J Vet Sci.
2020 Jan;21(1):e7. 10.4142/jvs.2020.21.e7.
Age-specific variations in hematological and biochemical parameters in middle- and large-sized of dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Theriogenology and Biotechnology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea. bclee@snu.ac.kr, jooya5@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2469022
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2020.21.e7
Abstract
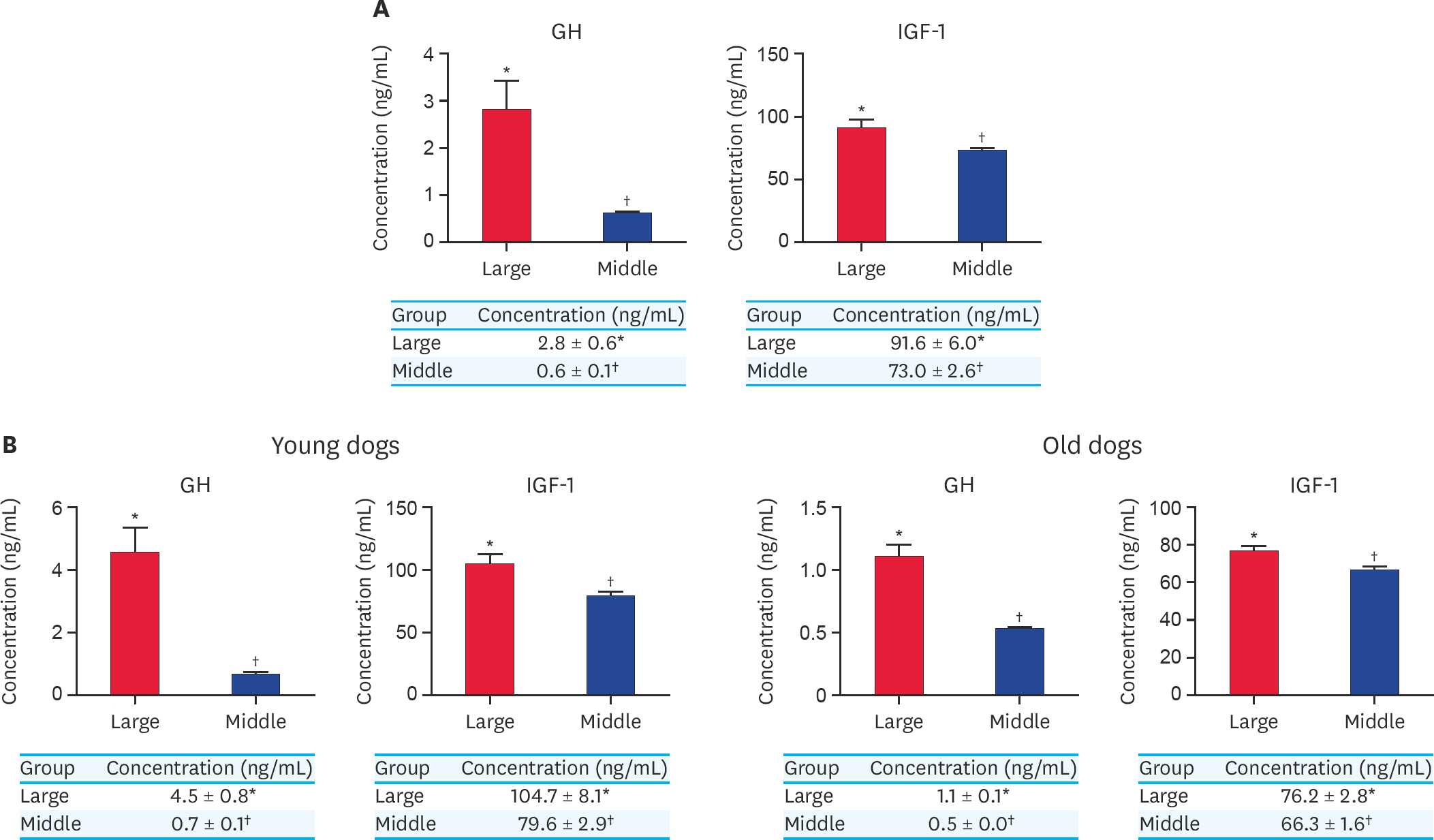
- Aging triggers cellular and molecular alterations, including genomic instability and organ dysfunction, which increases the risk of disease in mammals. Recently, due to the markedly growing number of aging dogs in the world, as much as 49% in total number of pet dogs, it is necessary to improve and maintain their quality of life by understanding of the biological effects of aging. Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine specific biomarkers in aging dogs as a means of defining a set of hematological/biochemical biomarkers that influence the aging process. Blood samples were collected from younger (1-3 years) and older (7-10 years) dogs of middle/large size. The hematological/biochemistry analysis was performed to evaluate parameters significantly associated with age. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to target growth hormone (GH)/insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1), one of the main regulators of the aging process. Declining levels of total protein and increased levels of glucose in young dogs was observed regardless of their body size. Notably, a significantly high concentration of GH and IGF-1 in the younger dogs compared to the older dogs was found in middle/large-sized dogs. GH and IGF-1 were also found at significantly high levels in large-sized dogs compared to middle-sized dogs, suggesting a similar trend to that of elderly humans. Consequently, glucose, total protein, GH, and IGF-1 were identified as potential biomarkers for regulating the aging process in large/middle-sized dogs. These findings provide an invaluable insight into the mechanism of aging for the field of aging research.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Fortney WD. Implementing a successful senior/geriatric health care program for veterinarians, veterinary technicians, and office managers. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2012; 42:823–834. viii.
