Immune Netw.
2011 Dec;11(6):428-430. 10.4110/in.2011.11.6.428.
Anti-CD137 mAb Deletes Both Donor CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells in Acute Graft-versus-host Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Biomedical Research Center, Ulsan University Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 680-749, Korea. bkwon@mail.ulsan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Ulsan University Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 680-749, Korea.
- 3School of Biological Sciences, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 680-749, Korea.
- KMID: 2150732
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2011.11.6.428
Abstract
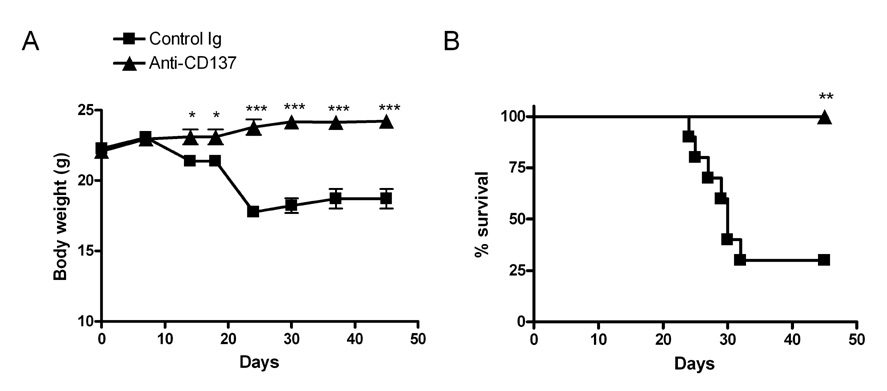
- We previously demonstrated that in vivo engagement of CD137, a member of TNF receptor superfamily, can delete allorective CD4+ T cells through the induction of activation-induced cell death (AICD) in chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) and subsequently reverse established cGVHD. In this study, we further showed that agonistic anti-CD137 mAb was highly effective in triggering AICD of donor CD8+ T cells as well as donor CD4+ T cells in the C57BL/6-->unirradiated (C57BL/6 x DBA/2)F1 acute GVHD model. Our results suggest that strong allostimulation should facilitate AICD of both alloreactive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells induced by CD137 stimulation. Therefore, depletion of pathogenic T cells using agonistic anti-CD137 mAb combined with potent TCR stimulation may be used to block autoimmune or inflammatory diseases mediated by T cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kwon B. CD137-CD137 ligand interactions in inflammation. Immune Netw. 2009. 9:84–89.
Article2. Melero I, Shuford WW, Newby SA, Aruffo A, Ledbetter JA, Hellström KE, Mittler RS, Chen L. Monoclonal antibodies against the 4-1BB T-cell activation molecule eradicate established tumors. Nat Med. 1997. 3:682–685.
Article3. Kwon B. Intervention with costimulatory pathways as a therapeutic approach for graft-versus-host disease. Exp Mol Med. 2010. 42:675–683.
Article4. Kim J, Choi WS, La S, Suh JH, Kim BS, Cho HR, Kwon BS, Kwon B. Stimulation with 4-1BB (CD137) inhibits chronic graft-versus-host disease by inducing activation-induced cell death of donor CD4+ T cells. Blood. 2005. 105:2206–2213.
Article5. Kim J, Kim HJ, Park K, Kim J, Choi HJ, Yagita H, Nam SH, Cho HR, Kwon B. Costimulatory molecule-targeted immunotherapy of cutaneous graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2007. 110:776–782.
Article6. Zhang B, Maris CH, Foell J, Whitmire J, Niu L, Song J, Kwon BS, Vella AT, Ahmed R, Jacob J, Mittler RS. Immune suppression or enhancement by CD137 T cell costimulation during acute viral infection is time dependent. J Clin Invest. 2007. 117:3029–3041.
Article7. Zhang B, Zhang Y, Niu L, Vella AT, Mittler RS. Dendritic cells and Stat3 are essential for CD137-induced CD8 T cell activation-induced cell death. J Immunol. 2010. 184:4770–4778.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Agonistic Anti-CD137 Monoclonal Antibody Treatment Induces CD11b+Gr-1+ Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells
- Maintenance of CD8+T-cell anergy by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in chronic graft-versus-host disease
- Acute Cutaneous Graft-Versus-Host Reaction
- Distribution of CD4+CD25+ T cells and graft-versus-host disease in human hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Alteration of Molecules and Cytokines Related to the Activation of T Lymphocyte in Immune Tolerance Induced Mice Model