondo BI, Diez OH, Holzer U, Ruck P, Bapat AS, Hoffmann MK, Mittler RS, Dannecker GE. Engagement of the CD137 (4-1BB) costimulatory molecule inhibits and reverses the autoimmune process in collagen-induced arthritis and establishes lasting disease resistance. Immunology. 2004. 113:89–98.
Article11. Kim J, Choi WS, La S, Suh JH, Kim BS, Cho HR, Kwon BS, Kwon B. Stimulation with 4-1BB (CD137) inhibits chronic graft-versus-host disease by inducing activation-induced cell death of donor CD4+ T cells. Blood. 2005. 105:2206–2213.
Article12. Kim YH, Seo SK, Choi BK, Kang WJ, Kim CH, Lee SK, Kwon BS. 4-1BB costimulation enhances HSV-1-specific CD8+ T cell responses by the induction of CD11c+CD8+ T cells. Cell Immunol. 2005. 238:76–86.
Article13. Vinay DS, Kim CH, Choi BK, Kwon BS. Origins and functional basis of regulatory CD11c+CD8+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2009. 39:1552–1563.14. Lee SW, Park Y, So T, Kwon BS, Cheroutre H, Mittler RS, Croft M. Identification of regulatory functions for 4-1BB and 4-1BBL in myelopoiesis and the development of dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 2008. 9:917–926.
Article15. Niu L, Strahotin S, Hewes B, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Archer D, Spencer T, Dillehay D, Kwon B, Chen L, Vella AT, Mittler RS. Cytokine-mediated disruption of lymphocyte trafficking, hemopoiesis, and induction of lymphopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia in anti-CD137-treated mice. J Immunol. 2007. 178:4194–4213.
Article16. Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009. 9:162–174.
Article17. Dubrot J, Azpilikueta A, Alfaro C, Murillo O, Arina A, Berraondo P, Hervas-Stubbs S, Melero I. Absence of surface expression of CD137 (4-1BB) on Myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Immunologia. 2007. 26:121–126.
Article18. Wang C, Lin GH, McPherson AJ, Watts TH. Immune regulation by 4-1BB and 4-1BBL: complexities and challenges. Immunol Rev. 2009. 229:192–215.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- CD11b+Gr-1low cells that accumulate in M.leprae-induced granulomas of the footpad skin of nude mice have the characteristics of monocytic-myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- CD137-CD137 Ligand Interactions in Inflammation
- Skewed Dendritic Cell Differentiation of MyD88-Deficient Donor Bone Marrow Cells, Instead of Massive Expansion as Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells, Aggravates GVHD
- Anti-CD137 mAb Deletes Both Donor CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells in Acute Graft-versus-host Disease
- Role of Clusterin and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors on the Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells