J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2004 Sep;29(5):470-478. 10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.470.
MMP-1 and TIMP-1 production in MG-63 cells stimulated with Prevotella nigrescens lipopolysaccharide
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Korea. hhson@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Conservative Dentistry, Asan Medical Center, Korea.
- KMID: 1987127
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.5.470
Abstract
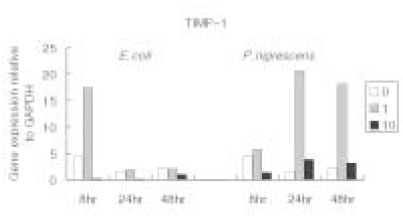
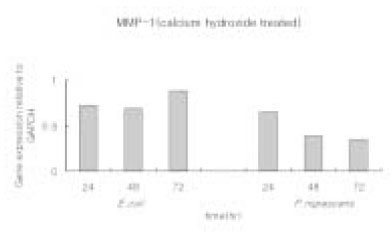
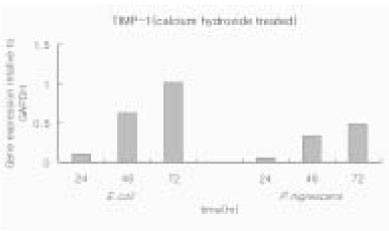
- The purpose of this study is to monitor the secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) produced by human osteosarcoma cell line (MG63) stimulated with Prevotella nigrescens lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and to compare the level of secretion before and after the treatment of calcium hydroxide on P. nigrescens LPS. LPS was extracted and purified from anaerobically cultured P. nigrescens. MG63 cells were stimulated by the LPS (0, 1, 10 microg/ml) or LPS (10 microg/ml) pretreated with 12.5 mg/ml of Ca(OH)2 for 3 days. Total RNA was isolated from the cell, and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed for quantification of MMP-1 and TIMP-1. The results were as follows. 1. MMP-1 mRNA expression at 48 hr was highly increased by stimulation with P. nigrescens LPS. The increase was dose-dependent. 2. When stimulated with 1 microg/ml of LPS, TIMP-1 mRNA expression was highly increased at 24 hr and 48 hr. However, TIMP-1 expression was suppressed at higher concentration (10 microg/ml). 3. When P. nigrescens LPS was pretreated with Ca(OH)2, MMP-1 and TIMP-1 gene expression was downregulated. The results of this study suggest that transcriptional regulation of MMP-1 and TIMP-1 by P. nigrescens LPS could be one of the important mechanisms in bone resorption of periapical inflammation. The result of calcium hydroxide on MMP-1 and TIMP-1 gene expression suppression shows that calcium hydroxide detoxified bacterial LPS and thus should be used the medication of choice for intracanal dressings in root canal infected with black-pigmented bacteria.
MeSH Terms
-
Bacteria
Bandages
Bone Resorption
Calcium Hydroxide
Cell Line
Dental Pulp Cavity
Gene Expression
Humans
Inflammation
Lipopolysaccharides
Matrix Metalloproteinase 1
Osteosarcoma
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Prevotella nigrescens*
Prevotella*
RNA
RNA, Messenger
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1*
Calcium Hydroxide
Lipopolysaccharides
Matrix Metalloproteinase 1
RNA
RNA, Messenger
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1
Figure
Reference
-
1. Trowbridge HO. Immunological aspects of chronic inflammation and repair. J Endod. 1990. 16:54–61.
Article2. Yang YY, Tsai HF, Lu SC, Huang YF, Chang YC. Regulation of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 gene expression by cytokines in human gingival fiboblasts. J Endod. 2002. 28:803–805.
Article3. Overall CM, Sodek J. Initial characterization of a neutral metalloproteinase, active of native 3/4 collagen fragments, synthesized by ROS 17/2.8 osteoblastic cells, periodontal fibroblasts, and Identified in gingival crevicular fluid. J Dent Res. 1987. 66:1271–1282.
Article4. Chang YC, Lai CC, Yang SF, Chan Y, Hsieh YS. Stimulation of matrix metalloproteinases by black-pigmented bacteroides in human pulp and periodontal ligament cell cultures. J Endod. 2002. 28:90–93.
Article5. Van der Zee E, Jansen I, Hoeben K, Beertsen W, Everts V. EGF and IL-1α modulate the release of collagenase, gelatinase and TIMP-1 as well as the release of calcium by rabbit calvarial bone explants. J Periodontal Res. 1998. 33:65–72.
Article6. Cury JD, Campbell EJ, Lazarus CJ, Albin RJ, Welgus HG. Selective up-regulation of human alveolar macrophage collagenase production by lipopolysaccharide and comparison to collagenase production by fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1988. 141:4306–4312.7. Séguier S, Gogly B, Bodineau A, Godeau G, Brousse N. Is collagen breakdown during periodontitis linked to inflammatory cells and expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human gingival tissue? J Periodontol. 2001. 72:1398–1406.
Article8. Lin SK, Chiang CP, Hong CY, Lin CP, Lan WH, Hsieh CC, Kuo MYP. Immunolocalization of interstitial collagenase(MMP-1) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1(TIMP-1) in radicular cysts. J Oral Pathol Med. 1997. 26:458–463.
Article9. Everts V, Hoegen K, Beertsen W. The release of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases by calvarial bone explants and its immunolicalizaiton. Bone Miner. 1993. 22:43–55.
Article10. Hill PA, Reynolds JJ, Meikle MC. Inhibition of stimulated bone resorption in vitro by TIMP-1 and TIMP-2. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1993. 1177:71–74.
Article11. Hosoya S, Matsushima K. Stimulation of interleukin-1β production of human dental pulp cells by Porphylomonas endodontalis lipopolysaccharides. J Endod. 1997. 23:39–42.
