J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Jul;58(1):22-29. 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.22.
Cognitive Dysfunction and Hippocampal Damage Induced by Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury and Prolonged Febrile Convulsions in Immature Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bleun@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy and Division of Brain Korea 21 Biomedical Science, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2067100
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.22
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and prolonged febrile seizures (pFS) are common neurologic problems that occur during childhood. However, there is insufficient evidence from experimental studies to conclude that pFS directly induces hippocampal injury. We studied cognitive function and histological changes in a rat model and investigated which among pFS, HIE, or a dual pathologic effect is most detrimental to the health of children.
METHODS
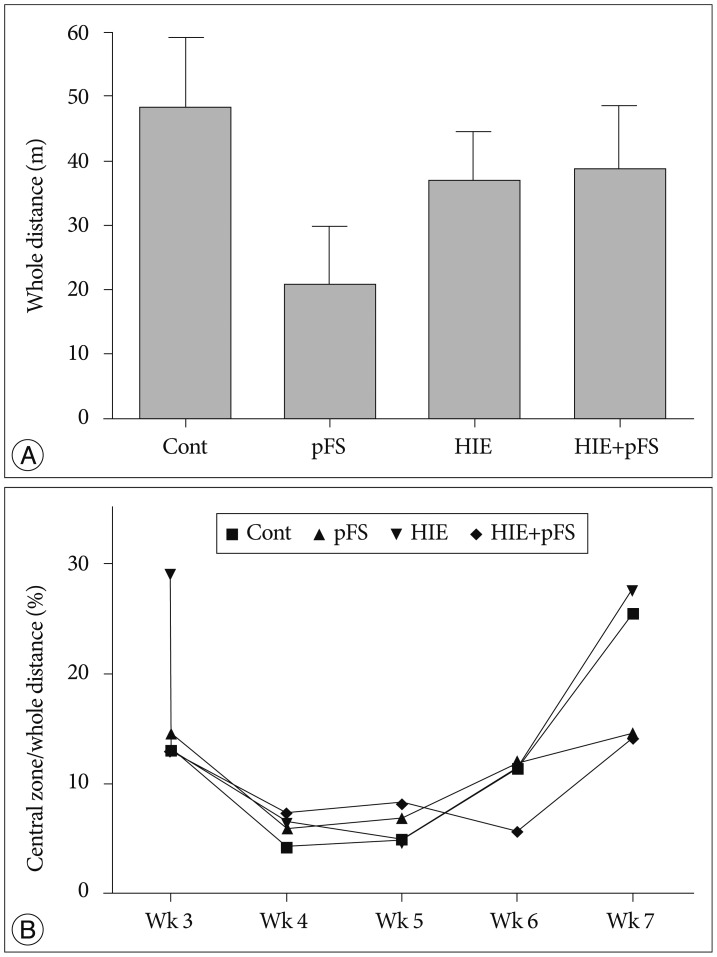
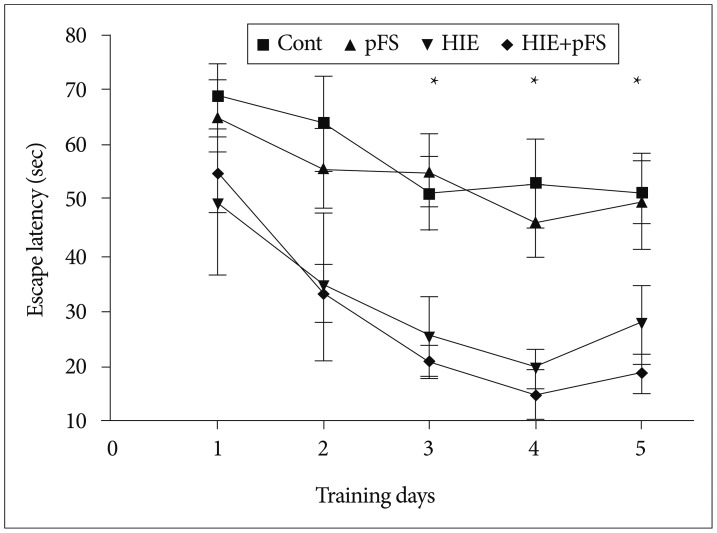
A rat model of HIE at postnatal day (PD) 7 and a pFS model at PD10 were used. Behavioral and cognitive functions were investigated by means of weekly open field tests from postnatal week (PW) 3 to PW7, and by daily testing with the Morris water maze test at PW8. Pathological changes in the hippocampus were observed in the control, pFS, HIE, and HIE+pFS groups at PW9.
