Nutr Res Pract.
2019 Apr;13(2):95-104. 10.4162/nrp.2019.13.2.95.
Anti-inflammatory effect of Lycium barbarum on polarized human intestinal epithelial cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Chungnam National University, 99, Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34134, Korea. jacho@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Agrofood Resources, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, RDA, Wanju, Jeonbuk 55365, Korea.
- 3Elohim Co. R&D Center, Daejeon 34025, Korea.
- 4Application Technology Center, Park System, Suwon, Gyeonggi 16229, Korea.
- KMID: 2442366
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2019.13.2.95
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) has rapidly escalated in Asia (including Korea) due to increasing westernized diet patterns subsequent to industrialization. Factors associated with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress are demonstrated to be one of the major causes of IBD. This study was conducted to investigate the effect of Lycium barbarum (L. barbarum) on ER stress.
MATERIALS/METHODS
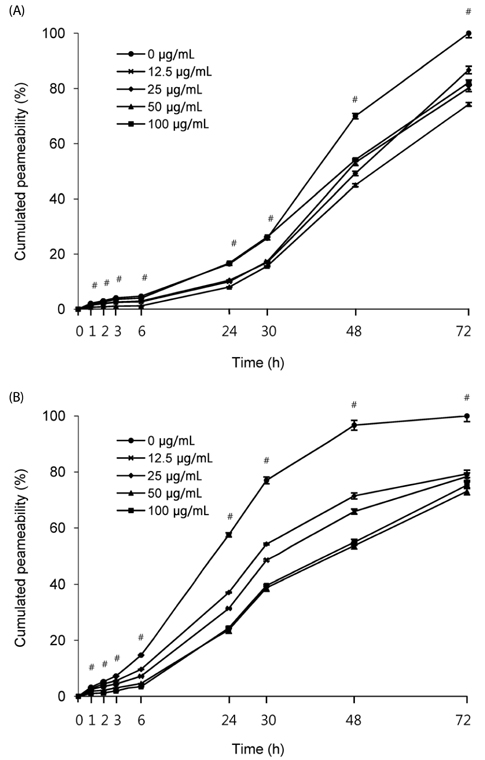
Mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cell line and polarized Caco-2 human intestinal epithelial cells were treated with crude extract of the L. chinense fruit (LF). Paracellular permeability was measured to examine the effect of tight junction (TJ) integrity. The regulatory pathways of ER stress were evaluated in MEF knockout (KO) cell lines by qPCR for interleukin (IL) 6, IL8 and XBP1 spliced form (XBP1s). Immunoglobulin binding protein (BiP), XBP1s and CCAAT/enhancer-binding homologous