Lab Anim Res.
2010 Mar;26(1):95-102. 10.5625/lar.2010.26.1.95.
A Novel Model for Human Atopic Dermatitis: Application of Repeated DNCB Patch in BALB/c Mice, in Comparison with NC/Nga Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea. yangkyuc@konkuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 1458946
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2010.26.1.95
Abstract
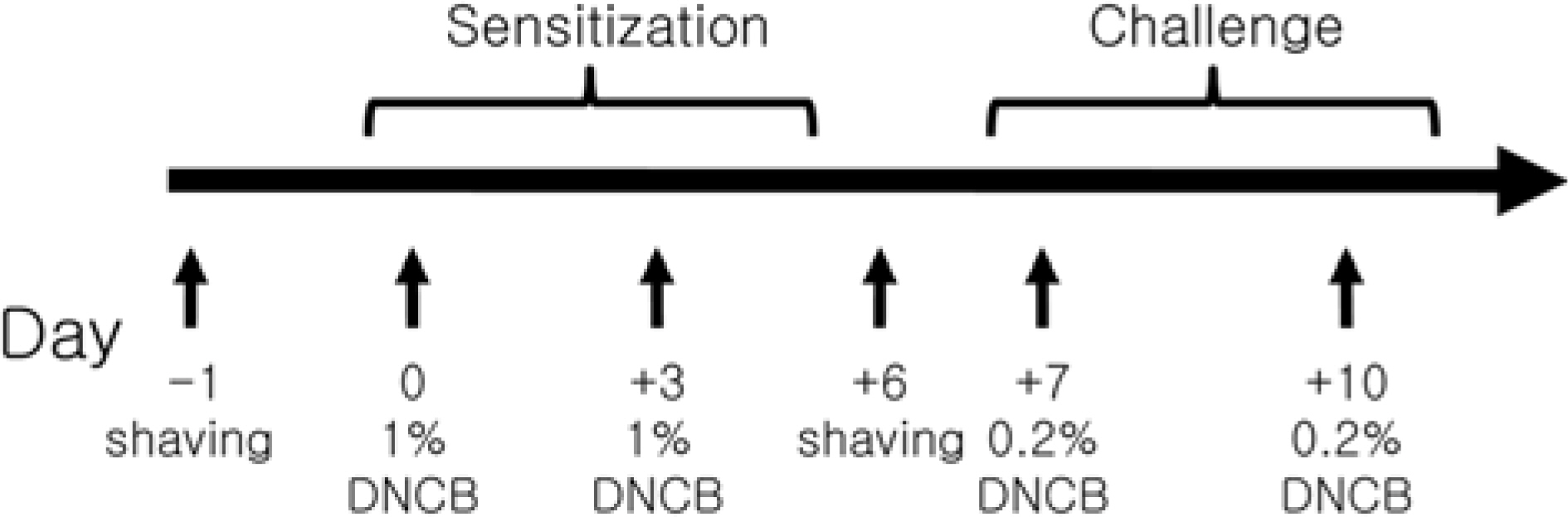
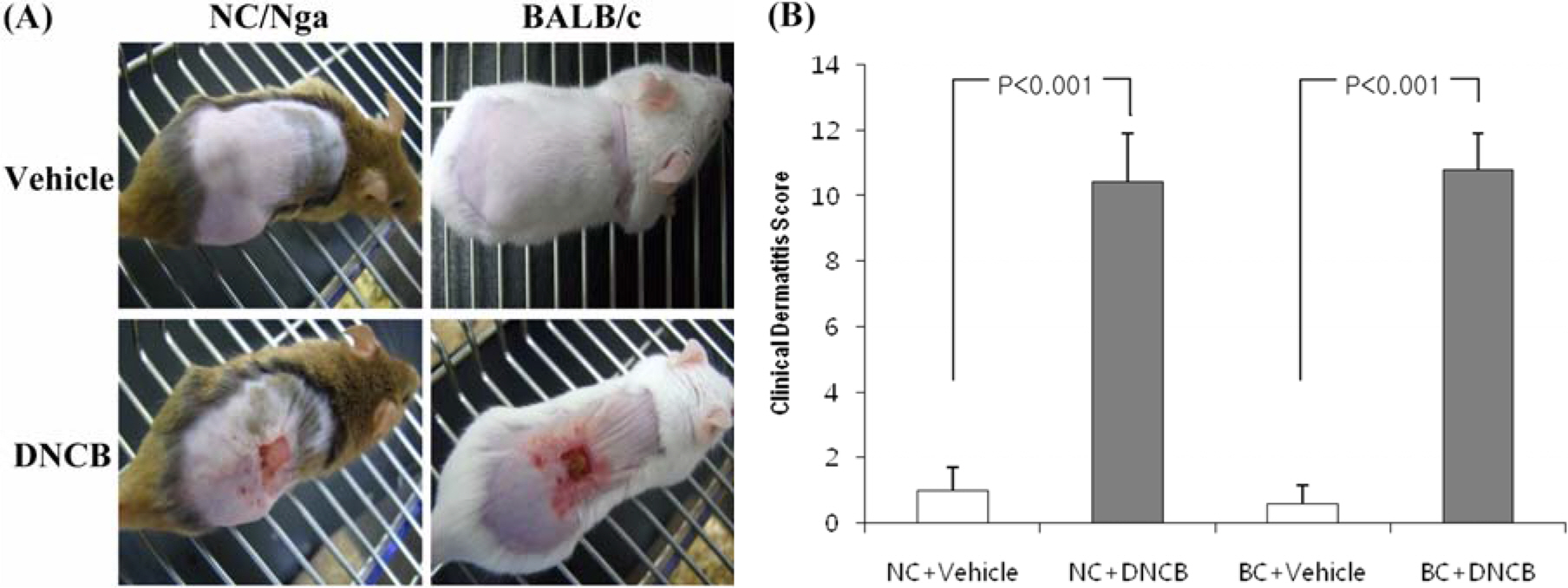
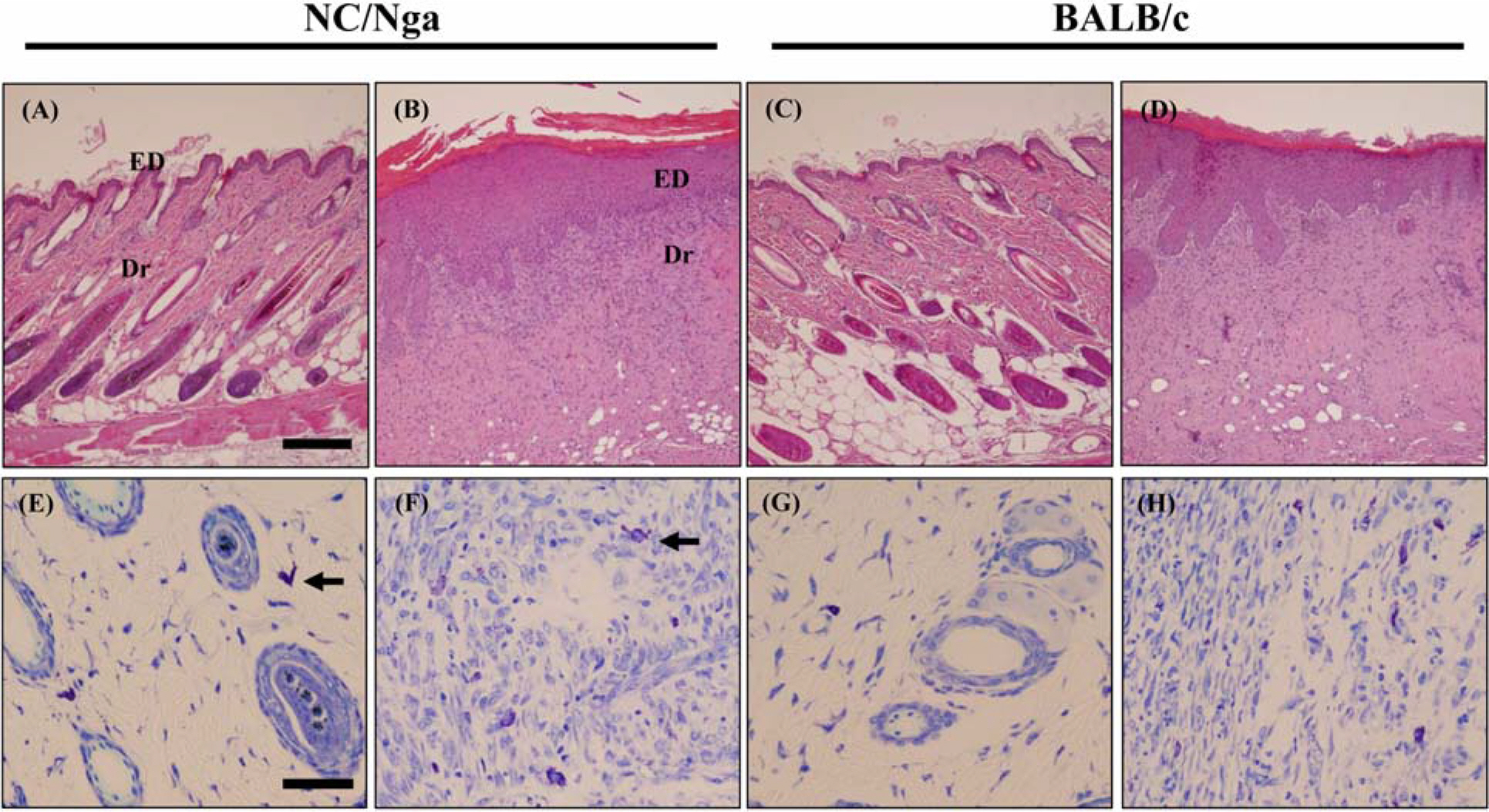
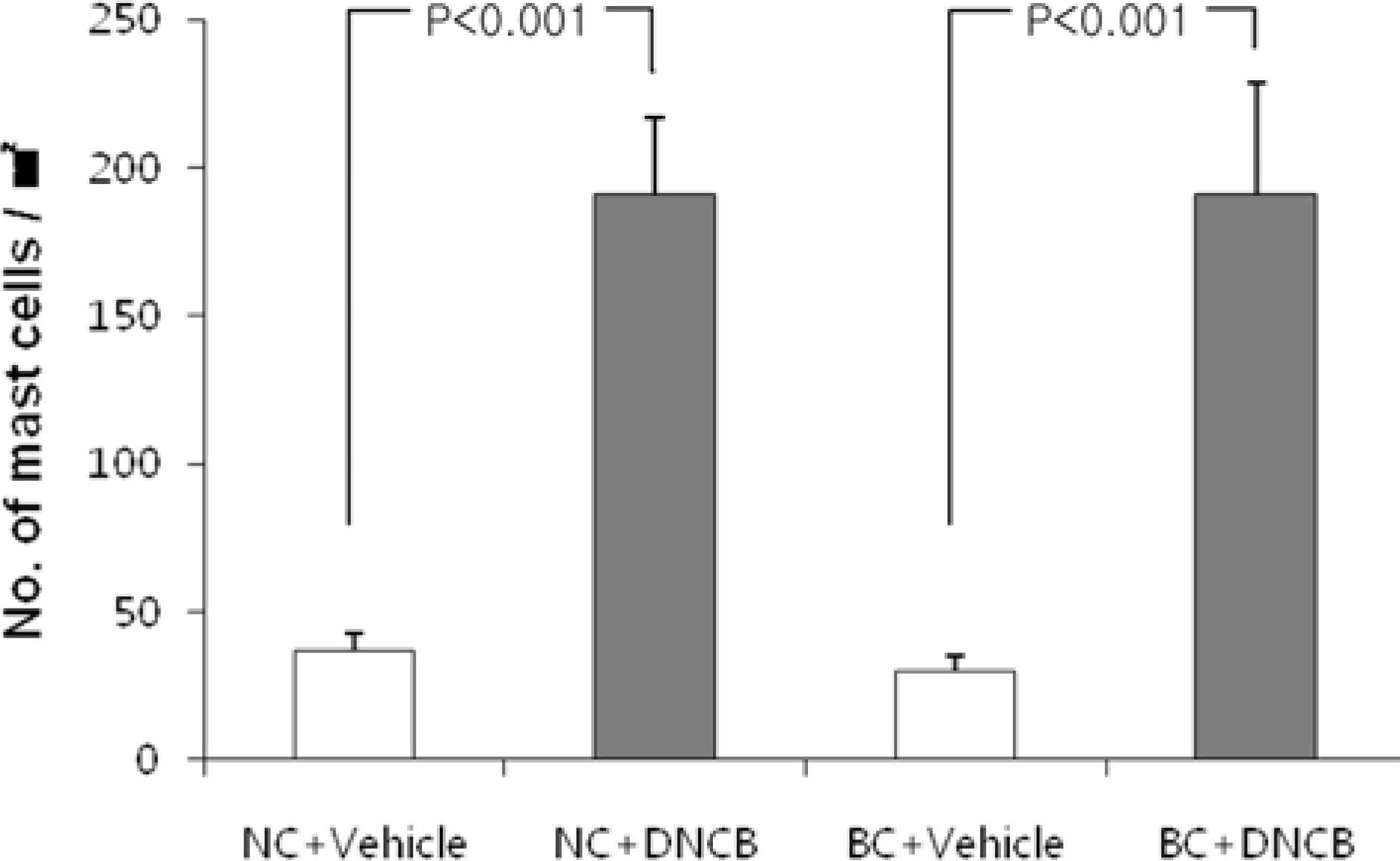
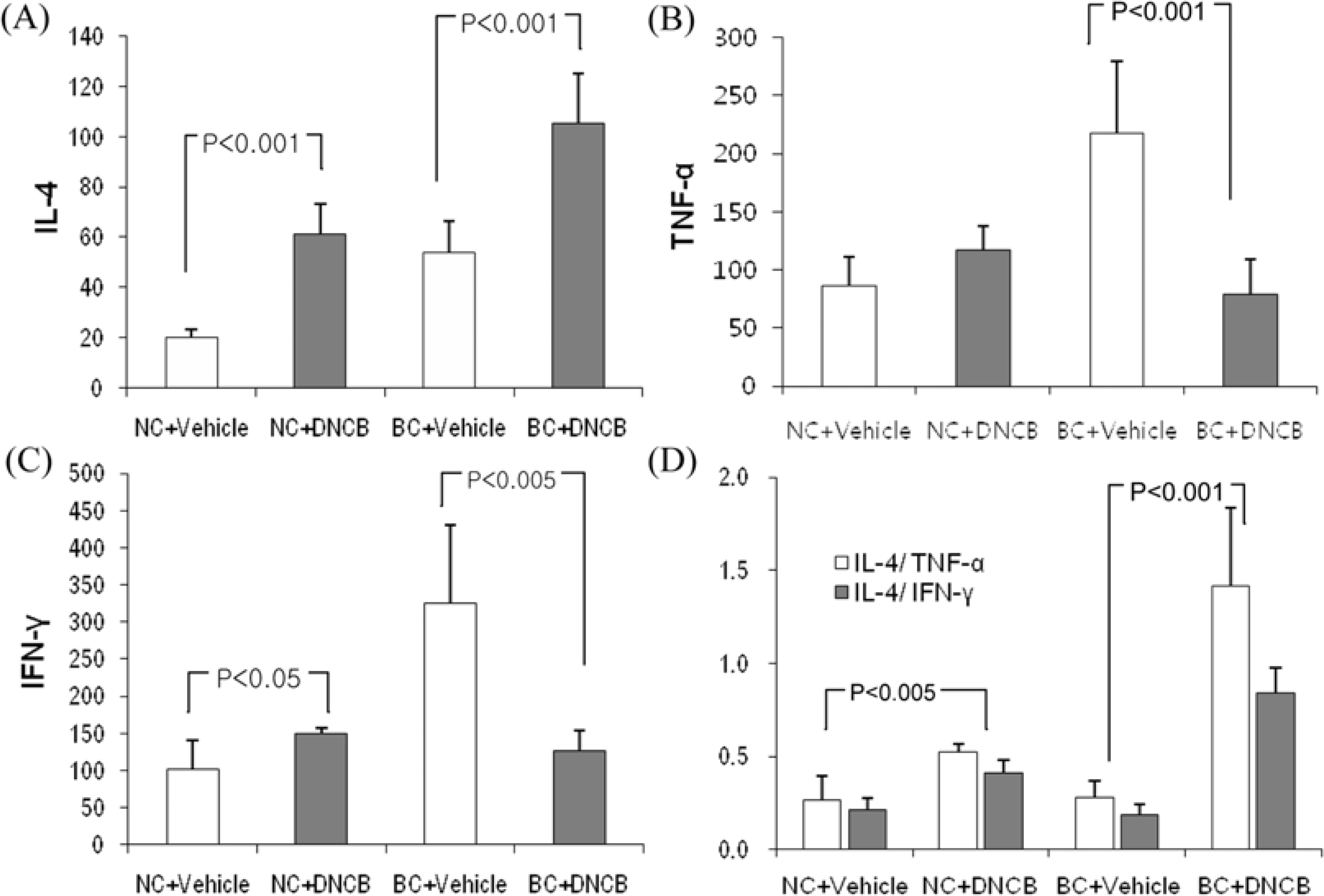
- The various murine models have contributed to the study of human atopic dermatitis (AD). However limitations of the models involve low reproducibility and long time to develop AD. In an