RESULTS
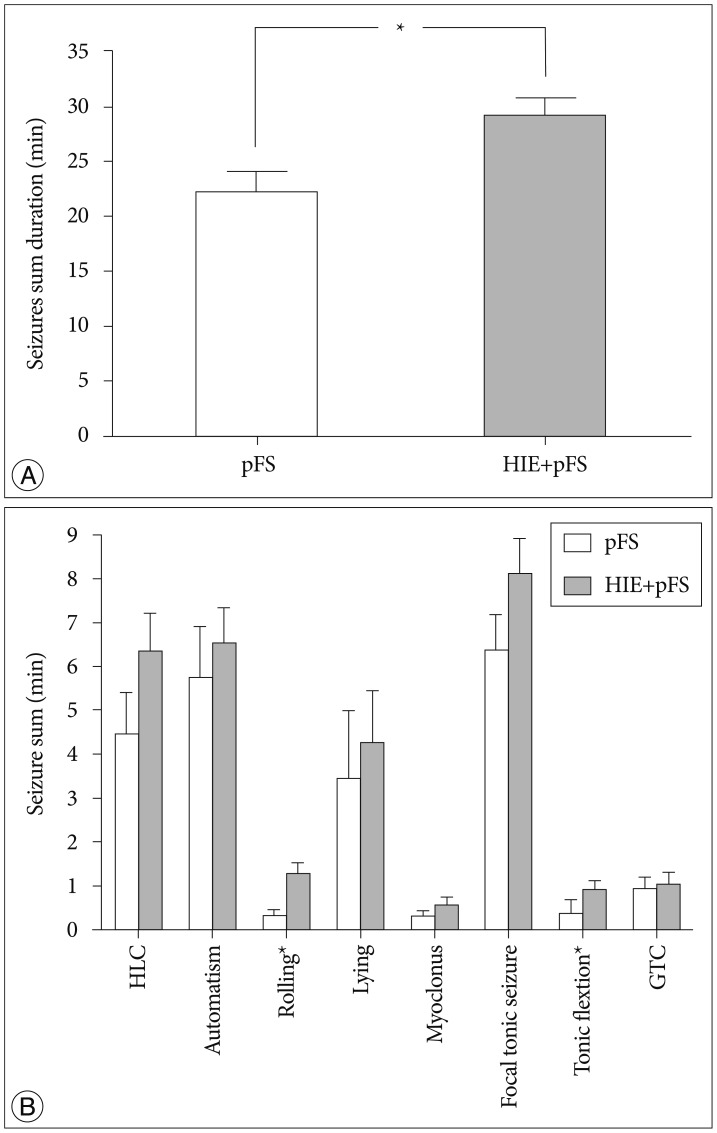
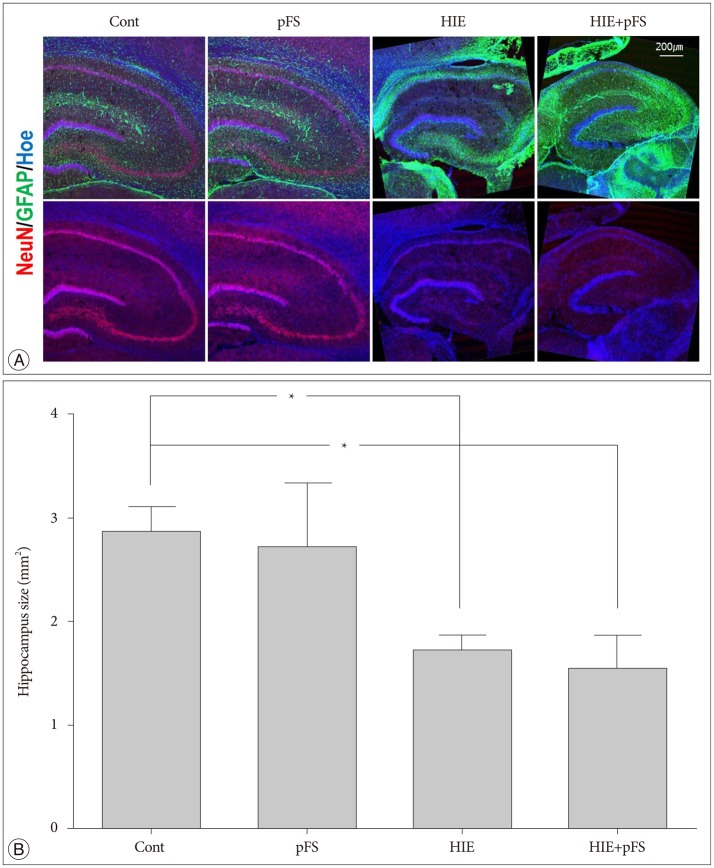
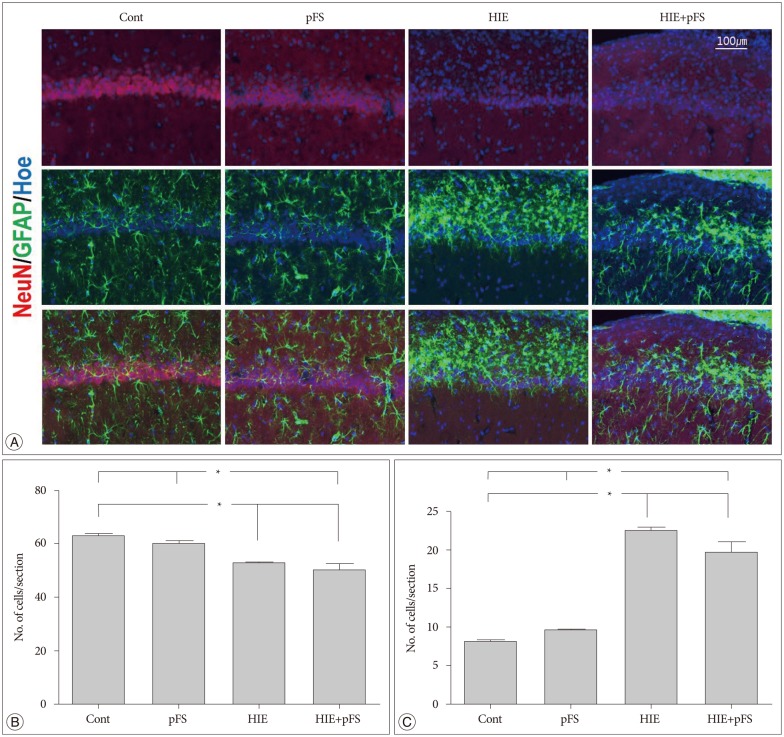
The HIE priming group showed a seizure-prone state. The Morris water maze test revealed a decline in cognitive function in the HIE and HIE+pFS groups compared with the pFS and control groups. Additionally, the HIE and HIE+pFS groups showed significant hippocampal neuronal damage, astrogliosis, and volume loss, after maturation. The pFS alone induced minimal hippocampal neuronal damage without astrogliosis or volume loss.
CONCLUSION
Our findings suggest that pFS alone causes no considerable memory or behavioral impairment, or cellular change. In contrast, HIE results in lasting memory impairment and neuronal damage, gliosis, and tissue loss. These findings may contribute to the understanding of the developing brain concerning conditions caused by HIE or pFS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ambalavanan N, Carlo WA, Shankaran S, Bann CM, Emrich SL, Higgins RD, et al. Predicting outcomes of neonates diagnosed with hypoxemic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:2084–2093. PMID: 17079582.
Article2. Astur RS, Taylor LB, Mamelak AN, Philpott L, Sutherland RJ. Humans with hippocampus damage display severe spatial memory impairments in a virtual Morris water task. Behav Brain Res. 2002; 132:77–84. PMID: 11853860.
Article3. Bangasser DA, Waxler DE, Santollo J, Shors TJ. Trace conditioning and the hippocampus : the importance of contiguity. J Neurosci. 2006; 26:8702–8706. PMID: 16928858.4. Baram TZ, Gerth A, Schultz L. Febrile seizures : an appropriate-aged model suitable for long-term studies. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1997; 98:265–270. PMID: 9051269.
Article5. Bender RA, Dubé C, Gonzalez-Vega R, Mina EW, Baram TZ. Mossy fiber plasticity and enhanced hippocampal excitability, without hippocampal cell loss or altered neurogenesis, in an animal model of prolonged febrile seizures. Hippocampus. 2003; 13:399–412. PMID: 12722980.
Article6. Bronen RA. The status of status : seizures are bad for your brain's health. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:1782–1783. PMID: 11110527.7. Dubé C, Richichi C, Bender RA, Chung G, Litt B, Baram TZ. Temporal lobe epilepsy after experimental prolonged febrile seizures : prospective analysis. Brain. 2006; 129(Pt 4):911–922. PMID: 16446281.
Article8. Dzhala V, Ben-Ari Y, Khazipov R. Seizures accelerate anoxia-induced neuronal death in the neonatal rat hippocampus. Ann Neurol. 2000; 48:632–640. PMID: 11026447.
