Cancer Res Treat.
2015 Jul;47(3):527-533. 10.4143/crt.2014.026.
In Vitro and In Vivo Radiosensitizing Effect of Valproic Acid on Fractionated Irradiation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ihkim@snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Radiation Medicine, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2148504
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.026
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was conducted in order to validate the radiosensitization effect of valproic acid, a biologically available histone deacetylase inhibitor, for fractionated radiation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
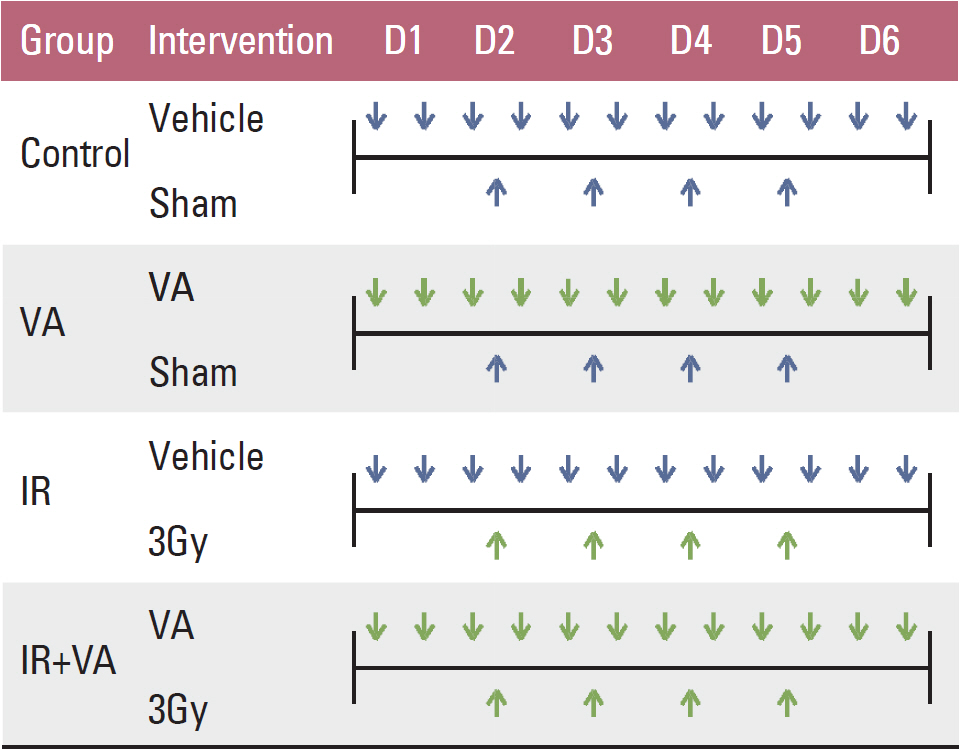
Radiosensitization effect of valproic acid was tested for the A549 cell line and U87MG cell line in vitro. Fractionated irradiation of 12 Gy in four fractions was