CD137-CD137 Ligand Interactions in Inflammation
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Biological Sciences, University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea. bkwon@ulsan.ac.kr
- KMID: 2150646
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2009.9.3.84
Abstract
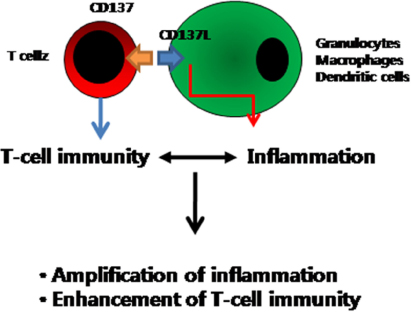
- The main stream of CD137 studies has been directed to the function of CD137 in CD8+ T-cell immunity, including its anti-tumor activity, and paradoxically the immunosuppressive activity of CD137, which proves to be of a great therapeutic potential for animal models of a variety of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Recent studies, however, add complexes to the biology of CD137. Accumulating is evidence supporting that there exists a bidirectional signal transduction pathway for the CD137 receptor and its ligand (CD137L). CD137/CD137L interactions are involved in the network of hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells in addition to the well characterized antigen-presenting cell-T cell interactions. Signaling through CD137L plays a critical role in the differentiation of myeloid cells and their cellular activities, suggesting that CD137L signals trigger and sustain inflammation. The overall consequence might be that the amplified inflammation by CD137L enhances the T-cell activity together with CD137 signals by upregulating costimulatory molecules, MHC molecules, cell adhesion molecules, cytokines, and chemokines. Solving this outstanding issue is urgent and will have an important clinical implication.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Recombinant TAT-CD137 Ligand Cytoplasmic Domain Fusion Protein Induces the Production of IL-6 and TNF-α in Peritoneal Macrophages
Jung Dae Kim, Eun Ah Lee, Nguyen N. Quang, Hong Rae Cho, Byungsuk Kwon
Immune Netw. 2011;11(4):216-222. doi: 10.4110/in.2011.11.4.216.Anti-CD137 mAb Deletes Both Donor CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells in Acute Graft-versus-host Disease
Juyang Kim, Hong Rae Cho, Byungsuk Kwon
Immune Netw. 2011;11(6):428-430. doi: 10.4110/in.2011.11.6.428.Regulation of Inflammation by Bidirectional Signaling through CD137 and Its Ligand
Byungsuk Kwon
Immune Netw. 2012;12(5):176-180. doi: 10.4110/in.2012.12.5.176.Integration of the Innate and Adaptive Immunity by CD137-CD137L Bidirectional Signals: Implications in Allograft Rejection
Sang June Park, Jong Soo Lee, Byungsuk Kwon, Hong Rae Cho
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2014;28(3):113-120. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2014.28.3.113.
Reference
-
1. Kwon B, Moon CH, Kang S, Seo SK, Kwon BS. 4-1BB: still in the midst of darkness. Mol Cells. 2000. 10:119–126.
Article2. Kwon B, Lee HW, Kwon BS. New insights into the role of 4-1BB in immune responses: beyond CD8+ T cells. Trends Immunol. 2002. 23:378–380.
Article3. Croft M. The role of TNF superfamily members in T-cell function and diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009. 9:271–285.
Article4. Shuford WW, Klussman K, Tritchler DD, Loo DT, Chalupny J, Siadak AW, Brown TJ, Emswiler J, Raecho H, Larsen CP, Pearson TC, Ledbetter JA, Aruffo A, Mittler RS. 4-1BB costimulatory signals preferentially induce CD8+ T cell proliferation and lead to the amplification in vivo of cytotoxic T cell responses. J Exp Med. 1997. 186:47–55.
Article5. Takahashi C, Mittler RS, Vella AT. Cutting edge: 4-1BB is a bona fide CD8 T cell survival signal. J Immunol. 1999. 162:5037–5040.6. McHugh RS, Whitters MJ, Piccirillo CA, Young DA, Shevach EM, Collin M, Byrne MC. CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells: gene expression analysis reveals a functional role for the glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor. Immunity. 2002. 16:311–323.7. Melero I, Shuford WW, Newby SA, Aruffo A, Ledbetter JA, Hellström KE, Mittler RS, Chen L. Monoclonal antibodies against the 4-1BB T-cell activation molecule eradicate established tumors. Nat Med. 1997. 3:682–685.
