Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2012 Sep;5(3):132-138. 10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.132.
Apoptosis Progression in the Hair Cells in the Organ of Corti of GJB2 Conditional Knockout Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, 309th Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing, China. yanping309@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, General Hospital of Chinese PLA, Beijing, China.
- KMID: 2134595
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.132
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Apoptosis may play an important role in the mechanism underlying the GJB2 gene conditional knockout (cCx26) mice cochlear cell death. The objective of this study was to explore the the damage mode of the outer hair cells (OHCs) and its real time point of apoptosis and provide information to further explore the role of apoptosis in the happening of hearing loss in cCx26 mice.
METHODS
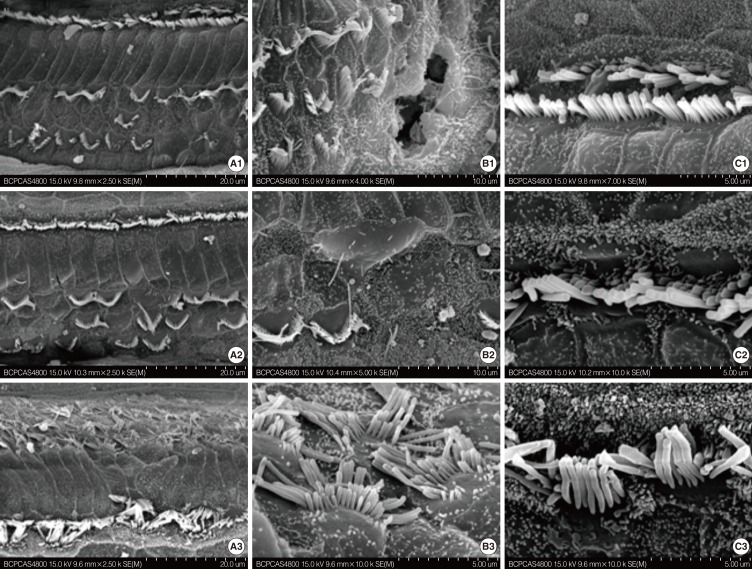
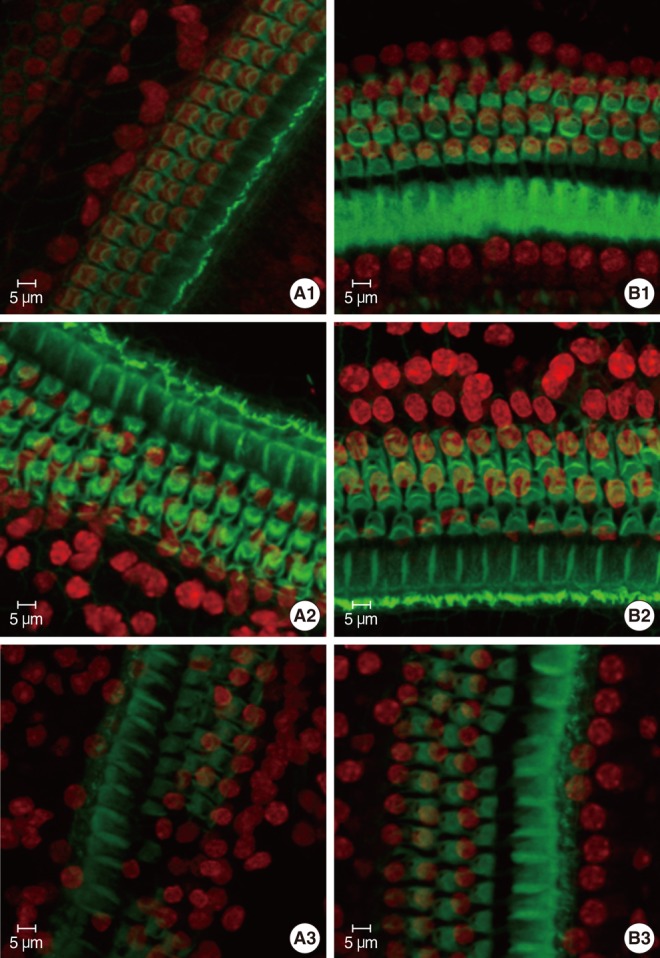
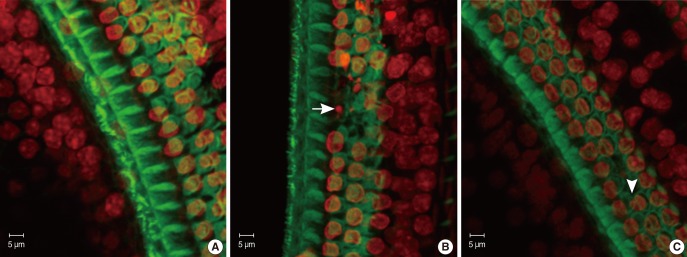
Cochleae from mice at various developmental stages (P8, P12, and P21) were dissected out and first used to be observed under the scanning electron microscope (SEM). Basilar membranes from mice at P8, P14, P18, and P21 were stained by fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated phalloidin and propidium iodide (PI) and examined under confocal microscope.
