Korean J Hematol.
2008 Mar;43(1):9-18. 10.5045/kjh.2008.43.1.9.
Significance of Notch Expression in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. minbrmmd@yuhs.ac
- 2Brain Korea 21 Research Team of Nanomaterials for the Cell-Based Implants, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1485152
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2008.43.1.9
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Notch is a gene family encoding receptors to transduce intercellular signals involved in cell-fate determination. Although several lines of evidence indicate that abnormal Notch signaling may contribute to neoplastic transformation, little is known regarding the role of Notch in the pathogenesis of leukemia.
METHODS
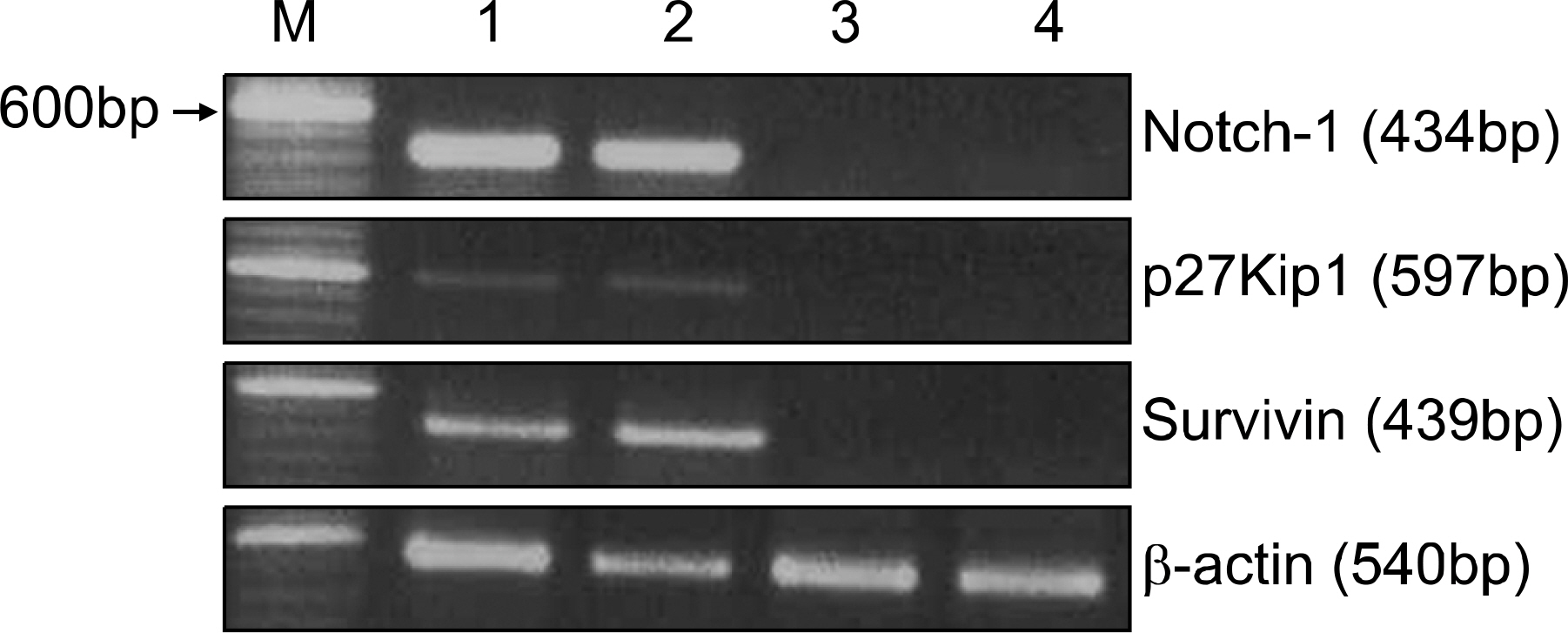
To explore the functional significance of Notch1 in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the expression of Notch1 and its association with survivin and p27Kip1 expression was examined in 50 patients with de novo AML.
