J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Jul;58(1):1-8. 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.1.
Recent Advancements of Treatment for Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of System Cancer Science, Graduate School of Cancer Science and Policy, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. nsghs@ncc.re.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Neuro-Oncology Clinic, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2067097
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.1
Abstract
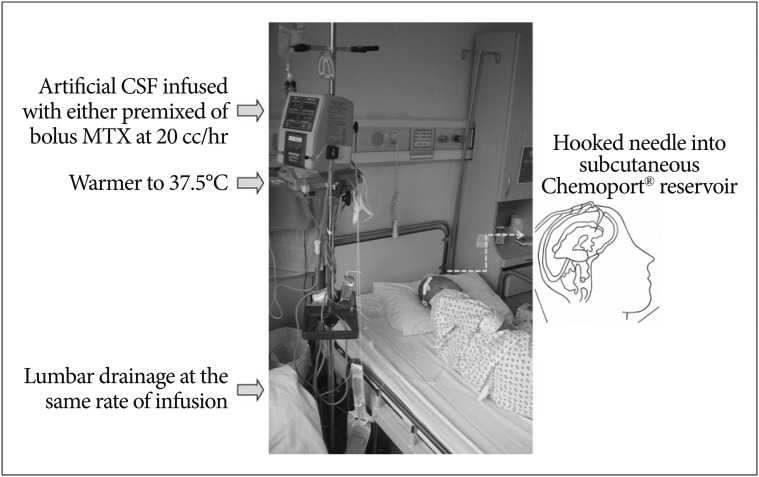
- Treatment of Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (LMC) from solid cancers has not advanced noticeably since the introduction of intra-cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) chemotherapy in the 1970's. The marginal survival benefit and difficulty of intrathecal chemotherapy injection has hindered its wide spread use. Even after the introduction of intraventricular chemotherapy with Ommaya reservoir, frequent development of CSF flow disturbance, manifested as increased intracranial pressure (ICP), made injected drug to be distributed unevenly and thus, the therapy became ineffective. Systemic chemotherapy for LMC has been limited as effective CSF concentration can hardly be achieved except high dose methotrexate (MTX) intravenous administration. However, the introduction of small molecular weight target inhibitors for primary cancer treatment has changed the old concept of 'blood-brain barrier' as the ultimate barrier to systemically administered drugs. Conventional oral administration achieves an effective concentration at the nanomolar level. Furthermore, many studies report that a combined treatment of target inhibitor and intra-CSF chemotherapy significantly prolongs patient survival. Ventriculolumbar perfusion (VLP) chemotherapy has sought to increase drug delivery to the subarachnoid CSF space even in patients with disturbed CSF flow. Recently authors performed phase 1 and 2 clinical trial of VLP chemotherapy with MTX, and 3/4th of patients with increased ICP got controlled ICP and the survival was prolonged. Further trials are required with newly available drugs for CSF chemotherapy. Additionally, new LMC biologic/pharmacodynamic markers for early diagnosis and monitoring of the treatment response are to be identified with the help of advanced molecular biology techniques.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Choroid Plexus Carcinoma in Adults: Two Case Reports
Taehoon Kim, Mee Rim Park, Eun Kyeong Hong, Ho-Shin Gwak
Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2019;7(1):48-52. doi: 10.14791/btrt.2019.7.e23.Lumboperitoneal Shunt Combined With Ommaya Reservoir Enables Continued Intraventricular Chemotherapy for Leptomeningeal Metastasis With Increased Intracranial Pressure
Byungjun Woo, Ho-Shin Gwak, Ji-Woong Kwon, Sang-Hoon Shin, Heon Yoo
Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2022;10(4):237-243. doi: 10.14791/btrt.2022.0022.
Reference
-
1. Balis FM, Blaney SM, McCully CL, Bacher JD, Murphy RF, Poplack DG. Methotrexate distribution within the subarachnoid space after intraventricular and intravenous administration. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2000; 45:259–264. PMID: 10663645.
Article2. Baraniskin A, Kuhnhenn J, Schlegel U, Schmiegel W, Hahn S, Schroers R. MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid as biomarker for disease course monitoring in primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Neurooncol. 2012; 109:239–244. PMID: 22729947.
