Korean J Radiol.
2007 Oct;8(5):365-371. 10.3348/kjr.2007.8.5.365.
Labeling Efficacy of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles to Human Neural Stem Cells: Comparison of Ferumoxides, Monocrystalline Iron Oxide, Cross-linked Iron Oxide (CLIO)-NH2 and tat-CLIO
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Clinical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. moonwk@radcom.snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, and the Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Applied Chemistry, Sejong University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1734284
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2007.8.5.365
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
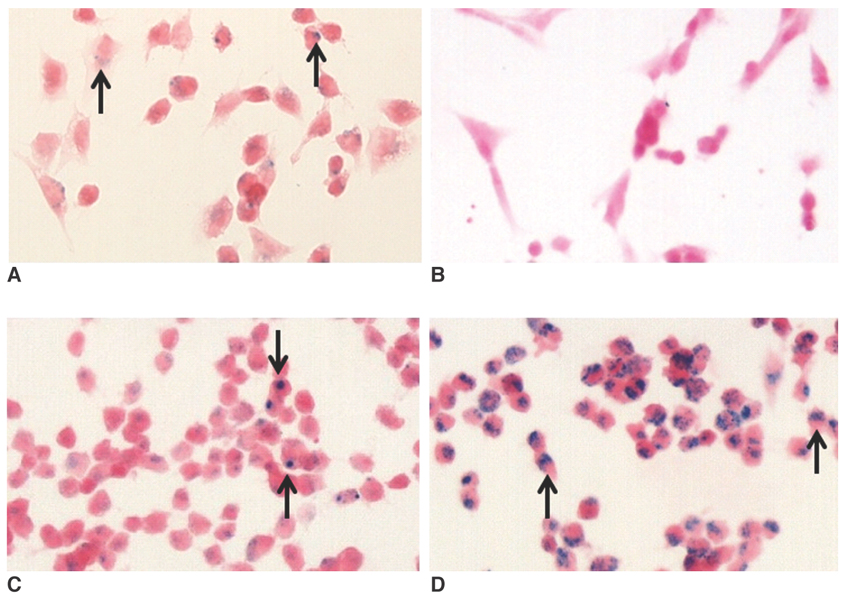
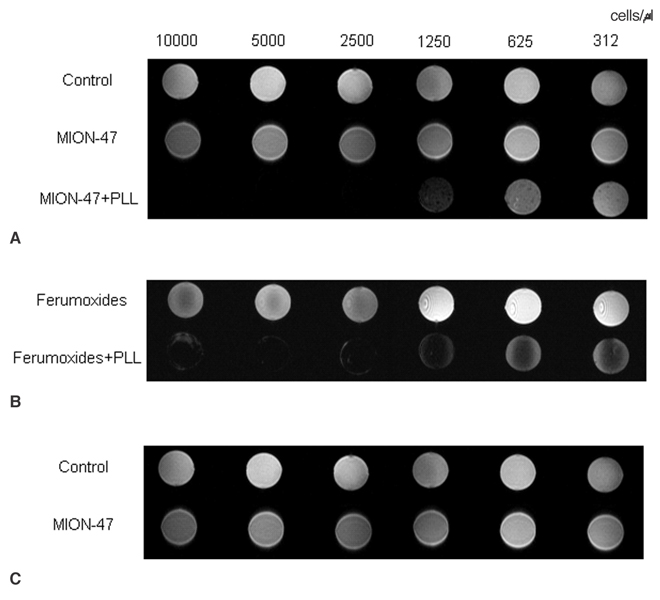
We wanted to compare the human neural stem cell (hNSC) labeling efficacy of different superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs), namely, ferumoxides, monocrystalline iron oxide (MION), cross-linked iron oxide (CLIO)-NH2 and tat-CLIO. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The hNSCs (5x105 HB1F3 cells/ml) were incubated for 24 hr in cell culture media that contained 25 microgram/ml of ferumoxides, MION or CLIO-NH2, and with or without poly-L-lysine (PLL) and tat-CLIO. The cellular iron uptake was analyzed qualitatively with using a light microscope and this was quantified via atomic absorption spectrophotometry. The visibility of the labeled cells was assessed with MR imaging. RESULTS: The incorporation of SPIONs into the hNSCs did not affect the cellular proliferations and viabilities. The hNSCs labeled with tat-CLIO showed the longest retention, up to 72 hr, and they contained 2.15+/-0.3 pg iron/cell, which are 59 fold, 430 fold and six fold more incorporated iron than that of the hNSCs labeled with ferumoxides, MION or CLIO-NH2, respectively. However, when PLL was added, the incorporation of ferumoxides, MION or CLIO-NH2 into the hNSCs was comparable to that of tat-CLIO. CONCLUSION: For MR imaging, hNSCs can be efficiently labeled with tat-CLIO alone or with a combination of ferumoxides, MION, CLIO-NH2 and the transfection agent PLL.
