Cancer Res Treat.
2005 Apr;37(2):122-128.
A Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Trichostatin A, Enhances Radiosensitivity by Abrogating G2/M Arrest in Human Carcinoma Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ihkim@snu.ac.kr
- 2Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 5Department of Radiation Oncology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiation Oncology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 7Department of Radiation Oncology, Konkuk University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Radiation Oncology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
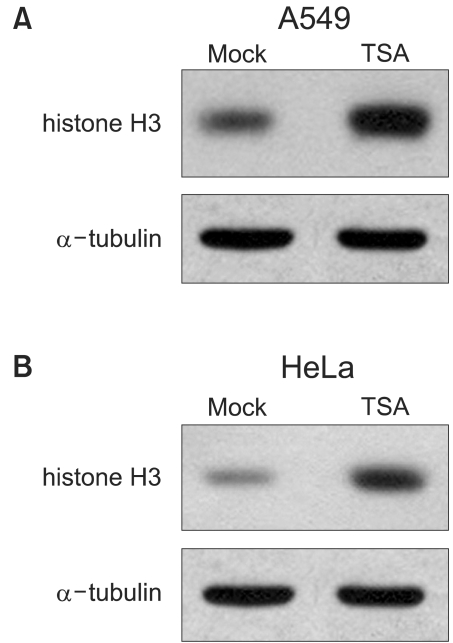
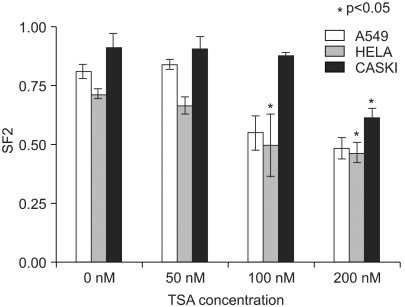
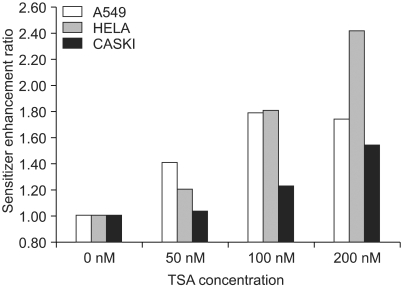
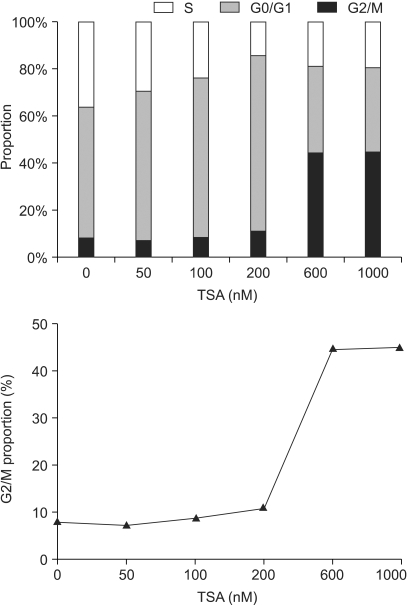
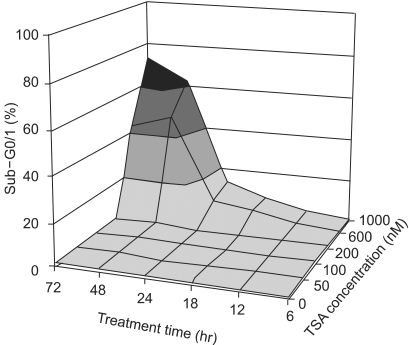
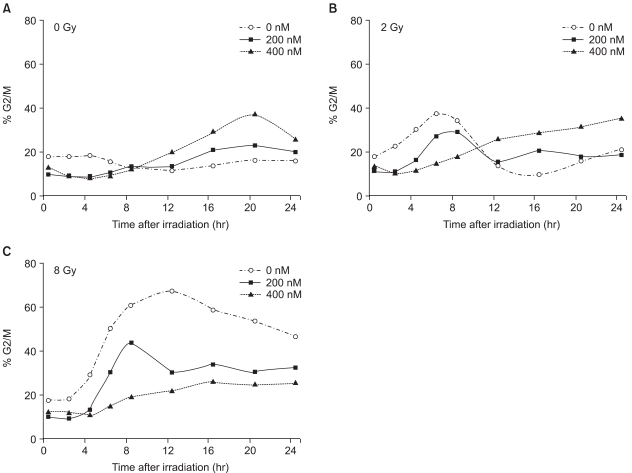
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDIs) are emerging as potentially useful components in anticancer therapy. In this study, we tried to confirm the radiosensitizing effect of trichostatin A (TSA) on a panel of human carcinoma cell lines and elucidate its mechanism of interaction. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A549, HeLa and Caski cells were exposed to TSA for 18 hr prior to irradiation, and the cell survival then measured using a clonogenic assay. Western blot and flow cytometric analyses, for histone acetylation, and cell cycle and apoptosis, respectively, were also performed. RESULTS: TSA increased the acetylation of histone H3. The pretreatment of TSA consistently radiosensitized all three cell lines. The SF2 (surviving fraction at 2 Gy) of TSA-treated cells was significantly lower than that of mock treated cells. The SER (sensitizer enhancement ratio) increased in all 3 cell lines, in concentration dependent manners. The TSA treated cells showed abrogation of radiation-induced G2/M arrest, in a concentration dependent manner. CONCLUSION: The pretreatment of TSA enhanced the radiosensitivity of a panel of human carcinoma cells, which was attributed, in part, to the abrogation of radiationinduced G2/M arrest.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yoshida M, Furumai R, Nishiyama M, Komatsu Y, Nishino N, Horinouchi S, et al. Histone deacetylase as a new target for cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001; 48(Suppl. 1):S20–S26. PMID: 11587361.
