Korean J Androl.
2011 Apr;29(1):43-52. 10.5534/kja.2011.29.1.43.
Role of Clusterin and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors on the Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. urojoo@dreamwiz.com
- KMID: 2298625
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/kja.2011.29.1.43
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In prostate cancer, the anti-apoptotic mechanism of sulfated glycoprotein-2 (clusterin) against tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) receptors and the action of type 2 TNF-alpha receptor (TNFR2) were investigated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
TNF-alpha, agonistic-TNF type 1 receptor (TNFR1) antibody, agonistic-TNF-R2 antibody and their combination were treated in PC3 cell line with or without anti-clusterin. Cytotoxicity was assessed by trypan blue dye exclusion assay. By using flowcytometric analysis, the exact amount of apoptosis and their changes were assessed.
RESULTS
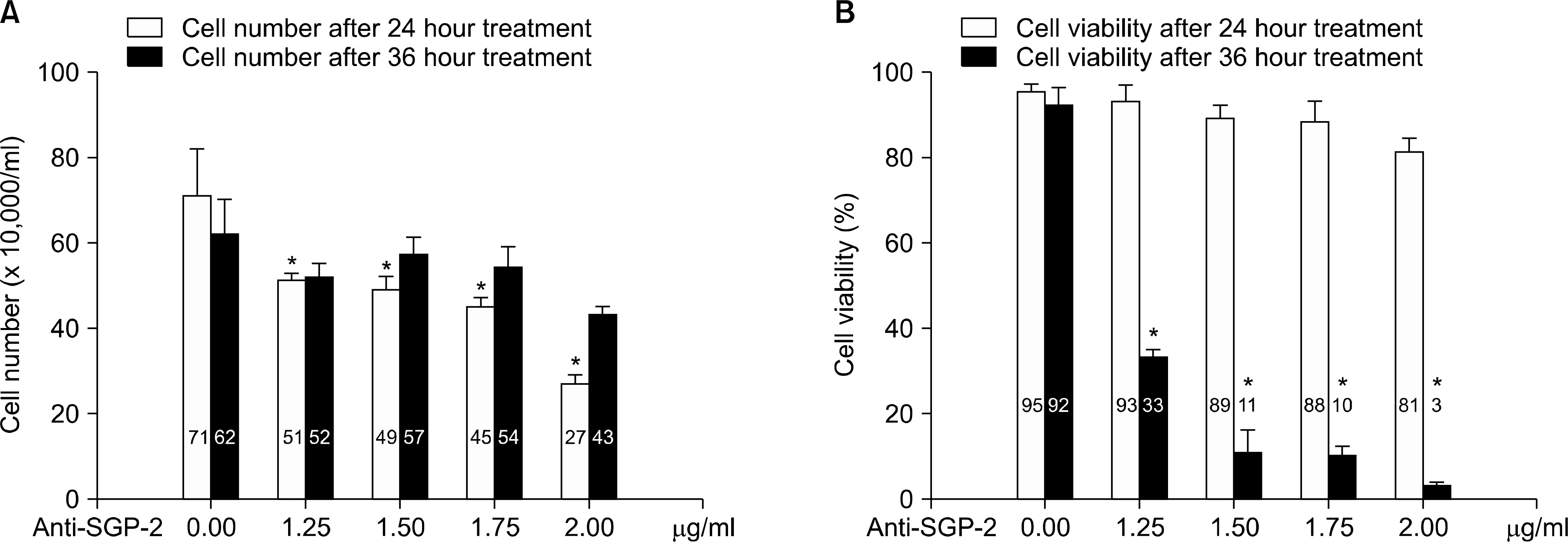
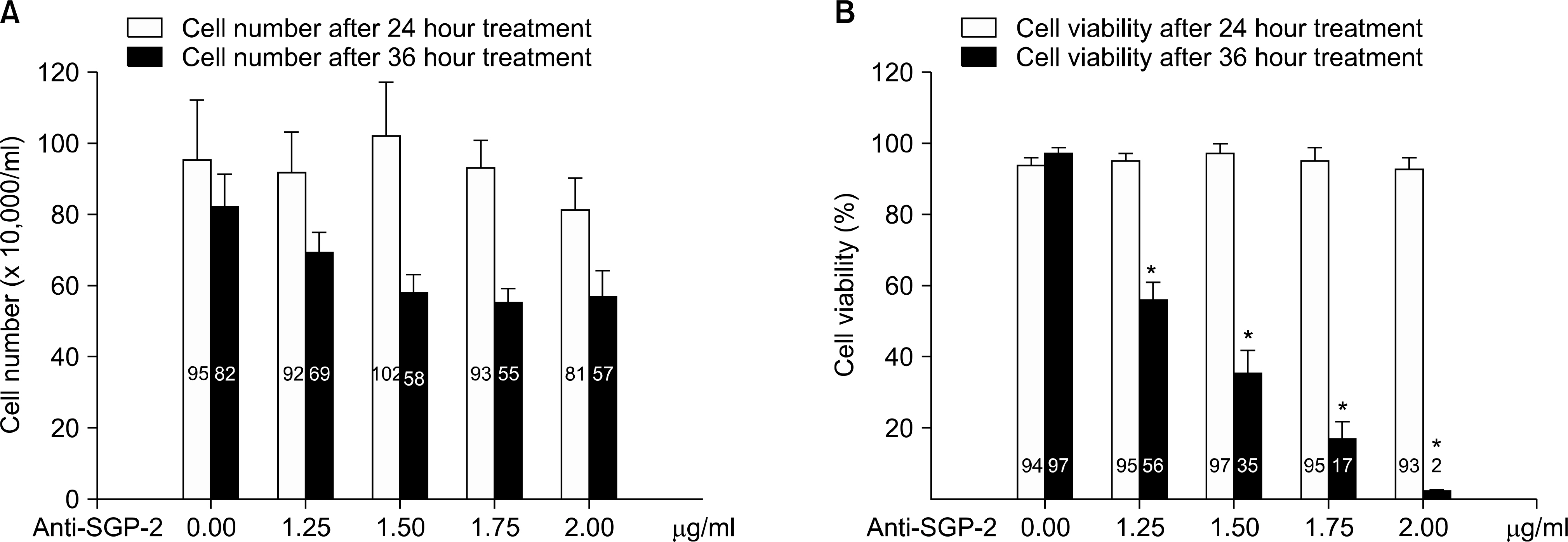
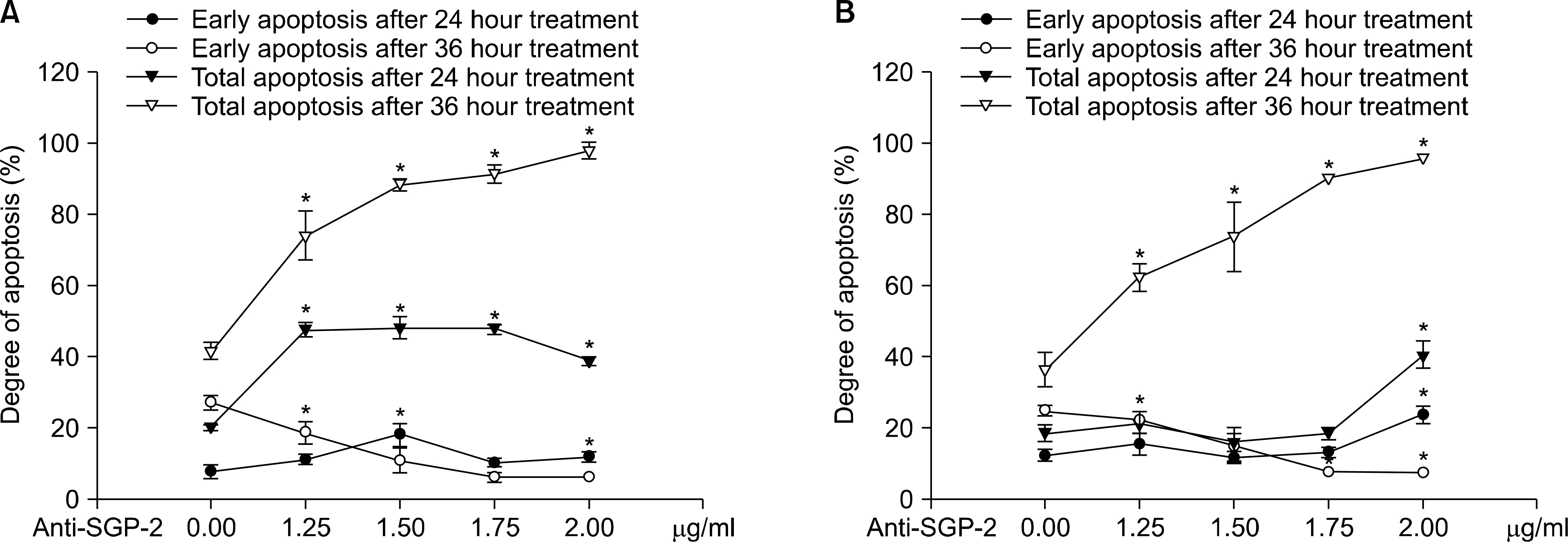
Apoptosis was significantly increased in both agonistic-TNFR1 antibody and TNF-alpha treated cases after blocking the activity of clusterin. The more the anti-clusterin antibody added, the more the apoptosis occurred. The increase of total apoptosis was greater in TNF-alpha treated cells than in agonistic-TNFR1 antibody treated ones. However, there was no increase of apoptosis in agonistic-TNFR2 antibody and TNF-alpha with agonistic-TNFR2 antibody treated cases, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Clusterin prevents TNF-alpha induced apoptosis by affecting TNFR1. The difference in degree of apoptosis between agonistic-TNFR1 antibody treated cells and TNF-alpha treated ones suggests the possibility of the action of TNFR2. It may be associated with affinity of TNF-alpha to the tumor cell surface.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Apoptosis
Cell Line
Clusterin
Diminazene
Prostate
Prostatic Neoplasms
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor, Type I
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor, Type II
Trypan Blue
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Clusterin
Diminazene
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor, Type I
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor, Type II
Trypan Blue
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Figure
Reference
-
1). Creasey AA, Doyle LV, Reynolds MT, Jung T, Lin LS, Vitt CR. Biological effects of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor and its novel muteins on tumor and normal cell lines. Cancer Res. 1987; 47:145–9.2). Schall TJ, Lewis M, Koller KJ, Lee A, Rice GC, Wong GH, et al. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990; 61:361–70.
Article3). Tartaglia LA, Goeddel DV. Tumor necrosis factor receptor signaling. A dominant negative mutation suppresses the activation of the 55-kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992; 267:4304–7.
Article4). Sylvester SR, Morales C, Oko R, Griswold MD. Localization of sulfated glycoprotein-2 (clusterin) on spermatozoa and in the reproductive tract of the male rat. Biol Reprod. 1991; 45:195–207.5). Sensibar JA, Griswold MD, Sylvester SR, Buttyan R, Bardin CW, Cheng CY, et al. Prostatic ductal system in rats: regional variation in localization of an androgen-repressed gene product, sulfated glycoprotein-2. Endocrinology. 1991; 128:2091–102.
