Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2020 Mar;12(2):338-358. 10.4168/aair.2020.12.2.338.
Epithelial PI3K-δ Promotes House Dust Mite-Induced Allergic Asthma in NLRP3 Inflammasome-Dependent and -Independent Manners
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Respiratory Medicine and Allergy, Department of Internal Medicine, Research Center for Pulmonary Disorders, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. sori@jbnu.ac.kr, leeyc@jbnu.ac.kr
- 2Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- 3Division of Allergy and Immunology, Internal Medicine, Morsani College of Medicine, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA.
- KMID: 2468466
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2020.12.2.338
Abstract
- PURPOSE
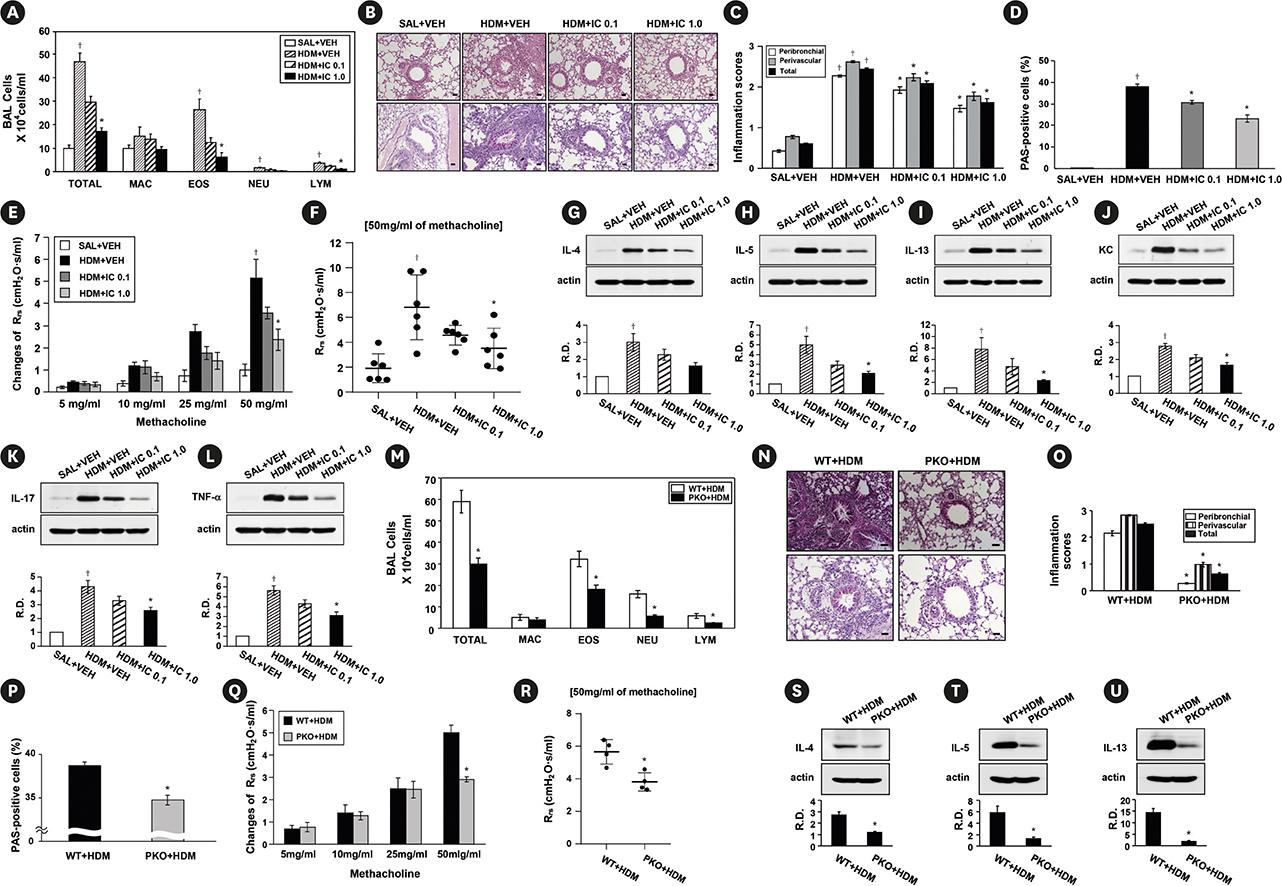
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-δ-dependent Akt activation is known to play critical roles in various immune responses of white blood cells in which PI3K-δ isoform is mostly expressed in contrast to the classes IA PI3Ks p110α and p110β. However, the immunological role of PI3K-δ isoform is still controversial in airway epithelium under house dust mite (HDM)-induced allergic response. This study aimed to evaluate the role of PI3K-δ isoform in HDM-induced allergic responses, focusing on NLRP3 inflammasome activation in airway epithelium.
