J Nutr Health.
2020 Feb;53(1):1-12. 10.4163/jnh.2020.53.1.1.
Dietary nobiletin suppresses TGF-β1-Src-caveolin-1 dependent signaling involved with high glucose-induced renal mesangial matrix accumulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Hallym University, Chuncheon 24252, Korea. mitholy@hallym.ac.kr
- KMID: 2471118
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/jnh.2020.53.1.1
Abstract
- PURPOSE
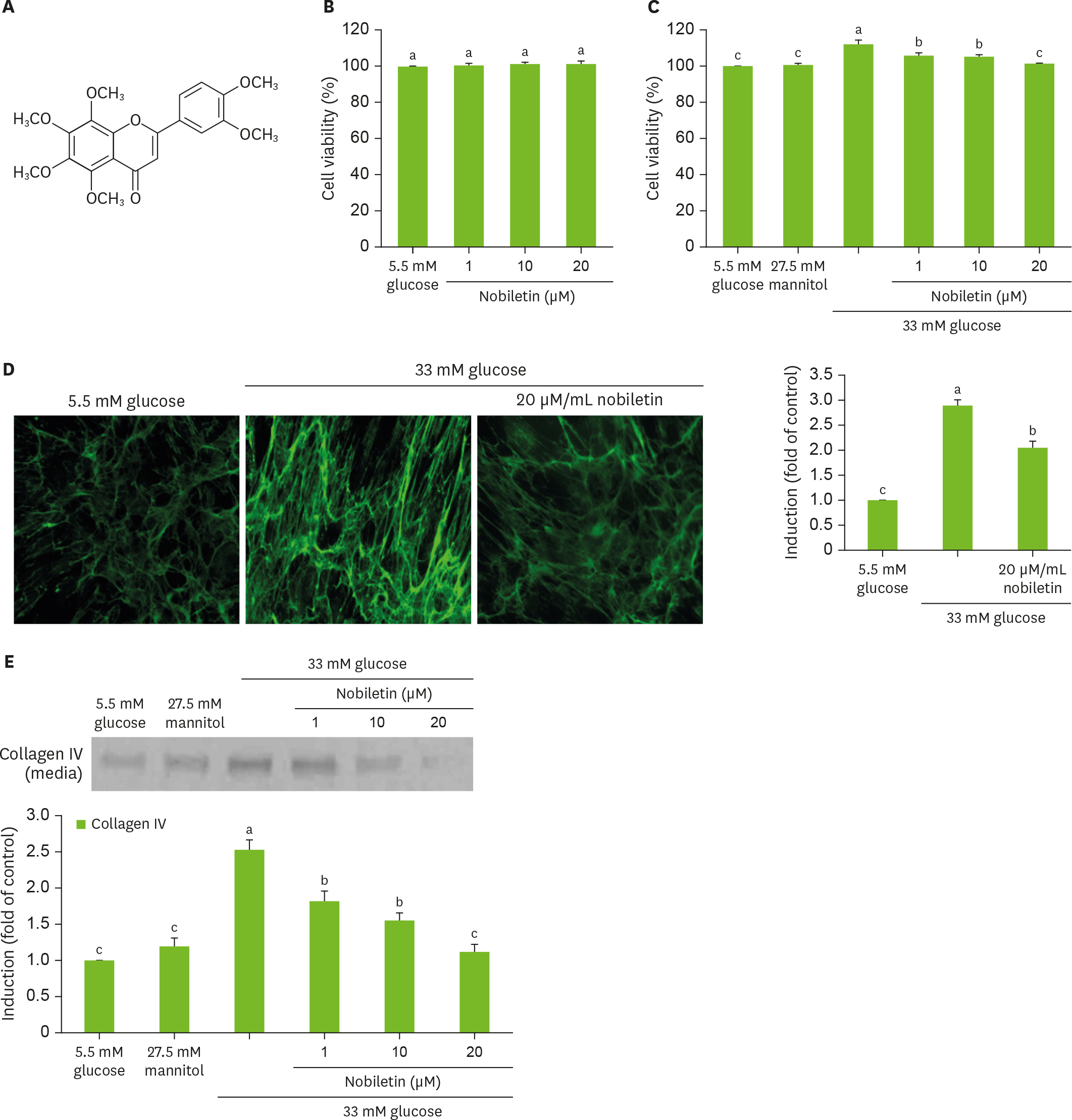
Diabetic nephropathy is one of the most important diabetic complications prompted by chronic hyperglycemia, characterized by glomerulosclerosis, tubular fibrosis, and it eventually causes kidney failure. Nobiletin is a polymethoxyflavone present in tangerine and other citrus peels, and has anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects. This study investigated the effects of nobiletin on glomerular fibrosis through inhibition of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1-Src-caveolin-1 pathway.