attempt to overcome these limitations and establish an atopic dermatitis murine model, we repeated the application of 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) patch in NC/Nga and BALB/c mice, which has advantages in reproduction and cost. For the sensitization, a 1 cm2 gauze-attached patch, where 1% or 0.2% DNCB was periodically attached on the back of NC/Nga and BALB/c mice. To estimate how homologous our model was with human atopic dermatitis, clinical, histological and immunological alterations were evaluated. Both strains showed severe atopic dermatitis, increase in subiliac lymph node weight, mast cells, epidermal hyperplasia and serum IgE levels. Though both exhibited a high IL-4/IFN-gamma and IL-4/TNF-beta ratio in the expression of mRNA, the shifting of DNCB-treated BALB/c mice was increased to more than double that of NC/Nga mice. These results suggest that our DNCB patched model using BALB/c mice were more suitable than NC/Nga mice in demonstrating the immune response. We anticipate that our novel model may be successfully used for pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis and assessment of therapeutic approaches.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
Hamid Q.., Boguniewicz M.., Leung D.Y.1994. Differential in situ cytokine gene expression in acute versus chronic atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest. 94:870–876.
ArticleHorsmanheimo L.., Harvima I.T.., Jarvikallio A.., Harvima R.J.., Naukkarinen A.., Horsmanheimo M.1994. Mast cells are one major source of interleukin-4 in atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 131:348–353.Akdis C.A.., Akdis M.., Bieber T.., Bindslev-Jensen C.., Boguniewicz M.., Eigenmann P.., Hamid Q.., Kapp A.., Leung D.Y.., Lipozencic J.., Luger T.A.., Muraro A.., Novak N.., Platts-Mills T.A.., Rosenwasser L.., Scheynius A.., Simons F.E.., Spergel J.., Turjanmaa K.., Wahn U.., Weidinger S.., Werfel T.., Zuberbier T.2006. Diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in children and adults: European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology/American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/PRACTALL Consensus Report. Allergy. 61:969–987.
ArticleChan L.S.., Robinson N.., Xu L.2001. Expression of interleukin-4 in the epidermis of transgenic mice results in a pruritic inflammatory skin disease: an experimental animal model to study atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 117:977–983.
ArticleDillon S.R.., Sprecher C.., Hammond A.., Bilsborough J.., Rosenfeld-Franklin M.., Presnell S.R.., Haugen H.S.., Maurer M.., Harder B.., Johnston J.., Bort S.., Mudri S.., Kuijper J.L.., Bukowski T.., Shea P.., Dong D.L.., Dasovich M.., Grant F.J.., Lockwood L.., Levin S.D.., LeCiel C.., Waggie K.., Day H.., Topouzis S.., Kramer J.., Kuestner R.., Chen Z.., Foster D.., Parrish-Novak J.., Gross J.A.2004. Interleukin 31, a cytokine produced by activated T cells, induces dermatitis in mice. Nat Immunol. 5:752–760.
ArticleFriedmann P.S.2006. Contact sensitisation and allergic contact dermatitis: immunobiological mechanisms. Toxicol Lett. 162:49–54.