RESULTS
The loss of OHCs of cCx26 knockout mice was first set between P12 and P21 under SEM. Whole mount phalloidin and PI staining revealed that obvious apoptotic appearance of the OHCs surface morphology was observed at P18.
CONCLUSION
Typical apoptotic morphology was found in the OHCs in the organ of Corti of the cCx26 mice at P18. This may provide information to further study the role of apoptosis in the occurrence of hearing loss of cCx26 mice.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hoang Dinh E, Ahmad S, Chang Q, Tang W, Stong B, Lin X. Diverse deafness mechanisms of connexin mutations revealed by studies using in vitro approaches and mouse models. Brain Res. 2009; 6. 1277:52–69. PMID: 19230829.
Article2. Gabriel HD, Jung D, Butzler C, Temme A, Traub O, Winterhager E, et al. Transplacental uptake of glucose is decreased in embryonic lethal connexin26-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 1998; 3. 140(6):1453–1461. PMID: 9508777.
Article3. Cohen-Salmon M, Ott T, Michel V, Hardelin JP, Perfettini I, Eybalin M, et al. Targeted ablation of connexin26 in the inner ear epithelial gap junction network causes hearing impairment and cell death. Curr Biol. 2002; 7. 12(13):1106–1111. PMID: 12121617.
Article4. Wang Y, Chang Q, Tang W, Sun Y, Zhou B, Li H, et al. Targeted connexin26 ablation arrests postnatal development of the organ of Corti. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009; 7. 385(1):33–37. PMID: 19433060.
Article5. Tadros SF, D'Souza M, Zhu X, Frisina RD. Apoptosis-related genes change their expression with age and hearing loss in the mouse cochlea. Apoptosis. 2008; 11. 13(11):1303–1321. PMID: 18839313.
Article6. Elmore S. Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 2007; 6. 35(4):495–516. PMID: 17562483.
Article7. Ding D, Jiang H, Salvi RJ. Mechanisms of rapid sensory hair-cell death following co-administration of gentamicin and ethacrynic acid. Hear Res. 2010; 1. 259(1-2):16–23. PMID: 19715747.
Article8. Majno G, Joris I. Apoptosis, oncosis, and necrosis: an overview of cell death. Am J Pathol. 1995; 1. 146(1):3–15. PMID: 7856735.9. Hu BH, Henderson D, Nicotera TM. Involvement of apoptosis in progression of cochlear lesion following exposure to intense noise. Hear Res. 2002; 4. 166(1-2):62–71. PMID: 12062759.
Article10. Hu BH, Henderson D, Yang WP. The impact of mitochondrial energetic dysfunction on apoptosis in outer hair cells of the cochlea following exposure to intense noise. Hear Res. 2008; 2. 236(1-2):11–21. PMID: 18082984.
Article11. Yang WP, Hu BH. Comparison of three methods for detecting the death modes of hair cells in the cochlea. Chin J Otol. 2004; 2(4):301–304.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of Vestibular Organ and Cochlea
- Comparison of Cochlear Morphology and Apoptosis in Mouse Models of Presbycusis
- Apoptotic Pattern of Cochlear Outer Hair Cells and Frequency-specific Hearing Threshold Shift in Noise-exposed BALB/c Mice
- Organotypic Culture of Organ of Corti with Floating Drop Method from Newborn Rat
- The Development of NKT Cells in Thymus is Defective in CD45 Knockout Mice