Article3. Bernardi RJ, Bomgaars L, Fox E, Balis FM, Egorin MJ, Lagattuta TF, et al. Phase I clinical trial of intrathecal gemcitabine in patients with neoplastic meningitis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008; 62:355–361. PMID: 17909804.
Article4. Blaney SM, Balis FM, Berg S, Arndt CA, Heideman R, Geyer JR, et al. Intrathecal mafosfamide : a preclinical pharmacology and phase I trial. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:1555–1563. PMID: 15735131.5. Blaney SM, Boyett J, Friedman H, Gajjar A, Geyer R, Horowtiz M, et al. Phase I clinical trial of mafosfamide in infants and children aged 3 years or younger with newly diagnosed embryonal tumors : a pediatric brain tumor consortium study (PBTC-001). J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:525–531. PMID: 15659498.
Article6. Blaney SM, Cole DE, Balis FM, Godwin K, Poplack DG. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetic study of topotecan in nonhuman primates. Cancer Res. 1993; 53:725–727. PMID: 8428353.7. Blaney SM, Heideman R, Berg S, Adamson P, Gillespie A, Geyer JR, et al. Phase I clinical trial of intrathecal topotecan in patients with neoplastic meningitis. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:143–147. PMID: 12506183.
Article8. Blaney SM, Kocak M, Gajjar A, Chintagumpala M, Merchant T, Kieran M, et al. Pilot study of systemic and intrathecal mafosfamide followed by conformal radiation for infants with intracranial central nervous system tumors : a pediatric brain tumor consortium study (PBTC-001). J Neurooncol. 2012; 109:565–571. PMID: 22790443.
Article9. Blaney SM, Poplack DG. New cytotoxic drugs for intrathecal administration. J Neurooncol. 1998; 38:219–223. PMID: 9696375.10. Blasberg RG, Patlak CS, Shapiro WR. Distribution of methotrexate in the cerebrospinal fluid and brain after intraventricular administration. Cancer Treat Rep. 1977; 61:633–641. PMID: 406996.11. Bokstein F, Lossos A, Lossos IS, Siegal T. Central nervous system relapse of systemic non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma : results of treatment based on high-dose methotrexate combination chemotherapy. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002; 43:587–593. PMID: 12002763.
Article12. Bokstein F, Lossos A, Siegal T. Leptomeningeal metastases from solid tumors : a comparison of two prospective series treated with and without intra-cerebrospinal fluid chemotherapy. Cancer. 1998; 82:1756–1763. PMID: 9576299.13. Boogerd W, van den Ben MJ, Koehler PJ, Heimans JJ, van der Sande JJ, Aaronson NK, et al. The relevance of intraventricular chemotherapy for leptomeningeal metastasis in breast cancer : a randomised study. Eur J Cancer. 2004; 40:2726–2733. PMID: 15571954.
Article14. Bruna J, González L, Miró J, Velasco R, Gil M, Tortosa A, et al. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis : prognostic implications of clinical and cerebrospinal fluid features. Cancer. 2009; 115:381–389. PMID: 19109820.15. Chamberlain MC. Leptomeningeal metastases : a review of evaluation and treatment. J Neurooncol. 1998; 37:271–284. PMID: 9524085.16. Chamberlain MC. Radioisotope CSF flow studies in leptomeningeal metastases. J Neurooncol. 1998; 38:135–140. PMID: 9696363.17. Chamberlain MC, Kormanik P. Carcinoma meningitis secondary to non-small cell lung cancer : combined modality therapy. Arch Neurol. 1998; 55:506–512. PMID: 9561978.
Article18. Chamberlain MC, Kormanik PA. Prognostic significance of 111indium-DTPA CSF flow studies in leptomeningeal metastases. Neurology. 1996; 46:1674–1677. PMID: 8649568.
Article19. Chamberlain MC, Kormanik PA, Barba D. Complications associated with intraventricular chemotherapy in patients with leptomeningeal metastases. J Neurosurg. 1997; 87:694–699. PMID: 9347977.
Article20. Clarke JL, Pao W, Wu N, Miller VA, Lassman AB. High dose weekly erlotinib achieves therapeutic concentrations in CSF and is effective in leptomeningeal metastases from epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung cancer. J Neurooncol. 2010; 99:283–286. PMID: 20146086.