protein (CHOP) expressions were measured by RT-PCR. Scanning Ion Conductance Microscopy (SICM) at high resolution was applied to observe morphological changes after treatments.
RESULTS
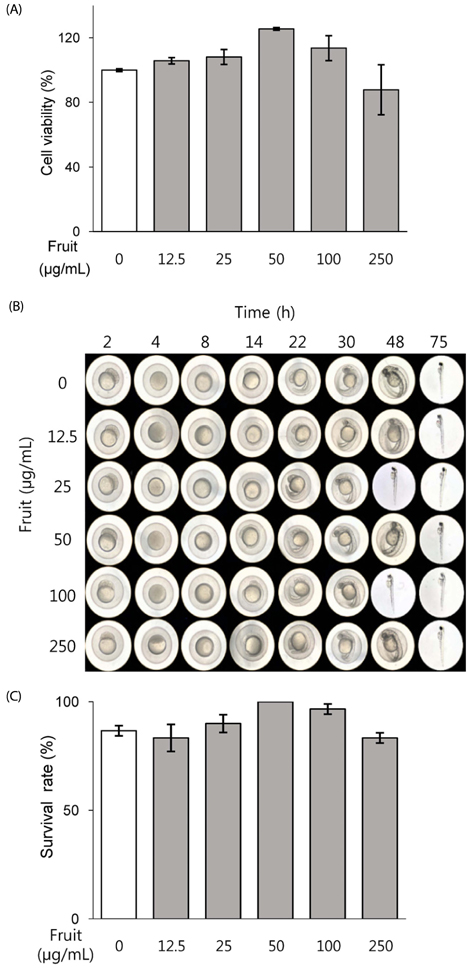
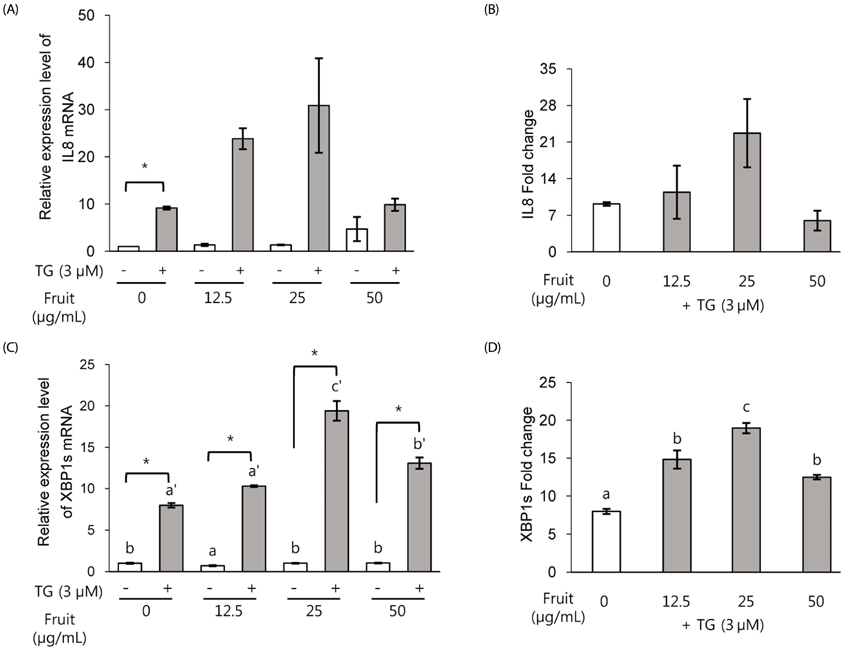
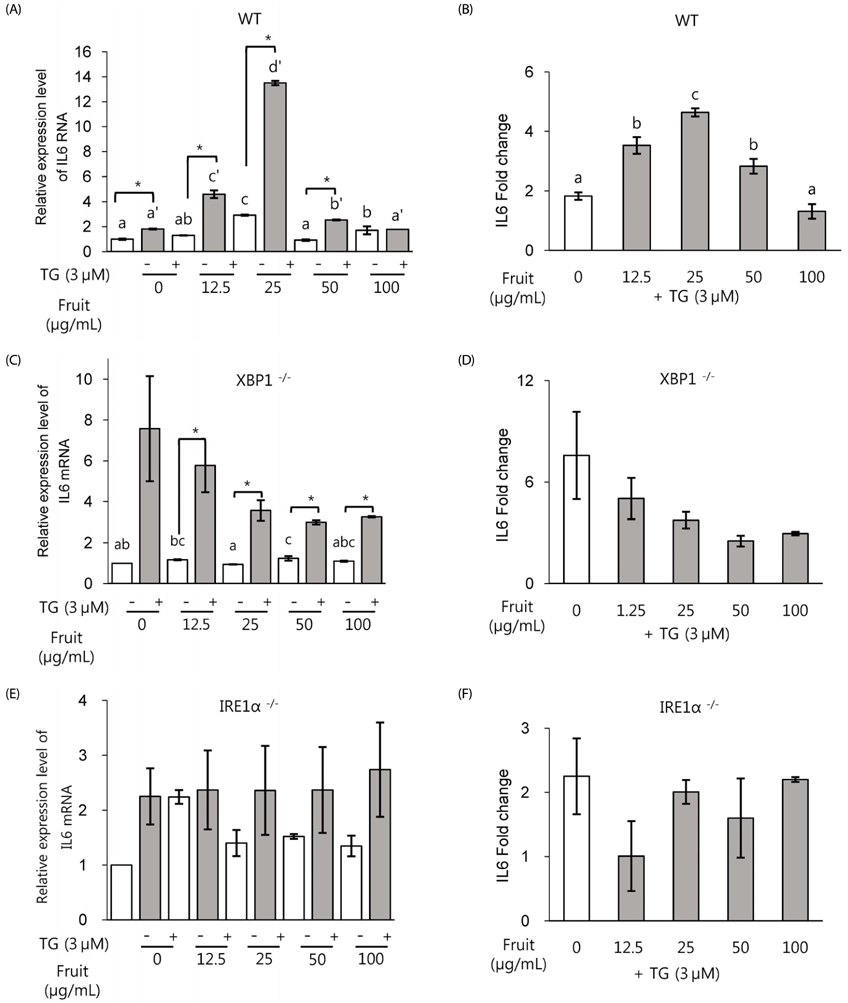
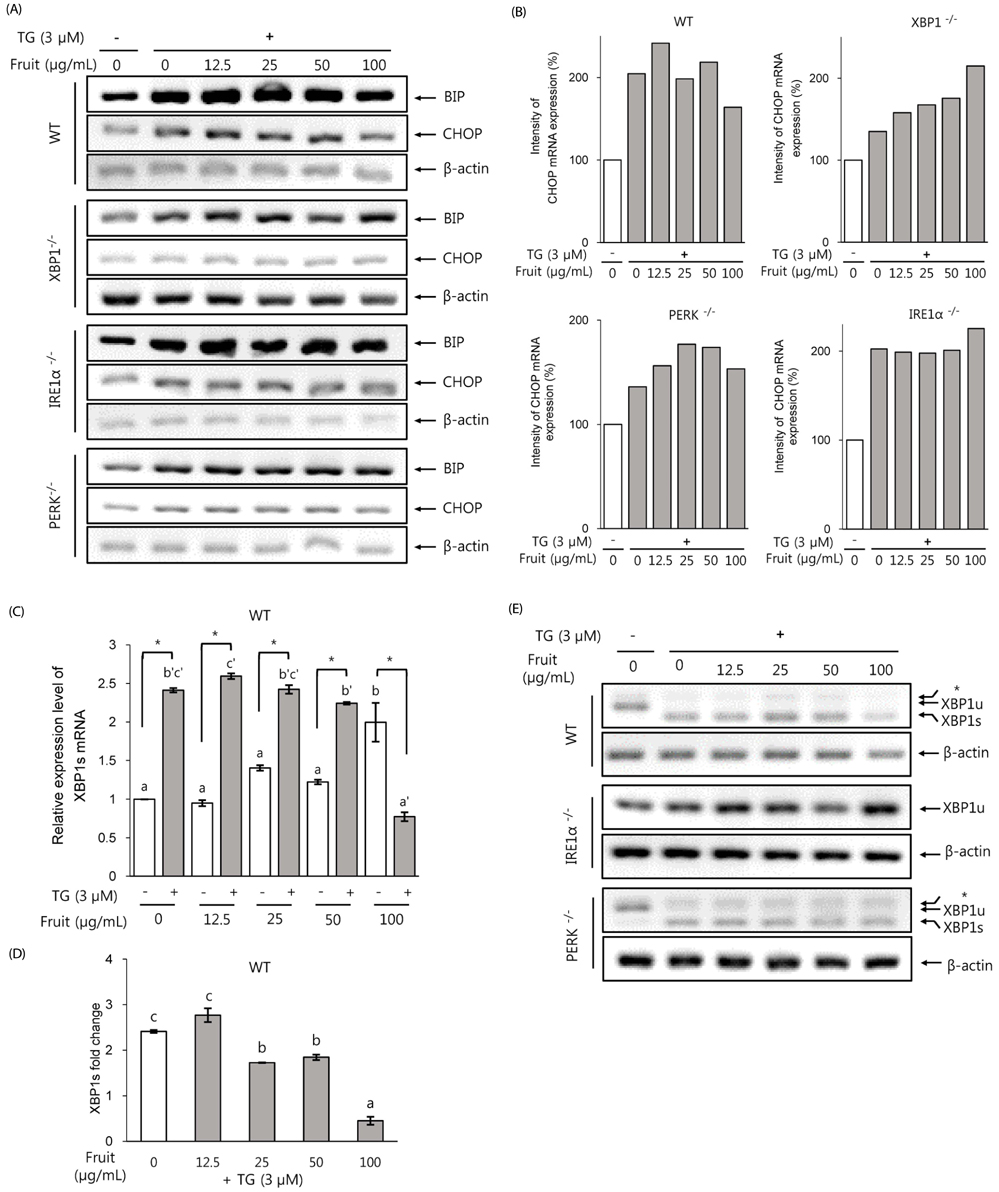
Exposure to LF extract strengthened the TJ, both in the presence and absence of inflammation. In polarized Caco-2 pretreated with LF, induction in the expression of proinflammatory marker IL8 was not significant, whereas ER stress marker XBP1s expression was significantly increased. In wild type (wt) MEF cells, IL6, CHOP and XBP1 spliced form were dose-dependently induced when exposed to 12.5-50 µg/mL extract. However, absence of XBP1 or IRE1α in MEF cells abolished this effect.
