J Korean Med Assoc.
2013 Mar;56(3):220-228. 10.5124/jkma.2013.56.3.220.
Prevention and management of the diabetic foot
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, Ulsan University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hosng@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2064827
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2013.56.3.220
Abstract
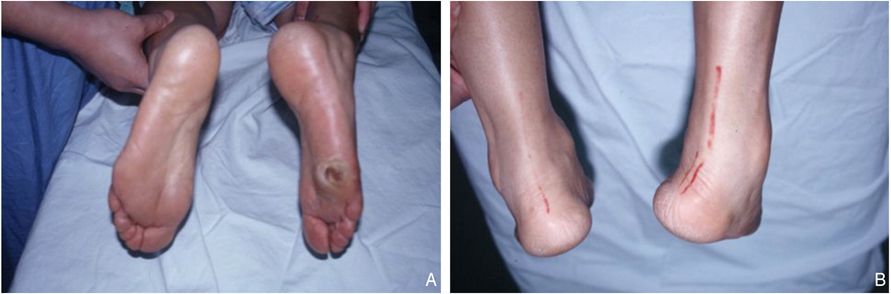
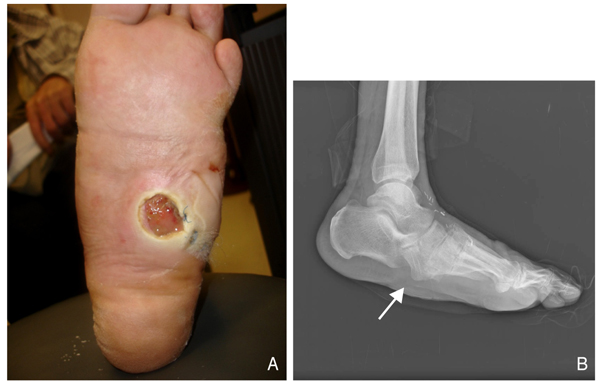
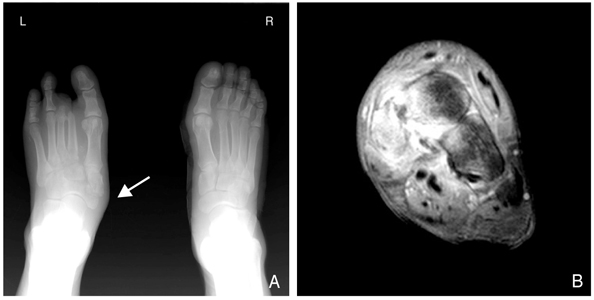
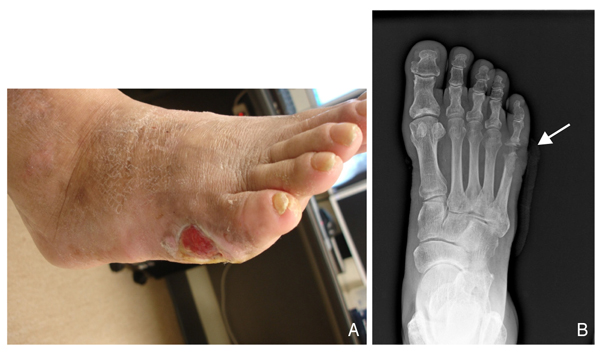
- In the diabetic foot, ulceration and amputation are the most serious causes of morbidity and disability in these patients. Peripheral arterial sclerosis, peripheral neuropathy, and foot deformities are major causes of foot problems. Foot deformities caused by autonomic and motor neuropathy lead, in turn, to over-pressured focal lesions causing the diabetic foot to be easily injured within the shoe while walking. Wound healing can be difficult in these patients because of impaired phagocytic activity by hyperglycemia, impaired migration of leukocytes due to a thickened basement membrane, malnutrition, and ischemia. Deformity correction or shoe modification to relieve the pressure of over-pressured points is necessary for ulcer management. Selective dressings allowing a moist environment following complete debridement of the necrotic tissue is mandatory. In the case of a large soft tissue defect due to aggressive debridement, a wound coverage procedure is necessary by either a distant flap operation or a skin graft. Amputation can be necessary in the case of an intractable ischemic toe or a life-threatening infected limb. The amputation level should be kept at its minimum to allow patients to walk, with or without a prosthesis, post-amputation. A foot with Charcot's joint should be stabilized and consolidated into a plantigrade foot. The bony prominence of a Charcot foot can be corrected by a bumpectomy for prevention of ulceration. The most effective management of the diabetic foot is ulcer prevention; measures include controlling blood sugar levels, controlling neuropathic pain, smoking cessation, stretching exercises, frequent inspection of the foot, and education on appropriate footwear. A multidisciplinary approach is also highly recommended for managing diabetic foot problems.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Amputation
Arthropathy, Neurogenic
Bandages
Basement Membrane
Blood Glucose
Congenital Abnormalities
Debridement
Diabetic Foot
Exercise
Extremities
Foot
Foot Deformities
Humans
Hyperglycemia
Ischemia
Leukocytes
Malnutrition
Neuralgia
Peripheral Nervous System Diseases
Prostheses and Implants
Sclerosis
Shoes
Skin
Smoking Cessation
Toes
Transplants
Ulcer
Walking
Wound Healing
Blood Glucose
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The Relationship between Body Mass Index and Diabetic Foot Ulcer, Sensory, Blood Circulation of Foot on Type II Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Yi Kyu Park, Jun Young Lee, Sung Jung, Kang Hyeon Ryu
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2018;53(2):136-142. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.2.136.Management and rehabilitation of moderate-to-severe diabetic foot infection: a narrative review
Chi Young An, Seung Lim Baek, Dong-Il Chun
J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(4):343-351. doi: 10.12701/jyms.2023.00717.
