J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Apr;23(2):302-306. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.2.302.
Expression of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Calcium-Induced Keratinocyte Differentiation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. parkjk@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Traditional Medicine and Bioscience, Daejeon University, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 1713465
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.2.302
Abstract
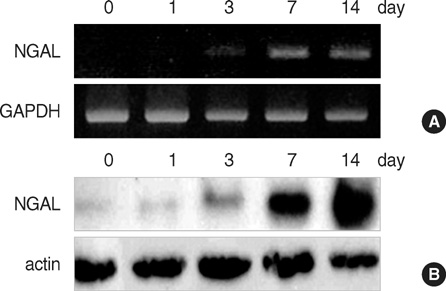
- In a previous search for the differentially expressed genes in keratinocyte differentiation, we identified neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a calcium- induced gene. In this study, we further verified the expression of NGAL in cultured keratinocytes as well as in several skin diseases. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), Western blot, and ELISA clearly showed that NGAL expression was markedly increased in calcium-induced keratinocyte differentiation in vitro. However, in our previous report, NGAL expression was not detected in normal skin tissue except for hair follicle by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry, indicating the difference of cell status between in vitro and in vitro conditions. Interestingly, NGAL expression was highly increased in psoriasis-like inflammatory disorders (lichen planus and pityriasis rubura pilaris) and skin cancers (keratoacanthoma and squamous cell carcinoma), implying that NGAL may be related with the epidermal hyperplasia. Collectively, these results reveal the potential importance of NGAL in the maintenance of skin homeostasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acute-Phase Proteins/*biosynthesis
Calcium/*metabolism
Cell Differentiation
Culture Media
Culture Media, Conditioned
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
*Gene Expression Regulation
Homeostasis
Humans
Keratinocytes/enzymology
Lipocalins/*biosynthesis
Models, Biological
Proto-Oncogene Proteins/*biosynthesis
Psoriasis/enzymology
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
Skin/*metabolism
Skin Neoplasms/enzymology
Figure
Reference
-
1. Flower DR. The lipocalin protein family: structure and function. Biochem J. 1996. 318:1–14.
Article2. Goetz DH, Willie ST, Armen RS, Bratt T, Borregaard N, Strong RK. Ligand preference inferred from the structure of neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin. Biochemistry. 2000. 39:1935–1941.
Article3. Flower DR. The lipocalin protein family: a role in cell regulation. FEBS Lett. 1994. 354:7–11.
Article4. Bratt T. Lipocalins and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. 1482:318–326.
Article5. Xu S, Venge P. Lipocalins as biochemical markers of disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. 1482:298–307.
Article6. Kjeldsen L, Johnsen AH, Sengelov H, Borregaard N. Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem. 1993. 268:10425–10432.
Article7. Bundgaard JR, Sengelov H, Borregaard N, Kjeldsen L. Molecular cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding NGAL: a lipocalin expressed in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994. 202:1468–1475.
Article8. Yan L, Borregaard N, Kjeldsen L, Moses MA. The high molecular weight urinary matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity is a complex of gelatinase B/MMP-9 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL). Modulation of MMP-9 activity by NGAL. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:37258–37265.9. Kjeldsen L, Bainton DF, Sengelov H, Borregaard N. Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel matrix protein of specific granules in human neutrophils. Blood. 1994. 83:799–807.
Article10. Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S, Rodriguez DJ, Holmes MA, Strong RK, Akira S, Aderem A. Lipocalin 2 mediates an innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating iron. Nature. 2004. 432:917–921.
Article11. Yang J, Goetz D, Li JY, Wang W, Mori K, Setlik D, Du T, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Strong R, Barasch J. An iron delivery pathway mediated by a lipocalin. Mol Cell. 2002. 10:1045–1056.
Article12. Yuspa SH, Kilkenny AE, Steinert PM, Roop DR. Expression of murine epidermal differentiation markers is tightly regulated by restricted extracellular calcium concentrations in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1989. 109:1207–1217.
Article13. Fuchs E. Epidermal differentiation and keratin gene expression. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993. 17:197–208.
Article14. Kalinin AE, Kajava AV, Steinert PM. Epithelial barrier function: assembly and structural features of the cornified cell envelope. Bioessays. 2002. 24:789–800.
Article15. Seo EY, Lee WH, Piao YJ, Kim KH, Lee KM, Ahn KS, Yang JM, Seo YJ, Kim CD, Park JK, Lee JH. Identification of calcium-inducible genes in primary keratinocytes using suppression-subtractive hybridization. Exp Dermatol. 2004. 13:163–169.
Article16. Kjeldsen L, Koch C, Arnljots K, Borregaard N. Characterization of two ELISAs for NGAL, a newly described lipocalin in human neutrophils. J Immunol Methods. 1996. 198:155–164.
Article17. Mallbris L, O'Brien KP, Hulthen A, Sandstedt B, Cowland JB, Borregaard N, Ståhle-Bäckdahl M. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a marker for dysregulated keratinocyte differentiation in human skin. Exp Dermatol. 2002. 11:584–591.
Article18. Friedl A, Stoesz SP, Buckley P, Gould MN. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Cell type-specific pattern of expression. Histochem J. 1999. 31:433–441.19. Seo SJ, Ahn JY, Hong CK, Seo EY, Kye KC, Lee WH, Lee SK, Lim JS, Hahn MJ, Kjeldsen L, Borregaard N, Kim CD, Park JK, Lee JH. Expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in skin epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 2006. 126:510–512.
Article20. Cowland JB, Borregaard N. Molecular characterization and pattern of tissue expression of the gene for neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin from humans. Genomics. 1997. 45:17–23.
Article21. Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, Mori K, Barasch J, Devarajan P. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet. 2005. 365:1231–1238.
Article22. van Renswoude J, Bridges KR, Harford JB, Klausner RD. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and the uptake of Fe in K562 cells: identification of a nonlysosomal acidic compartment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982. 79:6186–6190.
Article23. Kennedy ML, Douglas GC, King BF. Expression of transferrin receptors during differentiation of human placental trophoblast cells in vitro. Placenta. 1992. 13:43–53.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepcidin and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as a Biomarker for Acute Kidney Injury Linked Iron Metabolism
- The Role of Nkx2.5 in Keratinocyte Differentiation
- Plasma Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin and Leukocyte Differential Count in Children with Febrile Urinary Tract Infection
- Single Low-Dose Radiation Induced Regulation of Keratinocyte Differentiation in Calcium-Induced HaCaT Cells
- Expression Profiling of Calcium Induced Genes in Cultured Human Keratinocytes