CONCLUSION
Results of this study show that LF treatment enhances the barrier function and reduces inflammation and ER stress in an IRE1α-XBP1-dependent manner. These results suggest the preventive effect of LF on healthy intestine, and the possibility of reducing the degree of inflammatory symptoms in IBD patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Asia
Carrier Proteins
Cell Line
Diet
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Epithelial Cells*
Fibroblasts
Fruit
Humans*
Immunoglobulins
Inflammation
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
Intestines
Lycium*
Mice
Microscopy
Permeability
Tight Junctions
Carrier Proteins
Immunoglobulins
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Interleukins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ellgaard L, Molinari M, Helenius A. Setting the standards: quality control in the secretory pathway. Science. 1999; 286:1882–1888.
Article2. Stengel S, Messner B, Falk-Paulsen M, Sommer N, Rosenstiel P. Regulated proteolysis as an element of ER stress and autophagy: implications for intestinal inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017; 1864:2183–2190.
Article3. Hampton RY. ER stress response: getting the UPR hand on misfolded proteins. Curr Biol. 2000; 10:R518–R521.
Article4. Welihinda AA, Kaufman RJ. The unfolded protein response pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Oligomerization and trans-phosphorylation of Ire1p (Ern1p) are required for kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:18181–18187.5. Oakes SA, Papa FR. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol. 2015; 10:173–194.
Article6. Vembar SS, Brodsky JL. One step at a time: endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008; 9:944–957.
Article7. Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Chung P, Harding HP, Ron D. Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science. 2000; 287:664–666.
Article8. Zinszner H, Kuroda M, Wang X, Batchvarova N, Lightfoot RT, Remotti H, Stevens JL, Ron D. CHOP is implicated in programmed cell death in response to impaired function of the endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev. 1998; 12:982–995.
Article9. Luo K, Cao SS. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in intestinal epithelial cell function and inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015; 2015:328791.
Article10. Hosomi S, Kaser A, Blumberg RS. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy as interlinking pathways in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2015; 31:81–88.
Article11. Ng SC, Tang W, Ching JY, Wong M, Chow CM, Hui AJ, Wong TC, Leung VK, Tsang SW, Yu HH, Li MF, Ng KK, Kamm MA, Studd C, Bell S, Leong R, de Silva HJ, Kasturiratne A, Mufeena MNF, Ling KL, Ooi CJ, Tan PS, Ong D, Goh KL, Hilmi I, Pisespongsa P, Manatsathit S, Rerknimitr R, Aniwan S, Wang YF, Ouyang Q, Zeng Z, Zhu Z, Chen MH, Hu PJ, Wu K, Wang X, Simadibrata M, Abdullah M, Wu JC, Sung JJY, Chan FKL. Asia-Pacific Crohn's and Colitis Epidemiologic Study (ACCESS) Study Group. Incidence and phenotype of inflammatory bowel disease based on results from the Asia-pacific Crohn's and colitis epidemiology study. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145:158–165.e2.
Article12. Mulder DJ, Noble AJ, Justinich CJ, Duffin JM. A tale of two diseases: the history of inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2014; 8:341–348.
Article13. Cao SS, Zimmermann EM, Chuang BM, Song B, Nwokoye A, Wilkinson JE, Eaton KA, Kaufman RJ. The unfolded protein response and chemical chaperones reduce protein misfolding and colitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144:989–1000.e6.
Article14. Dixon LJ, Kabi A, Nickerson KP, McDonald C. Combinatorial effects of diet and genetics on inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015; 21:912–922.
Article15. Neish AS. Microbes in gastrointestinal health and disease. Gastroenterology. 2009; 136:65–80.