METHODS
We used wild-type mice and PI3K-δ knock-out (KO) mice for HDM-induced asthma animal model and also performed in vitro experiments using primary cultured murine tracheal epithelial cells and human airway epithelial cells.
RESULTS
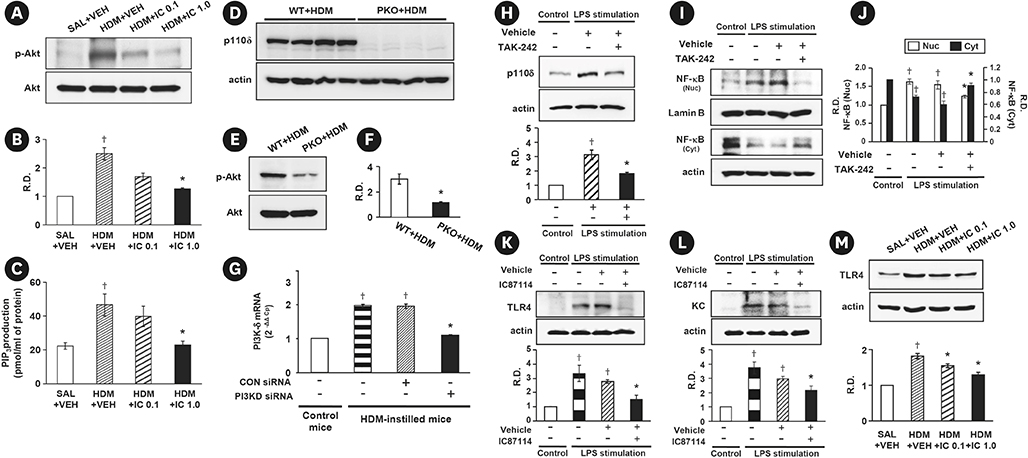
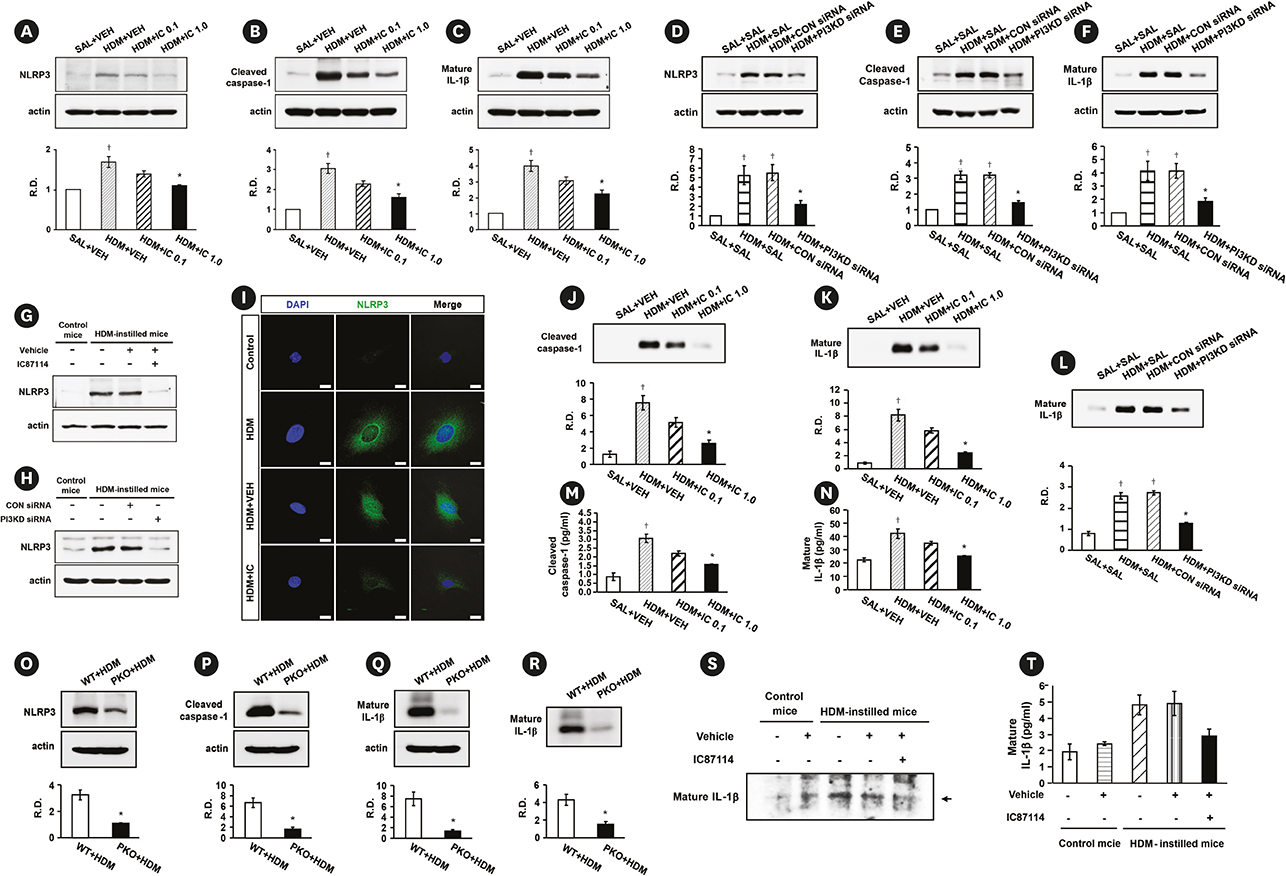
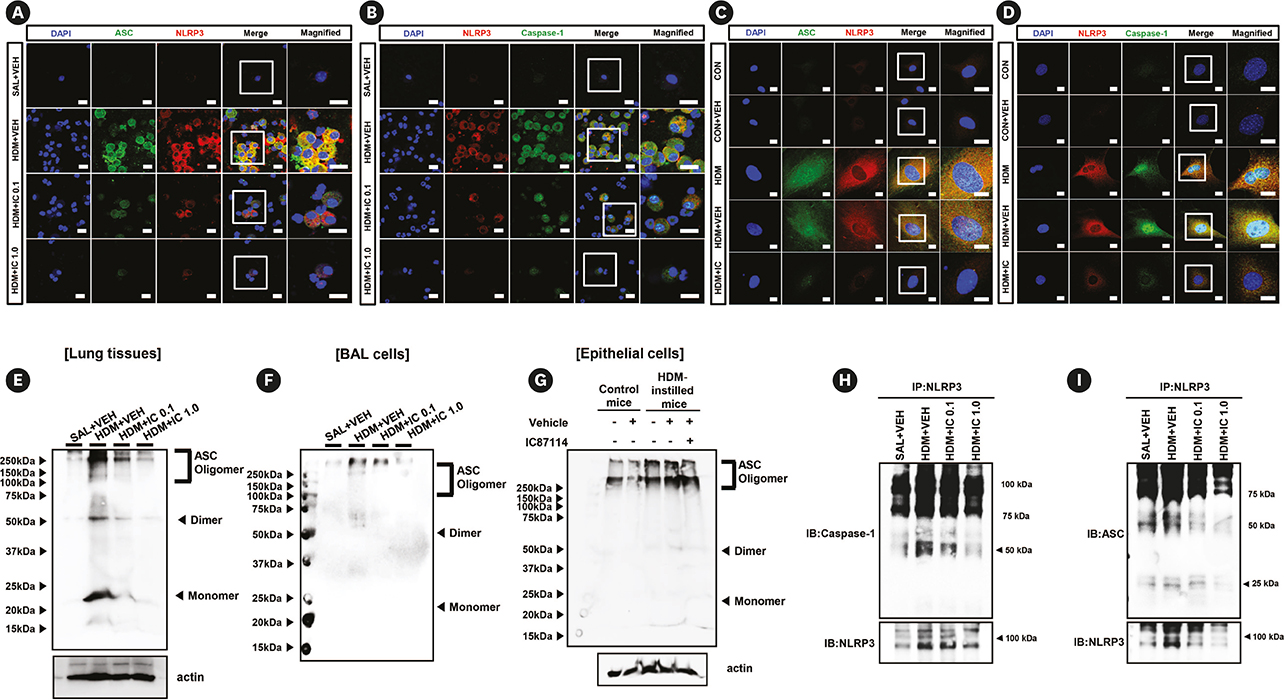
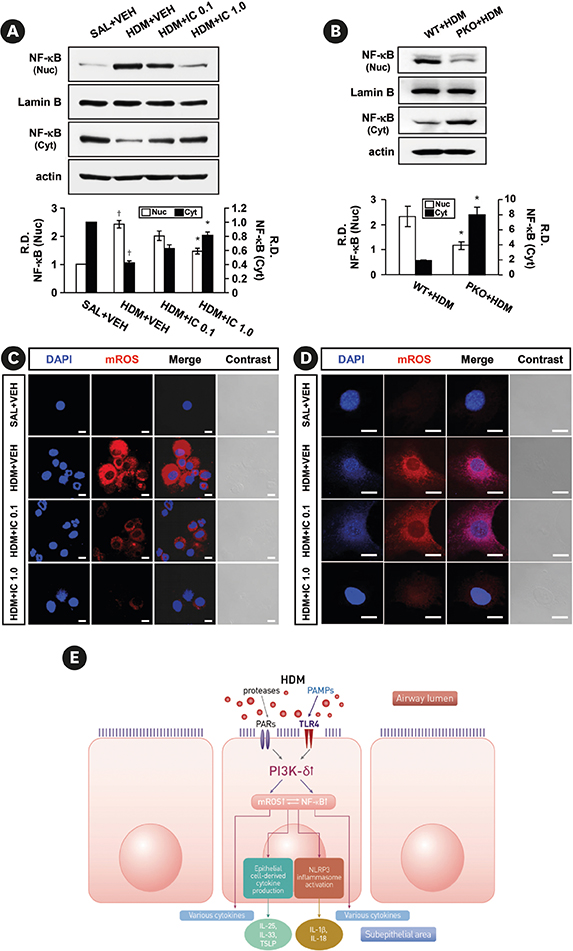
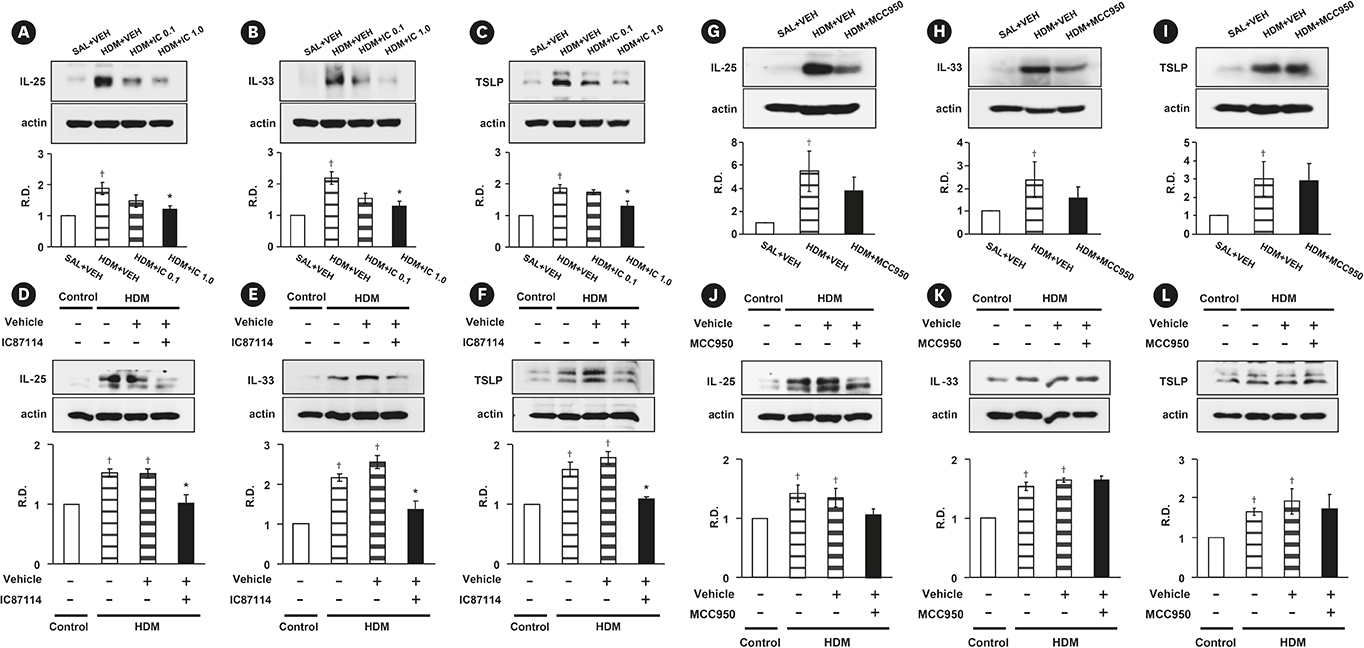
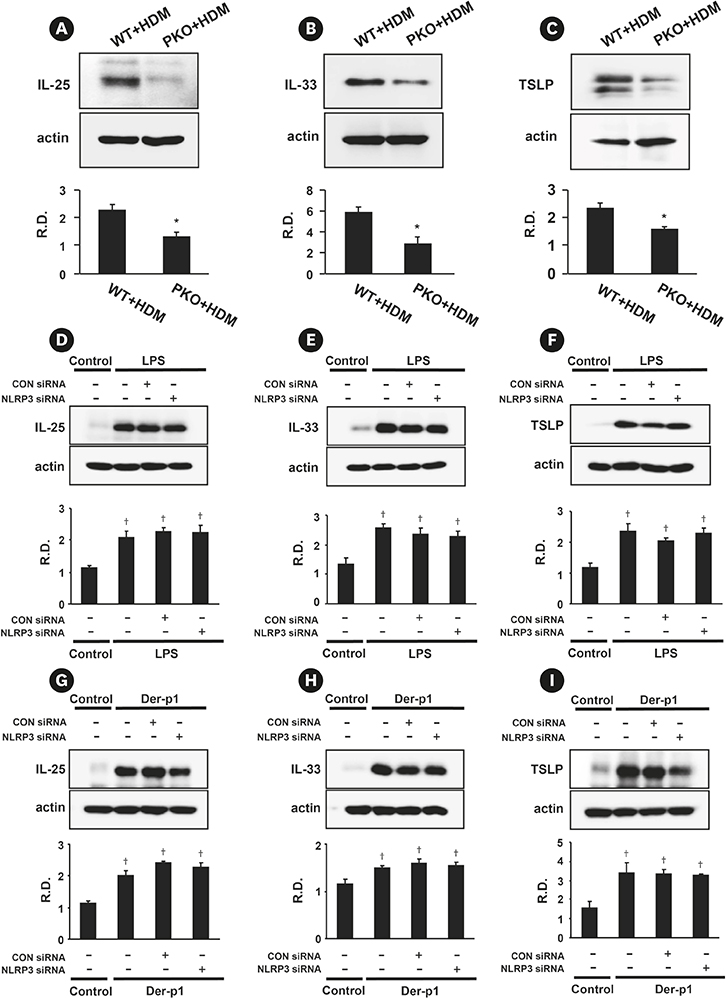
PI3K-δ activated HDM-induced NLRP3 inflammasome and epithelial cell-derived cytokines in the lung including airway epithelial cells. PI3K-δ KO mice or knock-down of PI3K-δ using siRNA exhibited the significant reduction in allergic asthmatic features and the suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome assembly as well as epithelial cell-derived cytokines. Interestingly, significantly increased expression of PI3K-δ isoform was observed in stimulated airway epithelial cells and the increases in epithelial cell-derived cytokines were markedly suppressed by blocking PI3K-δ, while these cytokine levels were independent of NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study suggest that PI3K-δ-isoform can promote HDM-induced allergic airway inflammation via NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent response as well as via NLRP3 inflammasome-independent epithelial cell activation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
MicroRNA-21 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration of human bronchial epithelial cells by targeting poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and activating PI3K/AKT signaling
Shiqing Zhang, Peng Sun, Xinru Xiao, Yujie Hu, Yan Qian, Qian Zhang
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2022;26(4):239-253. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2022.26.4.239.
Reference
-
1. Ito K, Caramori G, Adcock IM. Therapeutic potential of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors in inflammatory respiratory disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007; 321:1–8.
Article2. Vogt PK, Hart JR, Gymnopoulos M, Jiang H, Kang S, Bader AG, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: the oncoprotein. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010; 347:79–104.
Article3. Park SJ, Lee KS, Kim SR, Min KH, Moon H, Lee MH, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ inhibitor suppresses interleukin-17 expression in a murine asthma model. Eur Respir J. 2010; 36:1448–1459.
Article4. Lee KS, Lee HK, Hayflick JS, Lee YC, Puri KD. Inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta attenuates allergic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in murine asthma model. FASEB J. 2006; 20:455–465.5. To Y, Ito K, Kizawa Y, Failla M, Ito M, Kusama T, et al. Targeting phosphoinositide-3-kinase-delta with theophylline reverses corticosteroid insensitivity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010; 182:897–904.6. Acevedo N, Zakzuk J, Caraballo L. House dust mite allergy under changing environments. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019; 11:450–469.
Article7. Willart MA, Lambrecht BN. The danger within: endogenous danger signals, atopy and asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009; 39:12–19.
Article8. Nakahira K, Haspel JA, Rathinam VA, Lee SJ, Dolinay T, Lam HC, et al. Autophagy proteins regulate innate immune responses by inhibiting the release of mitochondrial DNA mediated by the NALP3 inflammasome. Nat Immunol. 2011; 12:222–230.
Article9. Besnard AG, Guillou N, Tschopp J, Erard F, Couillin I, Iwakura Y, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome is required in murine asthma in the absence of aluminum adjuvant. Allergy. 2011; 66:1047–1057.
Article10. Kool M, Pétrilli V, De Smedt T, Rolaz A, Hammad H, van Nimwegen M, et al. Cutting edge: alum adjuvant stimulates inflammatory dendritic cells through activation of the NALP3 inflammasome. J Immunol. 2008; 181:3755–3759.
Article11. Kim SR, Kim DI, Kim SH, Lee H, Lee KS, Cho SH, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation by mitochondrial ROS in bronchial epithelial cells is required for allergic inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2014; 5:e1498.
Article12. Dostert C, Pétrilli V, Van Bruggen R, Steele C, Mossman BT, Tschopp J. Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science. 2008; 320:674–677.
Article13. Pétrilli V, Papin S, Dostert C, Mayor A, Martinon F, Tschopp J. Activation of the NALP3 inflammasome is triggered by low intracellular potassium concentration. Cell Death Differ. 2007; 14:1583–1589.
Article14. Martinon F, Pétrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature. 2006; 440:237–241.
Article15. Jacquet A. The role of innate immunity activation in house dust mite allergy. Trends Mol Med. 2011; 17:604–611.
Article16. Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006; 13:816–825.
Article17. Laird MH, Rhee SH, Perkins DJ, Medvedev AE, Piao W, Fenton MJ, et al. TLR4/MyD88/PI3K interactions regulate TLR4 signaling. J Leukoc Biol. 2009; 85:966–977.
Article18. Cho JY, Miller M, Baek KJ, Han JW, Nayar J, Lee SY, et al. Inhibition of airway remodeling in IL-5-deficient mice. J Clin Invest. 2004; 113:551–560.
Article19. Takeda K, Hamelmann E, Joetham A, Shultz LD, Larsen GL, Irvin CG, et al. Development of eosinophilic airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in mast cell-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 1997; 186:449–454.
Article20. Kwak YG, Song CH, Yi HK, Hwang PH, Kim JS, Lee KS, et al. Involvement of PTEN in airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in bronchial asthma. J Clin Invest. 2003; 111:1083–1092.
Article21. Kim SR, Lee KS, Park HS, Park SJ, Min KH, Moon H, et al. HIF-1α inhibition ameliorates an allergic airway disease via VEGF suppression in bronchial epithelium. Eur J Immunol. 2010; 40:2858–2869.
Article22. Coll RC, Robertson AA, Chae JJ, Higgins SC, Muñoz-Planillo R, Inserra MC, et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat Med. 2015; 21:248–255.