administered on D2-5 with valproic acid, 150 mg/Kg, ip, bid for six consecutive days (D1-6) to A549 and U87MG tumors implanted in BALB/c-nude mice. A growth delay curve was formulated.
RESULTS
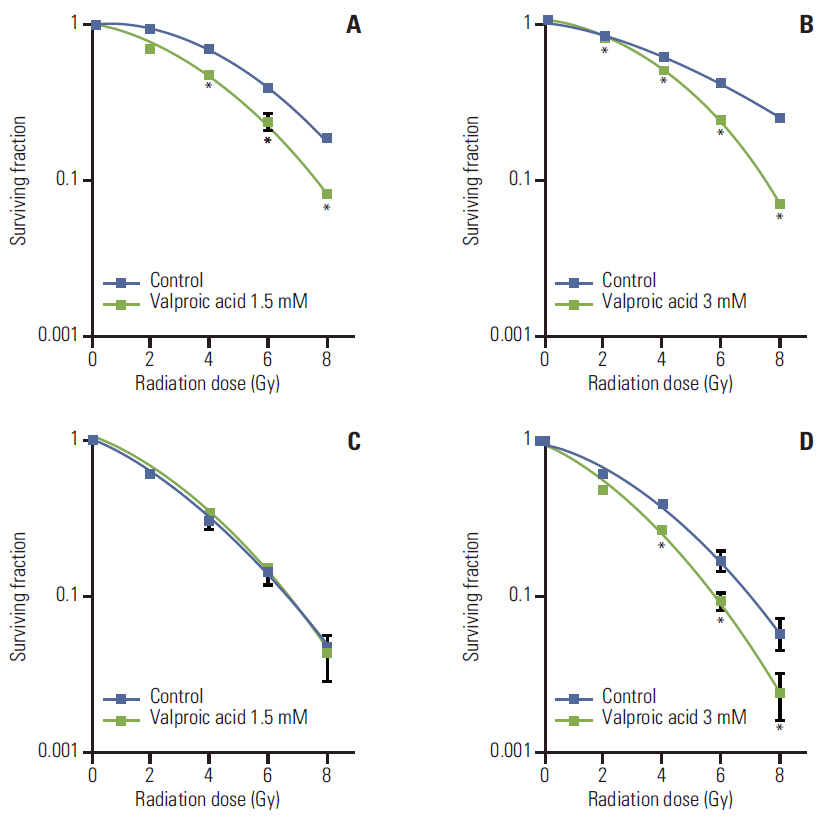
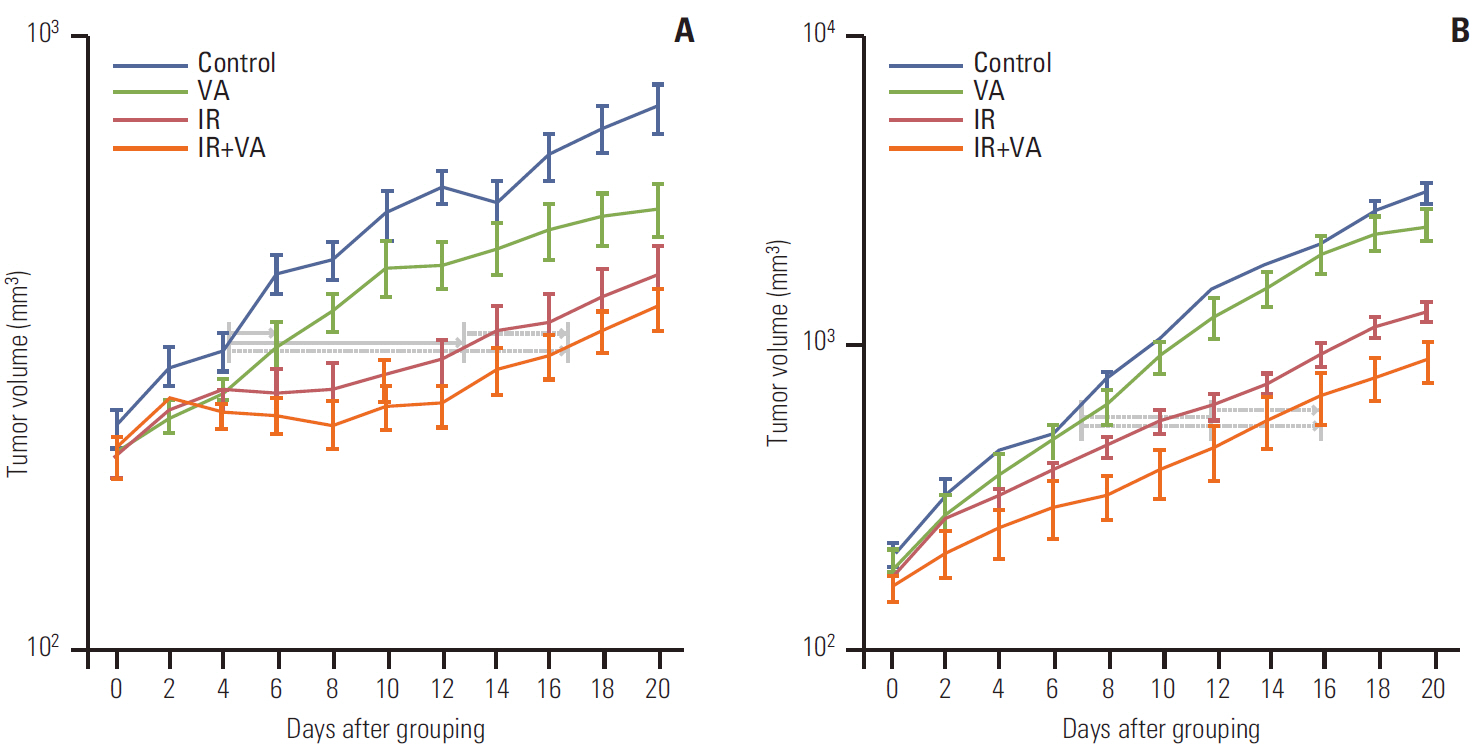
Radiosensitization effect of valproic acid was found for both cell lines; A549 at 1.5 mM and 3.0 mM concentration and U87MG at 3.0 mM concentration. In growth delay analysis, a statistically significant radiosensitization effect was observed for both tumors (p < 0.001 for both tumors). Difference for change in slope for control and valproic acid versus radiotherapy and radiotherapy plus valproic acid showed borderline significance for the U87MG cell line (p=0.065), indicating beyond additive effect, whereas this difference was statistically insignificant for A549 tumor (p=0.951), indicating additive effect.
