Int J Stem Cells.
2019 Nov;12(3):400-409. 10.15283/ijsc18143.
The Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Microvesicles on the Treatment of Experimental CCL4 Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. dinasabry@kasralainy.edu.eg
- 2Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt.
- KMID: 2465880
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15283/ijsc18143
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
The release of microvesicles (MVs) from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has been implicated in intercellular communication, and may contribute to beneficial paracrine effects of stem cell-based therapies. We investigated the effect of administration of MSC-MVs on the therapeutic potential of carbon tetrachloride (CCLâ‚„) induced liver fibrosis in rats.
METHODS
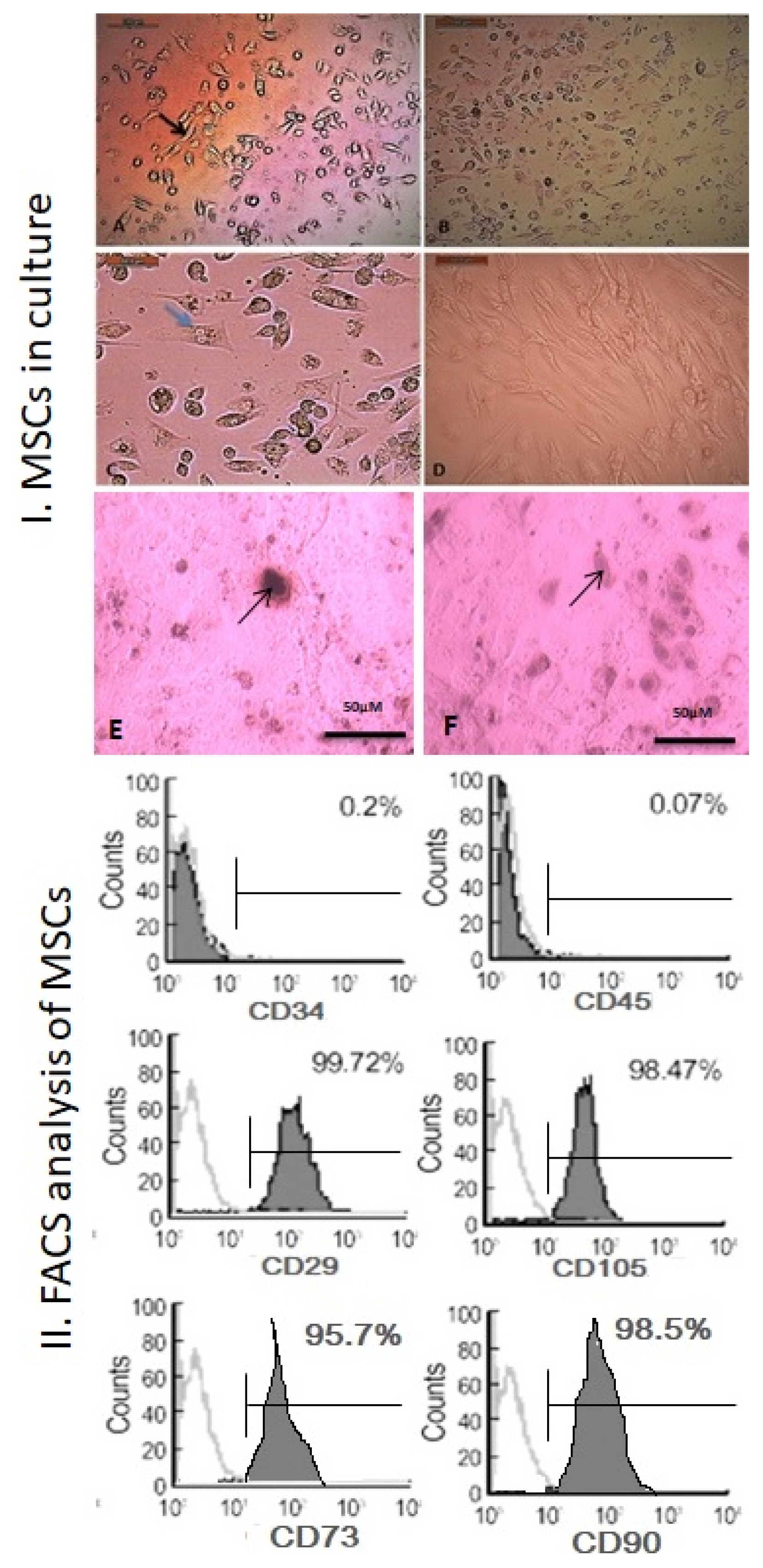
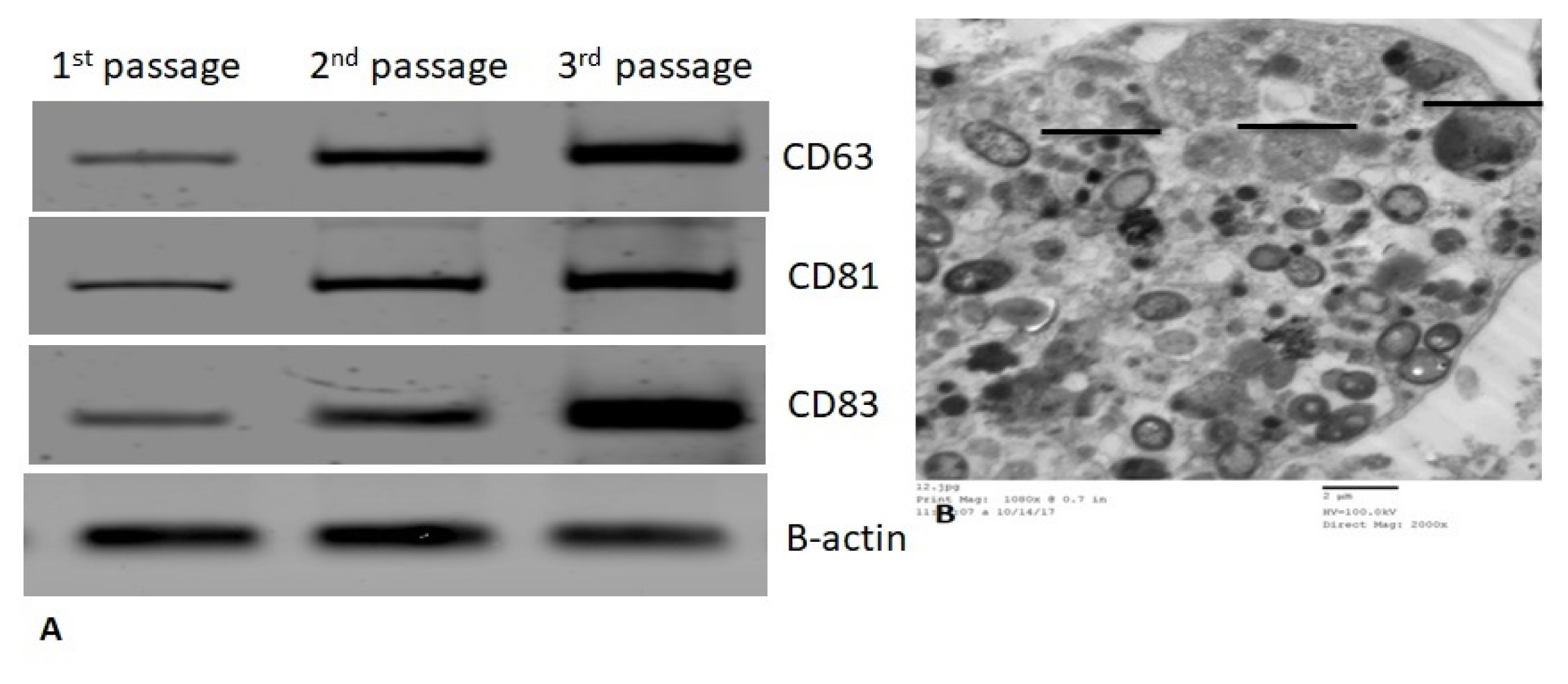
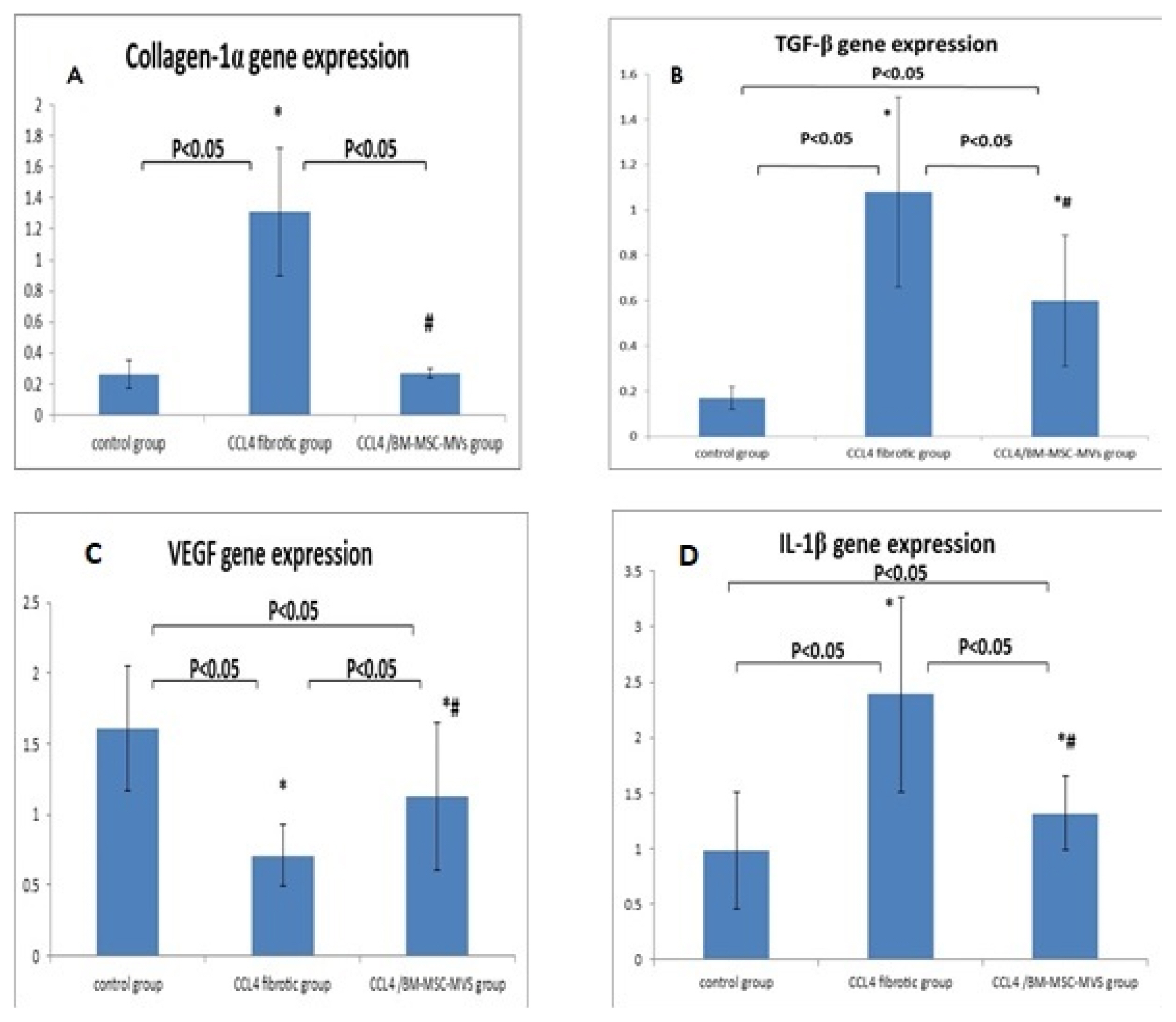
Our work included: isolation and further identification of bone marrow MSC-MVs by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Liver fibrosis was induced in rats by CCl4 followed by injection of prepared MSC-MVs in injured rats. The effects of MSC-MVs were evaluated by biochemical analysis of liver functions, RNA gene expression quantitation for collagen-1α, transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by real time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) techniques. Finally histopathological examination of the liver tissues was assessed for all studied groups.
RESULTS
BM-MSC-MVs treated group showed significant increase in serum albumin levels, VEGF quantitative gene expression (p < 0.05), while it showed a significant decrease in serum alanine transaminase (ALT) enzyme levels, quantitative gene expression of TGF-β, collagen-1α, IL-1β compared to CCL₄ fibrotic group (p < 0.05). Additionally, the histopathological assessment of the liver tissues of BM-MSC-MVs treated group showed marked decrease in the collagen deposition & improvement of histopathological picture in comparison with CCL₄ fibrotic group.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study demonstrates that BM-MSC-MVs possess anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and pro-angiogenic properties which can promote the resolution of CCLâ‚„ induced liver fibrosis in rats.
