Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 Sep;7(5):518-522. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.5.518.
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Caused by Cephalosporins With Identical R1 Side Chains
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. irisal@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2147962
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.5.518
Abstract
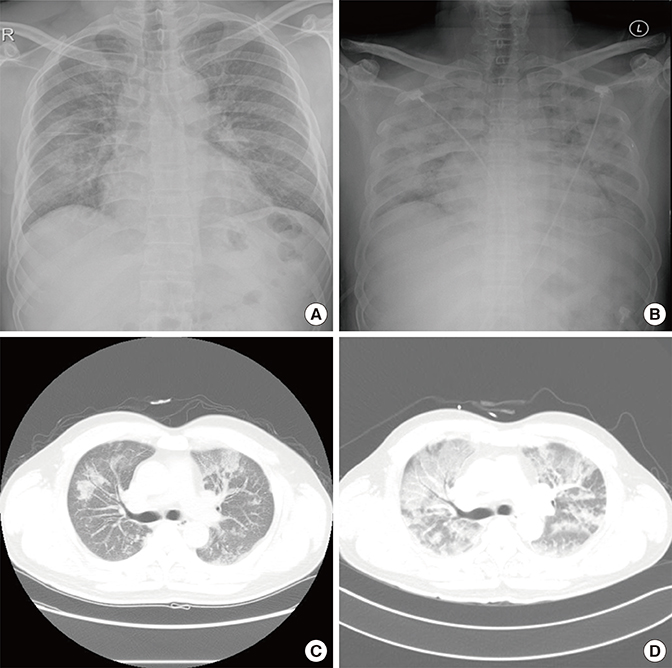
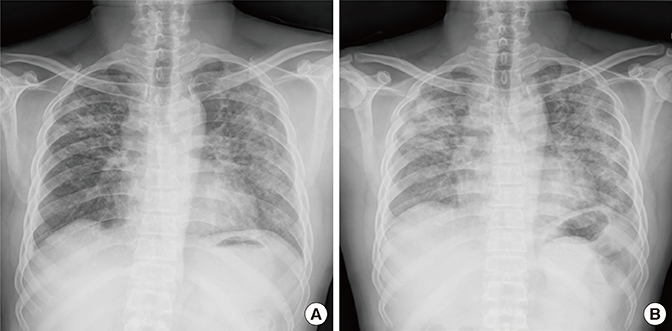
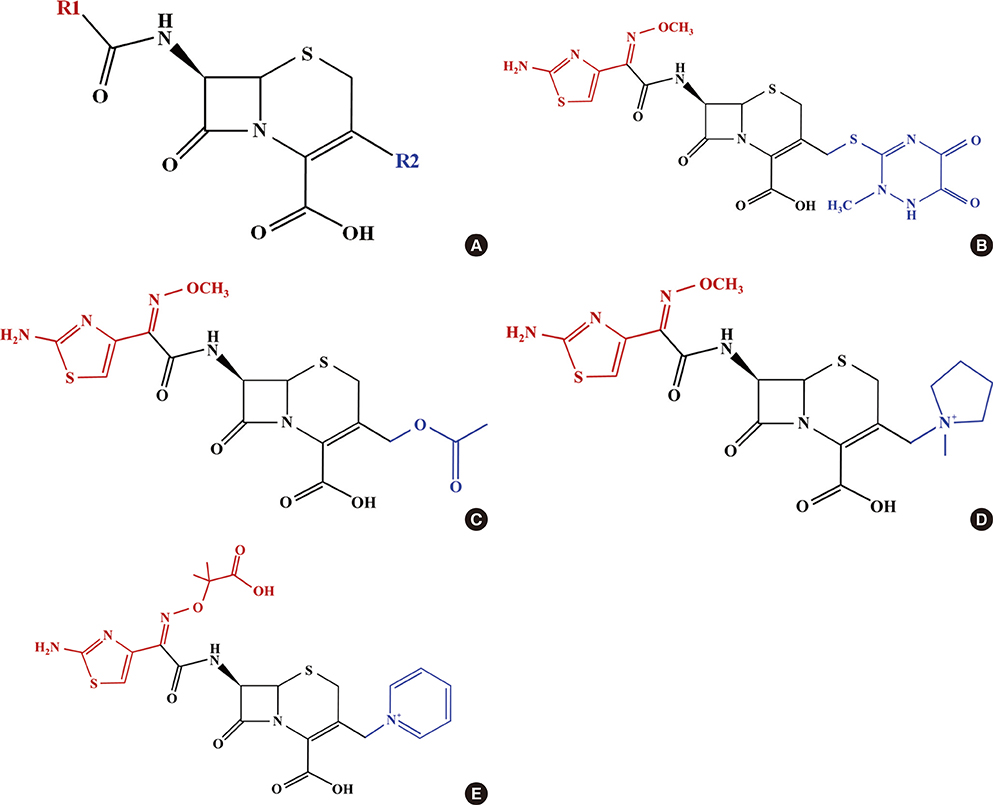
- Drug-induced hypersensitivity pneumonitis results from interactions between pharmacologic agents and the human immune system. We describe a 54-year-old man with hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by cephalosporins with identical R1 side chains. The patient, who complained of cough with sputum, was prescribed ceftriaxone and clarithromycin at a local clinic. The following day, he complained of dyspnea, and chest X-ray revealed worsening of inflammation. Upon admission to our hospital, antibiotics were changed to cefepime with levofloxacin, but his pneumonia appeared to progress. Changing antibiotics to meropenem with ciprofloxacin improved his symptoms and radiologic findings. Antibiotics were de-escalated to ceftazidime with levofloxacin, and his condition improved. During later treatment, he was mistakenly prescribed cefotaxime, which led to nausea, vomiting, dyspnea and fever, and indications of pneumonitis on chest X-ray. We performed bronchoalveolar lavage, and the findings included lymphocytosis (23%), eosinophilia (17%), and a low cluster of differentiation (CD) 4 to CD8 ratio (0.1), informing a diagnosis of drug-induced pneumonitis. After a medication change, his symptoms improved and he was discharged. One year later, he was hospitalized for acute respiratory distress syndrome following treatment with ceftriaxone and aminoglycosides for an upper respiratory tract infection. After steroid therapy, he recovered completely. In this patient, hypersensitivity reaction in the lungs was caused by ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, and cefepime, but not by ceftazidime, indicating that the patient's hypersensitivity pneumonitis was to the common R1 side chain of the cephalosporins.