ArticleGuo T.L.., Zhang X.L.., Leffel E.K.., Peachee V.L.., Karrow N.A.., Germolec D.R.., White, K.L. Jr.2002. Differential stimulation of IgE production, STAT activation and cytokine and CD86 expression by 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene and trimellitic anhydride. J Appl Toxicol. 22:397–403.
ArticleGustafsson D.., Sjoberg O.., Foucard T.2000. Development of allergies and asthma in infants and young children with atopic dermatitis–a prospective followup to 7 years of age. Allergy. 55:240–245.Hamid Q.., Boguniewicz M.., Leung D.Y.1994. Differential in situ cytokine gene expression in acute versus chronic atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest. 94:870–876.
ArticleHorsmanheimo L.., Harvima I.T.., Jarvikallio A.., Harvima R.J.., Naukkarinen A.., Horsmanheimo M.1994. Mast cells are one major source of interleukin-4 in atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 131:348–353.Inoue Y.., Isobe M.., Shiohara T.., Goto Y.., Hayashi H.2002. Protective and curative effects of topically applied CX-659S, a novel diaminouracil derivative, on chronic picryl chloride-induced contact hypersensitivity responses. Br J Dermatol. 147:675–682.
ArticleJin H.., He R.., Oyoshi M.., Geha R.S.2009. Animal models of atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 129:31–40.
ArticleKang J.S.., Lee K.., Han S.B.., Ahn J.M.., Lee H.., Han M.H.., Yoon Y.D.., Yoon W.K.., Park S.K.., Kim H.M.2006. Induction of atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome-like skin lesions by repeated topical application of a crude extract of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus in NC/Nga mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 6:1616–1622.
ArticleKim E.C.., Lee H.S.., Kim S.K.., Choi M.S.., Lee S.., Han J.B.., An H.J.., Um J.Y.., Kim H.M.., Lee N.Y.., Bae H.., Min B.I.2008. The bark of Betula platyphylla var. japonica inhibits the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 116:270–278.Kimber I.., Basketter D.A.., Berthold K.., Butler M.., Garrigue J.L.., Lea L.., Newsome C.., Roggeband R.., Steiling W.., Stropp G.., Waterman S.., Wiemann C.2001. Skin sensitization testing in potency and risk assessment. Toxicol Sci. 59:198–208.
ArticleKitagaki H.., Fujisawa S.., Watanabe K.., Hayakawa K.., Shiohara T.1995. Immediate-type hypersensitivity response followed by a late reaction is induced by repeated epicutaneous application of contact sensitizing agents in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 105:749–755.
ArticleKitagaki H.., Ono N.., Hayakawa K.., Kitazawa T.., Watanabe K.., Shiohara T.1997. Repeated elicitation of contact hypersensitivity induces a shift in cutaneous cytokine milieu from a T helper cell type 1 to a T helper cell type 2 profile. J Immunol. 159:2484–2491.Lee H.S.., Kim S.K.., Han J.B.., Choi H.M.., Park J.H.., Kim E.C.., Choi M.S.., An H.J.., Um J.Y.., Kim H.M.., Min B.I.2006. Inhibitory effects of Rumex japonicus Houtt. on the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Br J Dermatol. 155:33–38.Leung D.Y.., Boguniewicz M.., Howell M.D.., Nomura I.., Hamid Q.A.2004. New insights into atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest. 113:651–657.
ArticleMan M.Q.., Hatano Y.., Lee S.H.., Man M.., Chang S.., Feingold K.R.., Leung D.Y.., Holleran W.., Uchida Y.., Elias P.M.2008. Characterization of a hapten-induced, murine model with multiple features of atopic dermatitis: structural, immunologic, and biochemical changes following single versus multiple oxazolone challenges. J Invest Dermatol. 128:79–86.
ArticleMarsella R.., Olivry T.2003. Animal models of atopic dermatitis. Clin Dermatol. 21:122–133.
ArticleMatsuda H.., Watanabe N.., Geba G.P.., Sperl J.., Tsudzuki M.., Hiroi J.., Matsumoto M.., Ushio H.., Saito S.., Askenase P.W.., Ra C.1997. Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion with IgE hyperproduction in NC/Nga mice. Int Immunol. 9:461–466.
