Korean J Urol.
2007 Aug;48(8):815-825. 10.4111/kju.2007.48.8.815.
The Effect of Ring-type NF-kappa B(NF-kB) Decoy Oligodeoxynucleotide on the Kidney for an Experimental Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction in Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Daegu Catholic University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jspark@cu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Daegu Catholic University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2061275
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2007.48.8.815
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The transcription factor, NF-kB, is important in the coordinated expressions of various pro-inflammatory and adhesion molecules. Our hypothesis is that inhibiting the action of NF-kB using a synthetic decoy oligodeoxynucleotide(ODN) can block the underlying inflammatory response in glomerulonephritis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
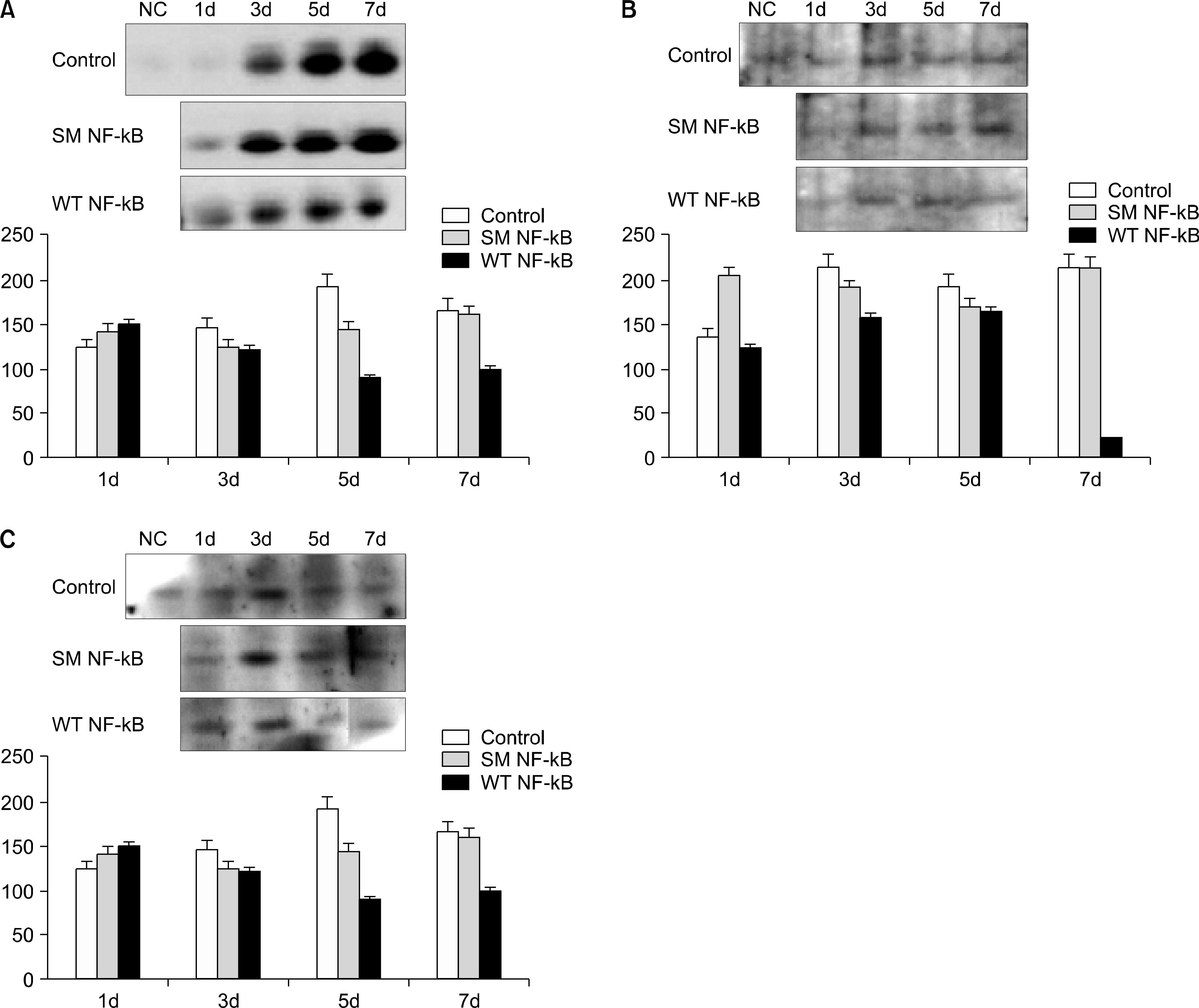
Forty two male C57BL6 mice, weighting 25g, were divided into four groups; in group 1, 2 mice were used as normal controls; in group 2, a unilateral ureteral obstruction(UUO) was induced in 12 mice; in group 3, 20 UUO mice were treated using ring-type NK-kB decoy ODN; and in group 4, 8 UUO mice were treated using scramble type NF-kB decoy ODN. The mice were killed 1, 3, 5 and 7 days after the NF-kB decoy ODN injections, and the blood urea nitrogen(BUN), and expressions of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-beta(IL-beta), fibronectin, vascular cell adhesion molecule(VCAM) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1(MCP-1), as well as the histopathological findings, analyzed in each group.