Article21. de Azevedo CR, Cruz MR, Chinen LT, Peres SV, Peterlevitz MA, de Azevedo Pereira AE, et al. Meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer : prognostic factors and outcome. J Neurooncol. 2011; 104:565–572. PMID: 21234642.
Article22. Egorin MJ, Zuhowski EG, McCully CM, Blaney SM, Kerr JZ, Berg SL, et al. Pharmacokinetics of intrathecal gemcitabine in nonhuman primates. Clin Cancer Res. 2002; 8:2437–2442. PMID: 12114450.23. Fizazi K, Asselain B, Vincent-Salomon A, Jouve M, Dieras V, Palangie T, et al. Meningeal carcinomatosis in patients with breast carcinoma. Clinical features, prognostic factors, and results of a high-dose intrathecal methotrexate regimen. Cancer. 1996; 77:1315–1323. PMID: 8608509.
Article24. Fleischhack G, Jaehde U, Bode U. Pharmacokinetics following intraventricular administration of chemotherapy in patients with neoplastic meningitis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005; 44:1–31. PMID: 15634030.
Article25. Freilich RJ, Krol G, DeAngelis LM. Neuroimaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis. Ann Neurol. 1995; 38:51–57. PMID: 7611725.
Article26. Gauthier H, Guilhaume MN, Bidard FC, Pierga JY, Girre V, Cottu PH, et al. Survival of breast cancer patients with meningeal carcinomatosis. Ann Oncol. 2010; 21:2183–2187. PMID: 20430906.
Article27. Glantz MJ, Jaeckle KA, Chamberlain MC, Phuphanich S, Recht L, Swinnen LJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing intrathecal sustained-release cytarabine (DepoCyt) to intrathecal methotrexate in patients with neoplastic meningitis from solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 1999; 5:3394–3402. PMID: 10589750.28. Glass JP, Melamed M, Chernik NL, Posner JB. Malignant cells in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): the meaning of a positive CSF cytology. Neurology. 1979; 29:1369–1375. PMID: 573381.
Article29. Gleissner B, Chamberlain MC. Neoplastic meningitis. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5:443–452. PMID: 16632315.
Article30. Grossman SA, Krabak MJ. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer Treat Rev. 1999; 25:103–119. PMID: 10395835.
Article31. Grossman SA, Reinhard CS, Loats HL. The intracerebral penetration of intraventricularly administered methotrexate : a quantitative autoradiographic study. J Neurooncol. 1989; 7:319–328. PMID: 2585028.
Article32. Grossman SA, Trump DL, Chen DC, Thompson G, Camargo EE. Cerebrospinal fluid flow abnormalities in patients with neoplastic meningitis. An evaluation using 111indium-DTPA ventriculography. Am J Med. 1982; 73:641–647. PMID: 6814249.
Article33. Gururangan S, Petros WP, Poussaint TY, Hancock ML, Phillips PC, Friedman HS, et al. Phase I trial of intrathecal spartaject busulfan in children with neoplastic meningitis : a Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium Study (PBTC-004). Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12:1540–1546. PMID: 16533779.
Article34. Gwak HS, Joo J, Kim S, Yoo H, Shin SH, Han JY, et al. Analysis of treatment outcomes of intraventricular chemotherapy in 105 patients for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013; 8:599–605. PMID: 23422833.
Article35. Gwak HS, Joo J, Shin SH, Yoo H, Han JY, Kim HT, et al. Ventriculolumbar perfusion chemotherapy with methotrexate for treating leptomeningeal carcinomatosis : a Phase II Study. Oncologist. 2014; 19:1044–1045. PMID: 25209375.
Article36. Gwak HS, Lim HS, Shin SH, Yoo H, Han JY, Kim HT, et al. Ventriculolumbar perfusion chemotherapy for the treatment of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis : a phase I study with pharmacokinetic data. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013; 36:491–499. PMID: 22781384.
Article37. Herrlinger U, Förschler H, Küker W, Meyermann R, Bamberg M, Dichgans J, et al. Leptomeningeal metastasis : survival and prognostic factors in 155 patients. J Neurol Sci. 2004; 223:167–178. PMID: 15337619.
