Diabetes Metab J.
2019 Oct;43(5):659-674. 10.4093/dmj.2018.0196.
Low-Frequency Intermittent Hypoxia Suppresses Subcutaneous Adipogenesis and Induces Macrophage Polarization in Lean Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, Hong Kong. msmip@hku.hk
- 2Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Center of Respiratory Medicine, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China.
- 3Research Centre of Heart, Brain, Hormone and Healthy Aging, The University of Hong Kong Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, Hong Kong.
- 4Department of Pharmacology & Pharmacy, The University of Hong Kong Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, Hong Kong.
- KMID: 2460959
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0196
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
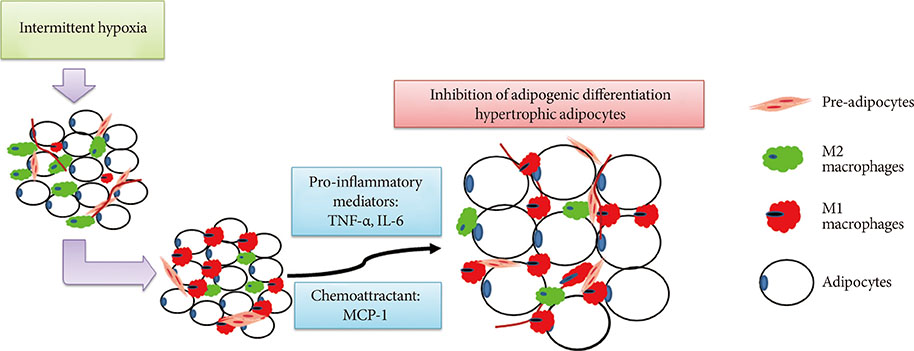
The relationship between obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) and metabolic disorders is complex and highly associated. The impairment of adipogenic capacity in pre-adipocytes may promote adipocyte hypertrophy and increase the risk of further metabolic dysfunction. We hypothesize that intermittent hypoxia (IH), as a pathophysiologic feature of OSA, may regulate adipogenesis by promoting macrophage polarization.
METHODS
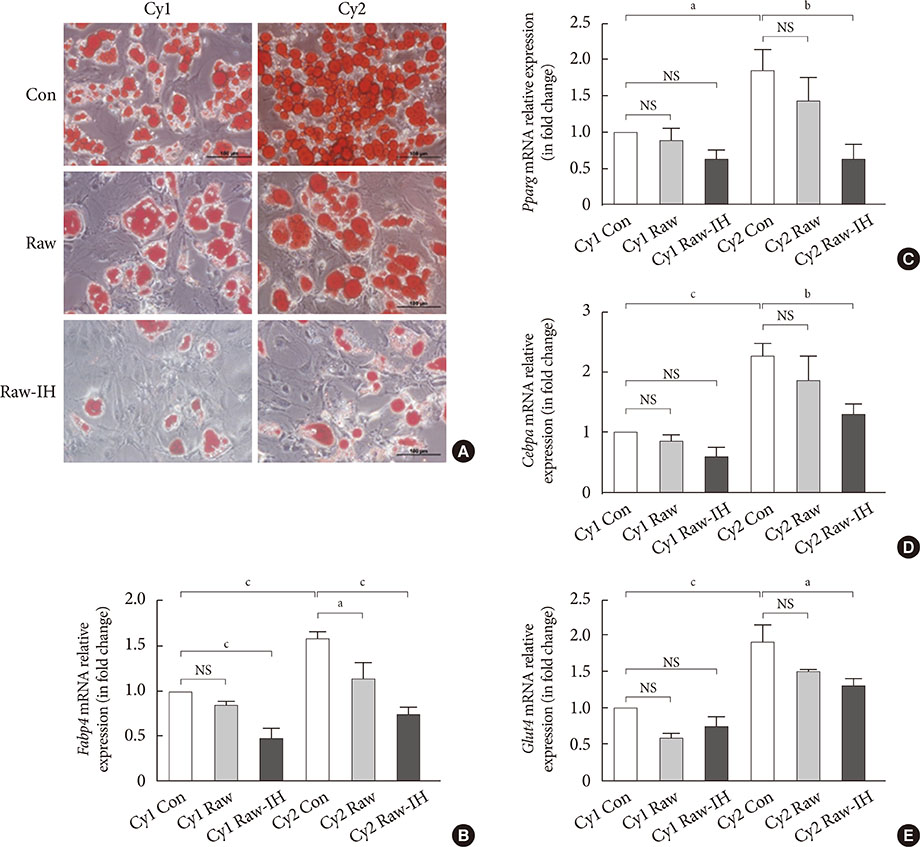
Male C57BL/6N mice were exposed to either IH (240 seconds of 10% Oâ‚‚ followed by 120 seconds of 21% Oâ‚‚, i.e., 10 cycles/hour) or intermittent normoxia (IN) for 6 weeks. Stromal-vascular fractions derived from subcutaneous (SUB-SVF) and visceral (VIS-SVF) adipose tissues were cultured and differentiated. Conditioned media from cultured RAW 264.7 macrophages after air (Raw) or IH exposure (Raw-IH) were incubated with SUB-SVF during adipogenic differentiation.
RESULTS
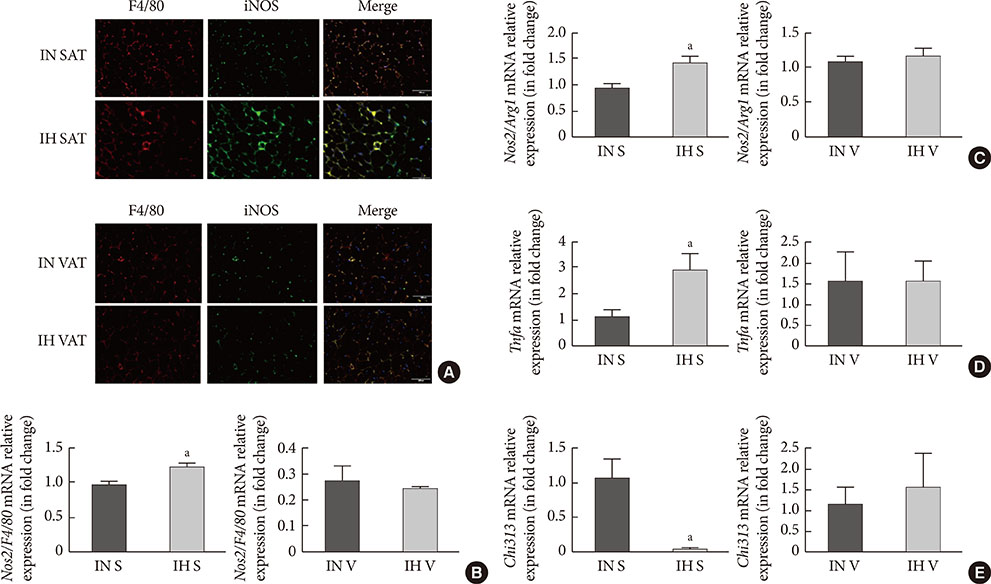
Adipogenic differentiation of SUB-SVF but not VIS-SVF from IH-exposed mice was significantly downregulated in comparison with that derived from IN-exposed mice. IH-exposed mice compared to IN-exposed mice showed induction of hypertrophic adipocytes and increased preferential infiltration of M1 macrophages in subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) compared to visceral adipose tissue. Complementary in vitro analysis demonstrated that Raw-IH media significantly enhanced inhibition of adipogenesis of SUB-SVF compared to Raw media, in agreement with corresponding gene expression levels of differentiation-associated markers and adipogenic transcription factors.
CONCLUSION
Low frequency IH exposure impaired adipogenesis of SAT in lean mice, and macrophage polarization may be a potential mechanism for the impaired adipogenesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rutkowski JM, Stern JH, Scherer PE. The cell biology of fat expansion. J Cell Biol. 2015; 208:501–512.2. Kryger MH, Roth T, Dement WC. Chapter 118, Obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic disorders. Principles and practice of sleep medicine. 6th ed. New York: Elsevier Inc.;2017. p. 1167–1178.3. Hoyos CM, Drager LF, Patel SR. OSA and cardiometabolic risk: what's the bottom line? Respirology. 2017; 22:420–429.4. Rosen ED, MacDougald OA. Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006; 7:885–896.5. Murphy AM, Thomas A, Crinion SJ, Kent BD, Tambuwala MM, Fabre A, Pepin JL, Roche HM, Arnaud C, Ryan S. Intermittent hypoxia in obstructive sleep apnoea mediates insulin resistance through adipose tissue inflammation. Eur Respir J. 2017; 49:1601731.6. Khalyfa A, Qiao Z, Gileles-Hillel A, Khalyfa AA, Akbarpour M, Popko B, Gozal D. Activation of the integrated stress response and metabolic dysfunction in a murine model of sleep apnea. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017; 57:477–486.7. Gozal D, Gileles-Hillel A, Cortese R, Li Y, Almendros I, Qiao Z, Khalyfa AA, Andrade J, Khalyfa A. Visceral white adipose tissue after chronic intermittent and sustained hypoxia in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017; 56:477–487.8. Carreras A, Zhang SX, Almendros I, Wang Y, Peris E, Qiao Z, Gozal D. Resveratrol attenuates intermittent hypoxia-induced macrophage migration to visceral white adipose tissue and insulin resistance in male mice. Endocrinology. 2015; 156:437–443.9. Hammarstedt A, Gogg S, Hedjazifar S, Nerstedt A, Smith U. Impaired adipogenesis and dysfunctional adipose tissue in human hypertrophic obesity. Physiol Rev. 2018; 98:1911–1941.10. Almendros I, Gileles-Hillel A, Khalyfa A, Wang Y, Zhang SX, Carreras A, Farre R, Gozal D. Adipose tissue macrophage polarization by intermittent hypoxia in a mouse model of OSA: effect of tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2015; 361:233–239.11. Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117:175–184.12. Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Staels B. Macrophage polarization in metabolic disorders: functions and regulation. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011; 22:365–372.13. Liu LF, Craig CM, Tolentino LL, Choi O, Morton J, Rivas H, Cushman SW, Engleman EG, McLaughlin T. Adipose tissue macrophages impair preadipocyte differentiation in humans. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0170728.14. McNicholas WT, Bonsignore MR, Levy P, Ryan S. Mild obstructive sleep apnoea: clinical relevance and approaches to management. Lancet Respir Med. 2016; 4:826–834.15. Hoffstedt J, Arner E, Wahrenberg H, Andersson DP, Qvisth V, Lofgren P, Ryden M, Thorne A, Wiren M, Palmer M, Thorell A, Toft E, Arner P. Regional impact of adipose tissue morphology on the metabolic profile in morbid obesity. Diabetologia. 2010; 53:2496–2503.16. Gustafson B, Hedjazifar S, Gogg S, Hammarstedt A, Smith U. Insulin resistance and impaired adipogenesis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 26:193–200.17. Esser N, Legrand-Poels S, Piette J, Scheen AJ, Paquot N. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014; 105:141–150.18. Amano SU, Cohen JL, Vangala P, Tencerova M, Nicoloro SM, Yawe JC, Shen Y, Czech MP, Aouadi M. Local proliferation of macrophages contributes to obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation. Cell Metab. 2014; 19:162–171.19. Boutens L, Stienstra R. Adipose tissue macrophages: going off track during obesity. Diabetologia. 2016; 59:879–894.20. Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 2003; 112:1796–1808.21. Gericke M, Weyer U, Braune J, Bechmann I, Eilers J. A method for long-term live imaging of tissue macrophages in adipose tissue explants. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 308:E1023–E1033.22. Fujisaka S, Usui I, Ikutani M, Aminuddin A, Takikawa A, Tsuneyama K, Mahmood A, Goda N, Nagai Y, Takatsu K, Tobe K. Adipose tissue hypoxia induces inflammatory M1 polarity of macrophages in an HIF-1α-dependent and HIF-1α-independent manner in obese mice. Diabetologia. 2013; 56:1403–1412.23. O'Rourke RW, Metcalf MD, White AE, Madala A, Winters BR, Maizlin II, Jobe BA, Roberts CT Jr, Slifka MK, Marks DL. Depot-specific differences in inflammatory mediators and a role for NK cells and IFN-gamma in inflammation in human adipose tissue. Int J Obes (Lond). 2009; 33:978–990.24. Harman-Boehm I, Bluher M, Redel H, Sion-Vardy N, Ovadia S, Avinoach E, Shai I, Kloting N, Stumvoll M, Bashan N, Rudich A. Macrophage infiltration into omental versus subcutaneous fat across different populations: effect of regional adiposity and the comorbidities of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:2240–2247.25. Zaragosi LE, Wdziekonski B, Villageois P, Keophiphath M, Maumus M, Tchkonia T, Bourlier V, Mohsen-Kanson T, Ladoux A, Elabd C, Scheideler M, Trajanoski Z, Takashima Y, Amri EZ, Lacasa D, Sengenes C, Ailhaud G, Clement K, Bouloumie A, Kirkland JL, Dani C. Activin a plays a critical role in proliferation and differentiation of human adipose progenitors. Diabetes. 2010; 59:2513–2521.26. Maumus M, Sengenes C, Decaunes P, Zakaroff-Girard A, Bourlier V, Lafontan M, Galitzky J, Bouloumie A. Evidence of in situ proliferation of adult adipose tissue-derived progenitor cells: influence of fat mass microenvironment and growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93:4098–4106.27. Constant VA, Gagnon A, Yarmo M, Sorisky A. The antiadipogenic effect of macrophage-conditioned medium depends on ERK1/2 activation. Metabolism. 2008; 57:465–472.28. Lacasa D, Taleb S, Keophiphath M, Miranville A, Clement K. Macrophage-secreted factors impair human adipogenesis: involvement of proinflammatory state in preadipocytes. Endocrinology. 2007; 148:868–877.29. Lee YH, Petkova AP, Granneman JG. Identification of an adipogenic niche for adipose tissue remodeling and restoration. Cell Metab. 2013; 18:355–367.30. Gileles-Hillel A, Kheirandish-Gozal L, Gozal D. Biological plausibility linking sleep apnoea and metabolic dysfunction. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016; 12:290–298.31. Schaefer E, Wu W, Mark C, Yang A, DiGiacomo E, Carlton-Smith C, Salloum S, Brisac C, Lin W, Corey KE, Chung RT. Intermittent hypoxia is a proinflammatory stimulus resulting in IL-6 expression and M1 macrophage polarization. Hepatol Commun. 2017; 1:326–337.32. Cawthorn WP, Heyd F, Hegyi K, Sethi JK. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibits adipogenesis via a beta-catenin/TCF4 (TCF7L2)-dependent pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2007; 14:1361–1373.33. Wang Y, Mak JCW, Lee MYK, Xu A, Ip MSM. Low-frequency intermittent hypoxia promotes subcutaneous adipogenic differentiation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018; 2018:4501757.34. Avram MM, Avram AS, James WD. Subcutaneous fat in normal and diseased states 3. Adipogenesis: from stem cell to fat cell. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007; 56:472–492.35. Garcia E, Lacasa M, Agli B, Giudicelli Y, Lacasa D. Modulation of rat preadipocyte adipose conversion by androgenic status: involvement of C/EBPs transcription factors. J Endocrinol. 1999; 161:89–97.36. Kirkland JL, Dobson DE. Preadipocyte function and aging: links between age-related changes in cell dynamics and altered fat tissue function. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997; 45:959–967.37. Casteilla L, Penicaud L, Cousin B, Calise D. Choosing an adipose tissue depot for sampling: factors in selection and depot specificity. Methods Mol Biol. 2008; 456:23–38.38. Jochmans-Lemoine A, Villalpando G, Gonzales M, Valverde I, Soria R, Joseph V. Divergent physiological responses in laboratory rats and mice raised at high altitude. J Exp Biol. 2015; 218:1035–1043.39. Poulain L, Mathieu H, Thomas A, Borel AL, Remy C, Levy P, Arnaud C, Dematteis M. Intermittent hypoxia-induced insulin resistance is associated with alterations in white fat distribution. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:11180.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Macrophage Polarization and Infection
- Generation of Connective Tissue-Free Microvascular Fragment Isolates from Subcutaneous Fat Tissue of Obese Mice
- Intermittent Fasting Modulates Immune Response by Generating Tregs via TGF-β Dependent Mechanisms in Obese Mice with Allergic Contact Dermatitis
- Retinoic acid ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by attenuating inflammation and modulating macrophage polarization through MKP-1/MAPK signaling pathway
- Paeonol accelerates skin wound healing by regulating macrophage polarization and inflammation in diabetic rats