RESULTS
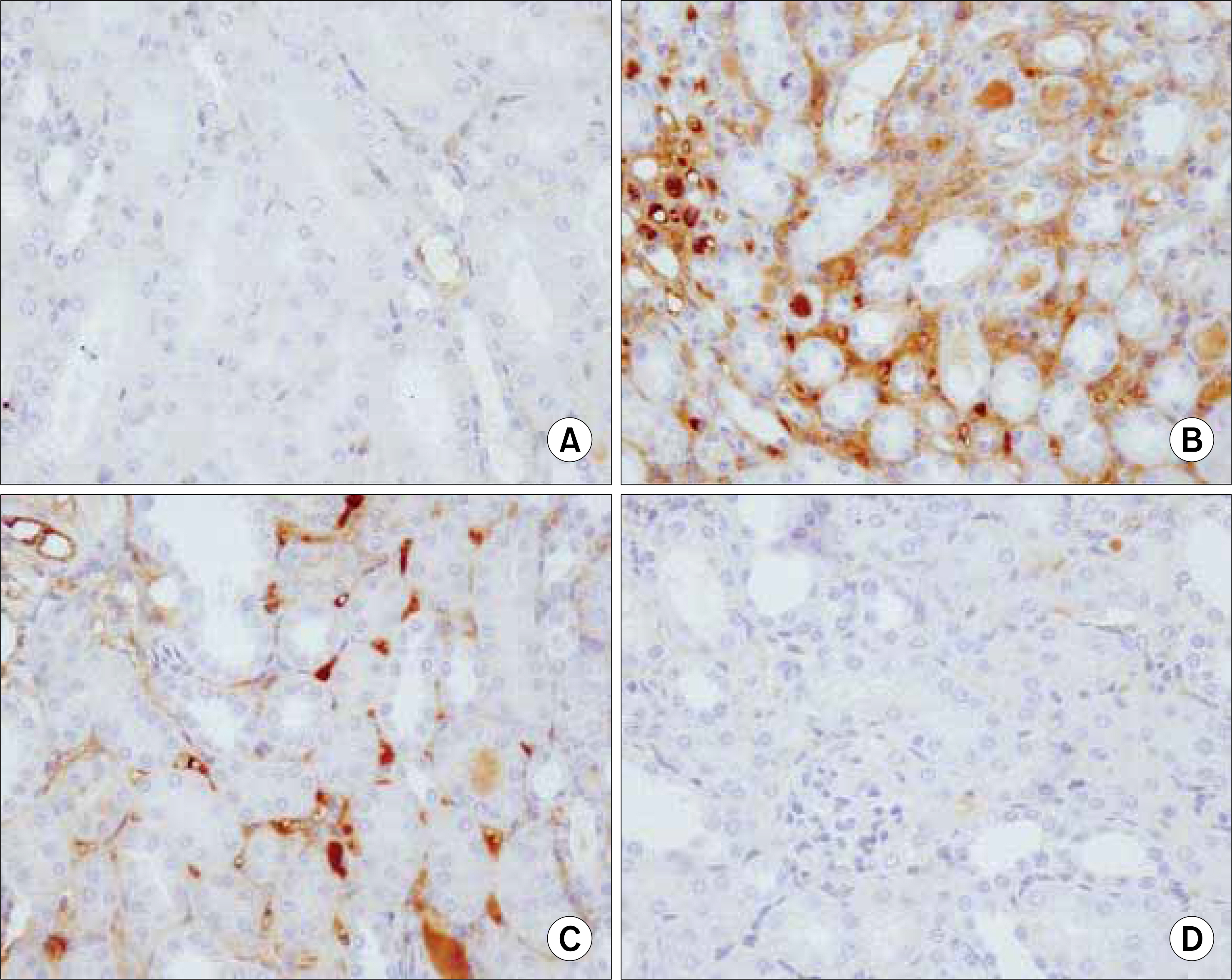
The serum levels of BUN, TNF-alpha, IL-beta, fibronectin, VCAM and MCP-1 were increased in group 2, but decreased in group 3. The histopathological findings of the kidneys in group 3 were most similar to those found in the control(group 1).
CONCLUSIONS
NF-kB decoy ODN treatment substantially inhibited the disease, with reductions in the histological damage and the renal expressions of inflammatory cytokines.
MeSH Terms
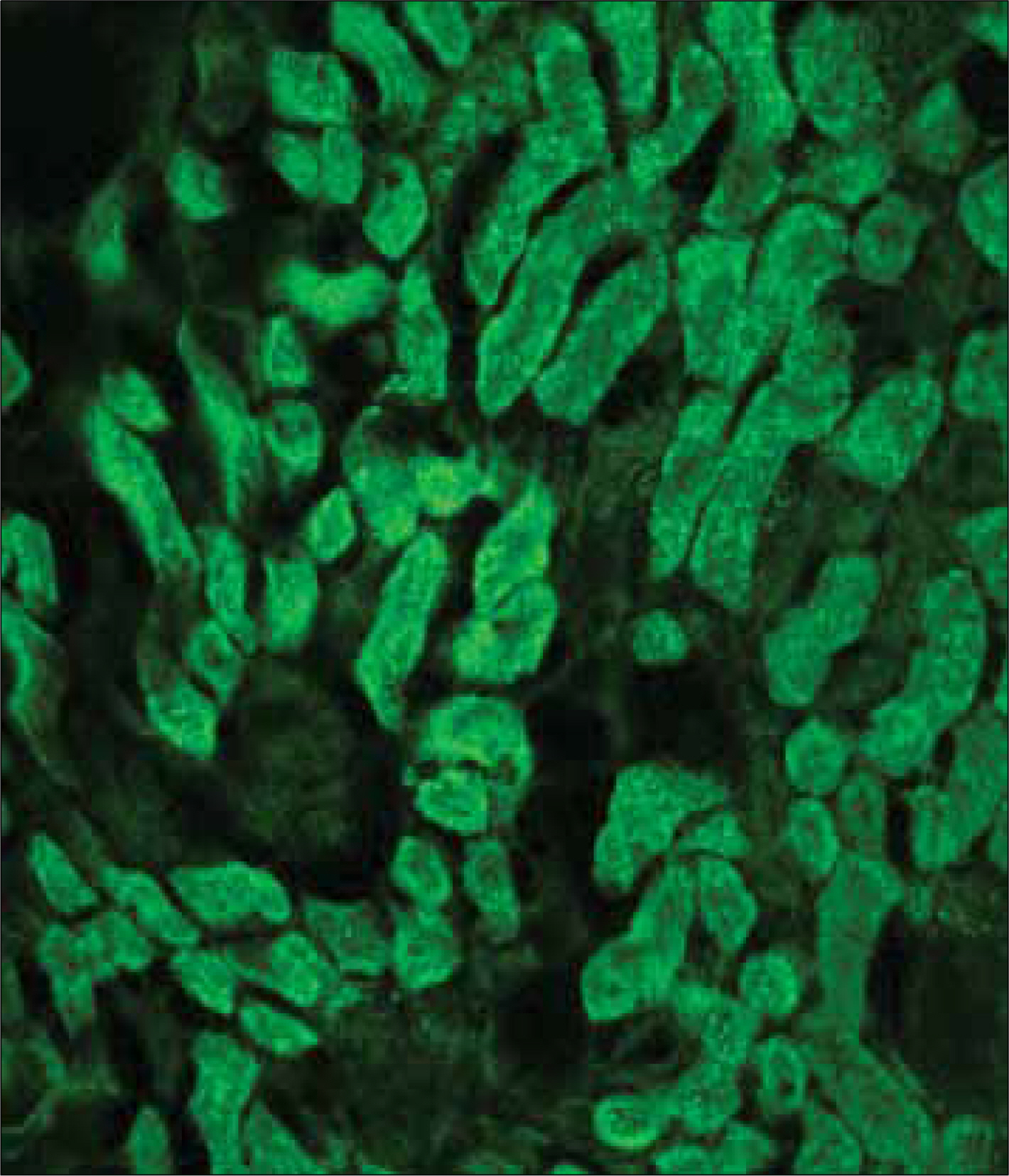
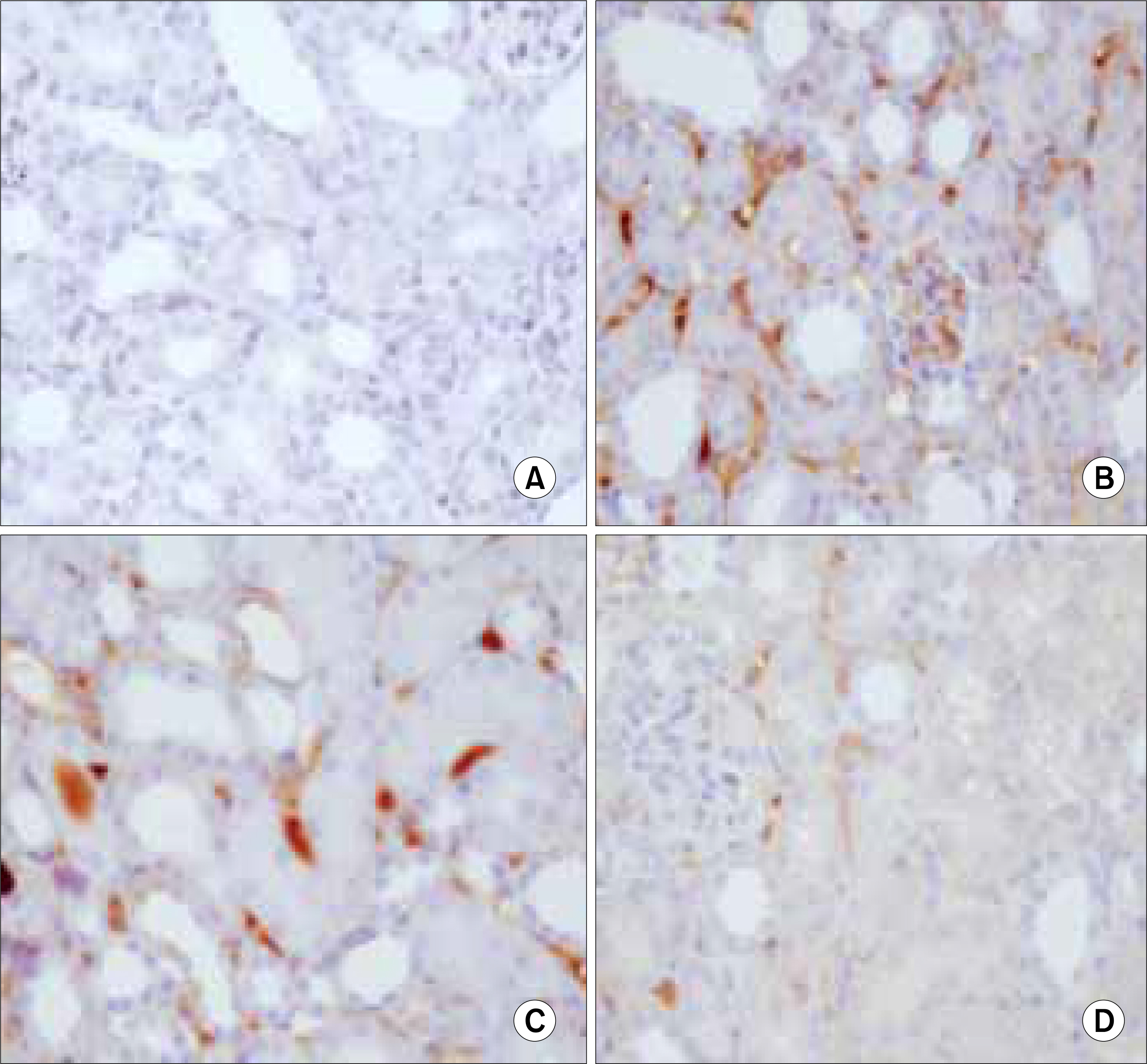
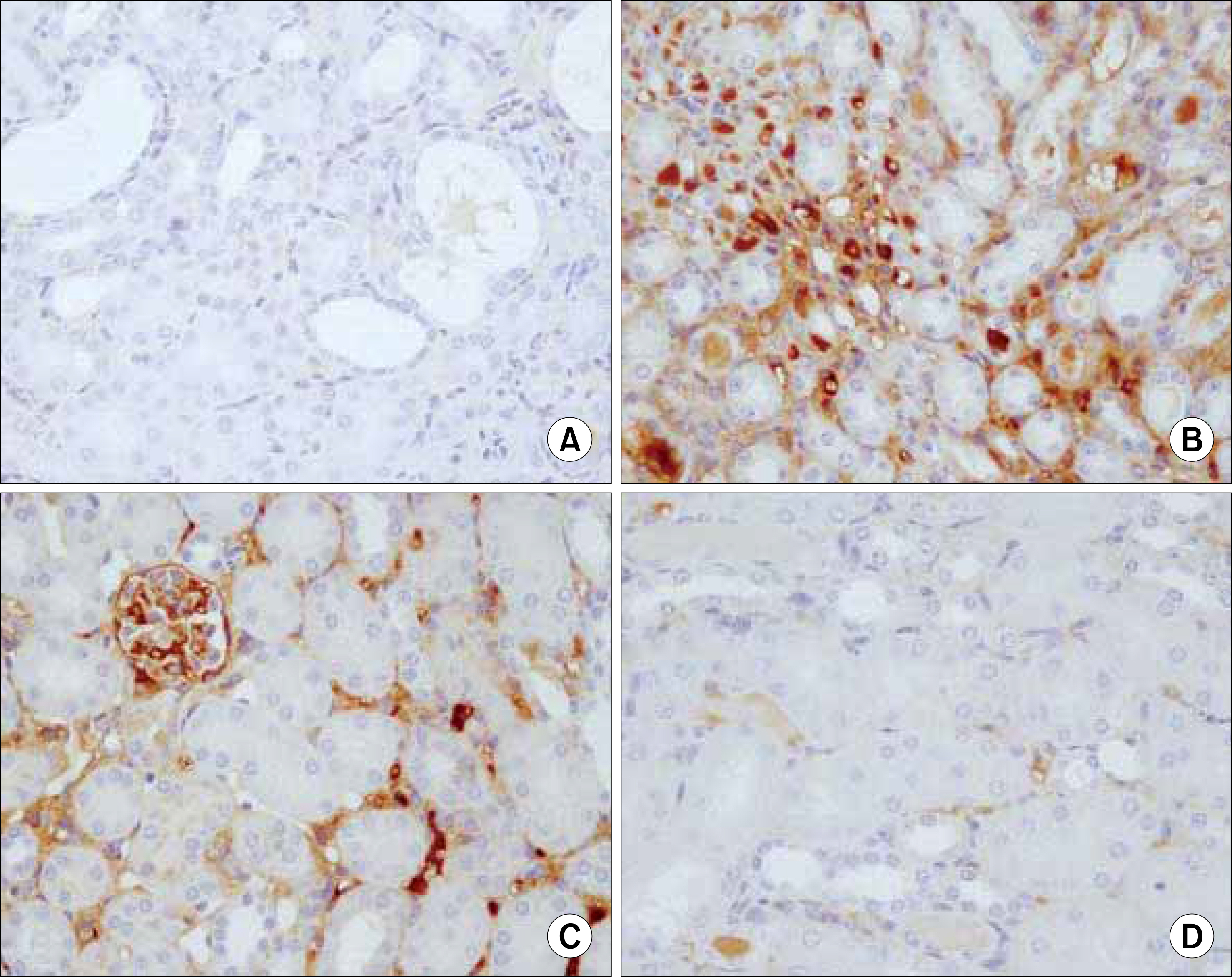
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cao CC, Ding XQ, Ou ZL, Liu CF, Li P, Wang L, et al. In vivo transfection of NF-kappaB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides attenuate renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Kidney Int. 2004; 65:834–45.2. Guijarro C, Egido J. Transcription factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B) and renal disease. Kidney Int. 2001; 59:415–24.3. Lee JI, Burckart GJ. Nuclear factor kappa (B) important transcription factor and therapeutic target. J Clin Pharmacol. 1998; 38:981–93.
Article4. Morrissey J, Klahr S. Transcription factor NF-kappaB regulation of renal fibrosis during ureteral obstruction. Semin Nephrol. 1998; 18:603–11.5. Park DM, Sohn DG, Han KH, Lee SY, Chae YM, Chang YC, et al. The effect of the transcriptional regulation of Sp1 for TGF-beta1 and CTGF expression in scar formation. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 33:39–45.6. Mann MJ, Dzau VJ. Therapeutic applications of transcription factor decoy oligonucleotides. J Clin Invest. 2000; 106:1071–5.
Article7. Kim HG, Kwak C, Kim HH, Paick SH, Lho YS, Lee JW, et al. The serial microscopic changes of cell proliferative and apoptotic phenomenon in obstructed ureters in the rat. Korean J Urol. 2005; 46:495–501.8. Isaka Y, Tsujie M, Ando Y, Nakamura H, Kaneda Y, Imai E, et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 antisense oligodeoxynucleotides block interstitial fibrosis in unilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int. 2000; 58:1885–92.
Article9. Eddy AA. Experimental insights into the tubulointerstitial disease accompanying primary glomerular lesions. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1994; 5:1273–87.