METHODS
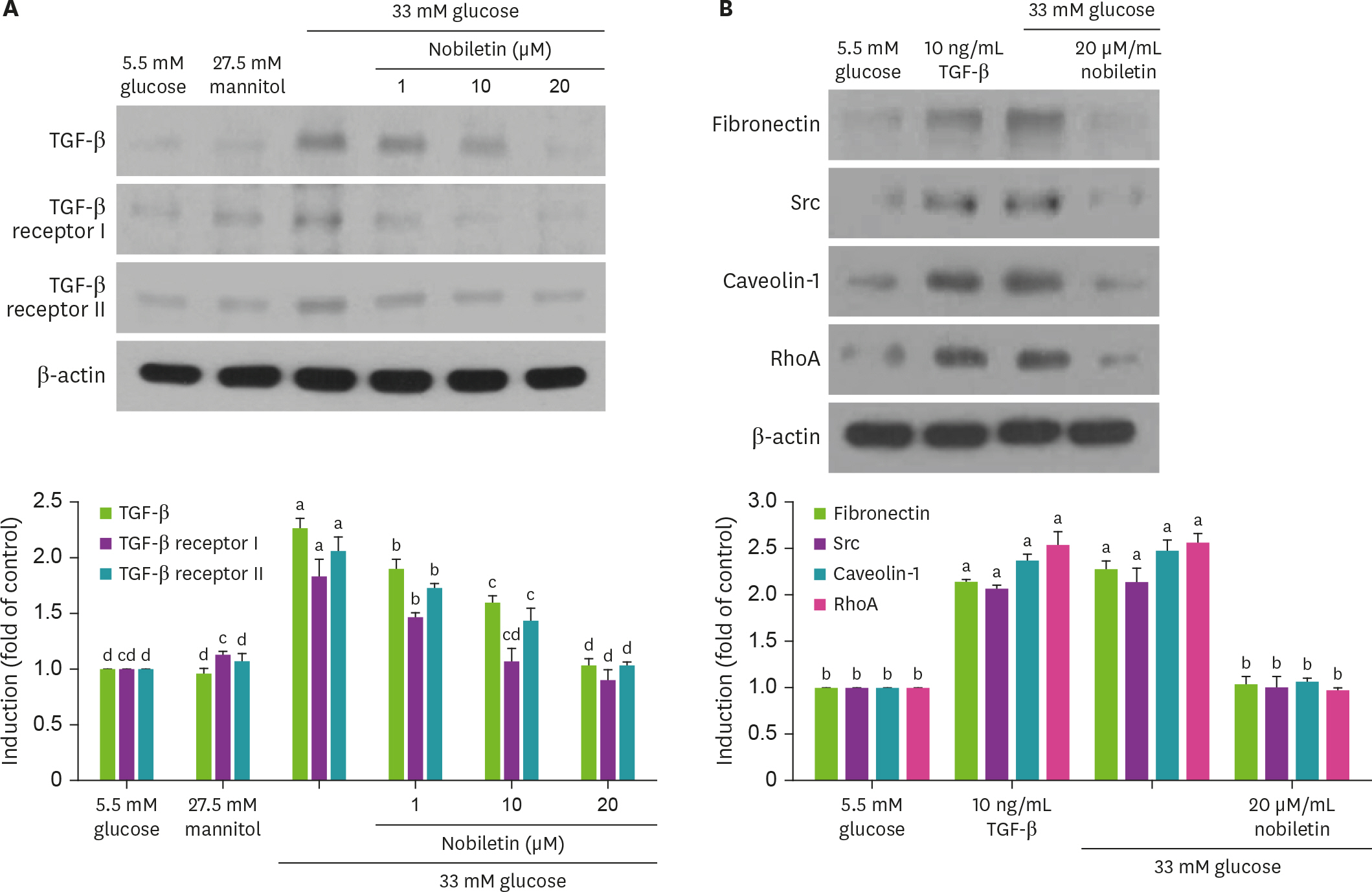
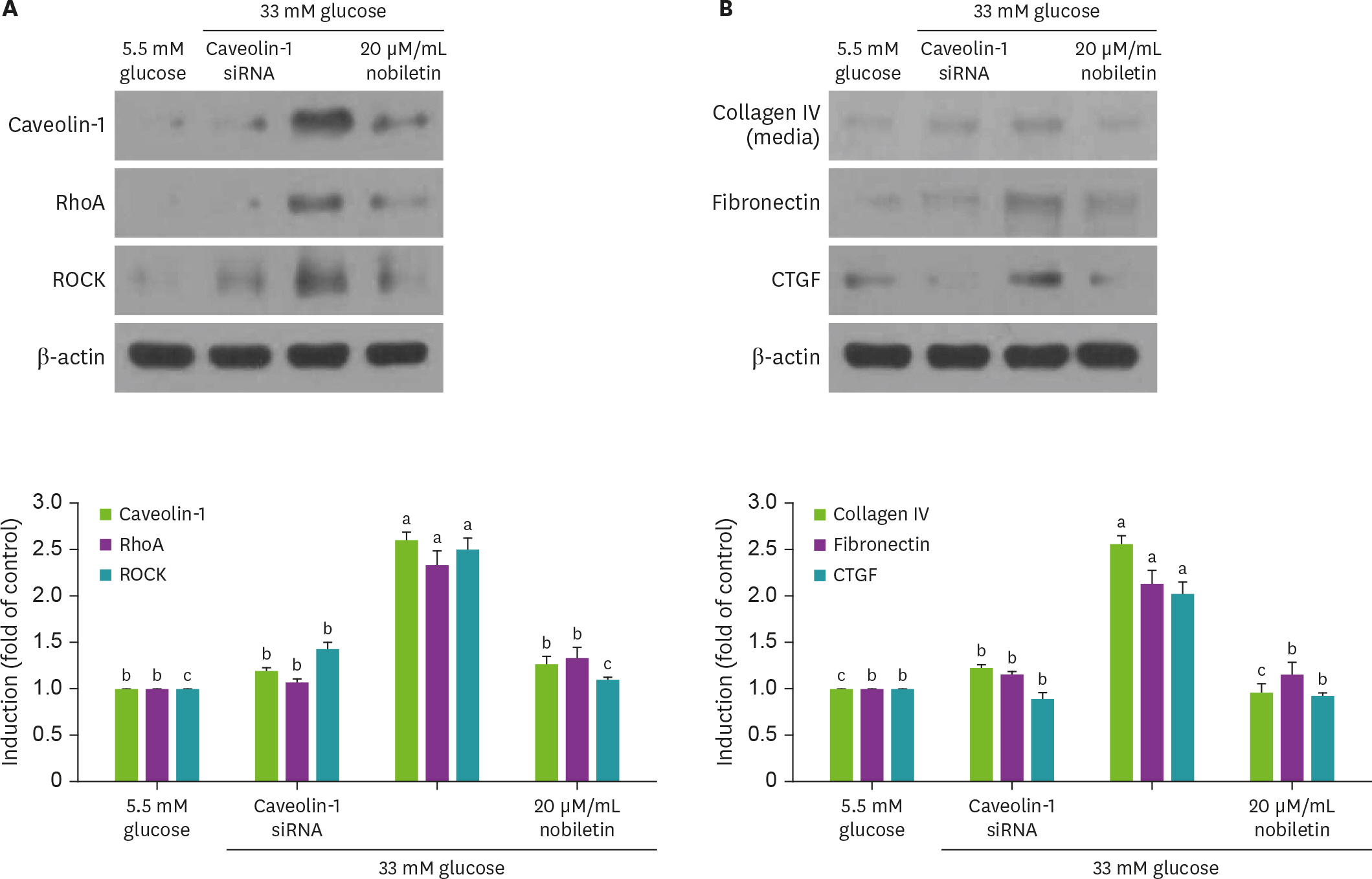
Human renal mesangial cells (HRMC) were incubated in media containing 33 mM glucose with or without 1-20 uM nobiletin for 3 day. The cellular expression levels of fibrogenic collagen IV, fibronectin, connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), TGF-β1, Src and caveolin-1 were all examined. In addition, TGF-β1, Src and caveolin-1 proteins were screened to reveal the relationship among TGF-β1-Src-caveolin-1 signaling in glomerular fibrosis.
RESULTS
High glucose promoted the production of collagen IV, fibronectin and CTGF in HRMC, which was inhibited in a dose dependent manner by 1-20 uM nobiletin. The Western blot data showed that high glucose elevated the expression of TGF-β1, Src, caveolin-1 and Rho GTPase. When nobiletin was treated to the HRMC exposed to high glucose, the expression of TGF-β1-Src-caveolin-1 was dampened. Finally, TGF-β1-Src-caveolin-1 signaling pathway was activated in high glucose-exposed HRMC, and such activation was encumbered by nobiletin.
CONCLUSION
These result demonstrated that nobiletin blunted high glucose-induced extracellular matrix accumulation via inhibition of the TGF-β1-Src-caveolin-1 related intracellular signaling pathway. Nobiletin may be a potent renoprotective agent to counteract diabetes-associated glomerular fibrosis that leads to kidney failure.