Article2. Walston J. Frailty–the search for underlying causes. Sci Aging Knowledge Environ. 2004; 2004:pe4.
Article3. Gou X, Wang Z, Li N, Qiu F, Xu Z, Yan D, Yang S, Jia J, Kong X, Wei Z, Lu S, Lian L, Wu C, Wang X, Li G, Ma T, Jiang Q, Zhao X, Yang J, Liu B, Wei D, Li H, Yang J, Yan Y, Zhao G, Dong X, Li M, Deng W, Leng J, Wei C, Wang C, Mao H, Zhang H, Ding G, Li Y. Whole-genome sequencing of six dog breeds from continuous altitudes reveals adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia. Genome Res. 2014; 24:1308–1315.
Article4. Li Y, Wu DD, Boyko AR, Wang GD, Wu SF, Irwin DM, Zhang YP. Population variation revealed high-altitude adaptation of Tibetan mastiffs. Mol Biol Evol. 2014; 31:1200–1205.
Article5. Fraser CG. Inherent biological variation and reference values. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2004; 42:758–764.
Article6. Harris EK. Effects of intra- and interindividual variation on the appropriate use of normal ranges. Clin Chem. 1974; 20:1535–1542.7. Metzger FL, Rebar AH. Clinical pathology interpretation in geriatric veterinary patients. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2012; 42:615–629. v.
Article8. Veldhuis JD, Norman C, Miles JM, Bowers CY. Sex steroids, GHRH, somatostatin, IGF-I, and IGFBP-1 modulate ghrelin's dose-dependent drive of pulsatile GH secretion in healthy older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97:4753–4760.
Article9. Maggio M, Ble A, Ceda GP, Metter EJ. Decline in insulin-like growth factor-I levels across adult life span in two large population studies. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006; 61:182–183.
Article10. Meites J. Neuroendocrine biomarkers of aging in the rat. Exp Gerontol. 1988; 23:349–358.
Article11. Westwood AJ, Beiser A, Decarli C, Harris TB, Chen TC, He XM, Roubenoff R, Pikula A, Au R, Braverman LE, Wolf PA, Vasan RS, Seshadri S. Insulin-like growth factor-1 and risk of Alzheimer dementia and brain atrophy. Neurology. 2014; 82:1613–1619.
Article12. Laughlin GA, Barrett-Connor E, Criqui MH, Kritz-Silverstein D. The prospective association of serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-1 levels with all cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in older adults: the Rancho Bernardo Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:114–120.
Article13. Bartke A, Sun LY, Longo V. Somatotropic signaling: trade-offs between growth, reproductive development, and longevity. Physiol Rev. 2013; 93:571–598.
Article14. Tsai KL, Clark LA, Murphy KE. Understanding hereditary diseases using the dog and human as companion model systems. Mamm Genome. 2007; 18:444–451.
Article15. Ostrander EA, Galibert F, Patterson DF. Canine genetics comes of age. Trends Genet. 2000; 16:117–124.
Article16. Lorenzini A. How much should we weigh for a long and healthy life span? the need to reconcile caloric restriction versus longevity with body mass index versus mortality data. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014; 5:121.
Article17. Ackermann M, Chao L, Bergstrom CT, Doebeli M. On the evolutionary origin of aging. Aging Cell. 2007; 6:235–244.
Article18. López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013; 153:1194–1217.
Article19. Lawrence J, Chang YM, Szladovits B, Davison LJ, Garden OA. Breed-specific hematological phenotypes in the dog: a natural resource for the genetic dissection of hematological parameters in a mammalian species. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e81288.