Article6). Shannan B, Seifert M, Leskov K, Willis J, Boothman D, Tilgen W, et al. Challenge and promise: roles for clusterin in pathogenesis, progression and therapy of cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2006; 13:12–9.
Article7). Shannan B, Seifert M, Boothman DA, Tilgen W, Reichrath J. Clusterin and DNA repair: a new function in cancer for a key player in apoptosis and cell cycle control. J Mol Histol. 2006; 37:183–8.
Article8). Sensibar JA, Sutkowski DM, Raffo A, Buttyan R, Griswold MD, Sylvester SR, et al. Prevention of cell death induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha in LNCaP cells by overexpression of sulfated glycoprotein-2 (clusterin). Cancer Res. 1995; 55:2431–7.9). Wilding G, Zugmeier G, Knabbe C, Flanders K, Gelmann E. Differential effects of transforming growth factor beta on human prostate cancer cells in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989; 62:79–87.10). Tartaglia LA, Weber RF, Figari IS, Reynolds C, Palladino MA Jr, Goeddel DV. The two different receptors for tumor necrosis factor mediate distinct cellular responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991; 88:9292–6.
Article11). Espevik T, Brockhaus M, Loetscher H, Nonstad U, Shalaby R. Characterization of binding and biological effects of monoclonal antibodies against a human tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Exp Med. 1990; 171:415–26.
Article12). Kyprianou N, Isaacs JT. Quantal relationship between prostatic dihydrotestosterone and prostatic cell content: critical threshold concept. Prostate. 1987; 11:41–50.
Article13). English HF, Kyprianou N, Isaacs JT. Relationship between DNA fragmentation and apoptosis in the programmed cell death in the rat prostate following castration. Prostate. 1989; 15:233–50.