RESULTS
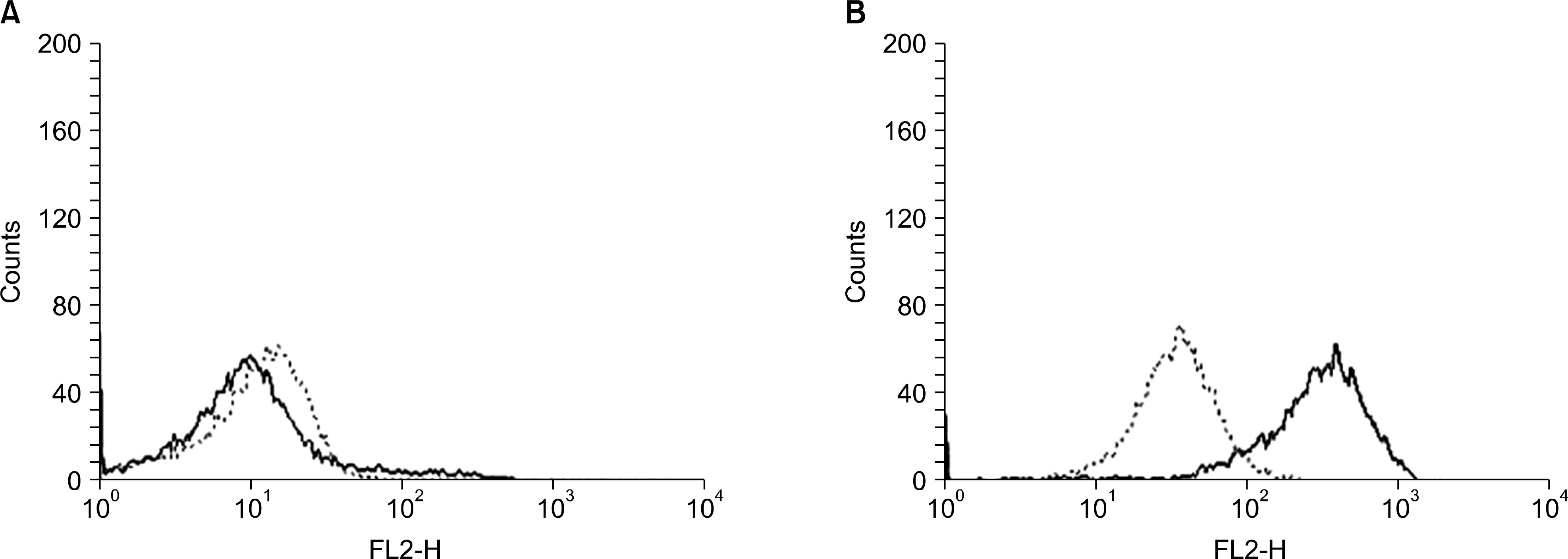
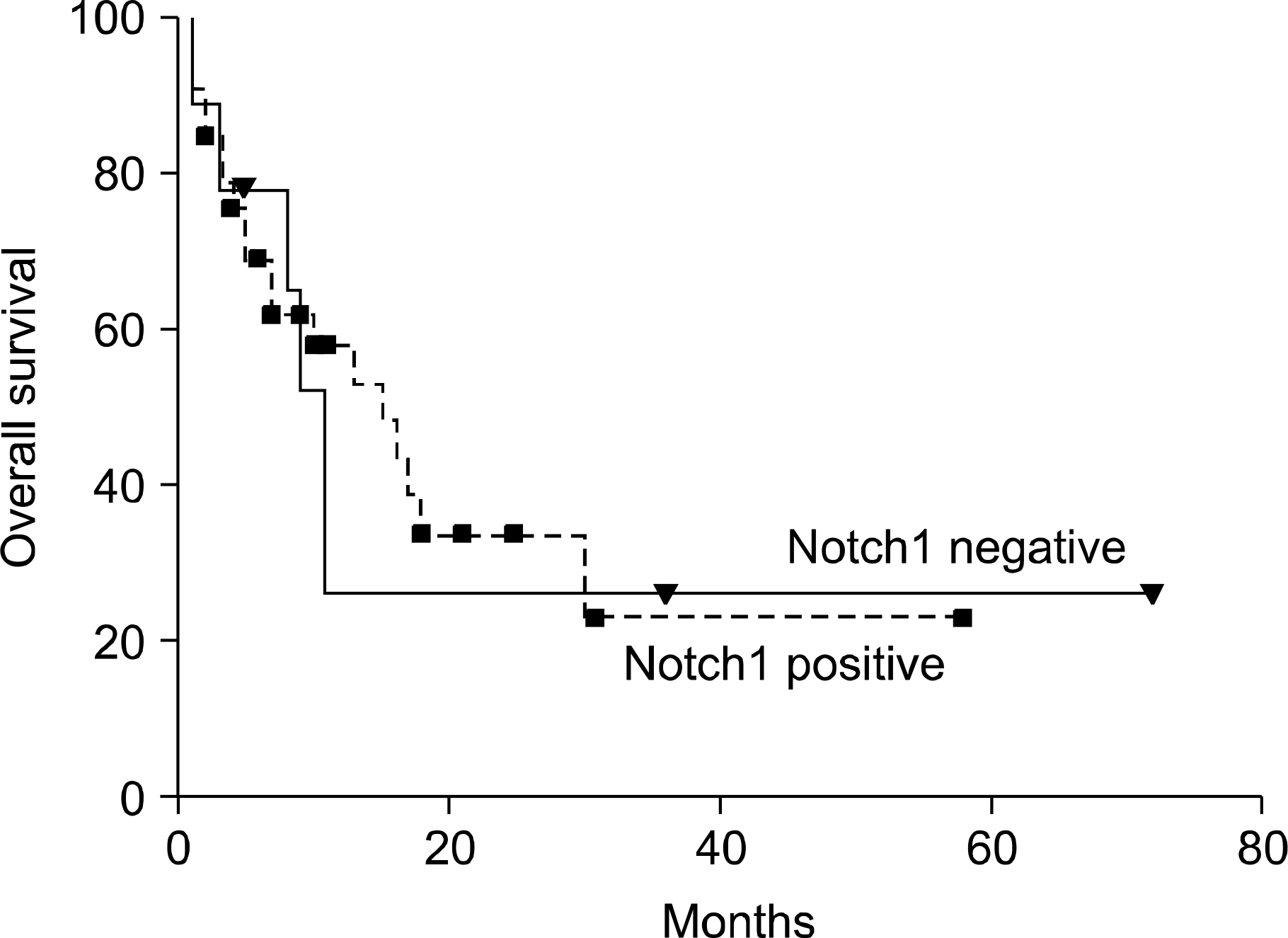
Notch1 transcripts were expressed in 40 (80%) cases with a variable degree of expression, and the fraction of AML cells in the G0/G1 phase was higher in Notch1-positive cases than in Notch1-negative cases. Survivin was shown to be present in 38 (76.0%) cases, and Notch1 expression highly correlated with survivin mRNA expression (r=0.7170, P<0.001). p27Kip1 was present in 40 (80.0%) cases of AML and p27Kip1 expression was significantly associated with Notch1 expression (r=0.8770, P<0.001). Except for one case, the simultaneous expression of survivin and p27Kip1 was not seen in all cases that were negative for Notch1 expression. There were no differences in clinical outcomes according to Notch1 expression.
CONCLUSION
Notch1 expression was a frequent event and has functional significance in the alteration of the cell cycle in AML cells. Notch1 expression was also significantly associated with survivin and p27kip1 expression in AML cells. To evaluate the clinical significanceand functional role of Notch1 expression in the aberrant regulation of survivin and p27Kip1 expression in de novo AML, a further study with a larger number of patients is necessary.
Figure
Reference
-
1). Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Rand MD., Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999. 284:770–6.
Article2). Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Matsuno K., Fortini ME. Notch signaling. Science. 1995. 268:225–32.
