J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Feb;25(2):211-219. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.211.
In vivo Tracking of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Labeled with a Novel Chitosan-coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles using 3.0T MRI
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kwakbk@cau.ac.kr
- 2Cell and Tissue Engineering Products Team, Korea Food and Drug Administration, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Minerals & Materials Processing Division, Nano-Materials Group, Korea Institute of Geoscience, Daejeon, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779249
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.211
Abstract
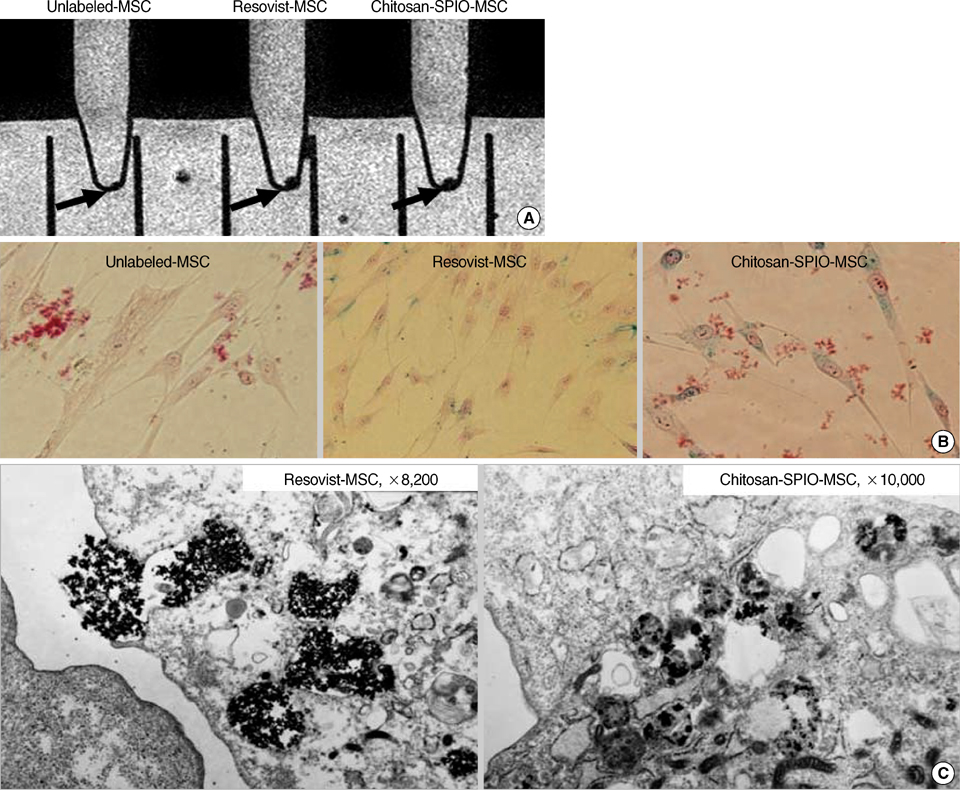
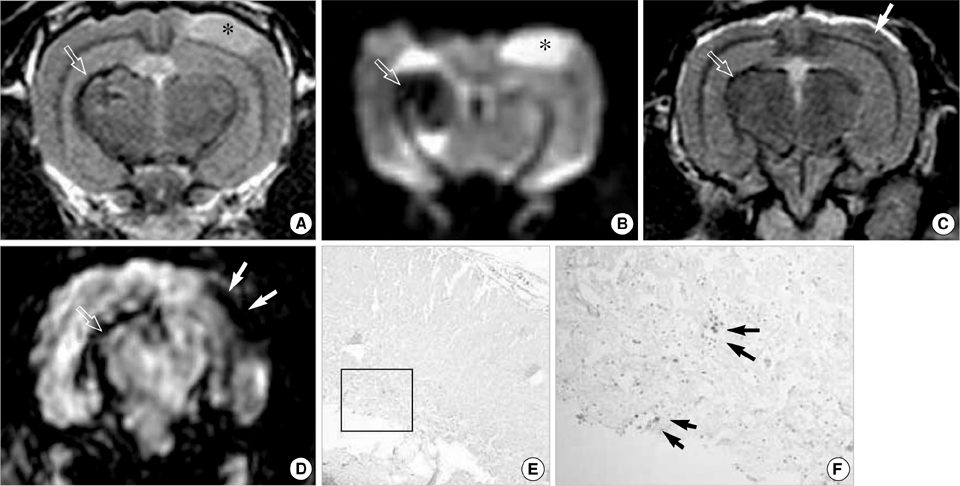
- This study aimed to characterize and MRI track the mesenchymal stem cells labeled with chitosan-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide (Chitosan-SPIO). Chitosan-SPIO was synthesized from a mixture of FeCl2 and FeCl3. The human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells (hBM-MSC) were labeled with 50 microg Fe/mL chitosan-SPIO and Resovist. The labeling efficiency was assessed by iron content, Prussian blue staining, electron microscopy and in vitro MR imaging. The labeled cells were also analyzed for cytotoxicity, phenotype and differentiation potential. Electron microscopic observations and Prussian blue staining revealed 100% of cells were labeled with iron particles. MR imaging was able to detect the labeled MSC successfully. Chitosan-SPIO did not show any cytotoxicity up to 200 microgram Fe/mL concentration. The labeled stem cells did not exhibit any significant alterations in the surface markers expression or adipo/osteo/chondrogenic differentiation potential when compared to unlabeled control cells. After contralateral injection into rabbit ischemic brain, the iron labeled stem cells were tracked by periodical in vivo MR images. The migration of cells was also confirmed by histological studies. The novel chitosan-SPIO enables to label and track MSC for in vivo MRI without cellular alteration.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Brain Ischemia/chemically induced/pathology/therapy