Article14). Sintich SM, Steinberg J, Kozlowski JM, Lee C, Pruden S, Sayeed S, et al. Cytotoxic sensitivity to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in PC3 and LNCaP prostatic cancer cells is regulated by extracellular levels of SGP-2 (clusterin). Prostate. 1999; 39:87–93.15). Slawin K, Sawczuk IS, Olsson CA, Buttyan R. Chromosomal assignment of the human homologue encoding SGP-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990; 172:160–4.
Article16). Lakins J, Bennett SA, Chen JH, Arnold JM, Morrissey C, Wong P, et al. Clusterin biogenesis is altered during apoptosis in the regressing rat ventral prostate. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:27887–95.
Article17). Ahuja HS, Tenniswood M, Lockshin R, Zakeri ZF. Expression of clusterin in cell differentiation and cell death. Biochem Cell Biol. 1994; 72:523–30.
Article18). Bruchovsky N, Snoek R, Rennie PS, Akakura K, Goldenberg LS, Gleave M. Control of tumor progression by maintenance of apoptosis. Prostate Suppl. 1996; 6:13–21.
Article19). Rittmaster RS, Magor KE, Manning AP, Norman RW, Lazier CB. Differential effect of 5 alpha-reductase inhibition and castration on androgen-regulated gene expression in rat prostate. Mol Endocrinol. 1991; 5:1023–9.20). Nickerson T, Pollak M, Huynh H. Castration-induced apoptosis in the rat ventral prostate is associated with increased expression of genes encoding insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 2,3,4 and 5. Endocrinology. 1998; 139:807–10.21). Fleshner NE, Trachtenberg J. Sequential androgen blockade: a biological study in the inhibition of prostatic growth. J Urol. 1992; 148:1928–31.
Article22). Shalaby MR, Sundan A, Loetscher H, Brockhaus M, Lesslauer W, Espevik T. Binding and regulation of cellular functions by monoclonal antibodies against human tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Exp Med. 1990; 172:1517–20.
Article23). Smith CA, Davis T, Anderson D, Solam L, Beckmann MP, Jerzy R, et al. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science. 1990; 248:1019–23.
Article24). Loetscher H, Gentz R, Zulauf M, Lustig A, Tabuchi H, Schlaeger EJ, et al. Recombinant 55-kDa tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor. Stoichiometry of binding to TNF alpha and TNF beta and inhibition of TNF activity. J Biol Chem. 1991; 266:18324–9.
Article25). Haranaka K, Satomi N. Cytotoxic activity of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) on human cancer cells in vitro. Jpn J Exp Med. 1981; 51:191–4.26). van Horssen R, Ten Hagen TL, Eggermont AM. TNF-alpha in cancer treatment: molecular insights, antitumor effects, and clinical utility. Oncologist. 2006; 11:397–408.27). Engelmann H, Holtmann H, Brakebusch C, Avni YS, Sarov I, Nophar Y, et al. Antibodies to a soluble form of a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor have TNF-like activity. J Biol Chem. 1990; 265:14497–504.
Article28). Tartaglia LA, Goeddel DV, Reynolds C, Figari IS, Weber RF, Fendly BM, et al. Stimulation of human T-cell proliferation by specific activation of the 75-kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Immunol. 1993; 151:4637–41.29). Gerspach J, Muller D, Munkel S, Selchow O, Nemeth J, Noack M, et al. Restoration of membrane TNF-like activity by cell surface targeting and matrix metalloproteinase-mediated processing of a TNF prodrug. Cell Death Differ. 2006; 13:273–84.
Article30). Tartaglia LA, Pennica D, Goeddel DV. Ligand passing: the 75-kDa tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor recruits TNF for signaling by the 55-kDa TNF receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993; 268:18542–8.
Article31). Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon AJ, Rader JA, van Schie RC, LaFace DM, et al. Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J Exp Med. 1995; 182:1545–56.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation of Clusterin Expression and Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer and Benign Hyperplastic Tissues
- Effect of Sulfated Glycoprotein-2 (Clusterin) on the Apoptosis of Prostatic Cancer
- Clusterin Expression and Apoptosis in Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder
- Apoptosis Induction and Clusterin Expression of NRP-152 Cells by Tamsulosin
- TNFalpha and TNFR2 Immunohistochemistry During Ovarian Follicular Development and Atresia in the Rat