Article3). Milner LA., Kopan R., Martin DI., Bernstein ID. A human homologue of the Drosophilia developmental gene, Notch, is expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic precursors. Blood. 1994. 83:2057–62.4). Li F., Ambrosini G., Chu EY, et al. Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 1998. 396:580–4.
Article5). Carlesso N., Aster JC., Sklar J., Scadden DT. Notch1-induced delay of human hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation is associated with altered cell cycle kinetics. Blood. 1999. 93:838–48.
Article6). Milner LA., Bigas A. Notch as a mediator of cell fate determination in hematopoiesis: evidence and speculation. Blood. 1999. 93:2431–48.
Article7). Reed JC. Dysregulation of apoptosis in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:2941–53.
Article8). Ambrosini G., Adida C., Altieri DC. A novel anti-apop-tosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med. 1997. 3:917–21.
Article9). Adida C., Recher C., Raffoux E, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of survivin in de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Br J Haematol. 2000. 111:196–203.10). Sherr CJ., Roberts JM. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 1995. 9:1149–63.
Article11). Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 1994. 79:573–82.
Article12). Chiarle R., Budel LM., Skolnik J, et al. Increased proteasome degradation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 is associated with a decreased overall survival in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 2000. 95:619–26.
Article13). Yokozawa T., Towatari M., Iida H, et al. Prognostic significance of the cell cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2000. 14:28–33.
Article14). Dubart A., Roméo PH., Vainchenker W., Dumenil D. Constitutive expression of GATA-1 interferes with the cell-cycle regulation. Blood. 1996. 87:3711–21.
Article15). Schlegelberger B., Metzke S., Harder S., Zuhlke-Jenisch R., Zhang Y., Siebert R. Classical and Molecular Cytogenetics of Tumor Cells. ,. In:. Wegner R, editor. Diagnostic Cytogenetics. 1st ed.New York, USA: Springer;1999. p. 151–85.
Article16). Zagouras P., Stifani S., Blaumueller CM., Carcangiu ML., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Alterations in Notch signaling in neoplastic lesions of the human cervix. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995. 92:6414–8.
Article17). Ellisen LW., Bird J., West DC, et al. TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell. 1991. 66:649–61.
Article18). Pear WS., Aster JC., Scott ML, et al. Exclusive development of T cell neoplasms in mice transplanted with bone marrow expressing activated Notch alleles. J Exp Med. 1996. 183:2283–91.
Article19). Fortini ME., Rebay I., Caron LA., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. An activated Notch receptor blocks cell-fate commitment in the developing Drosophila eye. Nature. 1993. 365:555–7.
Article20). Suzuki A., Hayashida M., Ito T, et al. Survivin initiates cell cycle entry by the competitive interaction with Cdk4/p16(INK4a) and Cdk2/cyclin E complex activation. Oncogene. 2000. 19:3225–34.
Article21). Yang Y., Fang S., Jensen JP., Weissman AM., Ashwell JD. Ubiquitin protein ligase activity of IAPs and their degradation in proteasomes in response to apoptotic stimuli. Science. 2000. 288:874–7.
Article22). Schweisguth F. Dominant-negative mutation in the beta2 and beta6 proteasome subunit genes affect alternative cell fate decisions in the Drosophila sense organ lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999. 96:11382–6.23). Koff A., Giordano A., Desai D, et al. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992. 257:1689–94.
Article24). Nourse J., Firpo E., Flanagan WM, et al. Interleukin-2-mediated elimination of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor prevented by rapamycin. Nature. 1994. 372:570–3.25). Shirane M., Harumiya Y., Ishida N, et al. Down-regulation of p27Kip1 by two mechanisms, ubiquitin-mediated degradation and proteolytic processing. J.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Intracardiac Thrombus Presenting as Acute Limb Ischemia
- Classification of acute myeloid leukemia
- Myeloid Sarcoma of Peritoneum in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Inversion of Chromosome 16
- A Case of Myeloid Sarcoma Preceding the Diagnosis of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- A Pediatric Case of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with t(3;5)(q25;q34)