CONCLUSION
Results of this study indicate that a radiosensitizing effect for fractionated radiotherapy of valproic acid for A549 and U87MG tumors in vivo is evident and that it may be more than additive for U87MG tumors. Further exploitation of histone deacetylase inhibitors in clinical trials is warranted.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Camphausen K, Tofilon PJ. Inhibition of histone deacetylation: a strategy for tumor radiosensitization. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:4051–6.2. Munshi A, Kurland JF, Nishikawa T, Tanaka T, Hobbs ML, Tucker SL, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors radiosensitize human melanoma cells by suppressing DNA repair activity. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:4912–22.3. Kim JH, Shin JH, Kim IH. Susceptibility and radiosensitization of human glioblastoma cells to trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004; 59:1174–80.4. Flatmark K, Nome RV, Folkvord S, Bratland A, Rasmussen H, Ellefsen MS, et al. Radiosensitization of colorectal carcinoma cell lines by histone deacetylase inhibition. Radiat Oncol. 2006; 1:25.5. Zhang Y, Jung M, Dritschilo A, Jung M. Enhancement of radiation sensitivity of human squamous carcinoma cells by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Radiat Res. 2004; 161:667–74.6. Gottlicher M, Minucci S, Zhu P, Kramer OH, Schimpf A, Giavara S, et al. Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J. 2001; 20:6969–78.7. Camphausen K, Cerna D, Scott T, Sproull M, Burgan WE, Cerra MA, et al. Enhancement of in vitro and in vivo tumor cell radiosensitivity by valproic acid. Int J Cancer. 2005; 114:380–6.8. Karagiannis TC, Kn H, El-Osta A. The epigenetic modifier, valproic acid, enhances radiation sensitivity. Epigenetics. 2006; 1:131–7.9. Baylin SB, Ohm JE. Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer: a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway addiction? Nat Rev Cancer. 2006; 6:107–16.10. Esteller M. Epigenetics provides a new generation of oncogenes and tumour-suppressor genes. Br J Cancer. 2006; 94:179–83.11. De Schutter H, Nuyts S. Radiosensitizing potential of epigenetic anticancer drugs. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2009; 9:99–108.12. Coyle TE, Bair AK, Stein C, Vajpayee N, Mehdi S, Wright J. Acute leukemia associated with valproic acid treatment: a novel mechanism for leukemogenesis? Am J Hematol. 2005; 78:256–60.13. Purrucker JC, Fricke A, Ong MF, Rube C, Rube CE, Mahlknecht U. HDAC inhibition radiosensitizes human normal tissue cells and reduces DNA double-strand break repair capacity. Oncol Rep. 2010; 23:263–9.14. Chung YL, Wang AJ, Yao LF. Antitumor histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress cutaneous radiation syndrome: implications for increasing therapeutic gain in cancer radiotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004; 3:317–25.15. Paoluzzi L, Figg WD. Histone deacetylase inhibitors are potent radiation protectants. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004; 3:612–3.16. Chen X, Wong P, Radany E, Wong JY. HDAC inhibitor, valproic acid, induces p53-dependent radiosensitization of colon cancer cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2009; 24:689–99.17. Driever PH, Knupfer MM, Cinatl J, Wolff JE. Valproic acid for the treatment of pediatric malignant glioma. Klin Padiatr. 1999; 211:323–8.18. Mehta MP, Buckner J, Sawaya RP, Cannon GM. Neoplasms of the central nervous system. In : DeVita VT, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA, editors. DeVita, Hellman, and Rosenberg's cancer: principles and practice of oncology. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;2008. p. 1967–2032.19. Munshi A, Tanaka T, Hobbs ML, Tucker SL, Richon VM, Meyn RE. Vorinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances the response of human tumor cells to ionizing radiation through prolongation of gamma-H2AX foci. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006; 5:1967–74.20. Kim BK. Radiosensitizing effect and mechanisms of action of a novel HDAC inhibitor, SK-7041 [dissertation]. Seoul: Seoul National University;2007. 19–25.21. Kim IA, Kim IH, Kim HJ, Chie EK, Kim JS. HDAC inhibitor-mediated radiosensitization in human carcinoma cells: a general phenomenon? J Radiat Res. 2010; 51:257–63.
Article22. Hall EJ, Giaccia AJ. Radiobiology for the radiologist. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2006. p. 30–397. 30-46, 378-97.23. U.S. National Institutes of Health. ClinicalTrials.gov. Search term “valproic acid” AND “radiotherapy” [Internet]. Bethesda: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; c2013 [cited 2013 Oct 10]. Available from: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=valproic+acid+radiotherapy.24. Chang AR, Kim IH, Chie EK. Histone deacetylase inhibitory activity of valproic acid in glioblastoma. J Korean Soc Ther Radiol Oncol. 2007; 25:s30.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Single and Fractionated Irradiation of Mammary Tumor of Rat
- Effect of 137Cs Whole Body Irradiation on the Peripheral Blood
- Case of Decreased Serum Valproic Acid Concentration During Concomitant Use of Meropenem in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury
- An experimental study on effect of tourniquet ischemia and hyperthermia on irradiation
- Effects of Valproic Acid on the Survival of Human Tennon's Capsule Fibroblasts