MeSH Terms
-
Alanine Transaminase
Animals
Bone Marrow
Carbon Tetrachloride
Collagen
Gene Expression
Liver Cirrhosis*
Liver*
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells*
Microscopy, Electron, Transmission
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Rats*
Reverse Transcription
RNA
Serum Albumin
Transforming Growth Factors
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Alanine Transaminase
Carbon Tetrachloride
Collagen
RNA
Serum Albumin
Transforming Growth Factors
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Koyama Y, Xu J, Liu X, Brenner DA. New developments on the treatment of liver fibrosis. Dig Dis. 2016; 34:589–956. DOI: 10.1159/000445269. PMID: 27332862. PMCID: PMC4961096.
Article2. Eom YW, Kim G, Baik SK. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for cirrhosis: present and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:10253–10261. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i36.10253. PMID: 26420953. PMCID: PMC4579873.
Article3. Guo Y, Chen B, Chen LJ, Zhang CF, Xiang C. Current status and future prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for liver fibrosis. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016; 17:831–841. DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1600101. PMID: 27819130. PMCID: PMC5120225.
Article4. Rengasamy M, Singh G, Fakharuzi NA, Siddikuzzaman , Balasubramanian S, Swamynathan P, Thej C, Sasidharan G, Gupta PK, Das AK, Rahman AZA, Fakiruddin KS, Nian LM, Zakaria Z, Majumdar AS. Transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells reduces liver fibrosis more effectively than Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017; 8:143. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-017-0595-1. PMID: 28610623. PMCID: PMC5470281.5. Kharaziha P, Hellström PM, Noorinayer B, Farzaneh F, Aghajani K, Jafari F, Telkabadi M, Atashi A, Honardoost M, Zali MR, Soleimani M. Improvement of liver function in liver cirrhosis patients after autologous mesenchymal stem cell injection: a phase I–II clinical trial. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 21:1199–1205. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32832a1f6c. PMID: 19455046.
Article6. Jang YO, Kim MY, Cho MY, Baik SK, Cho YZ, Kwon SO. Effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on hepatic fibrosis in a thioacetamide-induced cirrhotic rat model. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014; 14:198. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-014-0198-6. PMID: 25425284. PMCID: PMC4251876.
Article7. Milosavljevic N, Gazdic M, Simovic Markovic B, Arsenijevic A, Nurkovic J, Dolicanin Z, Jovicic N, Jeftic I, Djonov V, Arsenijevic N, Lukic ML, Volarevic V. Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate liver fibrosis by suppressing Th17 cells - an experimental study. Transpl Int. 2018; 31:102–115. DOI: 10.1111/tri.13023. PMID: 28805262.
Article8. Berardis S, Dwisthi Sattwika P, Najimi M, Sokal EM. Use of mesenchymal stem cells to treat liver fibrosis: current situation and future prospects. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:742–758. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.742. PMID: 25624709. PMCID: PMC4299328.
Article9. Jang YO, Jun BG, Baik SK, Kim MY, Kwon SO. Inhibition of hepatic stellate cells by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in hepatic fibrosis. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015; 21:141–149. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2015.21.2.141. PMID: 26157751. PMCID: PMC4493357.
Article10. Amin MA, Sabry D, Rashed LA, Aref WM, el-Ghobary MA, Farhan MS, Fouad HA, Youssef YA. Short-term evaluation of autologous transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with cirrhosis: Egyptian study. Clin Transplant. 2013; 27:607–612. DOI: 10.1111/ctr.12179. PMID: 23923970.
Article11. Wang N, Li Q, Zhang L, Lin H, Hu J, Li D, Shi S, Cui S, Zhou J, Ji J, Wan J, Cai G, Chen X. Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate peritoneal injury through secretion of TSG-6. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e43768. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043768. PMID: 22912904. PMCID: PMC3422344.
Article12. Baglio SR, Pegtel DM, Baldini N. Mesenchymal stem cell secreted vesicles provide novel opportunities in (stem) cell-free therapy. Front Physiol. 2012; 3:359. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00359. PMID: 22973239. PMCID: PMC3434369.
Article13. Bruno S, Grange C, Deregibus MC, Calogero RA, Saviozzi S, Collino F, Morando L, Busca A, Falda M, Bussolati B, Tetta C, Camussi G. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 20:1053–1067. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008070798. PMID: 19389847. PMCID: PMC2676194.
Article14. Biancone L, Bruno S, Deregibus MC, Tetta C, Camussi G. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012; 27:3037–3042. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfs168. PMID: 22851627.
Article15. Hulsmans M, Holvoet P. MicroRNA-containing microvesicles regulating inflammation in association with atherosclerotic disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2013; 100:7–18. DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvt161. PMID: 23774505.
Article16. Sabin K, Kikyo N. Microvesicles as mediators of tissue regeneration. Transl Res. 2014; 163:286–295. DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.10.005. PMID: 24231336. PMCID: PMC3976717.
Article17. Kilpinen L, Impola U, Sankkila L, Ritamo I, Aatonen M, Kilpinen S, Tuimala J, Valmu L, Levijoki J, Finckenberg P, Siljander P, Kankuri E, Mervaala E, Laitinen S. Extracellular membrane vesicles from umbilical cord blood-derived MSC protect against ischemic acute kidney injury, a feature that is lost after inflammatory conditioning. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013; DOI: 10.3402/jev.v2i0.21927. PMID: 24349659. PMCID: PMC3860334.
Article18. Yin H, Jiang H. Application prospect of stem cell-derived microvesicles in regeneration of injured tissues. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2015; 32:688–692. Chinese. PMID: 26486001.19. Abdel Aziz MT, Atta HM, Mahfouz S, Fouad HH, Roshdy NK, Ahmed HH, Rashed LA, Sabry D, Hassouna AA, Hasan NM. Therapeutic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on experimental liver fibrosis. Clin Biochem. 2007; 40:893–899. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2007.04.017. PMID: 17543295.
Article20. Gatti S, Bruno S, Deregibus MC, Sordi A, Cantaluppi V, Tetta C, Camussi G. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011; 26:1474–1483. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfr015. PMID: 21324974.
Article21. Zhao DC, Lei JX, Chen R, Yu WH, Zhang XM, Li SN, Xiang P. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against experimental liver fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:3431–3440. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i22.3431. PMID: 15948250. PMCID: PMC4315999.
Article22. Qu Y, Zhang Q, Cai X, Li F, Ma Z, Xu M, Lu L. Exosomes derived from miR-181-5p-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy activation. J Cell Mol Med. 2017; 21:2491–2502. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13170. PMID: 28382720. PMCID: PMC5618698.
Article23. Chan YH. Biostatistics 102: quantitative data--parametric & non-parametric tests. Singapore Med J. 2003; 44:391–396. PMID: 14700417.24. Chan YH. Biostatistics 104: correlational analysis. Singapore Med J. 2003; 44:614–619. PMID: 14770254.25. Truong NH, Nguyen NH, Le TV, Vu NB, Huynh N, Nguyen TV, Le HM, Phan NK, Pham PV. Comparison of the treatment efficiency of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation via tail and portal veins in CCl4-induced mouse liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Int. 2016; 2016:5720413. DOI: 10.1155/2016/5720413. PMID: 26839564. PMCID: PMC4709782.26. Nargesi AA, Lerman LO, Eirin A. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for renal repair. Curr Gene Ther. 2017; 17:29–42. DOI: 10.2174/1566523217666170412110724. PMID: 28403795. PMCID: PMC5628022.
Article27. Yu B, Zhang X, Li X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014; 15:4142–4157. DOI: 10.3390/ijms15034142. PMID: 24608926. PMCID: PMC3975389.
Article28. Rad F, Pourfathollah AA, Yari F, Mohammadi S, Kheirandish M. Microvesicles preparation from mesenchymal stem cells. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2016; 30:398. PMID: 27579288. PMCID: PMC5004526.29. Monsel A, Zhu YG, Gennai S, Hao Q, Hu S, Rouby JJ, Rosenzwajg M, Matthay MA, Lee JW. Therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles in severe pneumonia in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 192:324–336. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201410-1765OC. PMID: 26067592. PMCID: PMC4584251.
Article30. Zou X, Zhang G, Cheng Z, Yin D, Du T, Ju G, Miao S, Liu G, Lu M, Zhu Y. Microvesicles derived from human Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing CX3CL1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014; 5:40. DOI: 10.1186/scrt428. PMID: 24646750. PMCID: PMC4055103.
Article31. Salem M, Helal O, Metwaly H, El Hady A, Ahmed S. Histological and immunohistochemical study of the role of stem cells, conditioned medium and microvesicles in treatment of experimentally induced acute kidney injury in rats. J Med Histol. 2017; 1:69–83. DOI: 10.21608/jmh.2017.1108.1018.
Article32. Sharma AK, Lu G, Salmon MD, Gehrau RC, Mas VR, Weiss ML, Ailawadi G, Upchurch GR. Human mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles mitigate aortic smooth muscle cell activation via miR-147 and attenuate aortic aneurysm formation. Circulation. 2015; 132:A11550.33. Dong S, Chen QL, Song YN, Sun Y, Wei B, Li XY, Hu YY, Liu P, Su SB. Mechanisms of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis with combined transcriptomic and proteomic analysis. J Toxicol Sci. 2016; 41:561–572. DOI: 10.2131/jts.41.561. PMID: 27452039.
Article34. Shrestha N, Chand L, Han MK, Lee SO, Kim CY, Jeong YJ. Glutamine inhibits CCl4 induced liver fibrosis in mice and TGF-β1 mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mouse hepatocytes. Food Chem Toxicol. 2016; 93:129–137. DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.04.024. PMID: 27137983.
Article35. Lei Q, Liu T, Gao F, Xie H, Sun L, Zhao A, Ren W, Guo H, Zhang L, Wang H, Chen Z, Guo AY, Li Q. Microvesicles as potential biomarkers for the identification of senescence in human mesenchymal stem cells. Theranostics. 2017; 7:2673–2689. DOI: 10.7150/thno.18915. PMID: 28819455. PMCID: PMC5558561.
Article36. Haga H, Yan IK, Takahashi K, Matsuda A, Patel T. Extracellular Vesicles from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve survival from lethal hepatic failure in mice. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017; 6:1262–1272. DOI: 10.1002/sctm.16-0226. PMID: 28213967. PMCID: PMC5442843.
Article37. Senior JR. Alanine aminotransferase: a clinical and regulatory tool for detecting liver injury-past, present, and future. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 92:332–339. DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2012.108. PMID: 22871997.
Article38. Kang KS. Abnormality on liver function test. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2013; 16:225–232. DOI: 10.5223/pghn.2013.16.4.225. PMID: 24511518. PMCID: PMC3915727.
Article39. Song YM, Lian CH, Wu CS, Ji AF, Xiang JJ, Wang XY. Effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplanted via the portal vein or tail vein on liver injury in rats with liver cirrhosis. Exp Ther Med. 2015; 9:1292–1298. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2015.2232. PMID: 25780424. PMCID: PMC4353761.
Article40. Chen J, Li C, Chen L. The role of microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells in lung diseases. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:985814. DOI: 10.1155/2015/985814. PMID: 26064975. PMCID: PMC4443645.
Article41. DeLeve LD. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and liver regeneration. J Clin Invest. 2013; 123:1861–1866. DOI: 10.1172/JCI66025. PMID: 23635783. PMCID: PMC3635729.
Article42. Adas G, Koc B, Adas M, Duruksu G, Subasi C, Kemik O, Kemik A, Sakiz D, Kalayci M, Purisa S, Unal S, Karaoz E. Effects of mesenchymal stem cells and VEGF on liver regeneration following major resection. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2016; 401:725–740. DOI: 10.1007/s00423-016-1380-9. PMID: 27094936.
Article43. Lee SC, Jeong HJ, Lee SK, Kim SJ. Hypoxic conditioned medium from human adipose-derived stem cells promotes mouse liver regeneration through JAK/STAT3 signaling. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016; 5:816–825. DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0191. PMID: 27102647. PMCID: PMC4878330.
Article44. Zou X, Gu D, Xing X, Cheng Z, Gong D, Zhang G, Zhu Y. Human mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate renal ischemic reperfusion injury and enhance angiogenesis in rats. Am J Transl Res. 2016; 8:4289–4299. PMID: 27830012. PMCID: PMC5095321.45. Zhang HC, Liu XB, Huang S, Bi XY, Wang HX, Xie LX, Wang YQ, Cao XF, Lv J, Xiao FJ, Yang Y, Guo ZK. Microvesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells stimulated by hypoxia promote angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo. Stem Cells Dev. 2012; 21:3289–3297. DOI: 10.1089/scd.2012.0095. PMID: 22839741. PMCID: PMC3516422.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of CCL4 Induced Liver Fibrosis in Albino Rats: A Histological and Immunohistochemical Study
- The effects of Broad Spectrum Antibiotics and Endotoxin to the Carbon Tetrachloride-induced Liver Injury
- Therapeutic Potential of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Experimental Liver Injury Induced by Schistosoma mansoni: A Histological Study
- Inhibitory Effect of Tetrandrine on Extracellular Matrix Deposition in Rat Hepatic Fibrosis
- The Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles Versus Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Liver Damage