Article23. Rowan WC, Smith JL, Affleck K, Amour A. Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ for allergic asthma. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012; 40:240–245.
Article24. Lee KS, Park SJ, Kim SR, Min KH, Jin SM, Puri KD, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-delta inhibitor reduces vascular permeability in a murine model of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118:403–409.25. Chapman MD, Pomés A, Breiteneder H, Ferreira F. Nomenclature and structural biology of allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:414–420.26. Pomés A. Allergen structures and biologic functions: the cutting edge of allergy research. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2008; 8:425–432.
Article27. Fahlbusch B, Koch A, Douwes J, Bischof W, Gehring U, Richter K, et al. The effect of storage on allergen and microbial agent levels in frozen house dust. Allergy. 2003; 58:150–153.
Article28. Da Silva CA, Pochard P, Lee CG, Elias JA. Chitin particles are multifaceted immune adjuvants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010; 182:1482–1491.
Article29. Idzko M, Hammad H, van Nimwegen M, Kool M, Willart MA, Muskens F, et al. Extracellular ATP triggers and maintains asthmatic airway inflammation by activating dendritic cells. Nat Med. 2007; 13:913–919.
Article30. Kool M, Willart MA, van Nimwegen M, Bergen I, Pouliot P, Virchow JC, et al. An unexpected role for uric acid as an inducer of T helper 2 cell immunity to inhaled antigens and inflammatory mediator of allergic asthma. Immunity. 2011; 34:527–540.
Article31. Hammad H, Chieppa M, Perros F, Willart MA, Germain RN, Lambrecht BN. House dust mite allergen induces asthma via Toll-like receptor 4 triggering of airway structural cells. Nat Med. 2009; 15:410–416.
Article32. Johnson JR, Wiley RE, Fattouh R, Swirski FK, Gajewska BU, Coyle AJ, et al. Continuous exposure to house dust mite elicits chronic airway inflammation and structural remodeling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004; 169:378–385.
Article33. Hongjia L, Qingling G, Meiying L, Weixuan W, Lihong Z, Yongsheng G, et al. House dust mite regulate the lung inflammation of asthmatic mice through TLR4 pathway in airway epithelial cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 2010; 28:597–603.
Article34. Kagan JC, Medzhitov R. Phosphoinositide-mediated adaptor recruitment controls Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell. 2006; 125:943–955.
Article35. Dan HC, Cooper MJ, Cogswell PC, Duncan JA, Ting JP, Baldwin AS. Akt-dependent regulation of NF-κB is controlled by mTOR and Raptor in association with IKK. Genes Dev. 2008; 22:1490–1500.
Article36. Koyasu S. The role of PI3K in immune cells. Nat Immunol. 2003; 4:313–319.
Article37. Aksoy E, Taboubi S, Torres D, Delbauve S, Hachani A, Whitehead MA, et al. The p110δ isoform of the kinase PI(3)K controls the subcellular compartmentalization of TLR4 signaling and protects from endotoxic shock. Nat Immunol. 2012; 13:1045–1054.
Article38. Dai X, Sayama K, Tohyama M, Shirakata Y, Hanakawa Y, Tokumaru S, et al. Mite allergen is a danger signal for the skin via activation of inflammasome in keratinocytes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:806–814.e1-4.
Article39. Baldwin AS Jr. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996; 14:649–683.
Article40. Barnes PJ, Karin M. Nuclear factor-κB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:1066–1071.41. Holgate ST. The sentinel role of the airway epithelium in asthma pathogenesis. Immunol Rev. 2011; 242:205–219.
Article42. He R, Geha RS. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010; 1183:13–24.
Article43. Holgate ST. The epithelium takes centre stage in asthma and atopic dermatitis. Trends Immunol. 2007; 28:248–251.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Asthma Management Educational Program on The Disease Related Knowledge, Stress, and Self-efficacy of Asthmatics Allergic to House Dust Mite
- The Innate Immune Response in House Dust Mite-Induced Allergic Inflammation
- Distribution of House Dust Mites in the Bedroom of Patients with Allergic Rhinitis in Pusan Area
- House dust mite dose not directly activate the human peripheral blood eosinophils in house dust mite-sensitized asthmatics
- Repellent effect of Mate tea and Jasmine tea against house dust mites (Dermatophagoides farinae and D. pteronyssinus)