Yonsei Med J.
2016 Jan;57(1):153-164. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.153.
Association between Toll-Like Receptor 9-1237T/C Polymorphism and the Susceptibility of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology/Hepatology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, P.R. China. bingxia@aliyun.com
- 2The Hubei Clinical Center & Key Laboratory of Intestinal & Colorectal Diseases, Wuhan, P.R. China.
- KMID: 2466365
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.153
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The -1237T/C polymorphism of the Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) gene has been implicated in the susceptibility of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), but the results remain conflicting. We further investigated this association via meta-analysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
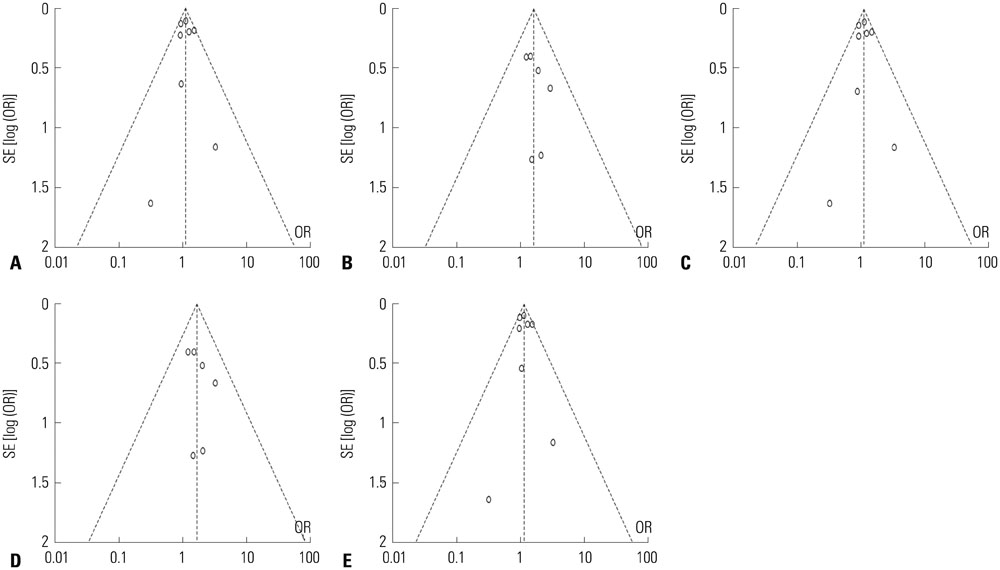