Article10. Akira M, Takeo K, Kaori S, Tomohiko A, Kazuo U, Masa-michi H. Novel nuclear factor kB activation inhibitor prevents inflammatory injury in unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Urol. 2003; 169:1559–63.11. Auphan N, DiDonato JA, Rosette C, Helmberg A, Karin M. Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-kappa B activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis. Science. 1995; 270:286.12. Yamamoto Y, Gaynor RB. Therapeutic potential of inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway in the treatment of inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107:135.13. Yamashita J, Yoshimasa T, Arai H, Hiraoka J, Tayaya K, Miyamoto Y, et al. Identification of cis-elements of the human endothelin-A receptor gene and inhibition of the gene expression by the decoy strategy. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:15993–9.
Article14. Suzuki J, Morishita R, Amano J, Kaneda Y, Isobe M. Decoy against nuclear factor-kappa B attenuates myocardial cell infiltration and arterial neointimal formation in murine cardiac allografts. Gene Ther. 2000; 7:1847–52.
Article15. Verrecchia F, Rossert J, Mauviel A. Blocking sp1 transcription factor broadly inhibits extracellular matrix gene expression in vitro and in vivo: implications for the treatment of tissue fibrosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2001; 116:755–63.
Article16. Chae YM, Park KK, Lee IK, Kim JK, Kim CH, Chang YC. Ring-Sp1 decoy oligonucleotide effectively suppresses extracellular matrix gene expression and fibrosis of rat kidney induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. Gene Ther. 2006; 13:430–9.