Article2. Grunstein M. Histone acetylation and chromatin structure and transcription. Nature. 1997; 389:349–352. PMID: 9311776.3. Marks PA, Richon VM, Rifkind RA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: inducers of differentiation or apoptosis of transformed cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; 92:1210–1216. PMID: 10922406.
Article4. Juan LJ, Shia WJ, Chen MH, Yang WM, Seto E, Lin YS, et al. Histone deacetylase specifically down-regulate p53-dependent gene activation. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:20436–20443. PMID: 10777477.5. Luo J, Su F, Chen D, Shiloh A, Gu W. Deacetylation of p53 modulates its effect on cell growth and apoptosis. Nature. 2000; 408:377–381. PMID: 11099047.
Article6. Verdin E, Dequiedt F, Kasler HG. Class II histone deacetylases: versatile regulators. Trends Genet. 2003; 19:286–293. PMID: 12711221.
Article7. de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN, Kemp S, van Kuilenburg AB. Histone deacetylase (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J. 2003; 370:737–749. PMID: 12429021.8. Kim TY, Bang YJ. Development of new anti-cancer agents targeting histone deacetylase. Cancer Res Treat. 2002; 34(Suppl. 2):9S–16S.9. Gilbert J, Baker SD, Bowling MK, Grochow L, Figg WD, Zabelina Y, et al. A phase I dose escalation and bioavailability study of oral sodium phenylbutyrate in patients with refractory solid tumor malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2001; 7:2292–2300. PMID: 11489804.10. Marshall JL, Rizvi N, Kauh J, Dahut W, Figuera M, Kang MH, et al. A phase I trial of depsipeptide (FR901228) in patients with advanced cancer. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2002; 2:325–332. PMID: 12440223.
Article11. Sandor V, Bakke S, Robey RW, Kang MH, Blagosklonny MV, Bender J, et al. Phase I trial of the histone deacetylase inhibitor, depsipeptide (FR901228, NSC 630176), in patients with refractory neoplasms. Clin Cancer Res. 2002; 8:718–728. PMID: 11895901.12. Arundel C, Glicksman A, Leith J. Enhancement of radiation injury in human colon tumor cells by the maturational agent sodium butyrate (NaB). Radiat Res. 1985; 104:443–448. PMID: 4080986.
