J Bacteriol Virol.
2014 Mar;44(1):95-101. 10.4167/jbv.2014.44.1.95.
Anti-inflammatory Effect of Plocamium telfairiae Extract in LPS-stimulated Bone Marrow-derived Macrophages and Dendritic Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. yskoh7@jejunu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Medical Science, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea.
- 3Jeju Biodiversity Research Institute, Jeju Technopark, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2135362
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2014.44.1.95
Abstract
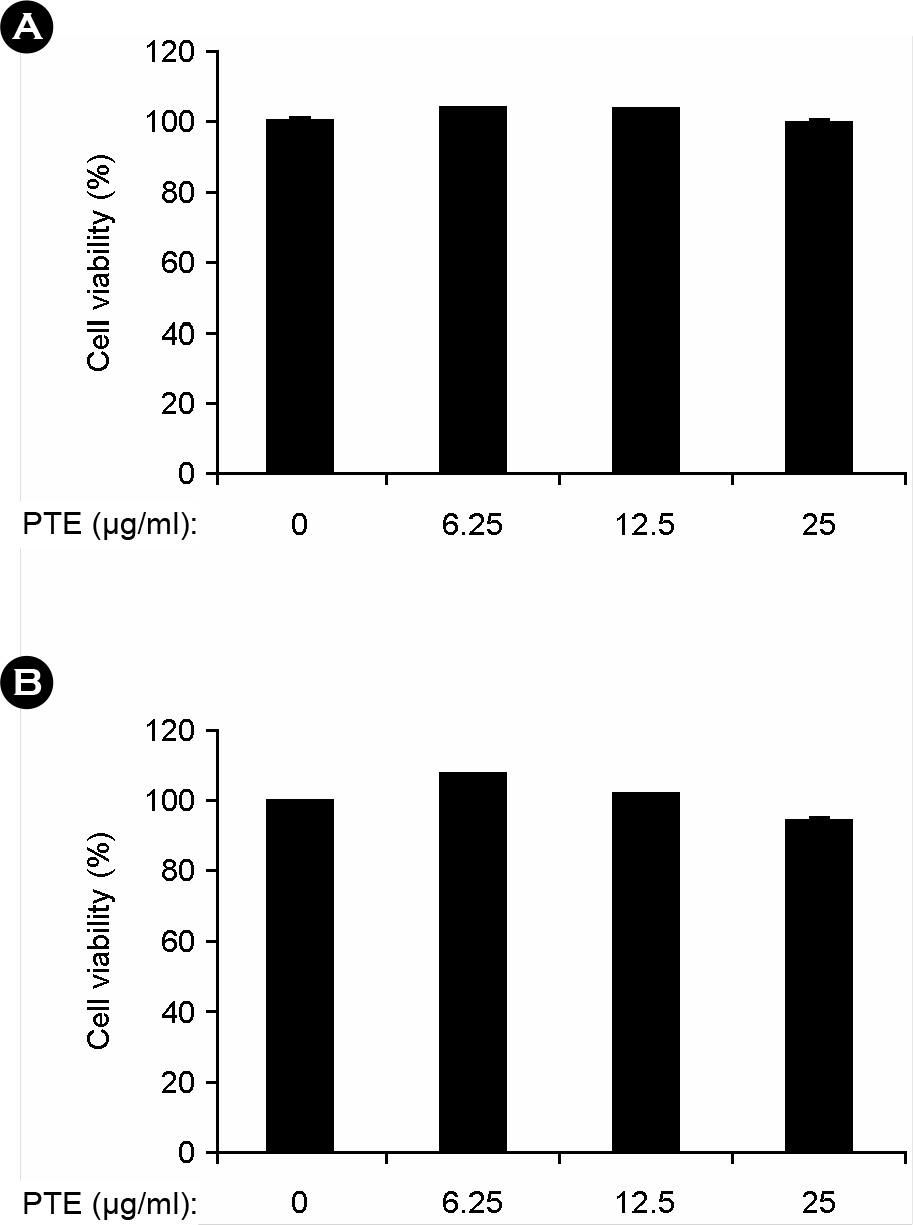
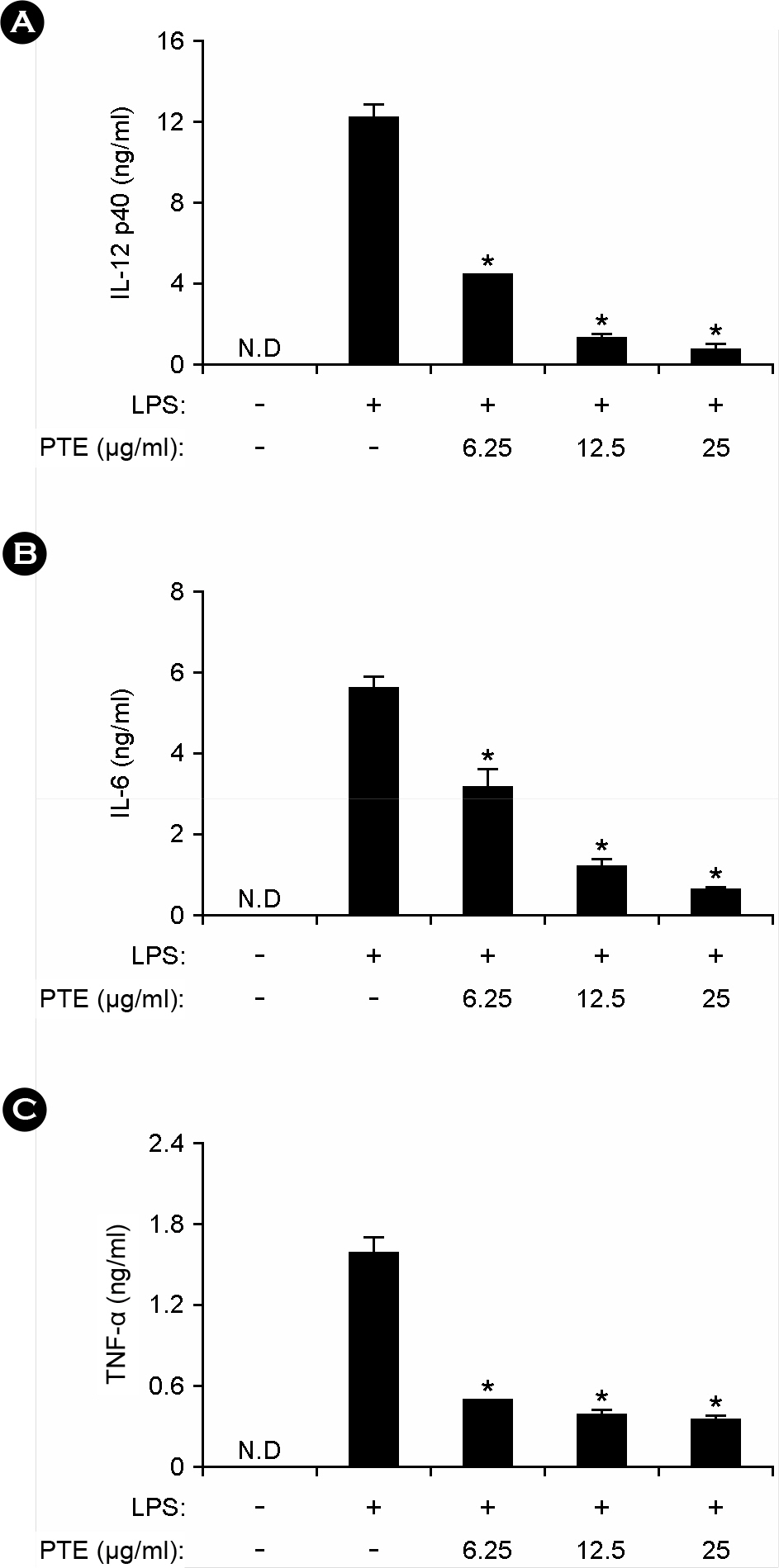
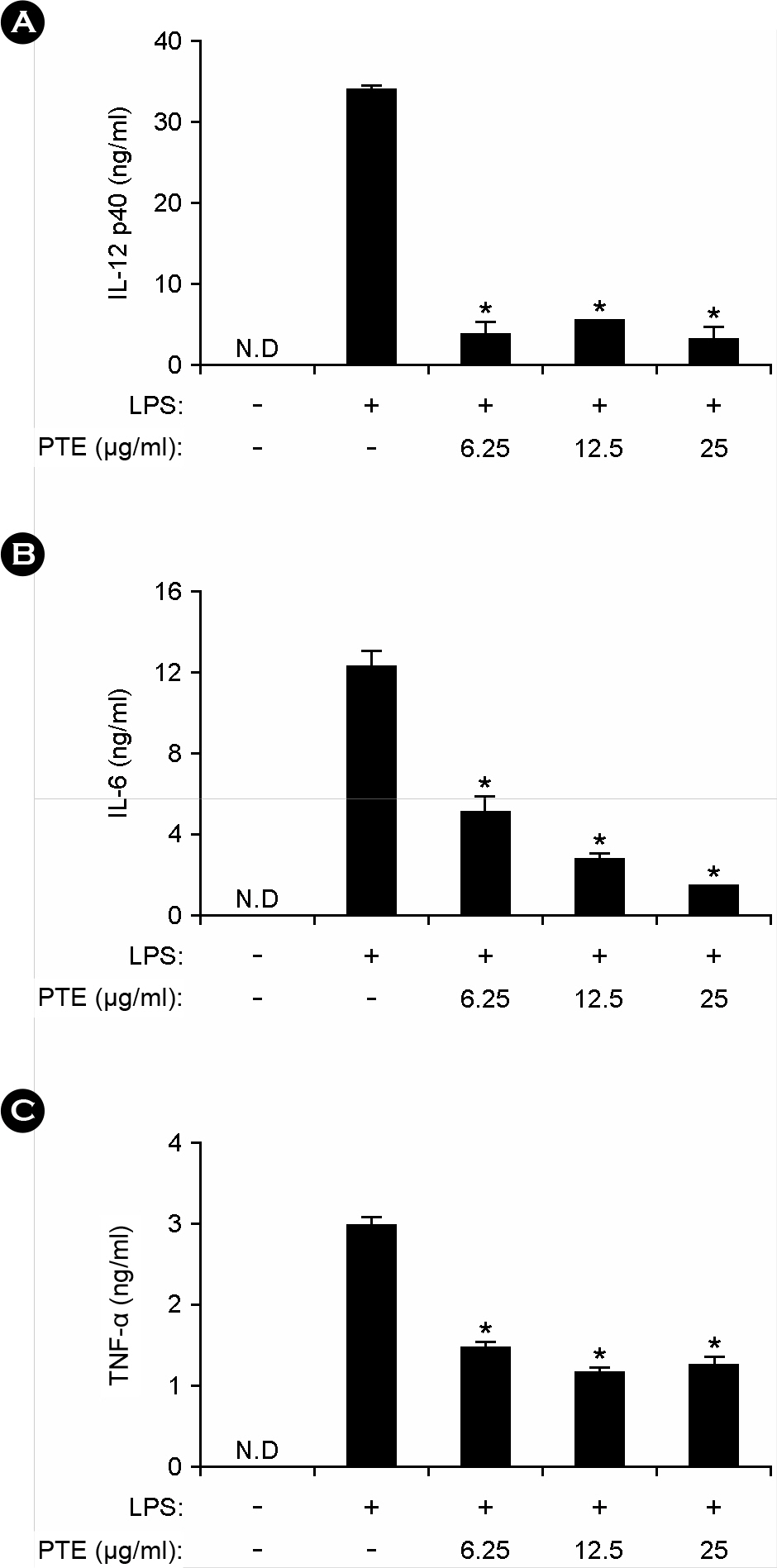
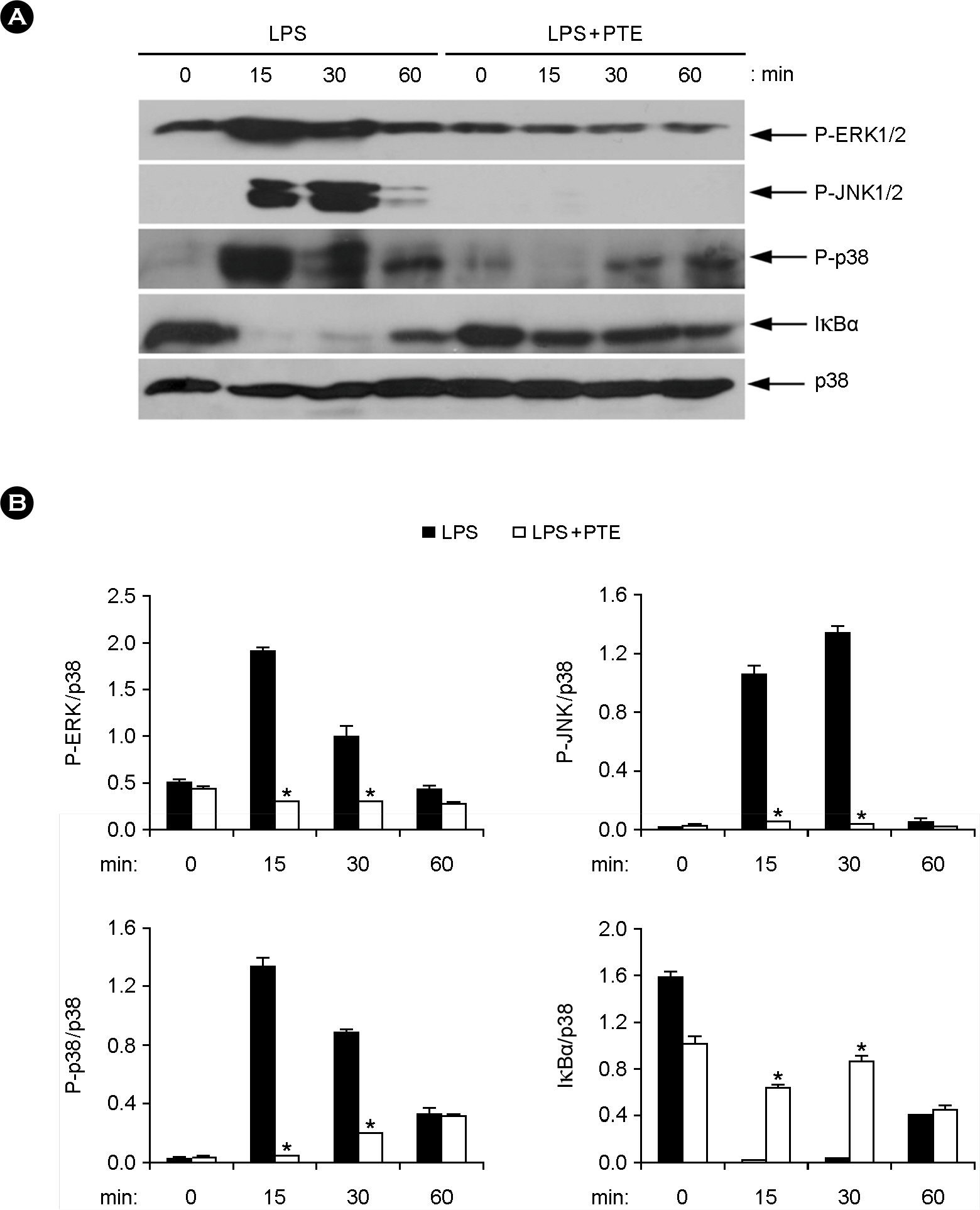
- Marine algae are rich sources of various biologically active compounds with potential pharmaceutical properties. In the present study, we investigated the inhibitory effects of Plocamium telfairiae extract (PTE) on proinflammatory cytokine production in bone marrow-derived macrophage (BMDMs) and dendritic cells (BMDCs). PTE pre-treatment in LPS-stimulated BMDMs and BMDCs showed a strong inhibition on interleukin (IL)-12 p40, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha production as compared to non-treated controls. PTE pre-treatment showed significant inhibition on phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and degradation of inhibitor of kappa B (IkappaBalpha). Taken together, these results suggest that PTE may have potential anti-inflammatory property and hence, warrant further studies concerning the potentials of PTE for medicinal purpose.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Medzhitov R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature. 2008; 454:428–35.
Article2). Barton GM. A calculated response: control of inflammation by the innate immune system. J Clin Invest. 2008; 118:413–20.
Article3). Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006; 124:783–801.
Article4). Takeuchi O, Akira S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 2010; 140:805–20.
Article5). Mogensen TH. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signalling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009; 22:240–73.6). Cohen J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature. 2002; 420:885–91.
