J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2008 Jun;49(6):979-986. 10.3341/jkos.2008.49.6.979.
Ischemic Preconditioning and the Role of Protein Kinase C in Cultured Retinal Ganglion Cell Line
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, The Institute of Vision Research, Seoul, Korea. kcyeye@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2110880
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2008.49.6.979
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To investigate the cellular protective effects of hypoxic preconditioning against oxidative stress in a staurosporine-differentiated RGC-5 cell line and the relevance of protein kinase C subtype expression.
METHODS
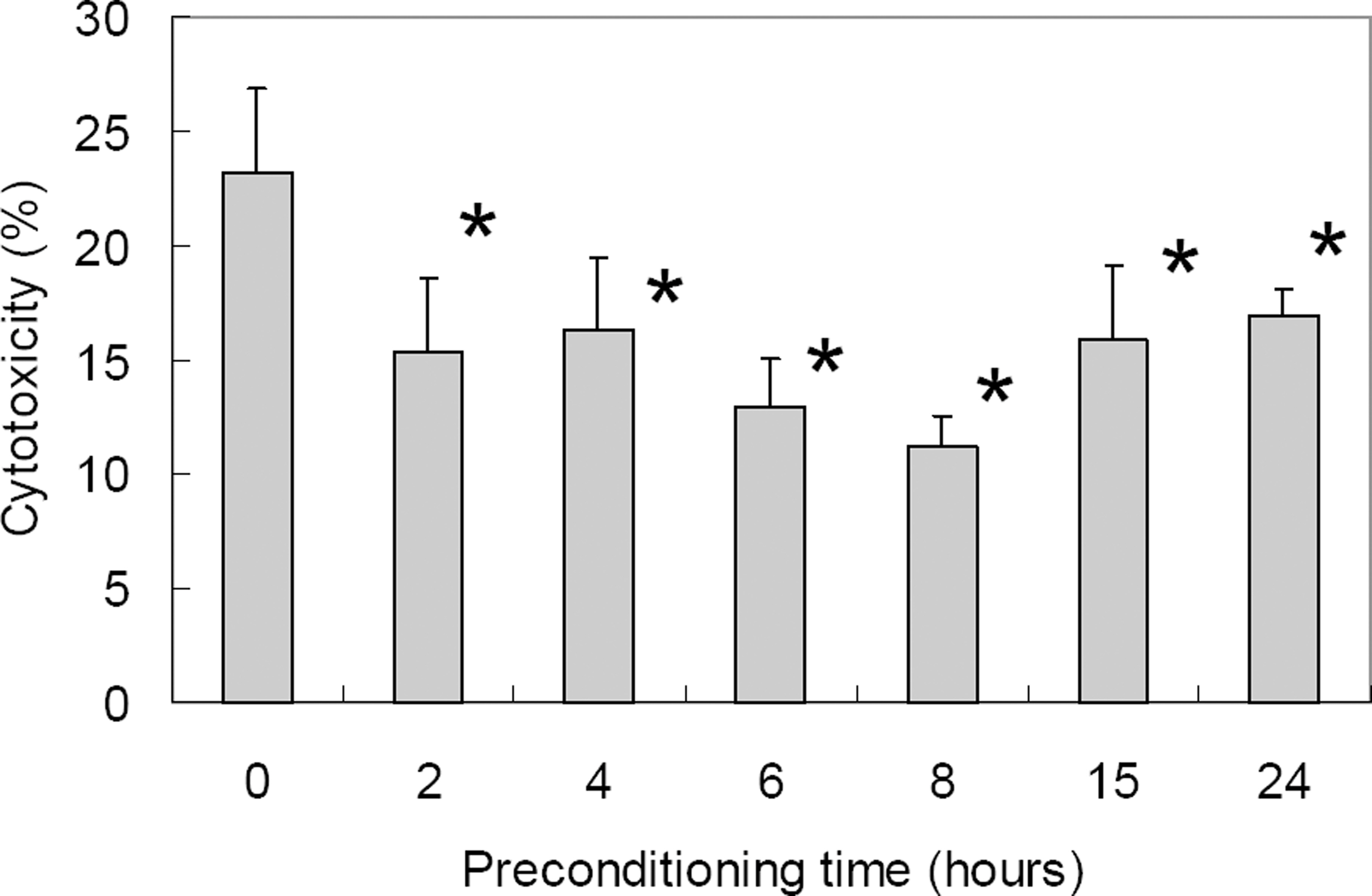
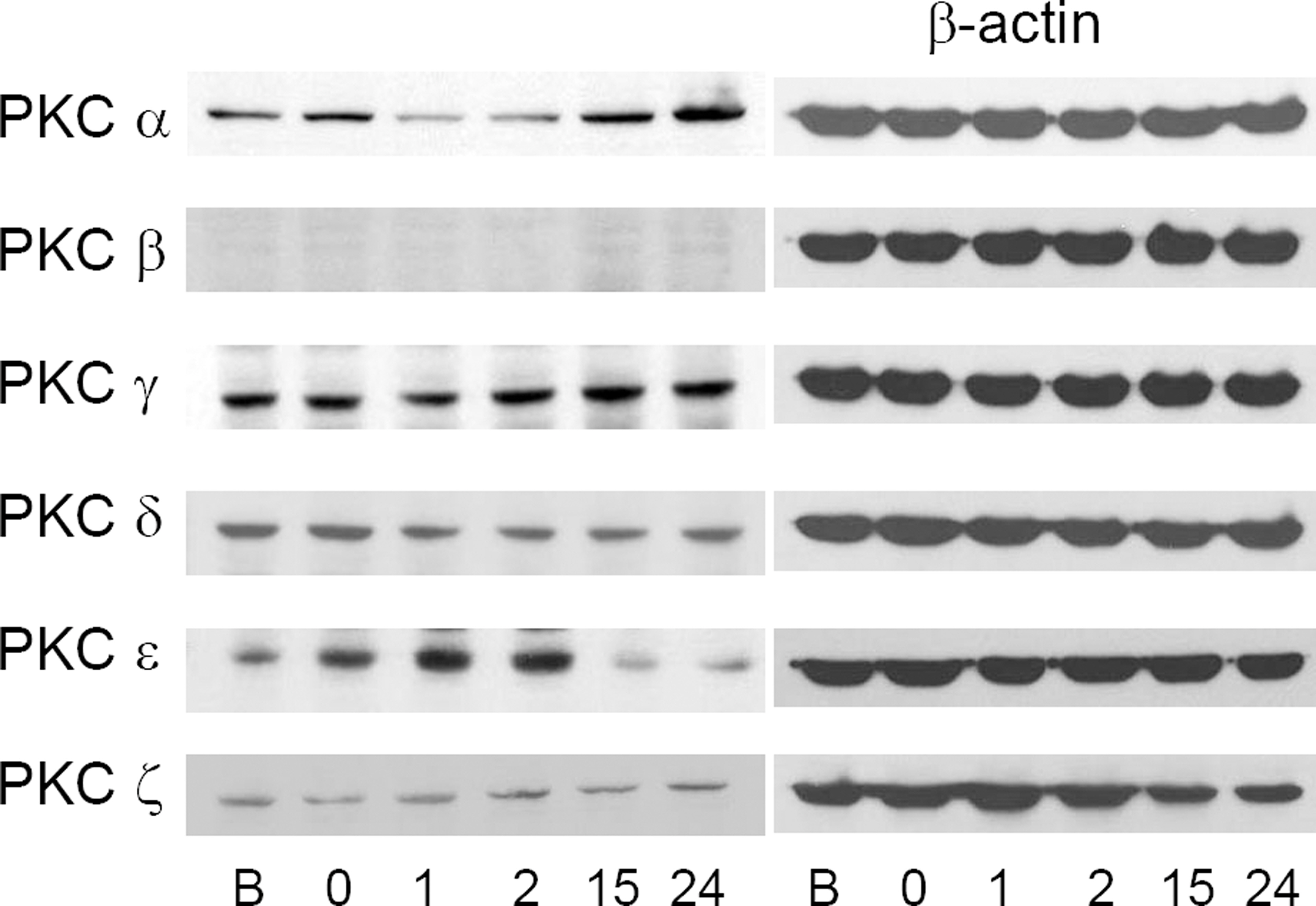
The minimum staurosporine concentration and exposure time necessary to morphologically fully differentiate RGC-5 cells were determined. Cytotoxic injury was provided by oxidative stress with 800 micrometer hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) for 15 hours to morphologically fully-differentiated cells. The cytoprotective effect of hypoxic preconditioning was found by exposing the cell line to 0.3% oxygen for different periods of time. Quantifiable changes in the expression of mRNAs and proteins of the isoenzymes alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon, zeta of protein kinase C were determined before and after 1, 2, 15, and 24 hours of hypoxic preconditioning.
RESULTS
Axonal growth in RGC-5 cells after the induction of differentiation with staurosporine caused these cells to resemble neurons. The minimal concentration and exposure time to staurosporine that evoked full differentiation of RGC-5 cells was exposure to 2 micrometer staurosporine for 1 hour. An LDH assay demonstrated that hypoxic preconditioning had neuroprotective effects against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress. Protein and mRNA levels of PKC isoforms alpha and epsilon increased after preconditioning.
CONCLUSIONS
Hypoxic preconditioning of staurosporine-differentiated RGC-5 cells had a cytoprotective effect against oxidative stress. The associated increase of mRNA and proteins of PKC isoenzymes alpha and epsilon suggest some functional relevance of these isoenzymes to the cytoprotective effects conferred by hypoxic preconditioning.
MeSH Terms
-
Axons
Cell Line
Hydrogen
Hydrogen Peroxide
Ischemic Preconditioning
Isoenzymes
Neurons
Neuroprotective Agents
Oxidative Stress
Oxygen
Protein Isoforms
Protein Kinase C
Protein Kinases
Proteins
Retinal Ganglion Cells
Retinaldehyde
RNA, Messenger
Staurosporine
Hydrogen
Hydrogen Peroxide
Isoenzymes
Neuroprotective Agents
Oxygen
Protein Isoforms
Protein Kinase C
Protein Kinases
Proteins
RNA, Messenger
Retinaldehyde
Staurosporine
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Goldberg I. Weinreb RN, Kitazawa J, Krieglestein GK, editors. How common is glaucoma worldwide? Glaucoma in the 21st Century. Landau, Germany: Mosby;2000:1–8.2. Giammanco R, Dardanoni G, Ponte F.Prevalence of glaucoma in a population. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1995; 73:222–5.3. Cedrone C, Culasso F, Cesareo M. . Prevalence of glaucoma in Ponza. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 1997; 4:59–72.4. Owsley C, McGwin G Jr, Ball K. Vision impairment, eye disease, and motor vehicle crashes in the elderly. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 1998; 5:101–13.5. The Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (AGIS): 7. The relationship between control of intraocular pressure and visual field deterioration. The AGIS Investigators. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000; 130:429–40.6. Collaborative Normal-Tension Glaucoma Study Group (CNTGSP). Comparison of glaucomatous progression between untreated patients with normal‐ tension glaucoma and patients with therapeutically reduced intraocular pressures. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:487–97.7. Chen JZ, Kadlubar FF. A new clue to glaucoma pathogenesis. Am J Med. 2003; 114:697–8.
Article8. Flammer J, Haefliger IO. Orgül S, Resink T. Vascular ysregulation: a principal risk factor for glaucoma damage? J Glaucoma. 1999; 8:212–9.9. Dowden J, Corbett D. Ischemic preconditioning in 18 to 20 month‐ old gerbils long‐ term survival with functional outcome measures. Stroke. 1999; 30:1240–6.10. Kristian T. Siesjö BK. Calcium in ischemic cell death. Stroke. 1998; 29:705–18.11. Chen J, Simon R. Ischemic tolerance in the brain. Neurology. 1997; 48:306–11.
Article12. Hawaleshka A, Jacobsohn E. Ischemic preconditioning: mechanisms and potential clinical applications (Review). Can J Anaesth. 1998; 45:670–82.13. Kitagawa K, Matsumoto M, Tagaya M. . Ischemic tolerance phenomenon found in the brain. Brain Res. 1990; 528:21–4.
Article14. Paratt JR. Protection of the heart by ischemic preconditioning: mechanisms and possibilities for pharmacological expression. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994; 15:19–25.15. Barone FC, White RF, Spera PA. . Ischemic preconditioning and brain tolerance. Stroke. 1998; 29:1937–51.16. Zhu Y, Ohlemiller KK, McMahan BK. . Constitutive nitric oxide synthase activity is required to trigger ischemic tolerance in mouse retina. Exp Eye Res. 2006; 82:153–63.
Article17. Ozbay D, Ozden S, Muftuoglu S. . Protective effect of ischemic preconditioning on retinal ischemia‐ reperfusion injury in rats. Can J Ophthalmol. 2004; 39:727–32.18. Sakamoto K, Yonoki Y, Kuwagata M. . Histological protection against ischemia‐ reperfusion injury by early ischemic preconditioning in rat retina. Brain Res. 2004; 1015:154–60.19. Matsumoto S, Shamloo M, Matsumoto E. . Protein kinase C-gamma and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha are persistently translocated to cell membranes of the rat brain during and after middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004; 24:54–61.20. Speechly‐ Dick ME, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM, Protein kinase C.Its role in ischemic preconditioning in the rat. Circ Res. 1994; 75:586–90.21. Piccoletti R, Bendinelli P, Arienti D. Bernelli-Zazzera A. State and activity of protein kinase C in postischemic reperfused liver. Exp Mol Pathol. 1992; 56:219–28.22. Padanilam BJ. Induction and subcellular localization of protein kinase C isozymes following renal ischemia. Kidney Int. 2001; 59:1789–97.
Article23. Tanaka C, Nishizuka Y. The protein kinase C family for neuronal signaling. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994; 17:551–67.
Article24. Chen L, Hahn H, Wu G. . Opposing cardioprotective actions and parallel hypertrophic effects of delta PKC and epsilon PKC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001; 98:11114–9.25. Whitlock NA, Agarwal N, Ma JX, Crosson CE. Hsp27 upregulation by HIF‐1 signaling offers protection against retinal ischemia in rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:1092–8.
Article26. Charles I, Khalyfa A, Kumar DM. . Serum deprivation induces apoptotic cell death of transformed rat retinal ganglion cells via mitochondrial signaling pathways. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:1330–8.
Article27. Maher P, Hanneken A. The molecular basis of oxidative stress-induced cell death in an immortalized retinal ganglion cell line. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:749–57.
Article28. Krishnamoorthy RR, Agarwal P, Prasanna G. . Characterization of a transformed rat retinal ganglion cell line. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2001; 86:1–12.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Protein Kinase C Signaling in Intestinal Ischemic Preconditioning
- The Role of the Adenosine Receptor Subtypes and Protein Kinase C in Ischemic Preconditioning in the in Vivo Cat Heart
- Protection of Cardiomyocytes from Acute Ischemic Injury by Protein Kinase Cepsilon Expression
- Mechanisms involved in adenosine pharmacological preconditioning-induced cardioprotection
- The Changes of the Retinal Ganglional Cells in the Pressure-induced Ischemic Rabbit Retina