Article12. Koga T, Nishihara T, Fujiwara T, Nisizawa T, Okahashi N, Noguchi T, Hamada S. Biochemical and immunological properties of lipopolysaccharide(LPS) from Bacteroides gingivalis and comparison with LPS from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985. 47:638–647.
Article13. Safavi KE, Nichols FC. Alteration of biological properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide by calcium hydroxide treatment. J Endod. 1994. 20:127–129.
Article14. Safavi KE, Nichols FC. Effects of calcium hydroxide on bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Endod. 1993. 19:76–78.15. Baumgartner JC, Watkins BJ, Bae KS, Xia T. Association of black-pigmented bacteria with endodontic infections. J Endod. 1999. 25:413–415.
Article16. Gharbia SE, Haapasalo M, Shah H, et al. Characterization of Prevotella intermedia and Prevotella nigrescens isolates from periodontic and endodontic origin. J Periodontol. 1994. 65:56–61.
Article17. Bae KS, Baumgartner JC, Shearer TR, David LL. Occurrence of Prevotella nigrescens and Prevotella intermedia in infections of endodontic origin. J Endod. 1997. 23:620–623.
Article18. Eidhin DN, Mouton C. A rapid method for preparation of rough and smooth lipopolysaccharides from Bacteroides, Porphylomonas and Prevotella. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993. 110:133–138.19. Birkedal-Hansen H, Moore WBI, Bodden MK, Winsor LJ, Brikedal-Hansen B, DeCarlo A, Engler JA. Matrix metalloproteinases: A review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1993. 4:197–250.
Article20. Alvares O, Klebe R, Grant G, Cochran DL. Growth factor effects on the expression of collagenase and TIMP-1 in periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontol. 1995. 66:552–558.
Article21. Bolcato-Bellemin AL, Elkaim R, Abehsera A, Fausser JL, Haikel Y, Tenenbaum H. Expression of mRNAs encoding for α and β integrin subunit, MMPs, and TIMPs in stretched human periodontal ligament and gingival fibroblast. J Dent Res. 2000. 79:1712–1716.
Article22. Nakaya H, Osawa G, Iwasaki N, Cochran DL, Kamoi K, Oates TW. Effects of bisphophonate enzymes in human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontol. 2000. 71:1158–1166.23. Otsuka K, Sodek J, Limeback H. Synthesis of collagenase and collagenase inhibitors by osteoblast-like cells in culture. Eur J Biochem. 1984. 145:123–129.
Article24. Rifas L, Halstead LR, Peck WA. Human osteoblasts in vitro secrete tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and gelatinase but not interstitial collagenase as major cellular products. J Clin Invest. 1989. 84:686–694.
Article25. de Bart AC, Quax PHA, Lowik CWGM, Verheijen . Regulation of plasminogen activation, matrix metalloproteinases and urokinase-type plasminogen activator-mediated extracellular matrix degradation in human osteosarcoma cell line MG63 by interleukin-1 alpha. J Bone Miner Res. 1995. 10:1374–1384.
Article26. Panagakos FS, Kumar S. Modulation of proteases by extracellular matrix and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Inflammation. 1995. 19:423–443.27. Lin SK, Wang CC, Huang S, Lee JJ, Chiang CP, Lan WH, Hong CY. Induction of dental pulp fibroblast matrix metalloproteinase-1 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 gene expression by interleukin-1α and tumor necrosis factor-α through a prostaglandin-dependent pathway. J Endod. 2001. 27:185–189.
Article28. Nakata K, Yamasaki M, Iwata T, Suzuki K, Nakane A, Nakamura H. Anaerobic bacterial extracts influence production of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors by human dental pulp cells. J Endod. 2000. 26:410–413.
Article29. Shin SJ, Lee JI, Baek SH, Lim SS. Tissue levels of matrix metalloproteinases in pulps and periapical lesions. J Endod. 2002. 28:313–315.
Article30. Douglas DA, Shi YE, Sang QA. Computational sequence analysis of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase family. J Protein Chem. 1997. 16:237–255.31. Dean DD, Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP, Howell DS, Woessner JF Jr. Evidence for metalloproteinase and metalloproteinase inhibitor imbalance in human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1989. 84:678–685.
Article32. Johansen JS, Williamson MK, Rice JS, Price PA. Identification of proteins secreted by human osteoblastic cells in culture. J Bone Miner Res. 1992. 7:501–512.
Article33. Uchida M, Shima M, Shimoaka T, Fujieda A, Obara K, Suzuki H, Nagai Y, Ikeda T, Yamato H, Kawaguchi H. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases(MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) by bone resorptive factors in osteoblastic cells. J Cell Physiol. 2000. 185:207–214.
Article34. Wahl LM, Olsen SE, Sandberg AL, Mergenhagen SE. Prostaglandin regulation of macrophage collagenase production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1977. 74:4955–4958.
Article35. Buck RA, Cai J, Eleazer PD, Staat RH, Hurst HE. Detoxification of endotoxin by endodontic irrigants and calcium hydroxide. J Endod. 2001. 27:325–327.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- MMP and TIMP production in periodontal ligament fibroblasts stimulated by Prevotella nigrescens lipopolysaccharide
- Interleukin-8 production and interleukin-8 mRNA expression induced by lipopolysaccharides from Prevotella intermedia and Prevotella nigrescens in monocyte-derived macrophages
- Chemical and Immunobiological Characterization of Lipopolysaccharides from Prevotella intermedia and Prevotella nigrescens
- Expression of mRNA for matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human gingival and periodontal ligament fibroblasts treated with lipopolysaccharide from Prevotella intermedia
- Cytotoxic effects of prevotella nigrescens on cultured cells