MeSH Terms
-
Blotting, Western
Caveolin 1
Citrus
Collagen
Connective Tissue Growth Factor
Diabetes Complications
Diabetic Nephropathies
Extracellular Matrix
Fibronectins
Fibrosis
Glucose
GTP Phosphohydrolases
Humans
Hyperglycemia
Mesangial Cells
Renal Insufficiency
Transforming Growth Factors
Caveolin 1
Collagen
Connective Tissue Growth Factor
Fibronectins
GTP Phosphohydrolases
Glucose
Transforming Growth Factors
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ban CR, Twigg SM. Fibrosis in diabetes complications: pathogenic mechanisms and circulating and urinary markers. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008; 4(3):575–596.2. Schena FP, Gesualdo L. Pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005; 16(Suppl 1):S30–S33.
Article3. Pozzi A, Voziyan PA, Hudson BG, Zent R. Regulation of matrix synthesis, remodeling and accumulation in glomerulosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2009; 15(12):1318–1333.
Article4. Fukuda N, Tahira Y, Matsuda H, Matsumoto K. Transforming growth factor-beta as a treatment target in renal diseases. J Nephrol. 2009; 22(6):708–715.5. Li J, Lim SS, Lee JY, Kim JK, Kang SW, Kim JL, et al. Purple corn anthocyanins dampened high-glucose-induced mesangial fibrosis and inflammation: possible renoprotective role in diabetic nephropathy. J Nutr Biochem. 2012; 23(4):320–331.
Article6. Ungefroren H, Witte D, Lehnert H. The role of small GTPases of the Rho/Rac family in TGF-β-induced EMT and cell motility in cancer. Dev Dyn. 2018; 247(3):451–461.
Article7. Li J, Lim SS, Lee ES, Gong JH, Shin D, Kang IJ, et al. Isoangustone A suppresses mesangial fibrosis and inflammation in human renal mesangial cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2011; 236(4):435–444.
Article8. Peng F, Wu D, Gao B, Ingram AJ, Zhang B, Chorneyko K, et al. RhoA/Rho-kinase contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetic renal disease. Diabetes. 2008; 57(6):1683–1692.
Article9. Razani B, Zhang XL, Bitzer M, von Gersdorff G, Böttinger EP, Lisanti MP. Caveolin-1 regulates transforming growth factor (TGF)-β/SMAD signaling through an interaction with the TGF-β type I receptor. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276(9):6727–6738.
Article10. Van Krieken R, Krepinsky JC. Caveolin-1 in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: potential therapeutic target? Curr Diab Rep. 2017; 17(3):19.
Article11. Lu Y, Tang L, Li Y, He Q. High glucose-induced fibronectin upregulation in cultured mesangial cells involves caveolin-1-dependent RhoA-GTP activation via Src kinase. Mol Med Rep. 2016; 14(1):963–968.
Article12. Youn K, Lee S, Jun M. Discovery of nobiletin from citrus peel as a potent inhibitor of β-amyloid peptide toxicity. Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2648.
Article13. Huang H, Li L, Shi W, Liu H, Yang J, Yuan X, et al. The multifunctional effects of nobiletin and its metabolites in vivo and in vitro. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016; 2016:2918796.14. Wilson HM, Stewart KN. Glomerular epithelial and mesangial cell culture and characterization. Methods Mol Biol. 2012; 806:187–201.
Article15. Li J, Kang SW, Kim JL, Sung HY, Kwun IS, Kang YH. Isoliquiritigenin entails blockade of TGF-β1-SMAD signaling for retarding high glucose-induced mesangial matrix accumulation. J Agric Food Chem. 2010; 58(5):3205–3212.
Article16. Kanwar YS, Wada J, Sun L, Xie P, Wallner EI, Chen S, et al. Diabetic nephropathy: mechanisms of renal disease progression. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008; 233(1):4–11.
Article17. Kim DY, Kang MK, Park SH, Lee EJ, Kim YH, Oh H, et al. Eucalyptol ameliorates Snail1/β-catenindependent diabetic disjunction of renal tubular epithelial cells and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(63):106190–106205.
Article18. Shihata WA, Putra MR, Chin-Dusting JP. Is there a potential therapeutic role for caveolin-1 in fibrosis? Front Pharmacol. 2017; 8:567.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Caveolin-1 is involved in high glucose accelerated human glomerular mesangial cell senescence
- The Effect of High Glucose and TGF-beta on the Cellular Injury in Cultured Glomerular Epithelial Cells
- Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Antisense Oligodeoxynucleotides Abrogate Mesangial Fibronectin Accumulation
- The Inhibitory Effect of siRNAs on The High Glucose-Induced Overexpression of TGF-beta1 in Mesangial Cells
- The effects of high glucose concentration on the synthesis of extracellular matrix and the fine structures of mesangial cells in culture