Multiple electronic databases were extensively searched until February, 2015. The strength of association was evaluated by calculating the pooled odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
RESULTS
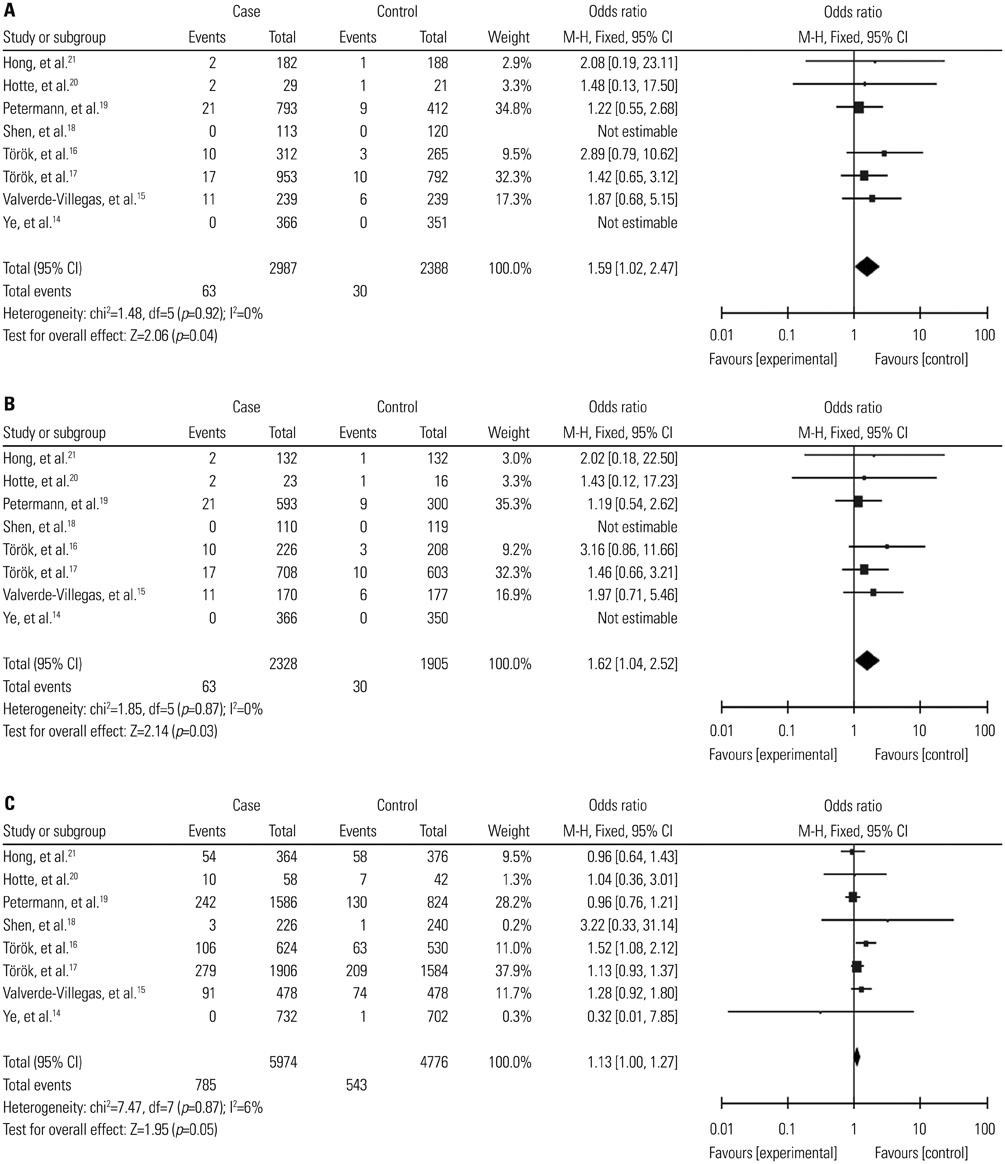
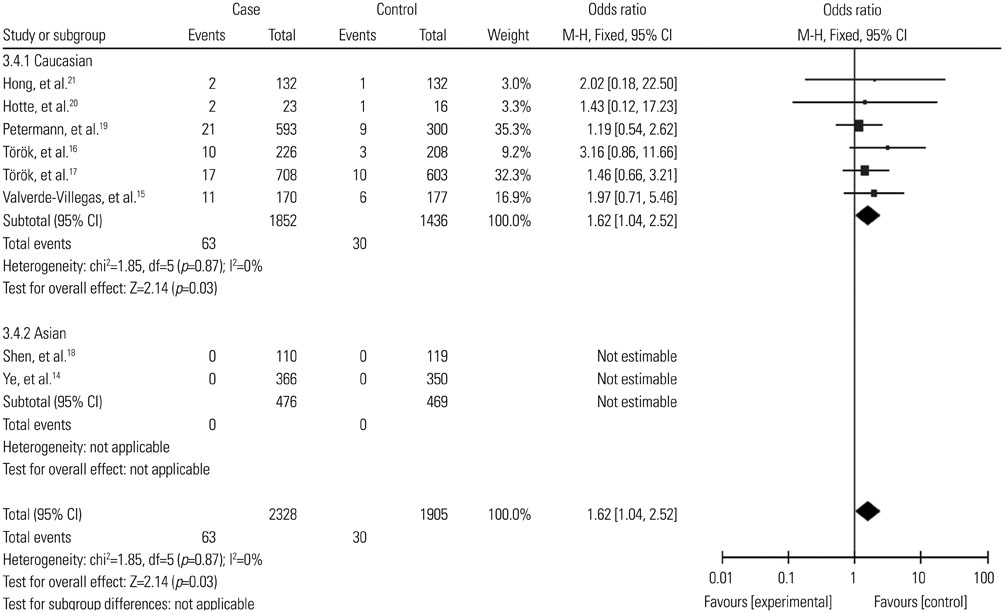
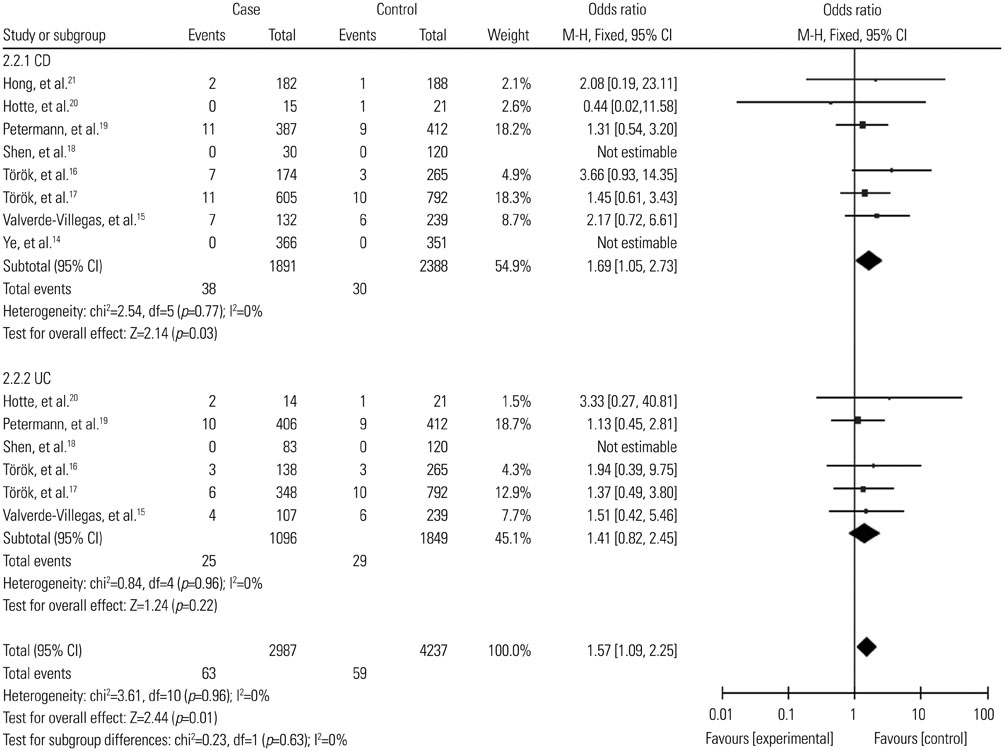
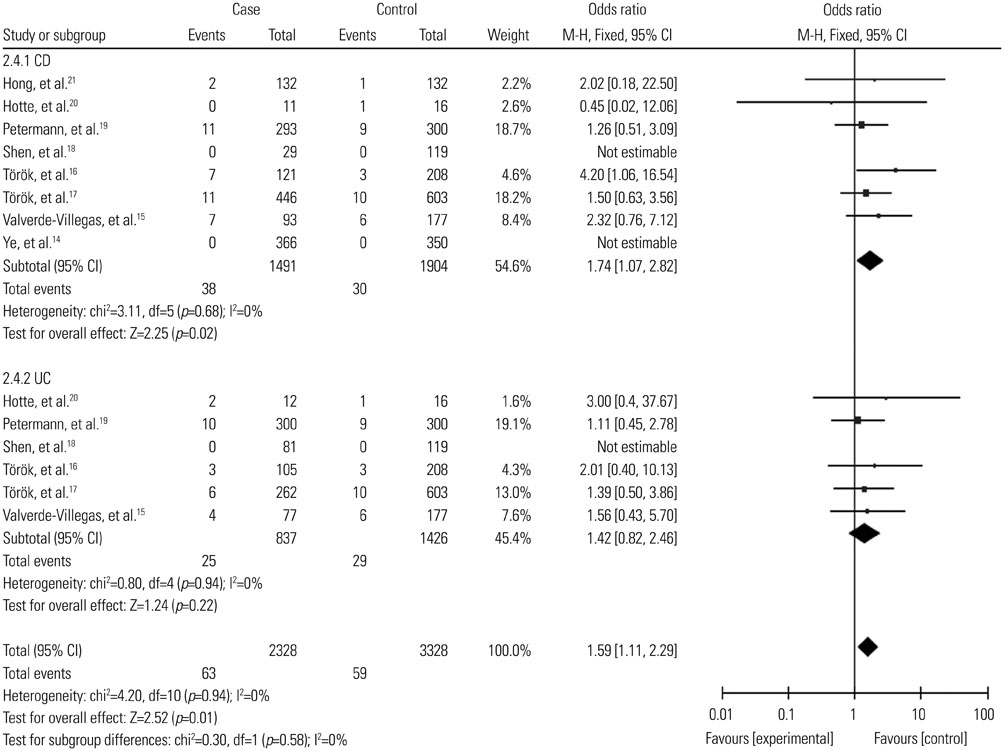
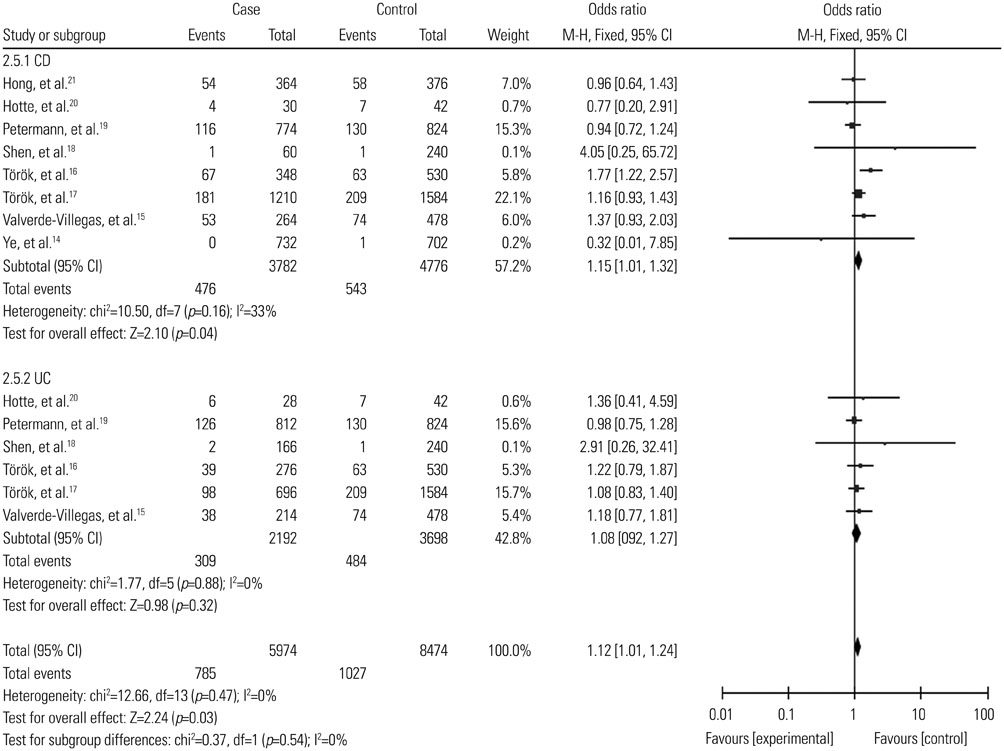
A total of 2987 cases and 2388 controls from eight studies were analyzed. Overall, association was found between TLR9 -1237T/C polymorphism and the risk of IBDs when all the studies were pooled (recessive model, OR: 1.59, 95% CI: 1.02-2.47, p=0.04; homozygote comparison, OR: 1.62, 95% CI: 1.04-2.52, p=0.03; allele model, OR: 1.13, 95% CI: 1.00-1.27, p=0.05). Stratification by ethnicity indicated an association between TLR9 -1237T/C polymorphism and IBDs risk in Caucasians (recessive model, OR: 1.59, 95% CI: 1.02-2.47, p=0.04; homozygote comparison, OR: 1.62, 95% CI: 1.04-2.52, p=0.03; allele model, OR: 1.12, 95% CI: 1.00-1.27, p=0.05). When stratified by disease type, significant correlation were only found in the Crohn's disease subgroup (recessive model, OR: 1.69, 95% CI: 1.05-2.73, p=0.03; homozygote model, OR: 1.74, 95% CI: 1.07-2.82, p=0.02; allele model, OR: 1.15, 95% CI: 1.01-1.32, p=0.04).
CONCLUSION
The present study suggested that the TLR9 -1237T/C polymorphism might act as a risk factor in the development of IBDs, particularly in Caucasians.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kaser A, Zeissig S, Blumberg RS. Inflammatory bowel disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 2010; 28:573–621.
Article2. Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and established and evolving therapies. Lancet. 2007; 369:1641–1657.
Article3. Loftus EV Jr. Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:1504–1517.
Article4. Xavier RJ, Podolsky DK. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2007; 448:427–434.
Article5. Khor B, Gardet A, Xavier RJ. Genetics and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2011; 474:307–317.
Article6. Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003; 21:335–376.
Article7. Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004; 4:499–511.
Article8. Wagner H. Interactions between bacterial CpG-DNA and TLR9 bridge innate and adaptive immunity. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2002; 5:62–69.
Article9. Hampe J, Lynch NJ, Daniels S, Bridger S, Macpherson AJ, Stokkers P, et al. Fine mapping of the chromosome 3p susceptibility locus in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2001; 48:191–197.
Article10. Omar AH, Yasunami M, Yamazaki A, Shibata H, Ofori MF, Akanmori BD, et al. Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) polymorphism associated with symptomatic malaria: a cohort study. Malar J. 2012; 11:168.
Article11. Berghöfer B, Frommer T, König IR, Ziegler A, Chakraborty T, Bein G, et al. Common human Toll-like receptor 9 polymorphisms and haplotypes: association with atopy and functional relevance. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:1147–1154.
Article12. Novak N, Yu CF, Bussmann C, Maintz L, Peng WM, Hart J, et al. Putative association of a TLR9 promoter polymorphism with atopic eczema. Allergy. 2007; 62:766–772.
Article13. Hamann L, Glaeser C, Hamprecht A, Gross M, Gomma A, Schumann RR. Toll-like receptor (TLR)-9 promotor polymorphisms and atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2006; 364:303–307.
Article14. Ye BD, Yang SK, Song K, Yang DH, Yoon SM, Kim KJ, et al. [Association of Toll-like receptor gene with Crohn's disease in Koreans]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2009; 54:377–383.
Article15. Valverde-Villegas JM, dos Santos BP, Machado MB, Jobim M, Jobim LF, Flores C, et al. G2848A and T-1237C polymorphisms of the TLR9 gene and susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease in patients from southern Brazil. Tissue Antigens. 2014; 83:190–192.
Article16. Török HP, Glas J, Tonenchi L, Bruennler G, Folwaczny M, Folwaczny C. Crohn's disease is associated with a toll-like receptor-9 polymorphism. Gastroenterology. 2004; 127:365–366.
Article17. Török HP, Glas J, Endres I, Tonenchi L, Teshome MY, Wetzke M, et al. Epistasis between Toll-like receptor-9 polymorphisms and variants in NOD2 and IL23R modulates susceptibility to Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:1723–1733.
Article18. Shen XY, Shi RH, Wang Y, Zhang HJ, Zhou XQ, Shen FC, et al. [Toll-like receptor gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease in Chinese Han and Caucasian populations]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010; 90:1416–1420.19. Petermann I, Huebner C, Browning BL, Gearry RB, Barclay ML, Kennedy M, et al. Interactions among genes influencing bacterial recognition increase IBD risk in a population-based New Zealand cohort. Hum Immunol. 2009; 70:440–446.
Article20. Hotte NS, Salim SY, Tso RH, Albert EJ, Bach P, Walker J, et al. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease exhibit dysregulated responses to microbial DNA. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e37932.
Article21. Hong J, Leung E, Fraser AG, Merriman TR, Vishnu P, Krissansen GW. TLR2, TLR4 and TLR9 polymorphisms and Crohn's disease in a New Zealand Caucasian cohort. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 22:1760–1766.
Article22. Nakaoka H, Inoue I. Meta-analysis of genetic association studies: methodologies, between-study heterogeneity and winner's curse. J Hum Genet. 2009; 54:615–623.
Article23. Dai YE, Tang L, Healy J, Sinnett D. Contribution of polymorphisms in IKZF1 gene to childhood acute leukemia: a meta-analysis of 33 case-control studies. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e113748.
Article24. Thakkinstian A, D'Este C, Eisman J, Nguyen T, Attia J. Meta-analysis of molecular association studies: vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and BMD as a case study. J Bone Miner Res. 2004; 19:419–428.
Article25. Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH. Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med. 1997; 127:820–826.
Article26. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327:557–560.
Article27. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.
Article28. Abraham C, Cho JH. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:2066–2078.
Article29. Bouma G, Strober W. The immunological and genetic basis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003; 3:521–533.
Article30. Van Limbergen J, Wilson DC, Satsangi J. The genetics of Crohn's disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2009; 10:89–116.
Article31. Duerr RH, Taylor KD, Brant SR, Rioux JD, Silverberg MS, Daly MJ, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science. 2006; 314:1461–1463.
Article32. Ogura Y, Bonen DK, Inohara N, Nicolae DL, Chen FF, Ramos R, et al. A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn's disease. Nature. 2001; 411:603–606.
Article33. Lazarus R, Klimecki WT, Raby BA, Vercelli D, Palmer LJ, Kwiatkowski DJ, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the Toll-like receptor 9 gene (TLR9): frequencies, pairwise linkage disequilibrium, and haplotypes in three U.S. ethnic groups and exploratory case-control disease association studies. Genomics. 2003; 81:85–91.
Article34. Hur JW, Shin HD, Park BL, Kim LH, Kim SY, Bae SC. Association study of Toll-like receptor 9 gene polymorphism in Korean patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Tissue Antigens. 2005; 65:266–270.
Article35. Etem EO, Elyas H, Ozgocmen S, Yıldırım A, Godekmerdan A. The investigation of toll-like receptor 3, 9 and 10 gene polymorphisms in Turkish rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatol Int. 2011; 31:1369–1374.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association Between Toll-Like Receptors/CD14 Gene Polymorphisms and Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Korean Population
- Lipopolysaccharide: Basic Biochemistry, Intracellular Signaling, and Physiological Impacts in the Gut
- Association of Toll-Like Receptor Gene with Crohn's Disease in Koreans
- Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor Genes With Asthma Risk: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Meta-Analysis of Genetic Association Studies