Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2019 Mar;23(2):131-139. 10.4196/kjpp.2019.23.2.131.
Dual deep neural network-based classifiers to detect experimental seizures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- 2Department of Biomedicine & Health Sciences, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea. kocho@catholic.ac.kr
- 3Catholic Neuroscience Institute, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- 4Institute of Aging and Metabolic Diseases, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- 5Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- KMID: 2438087
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2019.23.2.131
Abstract
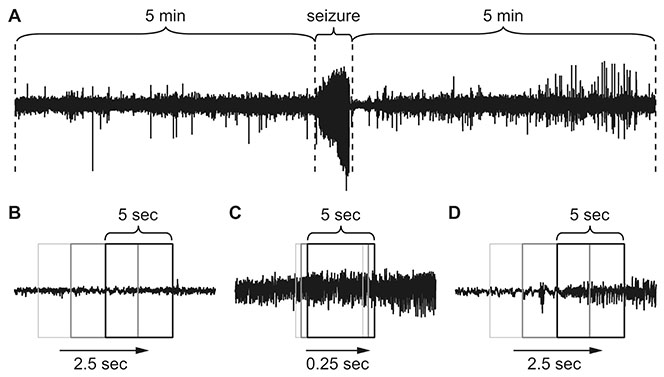
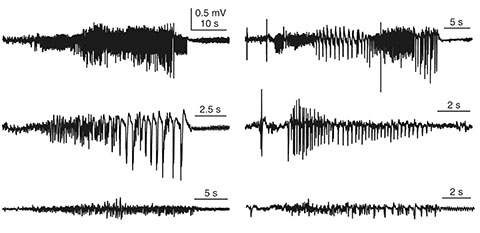
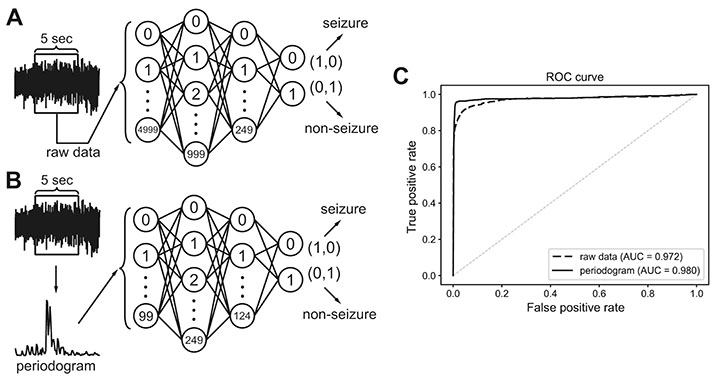
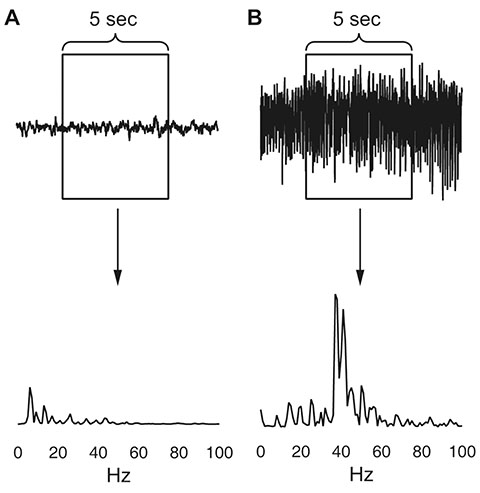
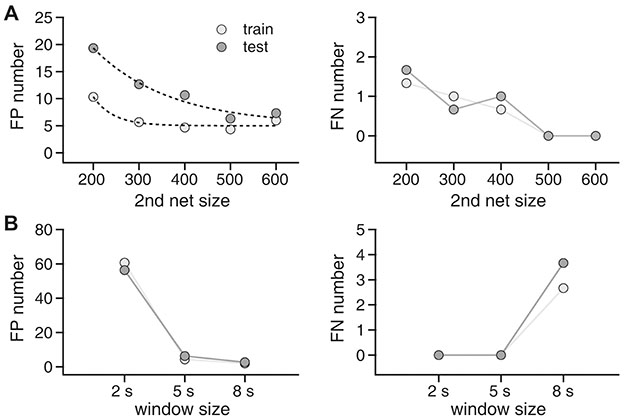
- Manually reviewing electroencephalograms (EEGs) is labor-intensive and demands automated seizure detection systems. To construct an efficient and robust event detector for experimental seizures from continuous EEG monitoring, we combined spectral analysis and deep neural networks. A deep neural network was trained to discriminate periodograms of 5-sec EEG segments from annotated convulsive seizures and the pre- and post-EEG segments. To use the entire EEG for training, a second network was trained with non-seizure EEGs that were misclassified as seizures by the first network. By sequentially applying the dual deep neural networks and simple pre- and post-processing, our autodetector identified all seizure events in 4,272 h of test EEG traces, with only 6 false positive events, corresponding to 100% sensitivity and 98% positive predictive value. Moreover, with pre-processing to reduce the computational burden, scanning and classifying 8,977 h of training and test EEG datasets took only 2.28 h with a personal computer. These results demonstrate that combining a basic feature extractor with dual deep neural networks and rule-based pre- and post-processing can detect convulsive seizures with great accuracy and low computational burden, highlighting the feasibility of our automated seizure detection algorithm.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Feasibility of fully automated classification of whole slide images based on deep learning
Kyung-Ok Cho, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;24(1):89-99. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.1.89.
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Epilepsy Fact Sheet. Geneva: World Health Organization;2018.2. Berg AT, Berkovic SF, Brodie MJ, Buchhalter J, Cross JH, van Emde Boas W, Engel J, French J, Glauser TA, Mathern GW, Moshé SL, Nordli D, Plouin P, Scheffer IE. Revised terminology and concepts for organization of seizures and epilepsies: report of the ILAE Commission on Classification and Terminology, 2005–2009. Epilepsia. 2010; 51:676–685.
Article3. Sirven JI. Epilepsy: a spectrum disorder. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015; 5:a022848.
Article4. Pitkänen A, Lukasiuk K. Molecular and cellular basis of epileptogenesis in symptomatic epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2009; 14:Suppl 1. 16–25.
Article5. Smith SJ. EEG in the diagnosis, classification, and management of patients with epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005; 76:Suppl 2. ii2–ii7.
Article6. Koessler L, Benar C, Maillard L, Badier JM, Vignal JP, Bartolomei F, Chauvel P, Gavaret M. Source localization of ictal epileptic activity investigated by high resolution EEG and validated by SEEG. Neuroimage. 2010; 51:642–653.
Article7. Aarabi A, Fazel-Rezai R, Aghakhani Y. A fuzzy rule-based system for epileptic seizure detection in intracranial EEG. Clin Neurophysiol. 2009; 120:1648–1657.
Article8. Chen D, Wan S, Xiang J, Bao FS. A high-performance seizure detection algorithm based on Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and EEG. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0173138.
Article9. Wilson SB, Emerson R. Spike detection: a review and comparison of algorithms. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002; 113:1873–1881.
Article10. Sinha S, Siddiqui KA. Definition of intractable epilepsy. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2011; 16:3–9.11. Grone BP, Baraban SC. Animal models in epilepsy research: legacies and new directions. Nat Neurosci. 2015; 18:339–343.
Article12. Palus M. Nonlinearity in normal human EEG: cycles, temporal asymmetry, nonstationarity and randomness, not chaos. Biol Cybern. 1996; 75:389–396.13. Subha DP, Joseph PK, Acharya UR, Lim CM. EEG signal analysis: a survey. J Med Syst. 2010; 34:195–212.
Article14. Jaiswal AK, Banka H. Epileptic seizure detection in EEG signal using machine learning techniques. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2018; 41:81–94.
Article15. LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015; 521:436–444.
Article16. Cho KO, Lybrand ZR, Ito N, Brulet R, Tafacory F, Zhang L, Good L, Ure K, Kernie SG, Birnbaum SG, Scharfman HE, Eisch AJ, Hsieh J. Aberrant hippocampal neurogenesis contributes to epilepsy and associated cognitive decline. Nat Commun. 2015; 6:6606.
Article17. Jeong KH, Lee KE, Kim SY, Cho KO. Upregulation of Krüppel-like factor 6 in the mouse hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Neuroscience. 2011; 186:170–178.
Article18. Racine RJ. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972; 32:281–294.
Article19. Brulet R, Zhu J, Aktar M, Hsieh J, Cho KO. Mice with conditional NeuroD1 knockout display reduced aberrant hippocampal neurogenesis but no change in epileptic seizures. Exp Neurol. 2017; 293:190–198.
Article20. Kim JE, Cho KO. The pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy and EEG monitoring using radiotelemetry system in mice. J Vis Exp. 2018; (132):e56831.
Article21. Osorio I, Lyubushin A, Sornette D. Automated seizure detection: unrecognized challenges, unexpected insights. Epilepsy Behav. 2011; 22:Suppl 1. S7–S17.
Article22. Dikanev T, Smirnov D, Wennberg R, Velazquez JL, Bezruchko B. EEG nonstationarity during intracranially recorded seizures: statistical and dynamical analysis. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005; 116:1796–1807.
Article23. Alarcon G, Binnie CD, Elwes RD, Polkey CE. Power spectrum and intracranial EEG patterns at seizure onset in partial epilepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1995; 94:326–337.
Article24. Akin M, Kiymik MK. Application of periodogram and AR spectral analysis to EEG signals. J Med Syst. 2000; 24:247–256.25. Mohseni HR, Maghsoudi A, Shamsollahi MB. Seizure detection in EEG signals: a comparison of different approaches. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006; Suppl. 6724–6727.
Article26. Acharya UR, Sree SV, Alvin AP, Yanti R, Suri JS. Application of non-linear and wavelet based features for the automated identification of epileptic EEG signals. Int J Neural Syst. 2012; 22:1250002.
Article27. Gajic D, Djurovic Z, Gligorijevic J, Di Gennaro S, Savic-Gajic I. Detection of epileptiform activity in EEG signals based on time-frequency and non-linear analysis. Front Comput Neurosci. 2015; 9:38.
Article28. Tzallas AT, Tsipouras MG, Fotiadis DI. Automatic seizure detection based on time-frequency analysis and artificial neural networks. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2007; 2007:80510.
Article29. Williamson JR, Bliss DW, Browne DW, Narayanan JT. Seizure prediction using EEG spatiotemporal correlation structure. Epilepsy Behav. 2012; 25:230–238.
Article30. Zhang Y, Zhou W, Yuan Q, Wu Q. A low computation cost method for seizure prediction. Epilepsy Res. 2014; 108:1357–1366.
Article31. Ansari AH, Cherian PJ, Caicedo A, Naulaers G, De Vos M, Van Huffel S. Neonatal seizure detection using deep convolutional neural networks. Int J Neural Syst. 2018; DOI: 10.1142/S0129065718500119.
Article32. Truong ND, Nguyen AD, Kuhlmann L, Bonyadi MR, Yang J, Ippolito S, Kavehei O. Convolutional neural networks for seizure prediction using intracranial and scalp electroencephalogram. Neural Netw. 2018; 105:104–111.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Preliminary Study of Experimental Neural Network Model in the Nervous System
- Detection and Weak Segmentation of Masses in Gray-Scale Breast Mammogram Images Using Deep Learning
- Convolutional Neural Network Based Sinogram Extrapolation for Truncated CT: Preliminary Study
- Overview of Deep Learning in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
- Perceptron: Basic Principles of Deep Neural Networks