Reference
-
1. Kim SG, Choi DS. The present state of diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008; 51:791–798.
Article2. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:303–308.
Article3. Kim KW. Diabetic foot. J Korean Med Assoc. 2007; 50:447–454.
Article4. Kim JM, Kim DY, Woo JT, Kim SW, Yang IM, Kim JW, Kim YS, Kim KW, Coi YK. A clinical study on the diabetic foot lesions. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1993; 17:387–394.5. Wagner FW. A classification and treatment program for diabetic, neuropathic, and dysvascular foot problems. Instr Course Lect. 1979; 28:143–165.6. Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA. 2002; 287:2570–2581.7. Park Y. Management of the patients with diabetes mellitus and macro- and microvascular complications. J Korean Med Assoc. 2005; 48:721–734.
Article8. Apelqvist J, Castenfors J, Larsson J, Stenstrom A, Agardh CD. Prognostic value of systolic ankle and toe blood pressure levels in outcome of diabetic foot ulcer. Diabetes Care. 1989; 12:373–378.
Article9. Donas KP, Torsello G, Schwindt A, Schonefeld E, Boldt O, Pitoulias GA. Below knee bare nitinol stent placement in high-risk patients with critical limb ischemia is still durable after 24 months of follow-up. J Vasc Surg. 2010; 52:356–361.
Article10. Coughlin MJ, Mann RA, Saltzman CL. Surgery of the foot and ankle. 2006. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby.11. Mann RA, Wapner KL. Tibial sesamoid shaving for treatment of intractable plantar keratosis. Foot Ankle. 1992; 13:196–198.
Article12. Lin SS, Lee TH, Wapner KL. Plantar forefoot ulceration with equinus deformity of the ankle in diabetic patients: the effect of tendo-Achilles lengthening and total contact casting. Orthopedics. 1996; 19:465–475.
Article13. Pitocco D, Ruotolo V, Caputo S, Mancini L, Collina CM, Manto A, Caradonna P, Ghirlanda G. Six-month treatment with alendronate in acute Charcot neuroarthropathy: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:1214–1215.14. Bamberger DM, Daus GP, Gerding DN. Osteomyelitis in the feet of diabetic patients. Long-term results, prognostic factors, and the role of antimicrobial and surgical therapy. Am J Med. 1987; 83:653–660.15. Oh TS, Lee HS, Hong JP. Diabetic foot reconstruction using free flaps increases 5-year-survival rate. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013; 66:243–250.
Article16. Prosdocimi M, Bevilacqua C. Impaired wound healing in diabetes: the rationale for clinical use of hyaluronic acid plus silver sulfadiazine. Minerva Med. 2012; 103:533–539.17. Valenzuela-Silva CM, Tuero-Iglesias AD, Garcia-Iglesias E, Gonzalez-Diaz O, Del Rio-Martin A, Yera Alos IB, Fernandez-Montequin JI, Lopez-Saura PA. Granulation response and partial wound closure predict healing in clinical trials on advanced diabetes foot ulcers treated with recombinant human epidermal growth factor. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:210–215.
Article18. Mendonca DA, Cosker T, Makwana NK. Vacuum-assisted closure to aid wound healing in foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle Int. 2005; 26:761–766.
Article19. Wheat LJ, Allen SD, Henry M, Kernek CB, Siders JA, Kuebler T, Fineberg N, Norton J. Diabetic foot infections: bacteriologic analysis. Arch Intern Med. 1986; 146:1935–1940.
Article20. Kwon YJ, Han KA, Sung SK, Yoo HJ. A clinical study on the diabetic foot lesions. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1989; 13:39–46.21. Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001; 414:782–787.
Article