Article20. Maeda S, Takeya Y, Oguro R, Akasaka H, Ryuno H, Kabayama M, Yokoyama S, Nagasawa M, Fujimoto T, Takeda M, Onishi-Takeya M, Itoh N, Takami Y, Yamamoto K, Sugimoto K, Inagaki H, Ogawa M, Nakagawa T, Yasumoto S, Masui Y, Arai Y, Ishizaki T, Ikebe K, Gondo Y, Kamide K, Rakugi H. Serum albumin/globulin ratio is associated with cognitive function in community-dwelling older people: the septuagenarians, octogenarians, nonagenarians investigation with centenarians study. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2019; 19:967–971.
Article21. Strasser A, Niedermüller H, Hofecker G, Laber G. The effect of aging on laboratory values in dogs. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A. 1993; 40:720–730.
Article22. Lowseth LA, Gillett NA, Gerlach RF, Muggenburg BA. The effects of aging on hematology and serum chemistry values in the beagle dog. Vet Clin Pathol. 1990; 19:13–19.
Article23. Blount DG, Pritchard DI, Heaton PR. Age-related alterations to immune parameters in Labrador retriever dogs. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2005; 108:399–407.
Article24. Kaspar LV, Norris WP. Serum chemistry values of normal dogs (beagles): associations with age, sex, and family line. Lab Anim Sci. 1977; 27:980–985.25. Radakovich LB, Pannone SC, Truelove MP, Olver CS, Santangelo KS. Hematology and biochemistry of aging-evidence of “anemia of the elderly” in old dogs. Vet Clin Pathol. 2017; 46:34–45.
Article26. Walton RM. Subject-based reference values: biological variation, individuality, and reference change values. Vet Clin Pathol. 2012; 41:175–181.
Article27. Kuwahara S, Kesuma Sari D, Tsukamoto Y, Tanaka S, Sasaki F. Age-related changes in growth hormone (GH)-releasing hormone and somatostatin neurons in the hypothalamus and in GH cells in the anterior pituitary of female mice. Brain Res. 2004; 1025:113–122.
Article28. Corpas E, Harman SM, Blackman MR. Human growth hormone and human aging. Endocr Rev. 1993; 14:20–39.
Article29. Vitale G, Barbieri M, Kamenetskaya M, Paolisso G. GH/IGF-I/insulin system in centenarians. Mech Ageing Dev. 2017; 165:107–114.
Article30. Austad SN. Cats, “rats,” and bats: the comparative biology of aging in the 21st century. Integr Comp Biol. 2010; 50:783–792.
Article31. Metcalfe NB, Monaghan P. Growth versus lifespan: perspectives from evolutionary ecology. Exp Gerontol. 2003; 38:935–940.
Article32. Kraus C, Pavard S, Promislow DE. The size-life span trade-off decomposed: why large dogs die young. Am Nat. 2013; 181:492–505.
Article33. Patronek GJ, Waters DJ, Glickman LT. Comparative longevity of pet dogs and humans: implications for gerontology research. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1997; 52:B171–178.
Article34. Li Y, Deeb B, Pendergrass W, Wolf N. Cellular proliferative capacity and life span in small and large dogs. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1996; 51:B403–408.
Article35. Speakman JR, van Acker A, Harper EJ. Age-related changes in the metabolism and body composition of three dog breeds and their relationship to life expectancy. Aging Cell. 2003; 2:265–275.
Article36. Fan R, Olbricht G, Baker X, Hou C. Birth mass is the key to understanding the negative correlation between lifespan and body size in dogs. Aging (Albany NY). 2016; 8:3209–3222.
Article37. Eklund J, Bradford GE. Longeveity and lifetime body weight in mice selected for rapid growth. Nature. 1977; 265:48–49.38. Kienzle E, Moik K. A pilot study of the body weight of purebred client-owned adult cats. Br J Nutr. 2011; 106(Suppl 1):S113–115.
Article39. Greer KA, Hughes LM, Masternak MM. Connecting serum IGF-1, body size, and age in the domestic dog. Age (Dordr). 2011; 33:475–483.
Article40. Brosnahan MM, Paradis MR. Demographic and clinical characteristics of geriatric horses: 467 cases (1989–1999). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2003; 223:93–98.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Age‑related changes in hematological and biochemical profiles of Wistar rats
- Effect of variable degrees of jejunal resection upon different clinico-biochemical parameters in dogs
- Changes of hematological references depends on storage period and temperature conditions in rats and dogs
- Acute and sublethal intoxication of malathion in an Indian major carp, Labeo rohita: haematological and biochemical responses.
- Basic data on the hematology, serum biochemistry, urology, and organ weights of beagle dogs