MeSH Terms
-
Cells, Cultured
Contrast Media/chemical synthesis/pharmacokinetics
Cross-Linking Reagents/chemistry
Ferric Compounds/chemistry/*pharmacokinetics
Ferrosoferric Oxide/chemical synthesis/pharmacokinetics
Gene Products, tat/chemistry
Humans
Iron/*pharmacokinetics
Magnetic Resonance Imaging/methods
Nanoparticles
Neural Tube
Oxides/*pharmacokinetics
Phantoms, Imaging
Polylysine/pharmacokinetics
Spectrophotometry, Atomic
Staining and Labeling/*methods
Stem Cells/cytology/*drug effects/metabolism
Time Factors
Transfection
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim SU. Human neural stem cells genetically modified for brain repair in neurological disorders. Neuropathology. 2004. 24:159–171.2. Lindvall O, Kokaia Z, Martinez-Serrano A. Stem cell therapy for human neurodegenerative disorders-how to make it work. Nat Med. 2004. 10:S42–S50.3. Bulte JW, Duncan ID, Frank JA. In vivo magnetic resonance tracking of magnetically labeled cells after transplantation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002. 22:899–907.4. Wang YX, Hussain SM, Krestin GP. Superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agents: physicochemical characteristics and applications in MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2001. 11:2319–2331.5. Jendelová P, Herynek V, Urdziková L, Glogarová K, Kroupová J, Andersson B, et al. Magnetic resonance tracking of transplanted bone marrow and embryonic stem cells labeled by iron oxide nanoparticles in rat brain and spinal cord. J Neurosci Res. 2004. 76:232–243.6. Daldrup-Link HE, Rudelius MR, Piontek G, Metz S, Brauer R, Debus G, et al. Migration of iron oxide-labeled human hematopoietic progenitor cells in a mouse model: in vivo monitoring with 1.5-T MR imaging equipment. Radiology. 2005. 234:197–205.7. Wunderbaldinger P, Josephson L, Weissleder R. Crosslinked Iron Oxides (CLIO): a new platform for the development of targeted MR contrast agents. Acad Radiol. 2002. 9:S304–S306.8. Kukowska-Latallo JF, Bielinska AU, Johnson J, Spindler R, Tomalia DA, Baker JR Jr. Efficient transfer of genetic material into mammalian cells using starburst polyamidoamine dendrimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996. 93:4897–4902.9. Tang MX, Redemann CT, Szoka FC Jr. In vitro gene delivery by degraded polyamidoamine dendrimers. Bioconjug Chem. 1996. 7:703–714.10. Plank C, Mechtler K, Szoka FC Jr, Wagner E. Activation of the complement system by synthetic DNA complexes: a potential barrier for intravenous gene delivery. Human Gene Ther. 1996. 7:1437–1446.11. DeLong R, Stephenson K, Loftus T, Fisher M, Alahari S, Nolting A, et al. Characterization of complexes of oligonucleotides with polyamidoamine starburst dendrimers and effects on intracellular delivery. J Pharm Sci. 1997. 86:762–764.12. Josephson L, Tung CH, Moore A, Weissleder R. High-efficiency intracellular magnetic labeling with novel superparamagnetic-tat peptide conjugate. Bioconjug Chem. 1999. 10:186–191.13. Lewin M, Carlesso N, Tung CH, Tang XW, Cory D, Scadden DT, et al. Tat peptide-derivatized magnetic nanoparticles allow in vivo tracking and recovery of progenitor cells. Nature Biotechnol. 2000. 18:410–414.14. Zhao M, Kircher MF, Josephson L, Weissleder R. Differential conjugation of tat peptide to superparamagnetic nanoparticles and its effect on cellular uptake. Bioconjug Chem. 2002. 13:840–844.15. Frankel AD, Pabo CO. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988. 55:1189–1193.16. Arbab AS, Yocum GT, Wilson LB, Parwana A, Jordan EK, Kalish H, et al. Comparison of transfection agents in forming complexes with ferumoxides, cell labeling efficiency, and cellular viability. Mol Imaging. 2004. 3:24–32.17. Arbab AS, Bashaw LA, Miller BR, Jordan EK, Lewis BK, Kalish H, et al. Characterization of biophysical and metabolic properties of cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and transfection agent for cellular MR imaging. Radiology. 2003. 229:838–846.18. Matuszewski L, Persigehl T, Wall A, Schwindt W, Tombach B, Fobker M, et al. Cell tagging with clinically approved iron oxides: feasibility and effect of lipofection, particle size, and surface coating on labeling efficiency. Radiology. 2005. 235:155–161.19. Montet-Abou K, Montet X, Weissleder R, Josephson L. Transfection agent induced nanoparticle cell loading. Mol Imaging. 2005. 4:165–171.20. Wunderbaldinger P, Josephson L, Weissleder R. Tat peptide directs enhanced clearance and hepatic permeability of magnetic nanoparticles. Bioconjug Chem. 2002. 13:264–268.21. Weissleder R, Cheng HC, Bogdanova A, Bogdanova A Jr. Magnetically labeled cells can be detected by MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1997. 7:258–263.22. Frank JA, Miller BR, Arbab AS, Zywicke HA, Jordan EK, Lewis BK, et al. Clinically applicable labeling of mammalian and stem cells by combining superparamagnetic iron oxides and transfection agents. Radiology. 2003. 228:480–487.23. Bulte JW, Kraitchman DL, Mackay AM, Pittenger MF. Chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells is inhibited after magnetic labeling of with ferumoxides. Blood. 2004. 104:3410–3412.24. Arbab AS, Yocum GT, Rad AM, Khakoo AY, Fellowes V, Read EJ, et al. Labeling of cells with ferumoxides-protamine sulfate complexes does not inhibit function or differentiation capacity of hematopoietic or mesenchymal stem cells. NMR Biomed. 2005. 18:553–559.25. Zhu DC, Penn RD. Full-brain T1 mapping through inversion recovery fast spin echo imaging with time-efficient slice ordering. Magn Reson Med. 2005. 54:725–731.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Optimal Combination of Commercially Available Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Transfection Agents for Labelling of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Application of Iron Oxide as a pH-dependent Indicator for Improving the Nutritional Quality
- Evaluation of thermally cross-linked superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the changes of concentration and toxicity on tissues of Sprague-Dawley rats
- Comparison of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Labeling Efficiency between Poly-L-Lysine and Protamine Sulfate for Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Quantitative Analysis Using Multi-Echo T2* Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Distribution and accumulation of 177Lu-labeled thermally cross-linked superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in the tissues of ICR mice