Cell Differentiation
Chitosan/*chemistry
Coordination Complexes/*chemistry/toxicity
Ferric Compounds/*chemistry
Humans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetics
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells/*chemistry/cytology
Metal Nanoparticles/*chemistry
Phenotype
Rabbits
Coordination Complexes
Ferric Compounds
Chitosan
Figure
Reference
-
1. Deans RJ, Moseley AB. Mesenchymal stem cells: biology and potential clinical uses. Exp Hematol. 2000. 28:875–884.2. Stauer BE, Kornowski R. Stem cell therapy in perspective. Circulation. 2003. 107:929–934.
Article3. Berry CC, Wells S, Charles S, Curtis AS. Dextran and albumin derivatised iron oxide nanoparticles: influence on fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials. 2003. 24:4551–4557.
Article4. Harris LA, Goff JD, Carmichael AY, Riffle JS, Harburn JJ, St Pierre TG, Saunders M. Magnetic nanoparticle dispersions stabilized with triblock copolymers. Chem Mater. 2003. 15:1367–1377.5. Kim EH, Lee HS, Kwak BK, Kim BK. Synthesis of ferrofluid with magnetic nanoparticles by sonochemical method for MRI contrast agent. J Magn Magn Mater. 2005. 289:328–330.6. Lee HS, Shao H, Huang Y, Kwak BK. Synthesis of MRI contrast agent by coating superparamagnetic iron oxide with chitosan. IEEE Trans Magn. 2005. 41:4102–4104.7. Sinha VR, Singla AK, Wadhawan S, Kaushik R, Kumaria R, Bansal K, Dhawan S. Chitosan microspheres as a potential carrier for drugs. Int J Pharm. 2004. 274:1–33.
Article8. Wang YX, Hussain SM, Krestin GP. Superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agents: physicochemical characteristics and applications in MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2001. 11:2319–2331.