Article8. Sun Y, Lin X, Chen HM, Wu Q, Subudhi SK, Chen L, Fu YX. Administration of agonistic anti-4-1BB monoclonal antibody leads to the amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2002. 168:1457–1465.
Article9. Sun Y, Chen HM, Subudhi SK, Chen J, Koka R, Chen L, Fu YX. Costimulatory molecule-targeted antibody therapy of a spontaneous autoimmune disease. Nat Med. 2002. 8:1405–1413.
Article10. Foell J, Strahotin S, O'Neil SP, McCausland MM, Suwyn C, Haber M, Chander PN, Bapat AS, Yan XJ, Chiorazzi N, Hoffmann MK, Mittler RS. CD137 costimulatory T cell receptor engagement reverses acute disease in lupus-prone NZB x NZW F1 mice. J Clin Invest. 2003. 111:1505–1518.
Article11. Seo SK, Choi JH, Kim YH, Kang WJ, Park HY, Suh JH, Choi BK, Vinay DS, Kwon BS. 4-1BB-mediated immunotherapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 2004. 10:1088–1094.
Article12. Foell JL, Diez-Mendiondo BI, Diez OH, Holzer U, Ruck P, Bapat AS, Hoffmann MK, Mittler RS, Dannecker GE. Engagement of the CD137 (4-1BB) costimulatory molecule inhibits and reverses the autoimmune process in collagen-induced arthritis and establishes lasting disease resistance. Immunology. 2004. 113:89–98.
Article13. Kim J, Choi WS, La S, Suh J-H, Kim B-S, Cho HR, Kwon BS, Kwon B. Stimulation with 4-1BB inhibits chronic graft-versus-host disease by inducing activation-induced cell death of donor CD4+ T cells. Blood. 2005. 105:2206–2213.
Article14. Kim J, Kim HJ, Park K, Kim J, Yagita H, Nam SK, Cho HR, Kwon B. Costimulatory molecule-targeted immunotherapy of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2007. 110:776–782.
Article15. Shao H, Fu Y, Liao T, Peng Y, Chen L, Kaplan HJ, Sun D. Anti-CD137 mAb treatment inhibits experimental autoimmune uveitis by limiting expansion and increasing apoptotic death of uveitogenic T cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. 46:596–603.
Article16. Fukushima A, Yamaguchi T, Ishida W, Fukata K, Mittler RS, Yagita H, Ueno H. Engagement of 4-1BB inhibits the development of experimental allergic conjunctivitis in mice. J Immunol. 2005. 175:4897–4903.
Article17. Cho YS, Kwon B, Lee T-H, Moon K-A, La S, Lee J, Lee SD, Oh Y-M, Moon H-B. 4-1BB stimulation inhibits allergen specific IgE, airway hyperreactivity, and eosinophilic inflammation in asthmatic mice. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006. 36:377–385.
Article18. Polte T, Foell J, Werner C, Hoymann HG, Braun A, Burdach S, Mittler RS, Hansen G. CD137-mediated immunotherapy for allergic asthma. J Clin Invest. 2006. 116:1025–1036.
Article19. Sun Y, Blink SE, Liu W, Lee Y, Chen B, Solway J, Weinstock J, Chen L, Fu YX. Inhibition of Th2-mediated allergic airway inflammatory disease by CD137 costimulation. J Immunol. 2006. 177:814–821.
Article20. Drenkard D, Becke FM, Langstein J, Spruss T, Kunz-Schughart LA, Tan TE, Lim YC, Schwarz H. CD137 is expressed on blood vessel walls at sites of inflammation and enhances monocyte migratory activity. FASEB J. 2007. 21:456–463.
Article21. Olofsson PS, Soderstrom LA, Wagstater D, Sheikine Y, Ocaya P, Lang F, Rabu C, Chen L, Paulsson-Berne GP, Sirsjo A, Hansson GK. CD137 is expressed in human atherosclerosis and promotes development of plaque inflammation in hypercholesterolemic mice. Circulation. 2008. 117:1292–1301.