MeSH Terms
-
Alveolitis, Extrinsic Allergic*
Aminoglycosides
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Bronchoalveolar Lavage
Cefotaxime
Ceftazidime
Ceftriaxone
Cephalosporins*
Ciprofloxacin
Clarithromycin
Cough
Diagnosis
Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Dyspnea
Eosinophilia
Fever
Humans
Hypersensitivity
Immune System
Inflammation
Levofloxacin
Lung
Lymphocytosis
Middle Aged
Nausea
Pneumonia
Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Adult
Respiratory Tract Infections
Sputum
Thorax
Vomiting
Aminoglycosides
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Cefotaxime
Ceftazidime
Ceftriaxone
Cephalosporins
Ciprofloxacin
Clarithromycin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Matsuno O. Drug-induced interstitial lung disease: mechanisms and best diagnostic approaches. Respir Res. 2012; 13:39.2. Cooper JA Jr, Matthay RA. Drug-induced pulmonary disease. Dis Mon. 1987; 33:61–120.3. Mark GJ, Lehimgar-Zadeh A, Ragsdale BD. Cyclophosphamide pneumonitis. Thorax. 1978; 33:89–93.4. Fujimori K, Yokoyama A, Kurita Y, Uno K, Saijo N. Paclitaxel-induced cell-mediated hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Diagnosis using leukocyte migration test, bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial lung biopsy. Oncology. 1998; 55:340–344.5. Tohyama M, Tamaki Y, Toyama M, Ishimine T, Miyazato A, Nakamoto A, et al. A case of loxoprofen-induced pneumonitis pathologically resembling hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2002; 40:123–128.6. Baldo BA. Penicillins and cephalosporins as allergens--structural aspects of recognition and cross-reactions. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999; 29:744–749.7. Suzuki K, Inagaki T, Adachi S, Matsuura T, Yamamoto T. A case of ceftazidime-induced pneumonitis. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1993; 31:512–516.8. Suzuki K, Yamamoto K, Kishimoto A, Hayakawa T, Yamamoto T. A case of ceftizoxime-induced pneumonitis. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1985; 23:1357–1361.9. Malmberg P, Rask-Andersen A, Rosenhall L. Exposure to microorganisms associated with allergic alveolitis and febrile reactions to mold dust in farmers. Chest. 1993; 103:1202–1209.10. Patel AM, Ryu JH, Reed CE. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: current concepts and future questions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:661–670.11. Selman M, Pardo A, King TE Jr. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: insights in diagnosis and pathobiology. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 186:314–324.12. Cormier Y, Brown M, Worthy S, Racine G, Müller NL. High-resolution computed tomographic characteristics in acute farmer's lung and in its follow-up. Eur Respir J. 2000; 16:56–60.13. Barrera L, Mendoza F, Zuñiga J, Estrada A, Zamora AC, Melendro EI, et al. Functional diversity of T-cell subpopulations in subacute and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 177:44–55.14. Lacasse Y, Selman M, Costabel U, Dalphin JC, Ando M, Morell F, et al. Clinical diagnosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 168:952–958.15. Saito M, Yagi M, Uno K, Takanaka K. Comparative study of the usefulness of the drug-induced lymphocyte stimulation test and the leukocyte migration test in drug allergies. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008; 31:299–304.16. Akoun GM, Cadranel JL, Milleron BJ, D'Ortho MP, Mayaud CM. Bronchoalveolar lavage cell data in 19 patients with drug-associated pneumonitis (except amiodarone). Chest. 1991; 99:98–104.17. Perez-Inestrosa E, Suau R, Montañez MI, Rodriguez R, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, et al. Cephalosporin chemical reactivity and its immunological implications. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 5:323–330.18. Sánchez-Sancho F, Perez-Inestrosa E, Suau R, Montañez MI, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, et al. Synthesis, characterization and immunochemical evaluation of cephalosporin antigenic determinants. J Mol Recognit. 2003; 16:148–156.19. Pichichero ME, Zagursky R. Penicillin and cephalosporin allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014; 112:404–412.20. Antunez C, Blanca-Lopez N, Torres MJ, Mayorga C, Perez-Inestrosa E, Montañez MI, et al. Immediate allergic reactions to cephalosporins: evaluation of cross-reactivity with a panel of penicillins and cephalosporins. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:404–410.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- IgE-Mediated Hypersensitivity Reactions to Cephalosporins
- Analysis of Fluoroquinolone Adverse Drug Reaction Reported in a Single Center
- A Case of Gold Induced Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Diagnosed by Lymphocyte Stimulation Test with Gold
- Diagnosis and Management of Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions to Cephalosporins
- A Case of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Caused by Mycobacterium terrae in a Fishery Worker