Article9. Cheng SL, Yang JW, Rifas L, Zhang SF, Avioli LV. Differentiation of human bone marrow osteogenic stromal cells in vitro: induction of the osteoblast phenotype by dexamethasone. Endocrinology. 1994. 134:277–286.
Article10. Mackay AM, Beck SC, Murphy JM, Barry FP, Chichester CO, Pittenger MF. Chondrogenic differentiation of cultured human mesenchymal stem cells from marrow. Tissue Eng. 1998. 4:415–428.
Article11. Bowen CV, Zhang X, Saab G, Gareau PJ, Rutt BK. Application of the static dephasing regime theory to superparamagnetic iron-oxide loaded cells. Magn Reson Med. 2002. 48:52–61.
Article12. Arbab AS, Bashaw LA, Miller BR, Jordan EK, Lewis BK, Kalish H, Frank JA. Characterization of biophysical and metabolic properties of cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and transfection agent for cellular MR imaging. Radiology. 2003. 229:838–846.
Article13. Arbab AS, Yocum GT, Kalish H, Jordan EK, Anderson SA, Khakoo AY, Read EJ, Frank JA. Efficient magnetic cell labeling with protamine sulfate complexed to ferumoxides for cellular MRI. Blood. 2004. 104:1217–1223.
Article14. Ittrich H, Lange C, Tögel F, Zander AR, Dahnke H, Westenfelder C, Adam G, Nolte-Ernsting C. In vivo magnetic resonance imaging of iron oxide labeled arterially injected mesenchymal stem cells in kidney of rats with acute ischemic kidney injury: detection and monitoring at 3T. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007. 25:1179–1191.15. Kostura L, Kraitchman DL, Mackay AM, Pittenger MF, Bulte JW. Feridex labeling of mesenchymal stem cells inhibits chondrogenesis but not adipogenesis or osteogenesis. NMR Biomed. 2004. 17:513–517.
Article16. Bulte JW, Kratchman DL, Mackay AM, Pittenger MF. Chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells is inhibited after magnetic labeling with ferumoxides. Blood. 2004. 104:3410–3413.
Article17. Arbab AS, Yocum GT, Rad AM, Khakoo AY, Fellowes V, Read EJ, Frank JA. Labeling of cells with ferumoxides. Protamine sulfate complexes does not inhibit function or differentiation capacity of hematopoitic or mesenchymal stem cells. NMR Biomed. 2005. 18:553–559.18. Taguchi A, Soma T, Tanaka H, Kanda T, Nishimura H, Yoshikawa H, Tsukamoto Y, Iso H, Fujimori Y, Stern DM, Naritomi H, Matsuyama T. Administration of CD34+ cells after stroke enhances neurogenesis via angiogenesis in a mouse model. J Clin Invest. 2004. 114:330–338.19. Werner N, Junk S, Laufs U, Link A, Walenta K, Bohm M, Nickenig G. Intravenous transfusion of endothelial progenitor cells reduces neointima formation after vascular injury. Circ Res. 2003. 93:e17–e24.
Article20. Newcomb CD, Ajmo CT Jr, Sanberg CD, Sanberg PR, Pennypacker KR, Willing AE. Timing of cord blood treatment after experimental stroke determines therapeutic efficacy. Cell Transplant. 2006. 15:213–223.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Engraftment of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide-Labeled Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Photothrombotic Cerebral Infarction Models of Rats
- Comparison of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Labeling Efficiency between Poly-L-Lysine and Protamine Sulfate for Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Quantitative Analysis Using Multi-Echo T2* Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Evaluation of Optimal Combination of Commercially Available Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Transfection Agents for Labelling of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Labeling Efficacy of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles to Human Neural Stem Cells: Comparison of Ferumoxides, Monocrystalline Iron Oxide, Cross-linked Iron Oxide (CLIO)-NH2 and tat-CLIO
- New Frontiers in Molecular Imaging with Superparamagnetic IronOxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs): Efficacy, Toxicity, and FutureApplications