Article22. Gavin MA, Clarke SR, Negrou E, Gallegos A, Rudensky A. Homeostasis and anergy of CD4+CD25+ suppressor T cells in vivo. Nat Immunol. 2002. 3:33–41.
Article23. MacHugh RS. CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells: gene expression analysis reveals a functional role for the glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor. Immunity. 2002. 16:311–323.24. Wilcox RA, TAmada K, Strome SE, Chen L. Signaling through NK cell-associated CD137 promotes both helper function for CD8+ cytolytic activity. J Immunol. 2002. 169:4230–4236.
Article25. Kim D-H, Chang W-S, Lee Y-S, Lee K-A, Kim Y-K, Kwon BS, Kang C-Y. 4-1BB engagement costimulates NKT cell activation and exacerbates NKT cell ligand-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. J Immunol. 2008. 180:2062–2068.
Article26. Lee S-C, Ju S-A, Pack H-N, Heo S-K, Suh J-H, Park S-M, Choi B-K, Kwon BS, Kim BS. 4-1BB (CD137) is required for rapid clearance of Listeria monocytogens infection. Infect Immun. 2005. 73:5144–5151.
Article27. Heinisch IVWM, Daigle I, Knopfli B, Simon H-W. CD137 activation abrogates granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-mediated anti-apoptosis in neutrophils. Eur J Immunol. 2000. 30:3441–3446.
Article28. Nishimoto H, Lee S-W, Hong H, Potter KG, Maeda-Yamaoto M, Kinoshita T, Kawakami Y, Mittler RS, Kwon BS, Ware CF, Croft M, Kawakami T. Costimulation of mast cells by 4-1BB, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, with the high-affinity IgE receptor. Blood. 2005. 106:4241–4248.
Article29. Heinisch IVWM, Bizer C, Volgger W, Simon H-W. Functional CD137 receptors are expressed by eosinophils form patients with IgE-mediated allergic responses but not by eosinophils from patients with non-IgE mediated eosinophilic disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. 108:21–28.
Article30. Haga T, Suzuki J-I, Kosuge H, Ogawa M, Saiki H, Haraguchi G, Maejima Y, Isobe M, Uede T. Attenuation of experimental autoimmune myocarditis by blocking T cell activation through 4-1BB pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009. 46:719–727.
Article31. Lee S-W, Park Y, So T, Kwon BS, Cheroutre H, Mittler RS, Croft M. Identification of regulatory functions for 4-1BB and 4-1BBL in myelopoiesis and the development of dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 2008. 9:917–926.
Article32. Saiki H, Suzuki J-I, Kosuge H, Hiraguchi G, Ishihara T, Haga T, Maejima Y, Isobe M, Uede T. Blockade of the 4-1BB pathway attenuates graft arterial disease in cardiac allografts. Int Heart J. 2008. 49:105–118.
Article33. Seaman S, Stevens J, Yang MY, Logsdon D, Graff-Cherry C, St Croix B. Gene that distinguishes physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2007. 11:539–554.
Article34. Seko Y, Takahashi N, Oshima H. Expression of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) ligand superfamily co-stimultory molecules CD30L, CD27L, OX40L, and 4-1BBL in murine hearts with acute myocarditis caused by Coxackievirus B3. J Pathol. 2001. 195:593–603.
Article35. Langstein J, Michel J, Fritsche J, Kreutz M, Andreesen R, Schwarz H. CD137 (ILA/4-1BB), a member of the TNF receptor family, induces monocyte activation via bidirectional signaling. J Immunol. 1998. 160:2488–2494.36. Jiang D, Chen Y, Schwarz H. CD137 induces proliferation of murine hematopoietic progenitor cells and differentiation to macrophages. J Immunol. 2008. 181:3923–3932.
Article37. Jiang D, Yue PS, Drenkard D, Schwarz H. Induction of proliferation and monocytic differentiation of human CD34+ cells by CD137 ligand signaling. Stem Cells. 2008. 26:2372–2381.