Article17. Ahn JD, Morishita R, Kaneda Y, Kim HJ, Kim YD, Lee HJ, et al. Transcription factor decoy for AP-1 reduces mesangial cell proliferation and extracellular matrix production in vitro and in vivo. Gene Ther. 2004; 11:916–23.
Article18. Chae YM, Park KK, Magae J, Lee IS, Kim CH, Kim HC, et al. Sp1-decoy oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits high glucose-induced mesangial cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 319:550–5.
Article19. Bielinska A, Shivdasani RA, Zhang LQ, Nabel GJ. Regulation of gene expression with double-stranded phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Science. 1990; 250:997–1000.
Article20. Morishita R, Gibbons GH, Horiuchi M, Ellison KE, Nakama M, Zhang L, et al. A gene therapy strategy using a transcription factor decoy of the E2F binding site inhibits smooth muscle proliferation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1995; 92:5855–9.
Article21. Gaubatz S, Wood JG, Livingston DM. Unusual proliferation arrest and transcriptional control properties of a newly discovered E2F family member, E2F–6. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1998; 95:9190–5.
Article22. Cho-Chung YS, Park YG, Nesterova M, Lee YN, Cho YS. CRE-decoy oligonucleotide-inhibition of gene expression and tumor growth. Mol Cell Biochem. 2000; 212:29–34.
Article23. Ishibashi H, Nakagawa K, Onimaru M, Castellanous EJ, Kaneda Y, Nakashima Y, et al. Sp1 decoy transfected to carcinoma cells suppresses the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, transforming growth factor beta1, and tissue factor and also cell growth and invasion activities. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:6531–6.24. Kawauchi M, Suzuki J, Morishita R, Wada Y, Izawa A, Tomita N, et al. Gene therapy for attenuating cardiac allograft arteriopathy using ex vivo E2F decoy transfection by HVJ-AVE-liposome method in mice and nonhuman primates. Circ Res. 2000; 87:1063–8.
Article25. Khaled AR, Butfiloski EJ, Sobel ES, Schiffenbauer J. Use of phosphorothioate-modified oligodeoxynucleotides to inhibit NF-kB expression and lymphocyte function. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1998; 86:170–9.26. Tomita N, Morishita R, Tomita S, Kaneda Y, Higaki J, Ogihara T, et al. Inhibition of TNF-α, induced cytokine and adhesion molecule. Expression in glomerular cells in vitro and in vivo by transcription factor decoy for NF-kB. Exp Nephrol. 2001; 9:181–90.27. Tomita N, Morishita R, Tomita S, Gibbons GH, Zhang L, Horiuchi M, et al. Transcription factor decoy for NF-kB inhibits TNF-α-induced cytokine and adhesion molecule expression in vivo. Gene Ther. 2000; 7:1326–32.28. Blaese RM, Culver KW, Miller AD, Carter CS, Fleisher T, Clerici M, et al. T lymphocyte-directed gene therapy for ADA-SCID: initial trial results after 4 years. Science. 1995; 270:475–80.29. Imai E, Akagi Y, Isaka Y. Towards gene therapy for renal diseases. Nephrologie. 1998; 19:397–402.30. Imai E, Isaka Y, Akagi Y, Kaneda Y. Gene transfer into the glomerulus by the hemagglutinating virus of Japan-liposome method. Exp Nephrol. 1997; 5:112–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intra-peritoneal NF-kappaB decoy oligodeoxynucleotide decreases postoperative intra-abdominal adhesion
- Inhibition of Allergic Response by Intranasal Selective NF-κB Decoy Oligodeoxynucleotides in a Murine Model of Allergic Rhinitis
- The Effects of Nuclear Factor-kappa B Decoy Oligodeoxynucleotide on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Direct Acute Lung Injury
- NF-kappa B decoy potentiates the effects of radiation on vascular smooth muscle cells by enhancing apoptosis
- Identification of a Variant Form of Cellular Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (c-IAP2) That Contains a Disrupted Ring Domain