Article13. Chung YL, Lee YH, Yen SH, Chi KH. A novel approach for nasopharyngeal carcinoma treatment uses phenylbutyrate as a protein kinase C modulators: implications for radiosensitization and EBV-targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2000; 6:1452–1458. PMID: 10778977.14. Biade S, Stobbe CC, Boyd JT, Chapman JD. Chemical agents that promote chromatin compaction radiosensitize tumour cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 2001; 77:1033–1042. PMID: 11682008.
Article15. Camphausen K, Burgan W, Cerra M, Oswald KA, Trepel JB, Lee MJ, et al. Enhanced radiation-induced cell killing and prolongation of γH2AX foci expression by the histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:316–321. PMID: 14729640.
Article16. Zhang Y, Adachi M, Zhao X, Kawamura R, Imai K. Histone deacetylase inhibitors FK228, N-(2-aminophenyl)-4-[N-(pyridin-3-yl-methoxycarbonyl)amino-methyl]benzamide and m-carboxycinnamic acid bis-hydroxamide augment radiation-induced cell death in gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2004; 110:301–308. PMID: 15069698.17. Kim JH, Shin JH, Kim IH. Susceptibility and radiosensitization of human glioblastoma cells to trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004; 59:1174–1180. PMID: 15234053.
Article18. Furumai R, Komatsu Y, Nishino N, Khochbin S, Yoshida , Horinouchi S. Potent histone deacetylase inhibitors built from trichostatin A and cyclic tetrapeptide antibiotics including trapoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001; 98:87–92. PMID: 11134513.
Article19. McBain JA, Eastman A, Nobel CS, Mueller GC. Apoptotic death in adenocarcinoma cell lines induced by butyrate and other histone deacetylase inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997; 53:1357–1368. PMID: 9214697.
Article20. Iliakis G, Wang Y, Guan J, Wang H. DNA damage checkpoint control in cells exposed to ionizing radiation. Oncogene. 2003; 22:5834–5847. PMID: 12947390.
Article21. Su LN, Little JB. Prolonged cell cycle delay in radioresistant human cell lines transfected with activated ras oncogene and/or simian virus 40T-antigen. Radiat Res. 1993; 133:73–79. PMID: 8434116.22. Kim GD, Choi YH, Dimtchev A, Jeong SJ, Dritschilo A, Jung M. Sensing of ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage by ATM through interaction with histone deacetylase. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:31127–31130. PMID: 10531300.
Article23. Kao GD, McKenna WG, Guenther MG, Muschel RJ, Lazar MA, Yen TJ. Histone deacetylase 4 interacts with 53BP1 to mediate the DNA damage response. J Cell Biol. 2003; 160:1017–1027. PMID: 12668657.
Article24. Van Lint C, Emiliani S, Verdn E. The expression of small fraction of cellular genes is changed in response to histone hyperacetylation. Gene Expr. 1996; 5:245–253. PMID: 8723390.25. Butler LM, Webb Y, Agus D, Higgins B, Tolentino TR, Kutko MC, et al. Inhibition of transformed cell growth and induction of cellular differentiation by pyroxamide: an inhibitor of histone deacetylase. Clin Cancer Res. 2001; 7:962–970. PMID: 11309347.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sequence-Dependent Radiosensitization of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Trichostatin A and SK-7041
- Apoptotic Effect of Combination Treatment with a Proteasome Inhibitor, Lactacystin, and a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Trichostatin A, on MCF-7 Cells
- Trichostatin A, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Potentiated Cytotoxic Effect of Ionizing Radiation in Human Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines
- Activation of ATM-dependent DNA Damage Signal Pathway by a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Trichostatin A
- Role of histone deacetylase activity in the developing lateral line neuromast of zebrafish larvae