Article38. Seo SK, Park HY, Choi JH, Kim WY, Kim YH, Jung HW, Kwon B, Lee HW, Kwon BS. Blocking 4-1BB/4-1BB ligand interactions prevents herpetic stromal keratitis. J Immunol. 2003. 171:576–583.
Article39. Wang J, Guo Z, Dong Y, Kim O, Hart J, Adams A, Larsen CP, Mittler RS, Newell KA. Role of 4-1BB in allograft rejection mediated by CD8+ T cells. Am J Transplant. 2003. 3:543–551.
Article40. Cho HR, Kwon B, Yagita H, La S, Lee EA, Kim JE, Akiba H, Kim J, Suh JH, Vinay DS, Ju SA, Kim BS, Mittler RS, Okumura K, Kwon BS. Blockade of 4-1BB (CD137)/4-1BB ligand interactions increases allograft survival. Transpl Int. 2004. 17:351–361.
Article41. Cheung CTY, Deisher TA, Luo H, Yanagawa B, Bonigut S, Samra A, Zhao H, Walker EK, McManus BM. Neutralizing anti-4-1BBL treatment improves cardiac function in viral myocarditis. Lab Invest. 2007. 87:651–661.
Article42. Kim W, Kim J, Jung D, Kim H, Cho H-J, Cho HR, Kwon B. Induction of lethal graft-versus-host disease by anti-CD137 monoclonal antibody in mice prone to chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009. 15:306–314.
Article43. Lee SW, Vella AT, Kwon BS, Croft M. Enhanced CD4 T cell responsiveness in the absence of 4-1BB. J Immunol. 2005. 174:6803–6808.
Article44. Vinay DS, Choi BK, Bae JS, Kim WY, Gebhardt BM, Kwon BS. CD137-deficient mice have reduced NK/NKT cell numbers and function, are resistant to lipopolysaccharide-induced shock syndromes, and have lower IL-4 responses. J Immunol. 2004. 173:4218–4229.
Article45. Sun M, Fink PJ. A new class of reverse signaling costimulators belongs to the TNF family. J Immunol. 2007. 179:4307–4312.
Article46. Pauly S, Broll K, Witmann M, Giegerich G, Schwarz H. CD137 is expressed by follicular dendritic cells and costimulates B lymphocytes in germinal centers. J Leukocyte Biol. 2002. 72:35–42.47. Schwarz H. Biological activities of reverse signal transduction through CD137 ligand. J Leukoc Biol. 2005. 77:281–286.
Article48. Lippert U, Zachmann K, Ferrari DM, Schwarz H, Brunner E, Nahhub-ul Latif AHM, Neumann C, Soruri A. CD137 lignd reverse signaling has multiple functions in human dendritic cells during an adaptive immune response. Eur J Immunol. 2008. 38:1024–1032.
Article49. Saito K, Ohara N, Hotokezaka H, Fukumoto F, Yuasa K, Naito M, Fujiwara T, Nakayama K. Infection-induced up-regulation of the costimulatory molecule 4-1BB in osteoblastic cells and its inhibitory effect on M-CSF/RANKL-induced in vitro osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2004. 279:13555–13563.
Article50. Kim D-K, Lee SC, Lee HW. CD137 ligand-memdiated reverse signals increase viability and cytokine expression in murine myeloid cells: involvement of mTOR/p70S6 kinase and AKT. Eur J Immunol. (In press).51. Kang YJ, Kim SO, Shhimada S, Otsuka M, Seit-Nebi A, Kwon BS, Watts TH, Han J. Cell surface 4-1BBL mediates sequential signaling pathways 'down-stream' of TLR and is required for sustained TNF production in macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2007. 8:601–609.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is CD137 Ligand (CD137L) Signaling a Fine Tuner of Immune Responses?
- Regulation of Inflammation by Bidirectional Signaling through CD137 and Its Ligand
- Agonistic Anti-CD137 Monoclonal Antibody Treatment Induces CD11b+Gr-1+ Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells
- The Roles of CD137 Signaling in Atherosclerosis
- Recombinant TAT-CD137 Ligand Cytoplasmic Domain Fusion Protein Induces the Production of IL-6 and TNF-alpha in Peritoneal Macrophages