Article7). Guha M, Mackman N. LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell Signal. 2001; 13:85–94.
Article8). Thalhamer T, McGrath MA, Harnett MM. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology. 2008; 47:409–14.
Article9). Manzoor Z, Koh YS. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in inflammation. J Bacteriol Virol. 2012; 42:189–95.
Article10). Weiss T, Shalit I, Blau H, Werber S, Halperin D, Levitov A, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of moxifloxacin on activated human monocytic cells: inhibition of NF-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and of synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004; 48:1974–82.11). O'Sullivan AW, Wang JH, Redmond HP. NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK inhibition improve survival in endotoxin shock and in a cecal ligation and puncture model sepsis in combination with antibiotic therapy. J Surg Res. 2009; 152:46–53.12). Shaked G, Czeiger D, Dukhno O, Levy I, Artru AA, Shapira Y, et al. Ketamine improves survival and suppresses IL-6 and TNF alpha production in a model of gram-negative bacterial sepsis in rats. Resuscitation. 2004; 62:237–42.13). Blunt JW, Copp BR, Hu WP, Munro MH, Northcote PT, Prinsep MR. Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep. 2009; 26:170–244.
Article14). Kim JY, Yoon MY, Cha MR, Hwang JH, Park E, Choi SU, et al. Methanolic extracts of Plocamium telfairiae induce cytotoxicity and caspase-dependent apoptosis in HT-29 human colon carcinoma cells. J Med Food. 2007; 10:587–93.15). Huang HL, Wang BG. Antioxidant capacity and lipophilic content of seaweeds collected from the Qingdao coastline. J Agric Food Chem. 2004; 52:4993–7.
Article16). Koo JE, Hong HJ, Dearth A, Kobayashi KS, Koh YS. Intracellular invasion of Orientia tsutsugamushi activates inflammasome in ASC-dependent manner. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e39042.17). Chae D, Manzoor Z, Kim SC, Kim S, Oh TH, Yoo ES, et al. Apo-9′-fucoxanthinone, isolated from Sargassum muticum, inhibits CpG-induced inflammatory response by attenuating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Mar Drugs. 2013; 11:3272–87.18). Manzoor Z, Kim S, Chae D, Yoo ES, Kang HK, Hyun JW, et al. Sea lettuce (Ulva fasciata) extract has an inhibitory effect on pro-inflammatory cytokine production in CpG-stimulated bone marrow-derived macrophages and dendritic cells. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2013; 22:781–6.19). Manzoor Z, Mathema VB, Chae D, Kang HK, Yoo ES, Jeon YJ, et al. Octaphlorethol A inhibits the CpG-induced inflammatory response by attenuating the mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-κB pathways. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2013; 77:1970–2.
Article20). Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 2010; 11:373–84.
Article21). Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003; 3:133–46.
Article22). Adorini L. Interleukin-12, a key cytokine in Th1-mediated autoimmune diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999; 55:1610–25.
Article23). Kishimoto T. IL-6: from its discovery to clinical applications. Int Immunol. 2010; 22:347–52.
Article24). Mudter J, Neurath MF. IL-6 signaling in inflammatory bowel disease: pathophysiological role and clinical relevance. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007; 13:1016–23.
Article25). Baud V, Karin M. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol. 2001; 11:372–7.
Article26). Bradley JR. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J Pathol. 2008; 214:149–60.
Article27). Rigato O, Ujvari S, Castelo A, Salomão R. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and sepsis: evidence for a role in host defense. Infection. 1996; 24:314–8.28). Beinke S, Ley SC. Functions of NF-κB1 and NF-κB2 in immune cell biology. Biochem J. 2004; 382:393–409.
Article29). Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996; 87:13–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anti-inflammatory Activity of Carpinus tschonoskii Leaves Extract in R848-stimulated Bone Marrow-derived Macrophages and Dendritic Cells
- 3-Hydroxy-4,7-megastigmadien-9-one, Isolated from Ulva pertusa Kjellman, Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response by Down-Regulating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and NF-κB Pathways
- Defects in the differentiation and function of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells in non-obese diabetic mice
- Anti-inflammatory effects of ethanolic extract of Annona muricata
- Acrosorium polyneurum Extract Inhibits the LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response by Impairing the MAPK and NF-κB Pathways