Article16. Kaser A, Lee AH, Franke A, Glickman JN, Zeissig S, Tilg H, Nieuwenhuis EE, Higgins DE, Schreiber S, Glimcher LH, Blumberg RS. XBP1 links ER stress to intestinal inflammation and confers genetic risk for human inflammatory bowel disease. Cell. 2008; 134:743–756.
Article17. Chassaing B, Darfeuille-Michaud A. The commensal microbiota and enteropathogens in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:1720–1728.
Article18. Cho JH, Brant SR. Recent insights into the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:1704–1712.
Article19. Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, Duerr RH, McGovern DP, Hui KY, Lee JC, Schumm LP, Sharma Y, Anderson CA, Essers J, Mitrovic M, Ning K, Cleynen I, Theatre E, Spain SL, Raychaudhuri S, Goyette P, Wei Z, Abraham C, Achkar JP, Ahmad T, Amininejad L, Ananthakrishnan AN, Andersen V, Andrews JM, Baidoo L, Balschun T, Bampton PA, Bitton A, Boucher G, Brand S, Büning C, Cohain A, Cichon S, D'Amato M, De Jong D, Devaney KL, Dubinsky M, Edwards C, Ellinghaus D, Ferguson LR, Franchimont D, Fransen K, Gearry R, Georges M, Gieger C, Glas J, Haritunians T, Hart A, Hawkey C, Hedl M, Hu X, Karlsen TH, Kupcinskas L, Kugathasan S, Latiano A, Laukens D, Lawrance IC, Lees CW, Louis E, Mahy G, Mansfield J, Morgan AR, Mowat C, Newman W, Palmieri O, Ponsioen CY, Potocnik U, Prescott NJ, Regueiro M, Rotter JI, Russell RK, Sanderson JD, Sans M, Satsangi J, Schreiber S, Simms LA, Sventoraityte J, Targan SR, Taylor KD, Tremelling M, Verspaget HW, De Vos M, Wijmenga C, Wilson DC, Winkelmann J, Xavier RJ, Zeissig S, Zhang B, Zhang CK, Zhao H. International IBD Genetics Consortium (IIBDGC). Silverberg MS, Annese V, Hakonarson H, Brant SR, Radford-Smith G, Mathew CG, Rioux JD, Schadt EE, Daly MJ, Franke A, Parkes M, Vermeire S, Barrett JC, Cho JH. IIBDGC), Silverberg MS, Annese V, Hakonarson H, Brant SR, Radford-Smith G, Mathew CG, Rioux JD, Schadt EE, Daly MJ, Franke A, Parkes M, Vermeire S, Barrett JC, Cho JH. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2012; 491:119–124.
Article20. Lee SH. Intestinal permeability regulation by tight junction: implication on inflammatory bowel diseases. Intest Res. 2015; 13:11–18.
Article21. Wu GD, Bushmanc FD, Lewis JD. Diet, the human gut microbiota, and IBD. Anaerobe. 2013; 24:117–120.
Article22. O'Sullivan M, O'Morain C. Nutrition in inflammatory bowel disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006; 20:561–573.23. Halmos EP, Christophersen CT, Bird AR, Shepherd SJ, Gibson PR, Muir JG. Diets that differ in their FODMAP content alter the colonic luminal microenvironment. Gut. 2015; 64:93–100.
Article24. Gilardi D, Fiorino G, Genua M, Allocca M, Danese S. Complementary and alternative medicine in inflammatory bowel diseases: what is the future in the field of herbal medicine? Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 8:835–846.
Article25. Langhorst J, Wulfert H, Lauche R, Klose P, Cramer H, Dobos GJ, Korzenik J. Systematic review of complementary and alternative medicine treatments in inflammatory bowel diseases. J Crohns Colitis. 2015; 9:86–106.
Article26. Hu S, Ciancio MJ, Lahav M, Fujiya M, Lichtenstein L, Anant S, Musch MW, Chang EB. Translational inhibition of colonic epithelial heat shock proteins by IFN-γ and TNF-α in intestinal inflammation. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:1893–1904.
Article27. Yao R, Heinrich M, Zou Y, Reich E, Zhang X, Chen Y, Weckerle CS. Quality variation of Goji (fruits of Lycium spp.) in China: a comparative morphological and metabolomic analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2018; 9:151.
