Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2018 Nov;10(6):698-715. 10.4168/aair.2018.10.6.698.
Differential Hrd1 Expression and B-Cell Accumulation in Eosinophilic and Non-eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China. yangjun@xinhuamed.com.cn, allergyli@163.com
- 2Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Shanghai Tenth People's Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
- 3Key Laboratory of Molecular Virology and Immunology, Vaccine Center, Institut Pasteur of Shanghai, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China.
- 4Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Affiliated Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
- KMID: 2441818
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2018.10.6.698
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Hrd1 has recently emerged as a critical regulator of B-cells in autoimmune diseases. However, its role in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) remains largely unexplored. This study aimed to examine Hrd1 expression and B-cell accumulation and their possible roles in CRSwNP.
METHODS
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, immunohistochemistry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blotting were used to assess gene and protein expression in nasal tissue extracts. Cells isolated from nasal tissues and peripheral blood mononuclear cells were characterized by flow cytometry. Local antibody production was measured in tissue extracts with a Bio-Plex assay. Additionally, changes in Hrd1 expression in response to specific inflammatory stimuli were measured in cultured dispersed polyp cells.
RESULTS
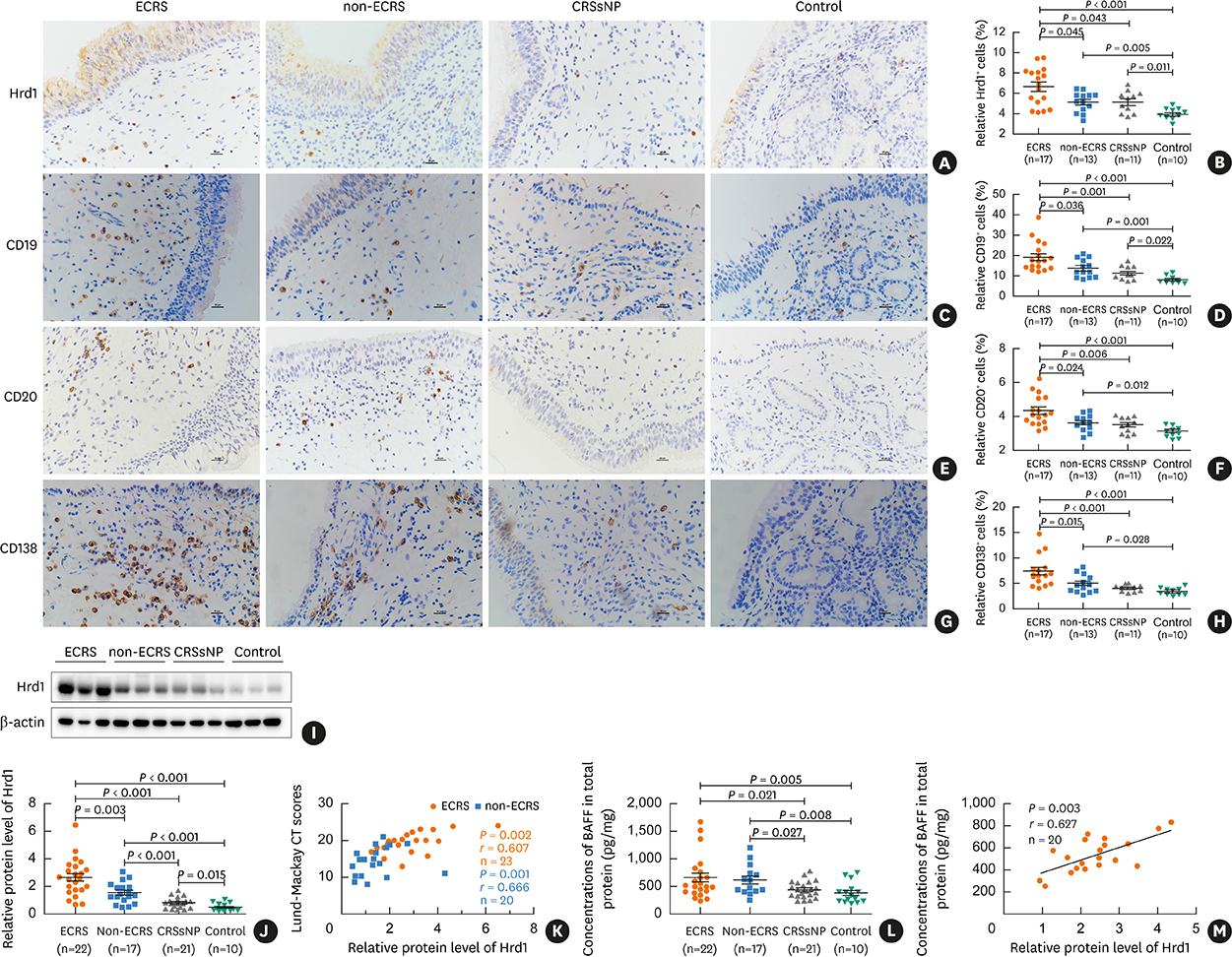
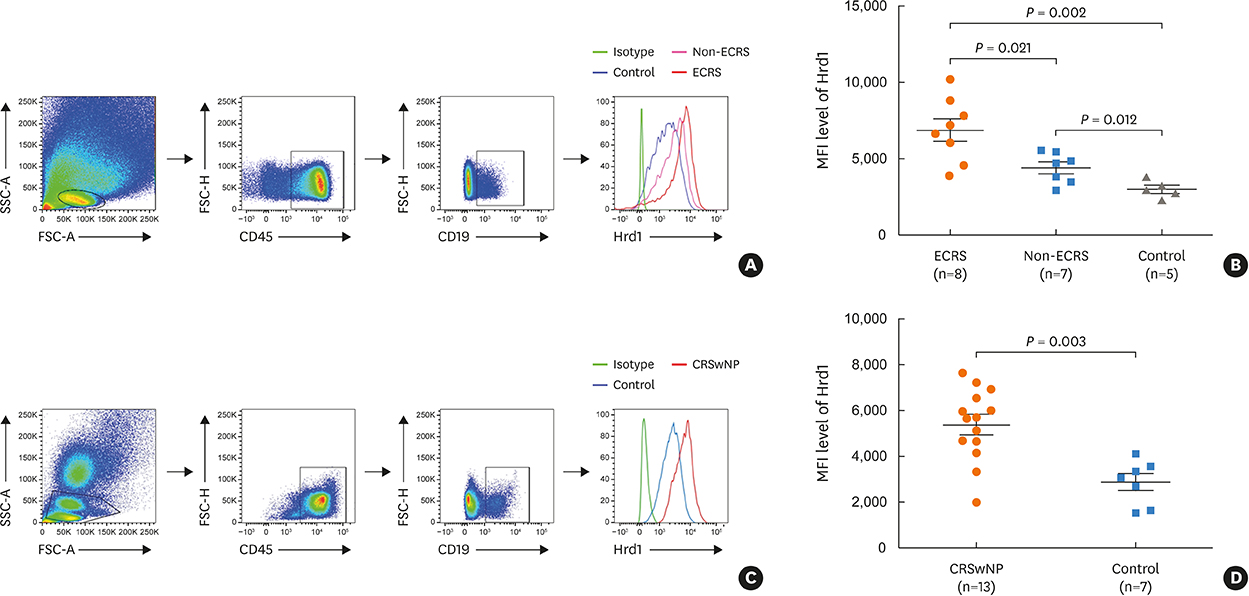
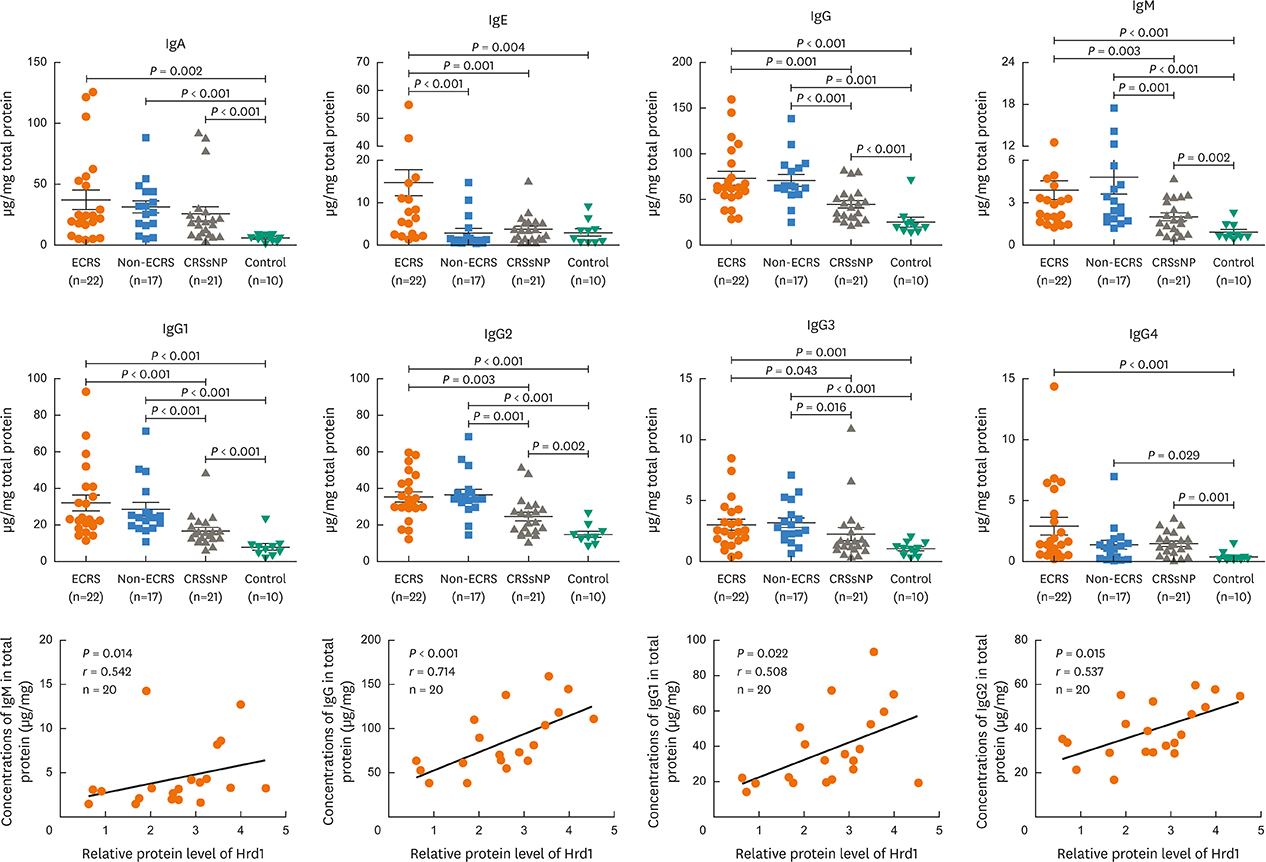
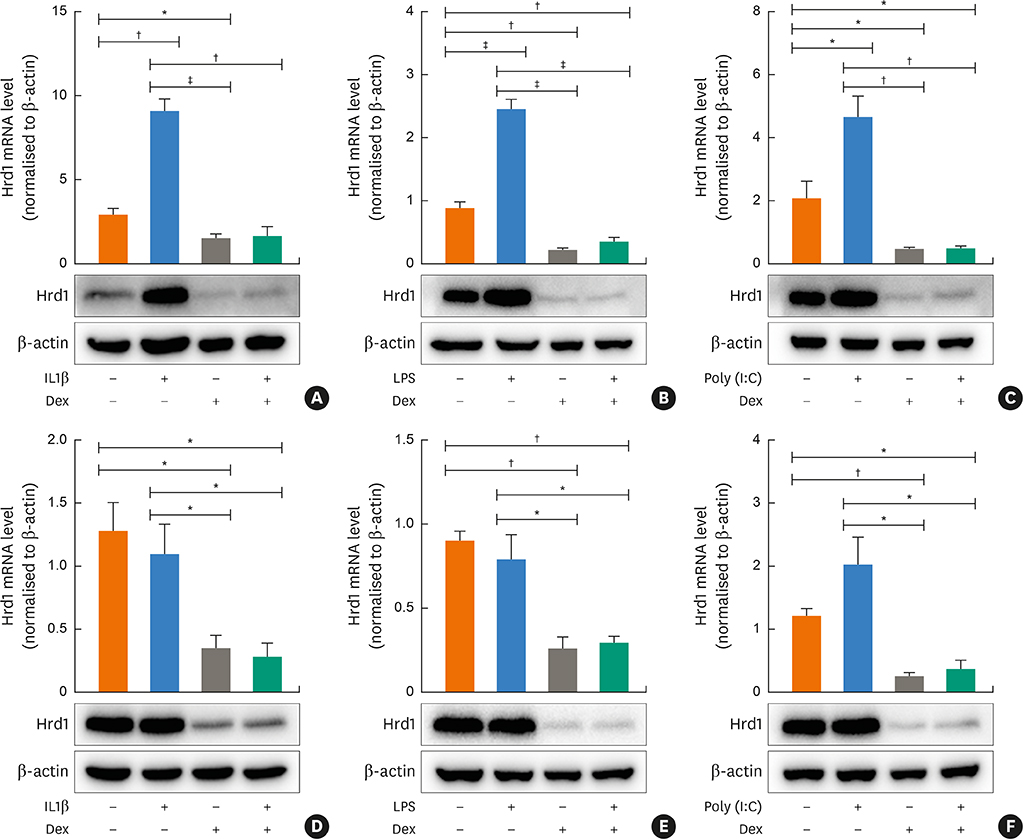
Nasal polyps (NPs) from patients with eosinophilic CRSwNP (ECRS) had increased levels of Hrd1, B-cells and plasma cells compared with NPs from patients with non-eosinophilic CRSwNP (non-ECRS) or other control subjects (P < 0.05). The average Hrd1 levels in B-cells in NPs from ECRS patients were significantly higher than those from non-ECRS patients and control subjects (P < 0.05). NPs also contained significantly increased levels of several antibody isotypes compared with normal controls (P < 0.05). Interestingly, Hrd1 expression in cultured polyp cells from ECRS patients, but not non-ECRS patients, was significantly increased by interleukin-1β, lipopolysaccharide and Poly(I:C) stimulation, and inhibited by dexamethasone treatment (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Differential Hrd1 expression and B-cell accumulation between the ECRS and non-ECRS subsets suggests that they can exhibit distinct pathogenic mechanisms and play important roles in NP.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology. 2012; 50:1–12.
Article2. Hsu J, Peters AT. Pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011; 25:285–290.
Article3. Akdis CA, Bachert C, Cingi C, Dykewicz MS, Hellings PW, Naclerio RM, et al. Endotypes and phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: a PRACTALL document of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:1479–1490.4. Payne SC, Borish L, Steinke JW. Genetics and phenotyping in chronic sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:710–720.
Article5. Hulse KE. Immune mechanisms of chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016; 16:1.
Article6. Khalmuratova R, Park JW, Shin HW. Immune cell responses and mucosal barrier disruptions in chronic rhinosinusitis. Immune Netw. 2017; 17:60–67.
Article7. Hulse KE, Stevens WW, Tan BK, Schleimer RP. Pathogenesis of nasal polyposis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015; 45:328–346.
Article8. Dörner T, Radbruch A, Burmester GR. B-cell-directed therapies for autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009; 5:433–441.
Article9. Kato A, Hulse KE, Tan BK, Schleimer RP. B-lymphocyte lineage cells and the respiratory system. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:933–957.
Article10. Kato A, Peters A, Suh L, Carter R, Harris KE, Chandra R, et al. Evidence of a role for B cell-activating factor of the TNF family in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:1385–1392. 1392.e1–1382.
Article11. Song J, Wang H, Zhang YN, Cao PP, Liao B, Wang ZZ, et al. Ectopic lymphoid tissues support local immunoglobulin production in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; 141:927–937.
Article12. Van Zele T, Gevaert P, Watelet JB, Claeys G, Holtappels G, Claeys C, et al. Staphylococcus aureus colonization and IgE antibody formation to enterotoxins is increased in nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114:981–983.
Article13. Tan BK, Li QZ, Suh L, Kato A, Conley DB, Chandra RK, et al. Evidence for intranasal antinuclear autoantibodies in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:1198–1206.e1.
Article14. Guerriero CJ, Brodsky JL. The delicate balance between secreted protein folding and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation in human physiology. Physiol Rev. 2012; 92:537–576.
Article15. Amano T, Yamasaki S, Yagishita N, Tsuchimochi K, Shin H, Kawahara K, et al. Synoviolin/Hrd1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, as a novel pathogenic factor for arthropathy. Genes Dev. 2003; 17:2436–2449.
Article16. Gao B, Lee SM, Chen A, Zhang J, Zhang DD, Kannan K, et al. Synoviolin promotes IRE1 ubiquitination and degradation in synovial fibroblasts from mice with collagen-induced arthritis. EMBO Rep. 2008; 9:480–485.
Article17. Toh ML, Marotte H, Blond JL, Jhumka U, Eljaafari A, Mougin B, et al. Overexpression of synoviolin in peripheral blood and synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients and continued elevation in nonresponders to infliximab treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:2109–2118.
Article18. Xu Y, Zhao F, Qiu Q, Chen K, Wei J, Kong Q, et al. The ER membrane-anchored ubiquitin ligase Hrd1 is a positive regulator of T-cell immunity. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:12073.
Article19. Kong S, Yang Y, Xu Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Melo-Cardenas J, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum-resident E3 ubiquitin ligase Hrd1 controls B-cell immunity through degradation of the death receptor CD95/Fas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016; 113:10394–10399.
Article20. Wen W, Liu W, Zhang L, Bai J, Fan Y, Xia W, et al. Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:1522–1528.e5.
Article21. Wei Y, Xia W, Ye X, Fan Y, Shi J, Wen W, et al. The antimicrobial protein short palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone 1 (SPLUNC1) is differentially modulated in eosinophilic and noneosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 133:420–428.e10.
Article22. Ba L, Du J, Liu F, Yang F, Han M, Liu S, et al. Distinct inflammatory profiles in atopic and nonatopic patients with chronic rhinosinustis accompanied by nasal polyps in Western china. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:346–358.
Article23. Lindqvist M, van Lunzen J, Soghoian DZ, Kuhl BD, Ranasinghe S, Kranias G, et al. Expansion of HIV-specific T follicular helper cells in chronic HIV infection. J Clin Invest. 2012; 122:3271–3280.
Article24. Hulse KE, Norton JE, Suh L, Zhong Q, Mahdavinia M, Simon P, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is characterized by B-cell inflammation and EBV-induced protein 2 expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:1075–1083. 1083.e1–1077.
Article25. Dilidaer , Zheng Y, Liu Z, Hu X, Zhang J, Hu L, et al. Increased BAFF expression in nasal polyps is associated with local IgE production, Th2 response and concomitant asthma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017; 274:1883–1890.
Article26. Feldman S, Kasjanski R, Poposki J, Hernandez D, Chen JN, Norton JE, et al. Chronic airway inflammation provides a unique environment for B cell activation and antibody production. Clin Exp Allergy. 2017; 47:457–466.
Article27. Chu VT, Fröhlich A, Steinhauser G, Scheel T, Roch T, Fillatreau S, et al. Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow. Nat Immunol. 2011; 12:151–159.
Article28. Jacobsen EA, Helmers RA, Lee JJ, Lee NA. The expanding role(s) of eosinophils in health and disease. Blood. 2012; 120:3882–3890.
Article29. Zhang YN, Song J, Wang H, Wang H, Zeng M, Zhai GT, et al. Nasal IL-4(+)CXCR5(+)CD4(+) T follicular helper cell counts correlate with local IgE production in eosinophilic nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 137:462–473.
Article30. Schleimer RP. Immunopathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2017; 12:331–357.
Article31. Hamilos DL. Host-microbial interactions in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 133:640–653.e4.
Article32. Ishii KJ, Koyama S, Nakagawa A, Coban C, Akira S. Host innate immune receptors and beyond: making sense of microbial infections. Cell Host Microbe. 2008; 3:352–363.
Article33. Lund FE, Randall TD. Effector and regulatory B cells: modulators of CD4+ T cell immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010; 10:236–247.
Article34. Yang H, Qiu Q, Gao B, Kong S, Lin Z, Fang D. Hrd1-mediated BLIMP-1 ubiquitination promotes dendritic cell MHCII expression for CD4 T cell priming during inflammation. J Exp Med. 2014; 211:2467–2479.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Medical treatment according to phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis
- Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- Distribution of Histologic Type of Nasal Polyp and Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor According to Nasal Polyp Type
- Role of Fungal and Bacterial Superantigen in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Polyps
- The Role of NF-κB in Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps