Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Busan St. Mary's Hospital, Busan, Korea. koje94@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2421298
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2018.19.3.168
Abstract
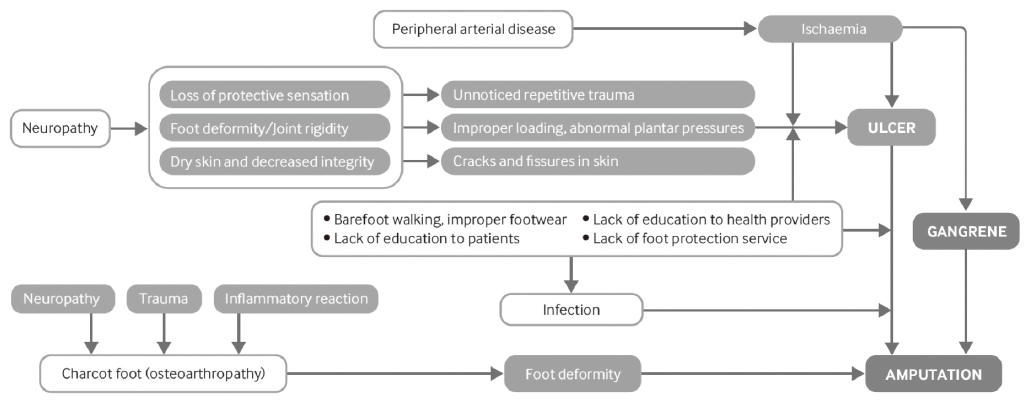
- Diabetic foot is one of the most significant and serious complications of diabetes, and is defined as the foot of diabetic patients with ulceration, infection and/or destruction of the deep tissues, associated with neurological abnormalities and various degrees of peripheral vascular disease in the lower limb. The most significant risk factors for foot ulceration are diabetic neuropathy, peripheral arterial disease, and consequent traumas of the foot. Most diabetic ulcers can be prevented with good foot care and screening for risk factors for a foot at risk of complications. Active foot examination and foot care education are methods to prevent diabetic foot at a minimum cost. I will focus on the recommendations for diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Management and rehabilitation of moderate-to-severe diabetic foot infection: a narrative review
Chi Young An, Seung Lim Baek, Dong-Il Chun
J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(4):343-351. doi: 10.12701/jyms.2023.00717.2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management in Korea: Full Version Recommendation of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jun Sung Moon, Shinae Kang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, Yoon Ju Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae Jin Kim, Hyun Min Kim, Jung Hae Ko, Nam Hoon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Jeeyun Ahn, Tae Jung Oh, Soo-Kyung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Eugene Han, Sang-Man Jin, Jaehyun Bae, Eonju Jeon, Ji Min Kim, Seon Mee Kang, Jung Hwan Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Bong-Soo Cha, Min Kyong Moon, Byung-Wan Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(4):546-708. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0249.
Reference
-
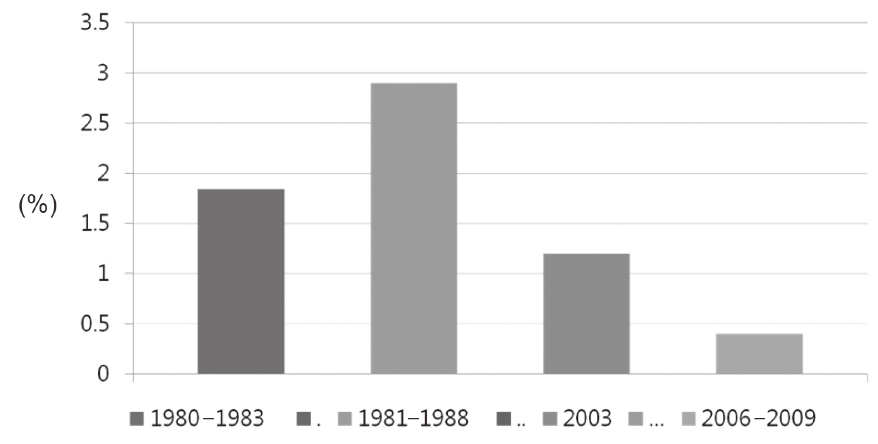
1. Lee JH, Chung CH. Diabetic foot: past and present. J Korean Diabetes. 2011; 12:69–71.
Article2. International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot. International consensus on the diabetic foot. Amsterdam: The International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot;1999. p. 20–96.3. Alexiadou K, Doupis J. Management of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Ther. 2012; 3:4.
Article4. Abbott CA, Carrington AL, Ashe H, Bath S, Every LC, Griffiths J, Hann AW, Hussein A, Jackson N, Johnson KE, Ryder CH, Torkington R, Van Ross ER, Whalley AM, Widdows P, Williamson S, Boulton AJ. North-West Diabetes Foot Care Study. The North-West Diabetes Foot Care Study: incidence of, and risk factors for, new diabetic foot ulceration in a community-based patient cohort. Diabet Med. 2002; 19:377–384.
Article5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Lower extremity disease among persons aged > or =40 with and without diabetes--United States, 1999-2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2005; 54:1158–1160.6. Lauterbach S, Kostev K, Kohlmann T. Prevalence of diabetic foot syndrome and its risk factors in the UK. J Wound Care. 2010; 19:333–337.
Article7. Singh N, Armstrong DG, Lipsky BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA. 2005; 293:217–228.
Article8. Zhang P, Lu J, Jing Y, Tang S, Zhu D, Bi Y. Global epidemiology of diabetic foot ulceration: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Med. 2017; 49:106–116.
Article9. Ahn KJ. Epidemiology of diabetic foot disease. J Korean Diabetes. 2011; 12:72–75.
Article10. Lee MK, Chung MH, Won AO, Kim SY, Lee HK, Min HK. A clinical observation on the diabetic foot lesions. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1984; 8:55–65.11. Kwon YJ, Han KA, Seo SG, You HJ. A clinical study on the diabetic foot lesions. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1989; 13:39–45.12. Chung CH, Kim DJ, Kim J, Kim H, Kim H, Min KW, Park SW, Park JH, Baik SH, Son HS, Ahn CW, Oh JY, Lee S, Lee J, Choi KM, Choi I, Park IB. Current status of diabetic foot in Korean patients using National Health Insurance database. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2006; 30:372–376.
Article13. Rhee SY, Chon S, Kwon MK, Park IeB, Ahn KJ, Kim IJ, Kim SH, Lee HW, Koh KS, Kim DM, Baik SH, Lee KW, Nam MS, Park YS, Woo JT, Kim YS. Prevalence of chronic complications in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on the Korean National Diabetes Program. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:504–512.
Article14. Bakker K, Apelqvist J, Schaper NC. International Working Group on Diabetic Foot Editorial Board. Practical guidelines on the management and prevention of the diabetic foot 2011. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012; 28:Suppl 1. 225–231.
Article15. Cha HJ. Foot care for diabetic patients. J Korean Diabetes. 2018; 19:41–45.
Article16. American Diabetes Association. 10. Microvascular complications and foot care: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:Suppl 1. S105–S118.18. Mishra SC, Chhatbar KC, Kashikar A, Mehndiratta A. Diabetic foot. BMJ. 2017; 359:j5064.
Article19. Hingorani A, LaMuraglia GM, Henke P, Meissner MH, Loretz L, Zinszer KM, Driver VR, Frykberg R, Carman TL, Marston W, Mills JL Sr, Murad MH. The management of diabetic foot: a clinical practice guideline by the Society for Vascular Surgery in collaboration with the American Podiatric Medical Association and the Society for Vascular Medicine. J Vasc Surg. 2016; 63:2 Suppl. 3S–21S.
Article20. Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes. 5th ed. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2013. p. 66–68.21. Bonner T, Foster M, Spears-Lanoix E. Type 2 diabetesrelated foot care knowledge and foot self-care practice interventions in the United States: a systematic review of the literature. Diabet Foot Ankle. 2016; 7:29758.
Article22. Rizzo L, Tedeschi A, Fallani E, Coppelli A, Vallini V, Iacopi E, Piaggesi A. Custom-made orthesis and shoes in a structured follow-up program reduces the incidence of neuropathic ulcers in high-risk diabetic foot patients. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2012; 11:59–64.
Article23. Lipsky BA, Berendt AR, Cornia PB, Pile JC, Peters EJ, Armstrong DG, Deery HG, Embil JM, Joseph WS, Karchmer AW, Pinzur MS, Senneville E. Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 54:e132–e173.
Article24. Boulton AJM, Cavanagh PR, Rayman G. The description and classification of diabetic foot lesions: systems for clinical care, for research and for audit. In : Boulton AJM, Cavanagh PR, Rayman G, editors. The foot in diabetes. 4th ed. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons;2006. p. 92–107.25. Doupis J, Veves A. Classification, diagnosis, and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Wounds. 2008; 20:117–126.26. Lee DY, Kim IY. Surgical treatment of diabetic foot disease. J Korean Diabetes. 2011; 12:88–94.
Article27. Task Force Team for Basic Statistical Study of Korean Diabetes Mellitus of Korean Diabetes Association. Park IeB, Kim J, Kim DJ, Chung CH, Oh JY, Park SW, Lee J, Choi KM, Min KW, Park JH, Son HS, Ahn CW, Kim H, Lee S, Lee IB, Choi I, Baik SH. Diabetes epidemics in Korea: reappraise nationwide survey of diabetes “diabetes in Korea 2007”. Diabetes Metab J. 2013; 37:233–239.
Article