Article28. Yao R, Heinrich M, Weckerle CS. The genus Lycium as food and medicine: a botanical, ethnobotanical and historical review. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018; 212:50–66.
Article29. Amagase H, Farnsworth NR. A review of botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, clinical relevance in efficacy and safety of Lycium barbarum fruit (Goji). Food Res Int. 2011; 44:1702–1717.
Article30. Chang RC, So KF. Use of anti-aging herbal medicine, Lycium barbarum, against aging-associated diseases. What do we know so far? Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2008; 28:643–652.
Article31. Wang CC, Chang SC, Inbaraj B, Stephen Chen BH. Isolation of carotenoids, flavonoids and polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum L. and evaluation of antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2010; 120:184–192.
Article32. Chan HC, Chang RC, Koon-Ching Ip A, Chiu K, Yuen WH, Zee SY, So KF. Neuroprotective effects of Lycium barbarum Lynn on protecting retinal ganglion cells in an ocular hypertension model of glaucoma. Exp Neurol. 2007; 203:269–273.
Article33. Luo Q, Cai Y, Yan J, Sun M, Corke H. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects and antioxidant activity of fruit extracts from Lycium barbarum. Life Sci. 2004; 76:137–149.
Article34. Nagpal R, Newman TM, Wang S, Jain S, Lovato JF, Yadav H. Obesity-linked gut microbiome dysbiosis associated with derangements in gut permeability and intestinal cellular homeostasis independent of diet. J Diabetes Res. 2018; 2018:3462092.
Article35. Ferraretto A, Bottani M, De Luca P, Cornaghi L, Arnaboldi F, Maggioni M, Fiorilli A, Donetti E. Morphofunctional properties of a differentiated Caco2/HT-29 co-culture as an in vitro model of human intestinal epithelium. Biosci Rep. 2018; 38:BSR20171497.
Article36. Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Vandenabeele P, Krysko DV, Agostinis P. ER stress-induced inflammation: does it aid or impede disease progression? Trends Mol Med. 2012; 18:589–598.
Article37. Korchev YE, Bashford CL, Milovanovic M, Vodyanoy I, Lab MJ. Scanning ion conductance microscopy of living cells. Biophys J. 1997; 73:653–658.
Article38. Rheinlaender J, Geisse NA, Proksch R, Schäffer TE. Comparison of scanning ion conductance microscopy with atomic force microscopy for cell imaging. Langmuir. 2011; 27:697–704.
Article39. Gorelik J, Zhang Y, Shevchuk AI, Frolenkov GI, Sánchez D, Lab MJ, Vodyanoy I, Edwards CR, Klenerman D, Korchev YE. The use of scanning ion conductance microscopy to image A6 cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2004; 217:101–108.
Article40. Ushiki T, Nakajima M, Choi M, Cho SJ, Iwata F. Scanning ion conductance microscopy for imaging biological samples in liquid: a comparative study with atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Micron. 2012; 43:1390–1398.
Article41. Anariba F, Anh JH, Jung GE, Cho NJ, Cho SJ. Biophysical applications of scanning ion conductance microscopy (SICM). Mod Phys Lett B. 2012; 26:1130003.
Article42. Gan L, Hua Zhang S, Liang Yang X, Bi Xu H. Immunomodulation and antitumor activity by a polysaccharide-protein complex from Lycium barbarum. Int Immunopharmacol. 2004; 4:563–569.
Article43. Jing L, Cui G, Feng Q, Xiao Y. Evaluation of hypoglycemic activity of the polysaccharides extracted from Lycium barbarum. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2009; 6:579–584.
Article44. Zhang Z, Liu X, Zhang X, Liu J, Hao Y, Yang X, Wang Y. Comparative evaluation of the antioxidant effects of the natural vitamin C analog 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid isolated from Goji berry fruit. Arch Pharm Res. 2011; 34:801–810.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anti-inflammatory effects of fruit and leaf extracts of Lycium barbarum in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and animal model
- Protective effect of chlorophyllremoved ethanol extract of Lycium barbarum leaves against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Antioxidant activity of ethanol extract of Lycium barbarum's leaf with removal of chlorophyll
- Curcumin utilizes the anti-inflammatory response pathway to protect the intestine against bacterial invasion
- Protective effect of Lycium barbarum leaf extracts on atopic dermatitis: in vitro and in vivo studies