Article9. Gottlieb A, Keydar I, Epstein HT. Rodent brain growth stages : an analytical review. Biol Neonate. 1977; 32:166–176. PMID: 603801.10. Kwon SK, Kovesdi E, Gyorgy AB, Wingo D, Kamnaksh A, Walker J, et al. Stress and traumatic brain injury : a behavioral, proteomics, and histological study. Front Neurol. 2011; 2:12. PMID: 21441982.11. Kwong KL, Wong SN, So KT. Epilepsy in children with cerebral palsy. Pediatr Neurol. 1998; 19:31–36. PMID: 9682882.
Article12. Lado FA, Sankar R, Lowenstein D, Moshé SL. Age-dependent consequences of seizures : relationship to seizure frequency, brain damage, and circuitry reorganization. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2000; 6:242–252. PMID: 11107189.
Article13. Lafemina MJ, Sheldon RA, Ferriero DM. Acute hypoxia-ischemia results in hydrogen peroxide accumulation in neonatal but not adult mouse brain. Pediatr Res. 2006; 59:680–683. PMID: 16627881.
Article14. Levine S. Anoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in rats. Am J Pathol. 1960; 36:1–17. PMID: 14416289.15. Lewis DV. Losing neurons : selective vulnerability and mesial temporal sclerosis. Epilepsia. 2005; 46(Suppl 7):39–44. PMID: 16201994.
Article16. Lipkind D, Sakov A, Kafkafi N, Elmer GI, Benjamini Y, Golani I. New replicable anxiety-related measures of wall vs center behavior of mice in the open field. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004; 97:347–359. PMID: 14990560.
Article17. Mathern GW, Babb TL, Vickrey BG, Melendez M, Pretorius JK. The clinical-pathogenic mechanisms of hippocampal neuron loss and surgical outcomes in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain. 1995; 118(Pt 1):105–118. PMID: 7894997.
Article18. McLean C, Ferriero D. Mechanisms of hypoxic-ischemic injury in the term infant. Semin Perinatol. 2004; 28:425–432. PMID: 15693399.
Article19. Morris R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 1984; 11:47–60. PMID: 6471907.
Article20. Provenzale JM, Barboriak DP, VanLandingham K, MacFall J, Delong D, Lewis DV. Hippocampal MRI signal hyperintensity after febrile status epilepticus is predictive of subsequent mesial temporal sclerosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:976–983. PMID: 18356445.
Article21. Radulovic J, Tronson NC. Molecular specificity of multiple hippocampal processes governing fear extinction. Rev Neurosci. 2010; 21:1–17. PMID: 20458884.
Article22. Rice JE 3rd, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol. 1981; 9:131–141. PMID: 7235629.
Article23. Scott RC, King MD, Gadian DG, Neville BG, Connelly A. Hippocampal abnormalities after prolonged febrile convulsion : a longitudinal MRI study. Brain. 2003; 126(Pt 11):2551–2557. PMID: 12937081.
Article24. Sloviter RS, Kudrimoti HS, Laxer KD, Barbaro NM, Chan S, Hirsch LJ, et al. "Tectonic" hippocampal malformations in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2004; 59:123–153. PMID: 15246116.
Article25. Thom M, Zhou J, Martinian L, Sisodiya S. Quantitative post-mortem study of the hippocampus in chronic epilepsy : seizures do not inevitably cause neuronal loss. Brain. 2005; 128(Pt 6):1344–1357. PMID: 15758032.
Article26. Tsien JZ, Huerta PT, Tonegawa S. The essential role of hippocampal CA1 NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity in spatial memory. Cell. 1996; 87:1327–1338. PMID: 8980238.
Article27. Unal-Cevik I, Kilinç M, Gürsoy-Ozdemir Y, Gurer G, Dalkara T. Loss of NeuN immunoreactivity after cerebral ischemia does not indicate neuronal cell loss : a cautionary note. Brain Res. 2004; 1015:169–174. PMID: 15223381.28. Vannucci RC, Connor JR, Mauger DT, Palmer C, Smith MB, Towfighi J, et al. Rat model of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. J Neurosci Res. 1999; 55:158–163. PMID: 9972818.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Neuroprotective Effects of the Platelet-Activating Factor Antagonist BN 52021 on Hypoxic-ischemic Brain Injury in the Immature Rat
- E-selectin Mrna and Protein Expression Increase Transiently After Unilateral Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in Neonatal Rats
- Alterations of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I mRNA and IGF Binding Protein-5 mRNA Expression Following Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Immature Rat
- Expression of ICAM-1 mRNA after Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats
- Neuroprotective Effect of Growth Hormone in Neonatal Rat with Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury