Nat Prod Sci.
2019 Sep;25(3):261-267. 10.20307/nps.2019.25.3.261.
Dioscorea japonica Thunb. Ethanolic Extract Attenuated Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions in BALB/c Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Pharmacy, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Korea. mhyang@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Natural Products Research Institute, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Gangneung 25451, Korea. snkim@kist.re.kr
- KMID: 2459970
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2019.25.3.261
Abstract
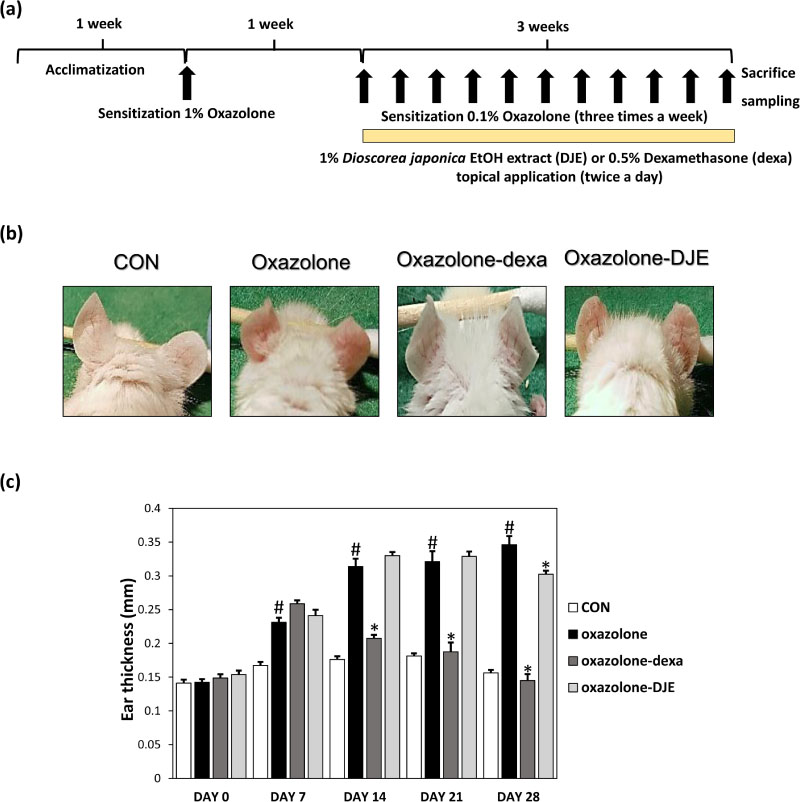
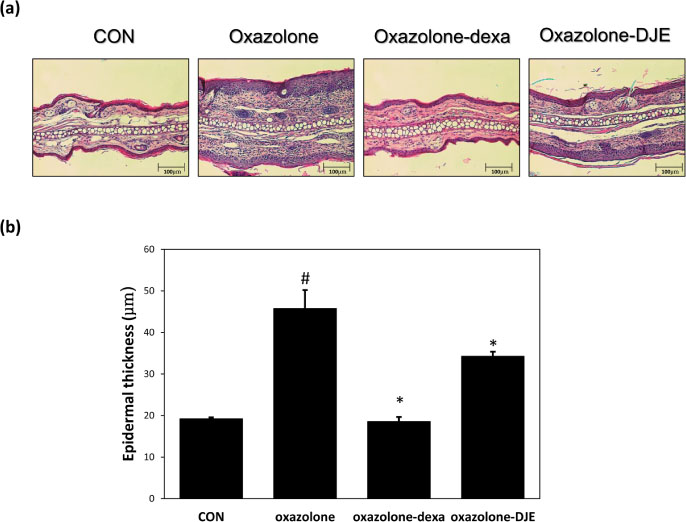
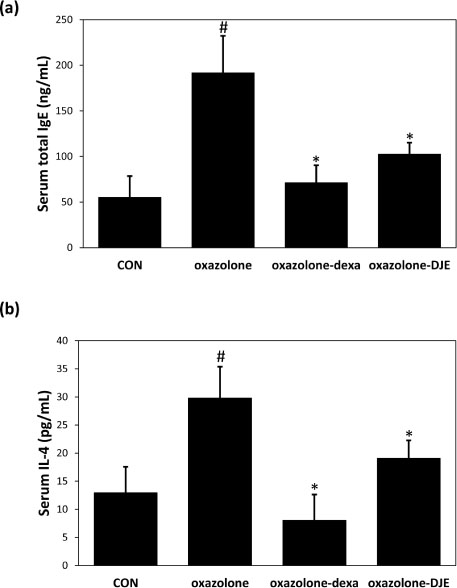
- The rhizomes of Dioscorea japonica Thunb. are widely consumed as food and also used to treat diabetes and polyuria in Korea. This study was undertaken to study the anti-atopic dermatitis effects of a 95% ethanolic extract (DJE) of D. japonica in an oxazolone-stimulated murine model of atopic dermatitis (AD). The therapeutic effects of DJE on AD-like skin lesions were assessed on both ears. DJE (1%) or dexamethasone (0.5%; the positive control) were applied to skin lesions for three weeks. Serum levels of IgE and IL-4 were assessed by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). Histopathological examinations were performed by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and toluidine blue staining and revealed DJE significantly reduced dermal thickness and inflammatory cell infiltration when applied to oxazolone-treated ear skin. DJE-treated AD mice also showed lower serum levels of IgE and IL-4 than oxazolone-stimulated controls. Our findings demonstrate DJE might be a useful safe, topical agent for the treatment of atopic diseases.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Dermatitis
Dermatitis, Atopic
Dexamethasone
Dioscorea*
Ear
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Eosine Yellowish-(YS)
Ethanol*
Hematoxylin
Immunoglobulin E
Interleukin-4
Korea
Mice*
Oxazolone
Polyuria
Rhizome
Skin*
Therapeutic Uses
Tolonium Chloride
Dexamethasone
Eosine Yellowish-(YS)
Ethanol
Hematoxylin
Immunoglobulin E
Interleukin-4
Oxazolone
Therapeutic Uses
Tolonium Chloride
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boguniewicz M, Leung DY. Immunol Rev. 2011; 242:233–246.2. Larsen FS, Hanifin JM. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2002; 22:1–24.3. Rhodes AR. Clin Rev Allergy. 1986; 4:87–99.4. Grewe M, Walther S, Gyufko K, Czech W, Schöpf E, Krutmann J. J Invest Dermatol. 1995; 105:407–410.5. Grewe M, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA, Schöpf E, Thepen T, Langeveld-Wildschut AG, Ruzicka T, Krutmann J. Immunol Today. 1998; 19:359–361.6. Jujo K, Renz H, Abe J, Gelfand EW, Leung DY. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992; 90:323–331.7. Gupta AK, Chow M. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003; 17:493–503.8. Stuetz A, Grassberger M, Meingassner JG. 1. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2001; 20:233–241.9. Kim MW. Korean J Nutr. 1998; 31:1377–1384.10. Kim MJ, Kim HN, Kang KS, Baek NI, Kim DK, Kim YS, Jeon BH, Kim SH. Int Immunopharmacol. 2004; 4:1489–1497.11. Hu K, Yao X. Cancer Invest. 2003; 21:389–393.12. Zhao G, Kan J, Li Z, Chen Z. Carbohydr Polym. 2005; 61:125–131.13. Wu JN. An illustrated Chinese Materia Medica. New York: Oxford University Press;2005. p. 264.14. Sautour M, Mitaine-Offer AC, Lacaille-Dubois MA. J Nat Med. 2007; 61:91–101.15. Liu H, Chou GX, Wu T, Guo YL, Wang SC, Wang CH, Wang ZT. 1. J Nat Prod. 2009; 72:1964–1968.16. Bellik Y, Hammoudi SM, Abdellah F, Iguer-Ouada M, Boukraâ L. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2012; 6:147–158.17. Dawid-Pać R. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013; 30:170–177.18. Kawai M, Hirano T, Higa S, Arimitsu J, Maruta M, Kuwahara Y, Ohkawara T, Hagihara K, Yamadori T, Shima Y, Ogata A, Kawase I, Tanaka T. Allergol Int. 2007; 56:113–123.19. Souto AL, Tavares JF, da Silva MS, Diniz Mde F, de Athayde-Filho PF, Barbosa Filho JM. Molecules. 2011; 16:8515–8534.20. Graf J. Skin Therapy Lett. 2000; 5:3–5.21. Lee KS, Jeong ES, Heo SH, Seo JH, Jeong DG, Choi YK. Lab Anim Res. 2010; 26:95–102.22. Man MQ, Hatano Y, Lee SH, Man M, Chang S, Feingold KR, Leung DY, Holleran W, Uchida Y, Elias PM. J Invest Dermatol. 2008; 128:79–86.23. Grewe M, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA, Schöpf E, Thepen T, Langeveld-Wildschut AG, Ruzicka T, Krutmann J. Immunol Today. 1998; 19:359–361.24. Smart JM, Kemp AS. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:796–802.25. Tao X, Yin L, Xu L, Peng J. Pharmacol Res. 2018; 137:259–269.26. Wu S, Xu H, Peng J, Wang C, Jin Y, Liu K, Sun H, Qin J. Biochimie. 2015; 110:62–72.27. Cao YJ, Xu Y, Liu B, Zheng X, Wu J, Zhang Y, Li XS, Qi Y, Sun YM, Wen WB, Hou L, Wan CP. Am J Chin Med. 2019; 47:423–437.28. Jegal J, Park NJ, Jo BG, Bong SK, Jegal H, Yang MH, Kim SN. Nutrients. 2018; 10:E1205.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gastrodia elata Blume Attenuates 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions in Balb/c Mice and SD Rats
- The Effect of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Cultured Media on Oxazolone Treated Atopic Dermatitis-Like Murine Model
- The Effect of High Dose UVA - 1 and UVA - 2 Irradiation on the Expression of Surface Markers of Epidermal Langerhans Cells and Induction of contact Hypersensitivity in Mice Skin
- Effect of DHEA Ingestion on Atopic Dermatitis-like Lesion in BALB/c Mice Sensitized by Ovalbumin
- A Novel Model for Human Atopic Dermatitis: Application of Repeated DNCB Patch in BALB/c Mice, in Comparison with NC/Nga Mice