Article38. Hitchins RN, Bell DR, Woods RL, Levi JA. A prospective randomized trial of single-agent versus combination chemotherapy in meningeal carcinomatosis. J Clin Oncol. 1987; 5:1655–1662. PMID: 3309199.
Article39. Hofer S, Mengele K, Stemmler HJ, Schmitt M, Pestalozzi B. Intrathecal trastuzumab : dose matters. Acta Oncol. 2012; 51:955–956. PMID: 22524214.40. Katayama T, Shimizu J, Suda K, Onozato R, Fukui T, Ito S, et al. Efficacy of erlotinib for brain and leptomeningeal metastases in patients with lung adenocarcinoma who showed initial good response to gefitinib. J Thorac Oncol. 2009; 4:1415–1419. PMID: 19692934.
Article41. Kim DY, Lee KW, Yun T, Park SR, Jung JY, Kim DW, et al. Comparison of intrathecal chemotherapy for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis of a solid tumor : methotrexate alone versus methotrexate in combination with cytosine arabinoside and hydrocortisone. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2003; 33:608–612. PMID: 14769837.
Article42. Laufman LR, Forsthoefel KF. Use of intrathecal trastuzumab in a patient with carcinomatous meningitis. Clin Breast Cancer. 2001; 2:235. PMID: 11899418.
Article43. Levin VA, Byrd D, Campbell J, Giannini DD, Borcich JK, Davis RL. Central nervous system toxicity and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of intraventricular 3-[(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)ethyl]-1-(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitro soureas and other nitrosoureas in beagles. Cancer Res. 1985; 45:3803–3809. PMID: 3860287.44. Levin VA, Chamberlain M, Silver P, Rodriguez L, Prados M. Phase I/II study of intraventricular and intrathecal ACNU for leptomeningeal neoplasia. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1989; 23:301–307. PMID: 2706735.
Article45. Liu S, Sun J, Lan Q. Glioblastoma microvesicles promote endothelial cell proliferation through Akt/beta-catenin pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014; 7:4857–4866. PMID: 25197356.46. Masuda T, Hattori N, Hamada A, Iwamoto H, Ohshimo S, Kanehara M, et al. Erlotinib efficacy and cerebrospinal fluid concentration in patients with lung adenocarcinoma developing leptomeningeal metastases during gefitinib therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011; 67:1465–1469. PMID: 21274533.
Article47. Mittl RL Jr, Yousem DM. Frequency of unexplained meningeal enhancement in the brain after lumbar puncture. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994; 15:633–638. PMID: 8010262.48. Morris PG, Reiner AS, Szenberg OR, Clarke JL, Panageas KS, Perez HR, et al. Leptomeningeal metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer : survival and the impact of whole brain radiotherapy. J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7:382–385. PMID: 22089116.
Article49. Nakagawa H, Fujita T, Kubo S, Izumoto S, Nakajima Y, Tsuruzono K, et al. Ventriculolumbar perfusion chemotherapy with methotrexate and cytosine arabinoside for meningeal carcinomatosis : a pilot study in 13 patients. Surg Neurol. 1996; 45:256–264. PMID: 8638223.50. Ongerboer de Visser BW, Somers R, Nooyen WH, van Heerde P, Hart AA, McVie JG. Intraventricular methotrexate therapy of leptomeningeal metastasis from breast carcinoma. Neurology. 1983; 33:1565–1572. PMID: 6685829.
Article51. Park JH, Kim YJ, Lee JO, Lee KW, Kim JH, Bang SM, et al. Clinical outcomes of leptomeningeal metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer in the modern chemotherapy era. Lung Cancer. 2012; 76:387–392. PMID: 22186628.
Article52. Rubin RC, Ommaya AK, Henderson ES, Bering EA, Rall DP. Cerebrospinal fluid perfusion for central nervous system neoplasms. Neurology. 1966; 16:680–692. PMID: 5949435.
Article53. Sato Y, Ohta Y, Kaji M, Oizumi K, Kaji M. Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in cerebrospinal fluid and within malignant cells in a case of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998; 65:402–403. PMID: 9728963.