ArticleNavi D.., Saegusa J.., Liu F.T.2007. Mast cells and immunological skin diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 33:144–155.
ArticleNomura I.., Goleva E.., Howell M.D.., Hamid Q.A.., Ong P.Y.., Hall C.F.., Darst M.A.., Gao B.., Boguniewicz M.., Travers J.B.., Leung D.Y.2003. Cytokine milieu of atopic dermatitis, as compared to psoriasis, skin prevents induction of innate immune response genes. J Immunol. 171:3262–3269.
ArticleNovak N.2009. New insights into the mechanism and management of allergic diseases: atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 64:265–275.
ArticleNovak N.., Bieber T.2005. The role of dendritic cell subtypes in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 53:S171–176.
ArticleOpal S.M.., DePalo V.A.2000. Anti-inflammatory cytokines. Chest. 117:1162–1172.
ArticleShiohara T.., Hayakawa J.., Mizukawa Y.2004. Animal models for atopic dermatitis: are they relevant to human disease? J Dermatol Sci. 36:1–9.
ArticleSpergel J.M.., Mizoguchi E.., Brewer J.P.., Martin T.R.., Bhan A.K.., Geha R.S.1998. Epicutaneous sensitization with protein antigen induces localized allergic dermatitis and hyperresponsiveness to methacholine after single exposure to aerosolized antigen in mice. J Clin Invest. 101:1614–1622.
ArticleSugiura K.., Shamoto M.., Sakamoto N.., Shinzato M.., Osada A.., Sugiura M.., Hayakawa R.., Kato Y.2003. It is true that, when Langerhans cells migrate from the skin to the lymph node, they are transported via lymph vessels. Dermatology. 206:222–224.
ArticleSunada Y.., Nakamura S.., Kamei C.2008. Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus strain L-55 on the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 8:1761–1766.
ArticleTanaka T.., Tsutsui H.., Yoshimoto T.., Kotani M.., Matsumoto M.., Fujita A.., Wang W.., Higa S.., Koshimoto T.., Nakanishi K.., Suemura M.2001. Interleukin-18 is elevated in the sera from patients with atopic dermatitis and from atopic dermatitis model mice, NC/Nga. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 125:236–240.
ArticleTaniguchi Y.., Kohno K.., Inoue S.., Koya-Miyata S.., Okamoto I.., Arai N.., Iwaki K.., Ikeda M.., Kurimoto M.2003. Oral administration of royal jelly inhibits the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 3:1313–1324.
ArticleTheiner G.., Gessner A.., Lutz M.B.2006. The mast cell mediator PGD2 suppresses IL-12 release by dendritic cells leading to Th2 polarized immune responses in vivo. Immunobiology. 211:463–472.
ArticleWollenberg A.., Klein E.2007. Current aspects of innate and adaptive immunity in atopic dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 33:35–44.
ArticleYamanaka K.., Tanaka M.., Tsutsui H.., Kupper T.S.., Asahi K.., Okamura H.., Nakanishi K.., Suzuki M.., Kayagaki N.., Black R.A.., Miller D.K.., Nakashima K.., Shimizu M.., Mizutani H.2000. Skin-specific caspase-1-transgenic mice show cutaneous apoptosis and pre-endotoxin shock condition with a high serum level of IL-18. J Immunol. 165:997–1003.
ArticleYatsuzuka R.., Inoue T.., Jiang S.., Nakano Y.., Kamei C.2007. Development of new atopic dermatitis models characterized by not only itching but also inflammatory skin in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 565:225–231.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Developing an Atopic Dermatitis Model and the Effects of Actinidia Extract on Dermatitis in NC/Nga Mice
- Topical Application of S1P2 Antagonist JTE-013 Attenuates 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Mice
- Alteration of Innate Immune T and B Cells in the NC/Nga Mouse
- A Study on Tests of Skin Safety and Inhibition of Atopic Dermatitis Using a StoneTouch(R) Infrared Scanner in a Mouse Model
- Effect of German chamomile oil application on alleviating atopic dermatitis-like immune alterations in mice