Article54. Schabet M, Kloeter I, Adam T, Heidemann E, Wiethölter H. Diagnosis and treatment of meningeal carcinomatosis in ten patients with breast cancer. Eur Neurol. 1986; 25:403–411. PMID: 3792399.
Article55. Shapiro WR, Young DF, Mehta BM. Methotrexate : distribution in cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous, ventricular and lumbar injections. N Engl J Med. 1975; 293:161–166. PMID: 806016.
Article56. Siegal T, Lossos A, Pfeffer MR. Leptomeningeal metastases : analysis of 31 patients with sustained off-therapy response following combined-modality therapy. Neurology. 1994; 44:1463–1469. PMID: 8058150.57. Straathof CS, de Bruin HG, Dippel DW, Vecht CJ. The diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in leptomeningeal metastasis. J Neurol. 1999; 246:810–814. PMID: 10525979.
Article58. Swinkels DW, de Kok JB, Hanselaar A, Lamers K, Boerman RH. Early detection of leptomeningeal metastasis by PCR examination of tumor-derived K-ras DNA in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem. 2000; 46:132–133. PMID: 10620587.
Article59. Taillibert S, Laigle-Donadey F, Chodkiewicz C, Sanson M, Hoang-Xuan K, Delattre JY. Leptomeningeal metastases from solid malignancy : a review. J Neurooncol. 2005; 75:85–99. PMID: 16215819.
Article60. Teplyuk NM, Mollenhauer B, Gabriely G, Giese A, Kim E, Smolsky M, et al. MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid identify glioblastoma and metastatic brain cancers and reflect disease activity. Neuro Oncol. 2012; 14:689–700. PMID: 22492962.
Article61. Tetef ML, Margolin KA, Doroshow JH, Akman S, Leong LA, Morgan RJ Jr, et al. Pharmacokinetics and toxicity of high-dose intravenous methotrexate in the treatment of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2000; 46:19–26. PMID: 10912573.
Article62. Tran HC, Gardner S, Weiner HL, Liebes LF, Finlay JL. Pilot study assessing a seven-day continuous intrathecal topotecan infusion for recurrent or progressive leptomeningeal metastatic cancer. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2014; 20:229–232. PMID: 23929729.
Article63. Twijnstra A, van Zanten AP, Hart AA, Ongerboer de Visser BW. Serial lumbar and ventricle cerebrospinal fluid lactate dehydrogenase activities in patients with leptomeningeal metastases from solid and haematological tumours. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987; 50:313–320. PMID: 3559613.
Article64. Twijnstra A, van Zanten AP, Nooyen WJ, Ongerboer de Visser BW. Sensitivity and specificity of single and combined tumour markers in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis from breast cancer. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986; 49:1246–1250. PMID: 3540216.
Article65. Waki F, Ando M, Takashima A, Yonemori K, Nokihara H, Miyake M, et al. Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes in patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors. J Neurooncol. 2009; 93:205–212. PMID: 19043775.
Article66. Wasserstrom WR, Glass JP, Posner JB. Diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal metastases from solid tumors : experience with 90 patients. Cancer. 1982; 49:759–772. PMID: 6895713.
Article67. Yi HG, Kim HJ, Kim YJ, Han SW, Oh DY, Lee SH, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are effective for leptomeningeal metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer patients with sensitive EGFR mutation or other predictive factors of good response for EGFR TKI. Lung Cancer. 2009; 65:80–84. PMID: 19059670.
Article68. Yousem DM, Patrone PM, Grossman RI. Leptomeningeal metastases : MR evaluation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990; 14:255–261. PMID: 2312855.69. Zagouri F, Sergentanis TN, Bartsch R, Berghoff AS, Chrysikos D, de Azambuja E, et al. Intrathecal administration of trastuzumab for the treatment of meningeal carcinomatosis in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer : a systematic review and pooled analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013; 139:13–22. PMID: 23588955.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intrathecal Trastuzumab Treatment in Patients with Breast Cancer and Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
- A Case of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Presenting as a Neurological Complication of Stomach Cancer
- Clinical Features and Prognosis of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
- Unilateral Oculomotor Nerve Palsy Associated with Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis and Intracranial Hypertension
- Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis of Gastric Cancer Misdiagnosed as Vestibular Schwannoma