Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2019 Jan;36(1):26-35. 10.12701/yujm.2019.00059.
Telmisartan increases hepatic glucose production via protein kinase C ζ-dependent insulin receptor substrate-1 phosphorylation in HepG2 cells and mouse liver
- Affiliations
-
- 1Soonchunhyang Institute of Medi-bio Science (SIMS), Soonchunhyang University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pharmacology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. biohyong@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2434096
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00059
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Dysregulation of hepatic glucose production (HGP) contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Telmisartan, an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker (ARB), has various ancillary effects in addition to common blood pressure-lowering effects. The effects and mechanism of telmisartan on HGP have not been fully elucidated and, therefore, we investigated these phenomena in hyperglycemic HepG2 cells and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice.
METHODS
Glucose production and glucose uptake were measured in HepG2 cells. Expression levels of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase α (G6Pase-α), and phosphorylation levels of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) and protein kinase C ζ (PKCζ) were assessed by western blot analysis. Animal studies were performed using HFD-fed mice.
RESULTS
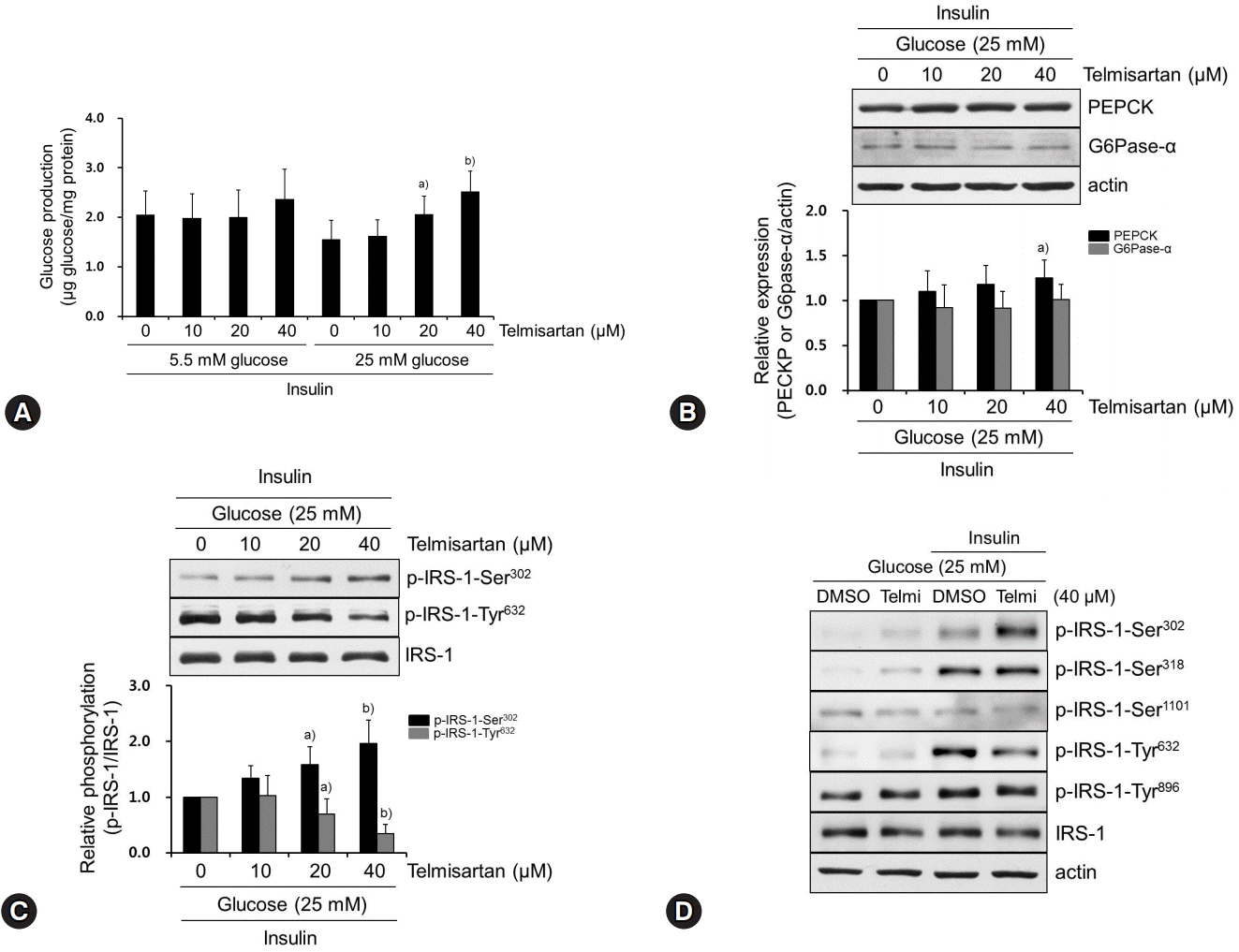
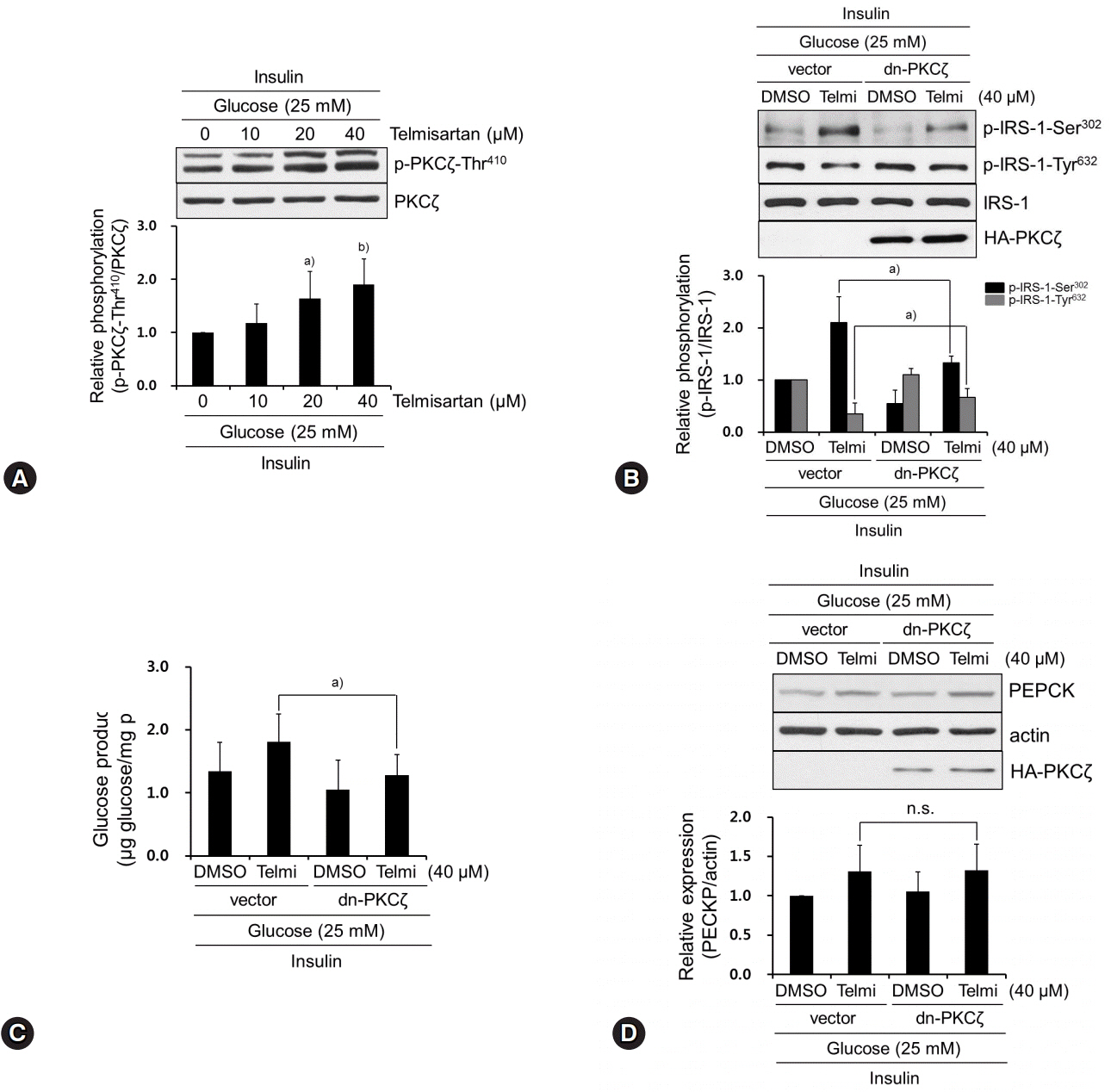
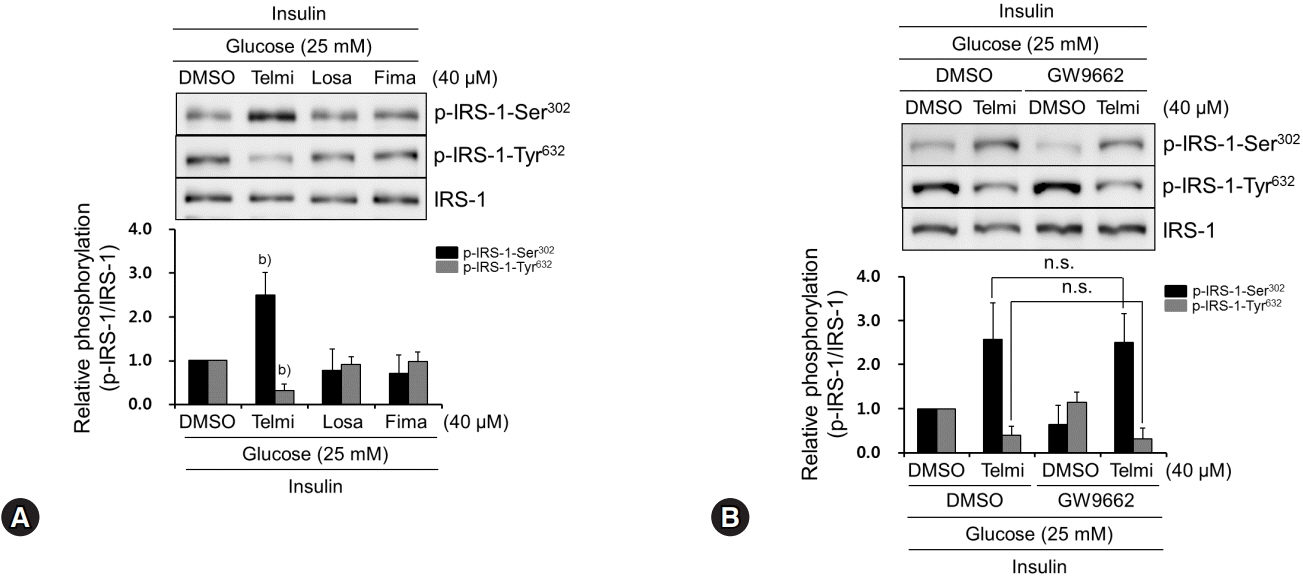
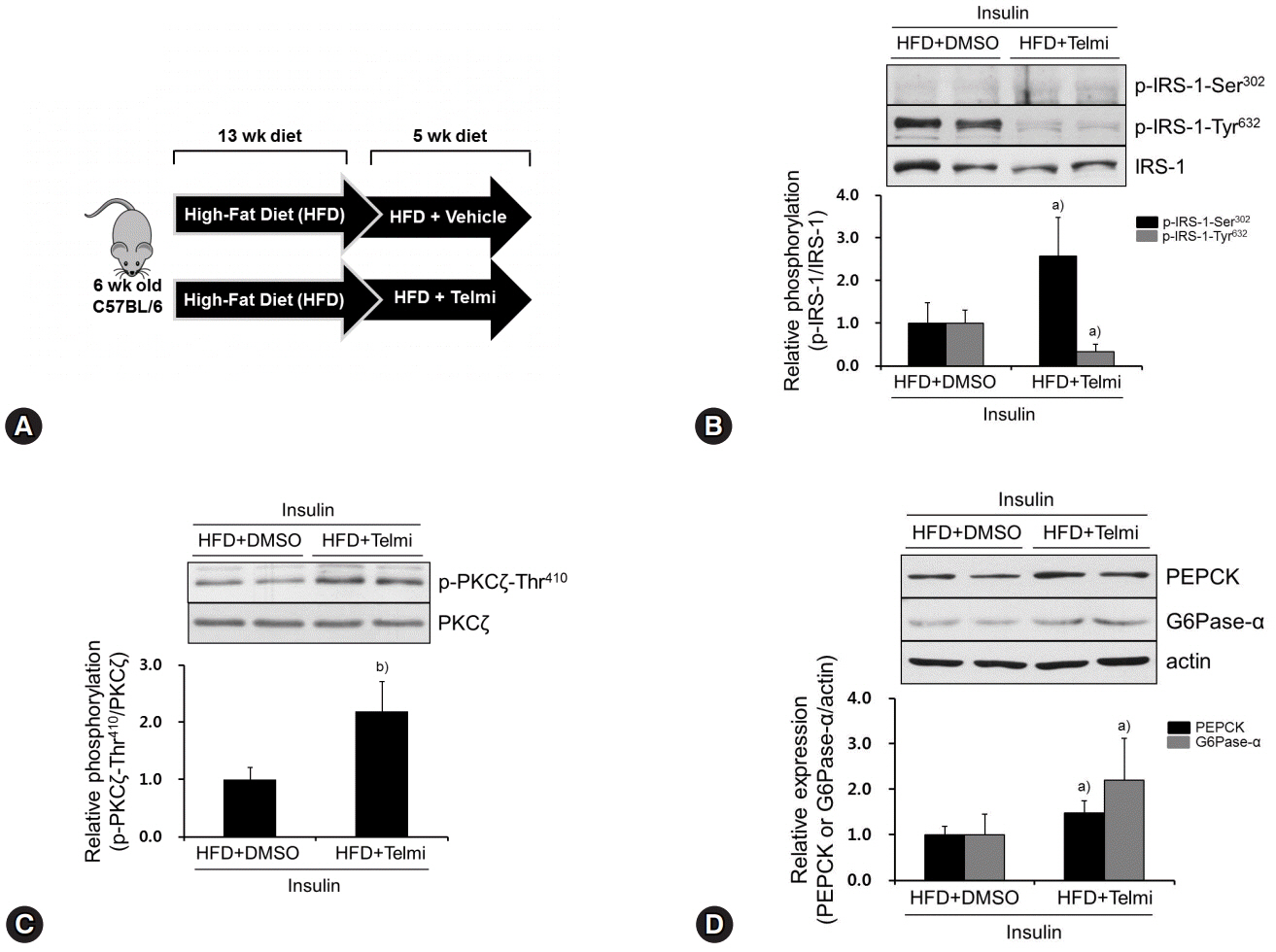
Telmisartan dose-dependently increased HGP, and PEPCK expression was minimally increased at a 40 μM concentration without a change in G6Pase-α expression. In contrast, telmisartan increased phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser302 (p-IRS-1-Ser302) and decreased p-IRS-1-Tyr632 dose-dependently. Telmisartan dose-dependently increased p-PKCζ-Thr410 which is known to reduce insulin action by inducing IRS-1 serine phosphorylation. Ectopic expression of dominant-negative PKCζ significantly attenuated telmisartan-induced HGP and p-IRS-1-Ser302 and -inhibited p-IRS-1-Tyr632. Among ARBs, including losartan and fimasartan, only telmisartan changed IRS-1 phosphorylation and pretreatment with GW9662, a specific and irreversible peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) antagonist, did not alter this effect. Finally, in the livers from HFD-fed mice, telmisartan increased p-IRS-1-Ser302 and decreased p-IRS-1-Tyr632, which was accompanied by an increase in p-PKCζ-Thr410.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that telmisartan increases HGP by inducing p-PKCζ-Thr410 that increases p-IRS-1-Ser302 and decreases p-IRS-1-Tyr632 in a PPARγ-independent manner.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Blotting, Western
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2
Diet, High-Fat
Ectopic Gene Expression
Glucose*
Glucose-6-Phosphatase
Hep G2 Cells*
Insulin Receptor Substrate Proteins*
Insulin*
Liver*
Losartan
Mice*
Peroxisomes
Phosphoenolpyruvate
Phosphorylation
Protein Kinase C*
Protein Kinases*
Receptor, Angiotensin, Type 1
Receptor, Insulin*
Serine
Glucose
Glucose-6-Phosphatase
Insulin
Insulin Receptor Substrate Proteins
Losartan
Phosphoenolpyruvate
Protein Kinase C
Protein Kinases
Receptor, Angiotensin, Type 1
Receptor, Insulin
Serine
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ekberg K, Landau BR, Wajngot A, Chandramouli V, Efendic S, Brunengraber H, et al. Contributions by kidney and liver to glucose production in the postabsorptive state and after 60 h of fasting. Diabetes. 1999; 48:292–8.
Article2. Hatting M, Tavares CDJ, Sharabi K, Rines AK, Puigserver P. Insulin regulation of gluconeogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018; 1411:21–35.
Article3. Saltiel AR, Kahn CR. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature. 2001; 414:799–806.
Article4. Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B, Kahn CR. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006; 7:85–96.
Article5. Boura-Halfon S, Zick Y. Phosphorylation of IRS proteins, insulin action, and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 296:E581–91.
Article6. Tamemoto H, Kadowaki T, Tobe K, Yagi T, Sakura H, Hayakawa T, et al. Insulin resistance and growth retardation in mice lacking insulin receptor substrate-1. Nature. 1994; 372:182–6.
Article7. Schmitz-Peiffer C, Biden TJ. Protein kinase C function in muscle, liver, and beta-cells and its therapeutic implications for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2008; 57:1774–83.8. Andros V, Egger A, Dua U. Blood pressure goal attainment according to JNC 7 guidelines and utilization of antihypertensive drug therapy in MCO patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. J Manag Care Pharm. 2006; 12:303–9.
Article9. Michel MC, Foster C, Brunner HR, Liu L. A systematic comparison of the properties of clinically used angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists. Pharmacol Rev. 2013; 65:809–48.
Article10. Takagi H, Umemoto T; All-Literature Investigation of Cardiovascular Evidence Group. A meta-analysis of randomized trials of telmisartan versus active controls for insulin resistance in hypertensive patients. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2014; 8:578–92.
Article11. Kubik M, Chudek J, Adamczak M, Wiecek A. Telmisartan improves cardiometabolic profile in obese patients with arterial hypertension. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2012; 35:281–9.
Article12. Li L, Luo Z, Yu H, Feng X, Wang P, Chen J, et al. Telmisartan improves insulin resistance of skeletal muscle through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-δ activation. Diabetes. 2013; 62:762–74.
Article13. Ushijima K, Takuma M, Ando H, Ishikawa-Kobayashi E, Nozawa M, Maekawa T, et al. Effects of telmisartan and valsartan on insulin sensitivity in obese diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013; 698:505–10.
Article14. Cho DH, Seo J, Park JH, Jo C, Choi YJ, Soh JW, et aI. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 phosphorylates endothelial nitric oxide synthase at serine 116. Hypertension. 2010; 55:345–52.
Article15. Soh JW, Lee EH, Prywes R, Weinstein IB. Novel roles of specific isoforms of protein kinase C in activation of the c-fos serum response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1999; 19:1313–24.
Article16. Bhattacharya S, Ghosh R, Maiti S, Khan GA, Sinha AK. The activation by glucose of liver membrane nitric oxide synthase in the synthesis and translocation of glucose transporter-4 in the production of insulin in the mice hepatocytes. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e81935.
Article17. Burgess SC, He T, Yan Z, Lindner J, Sherry AD, Malloy CR, et al. Cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase does not solely control the rate of hepatic gluconeogenesis in the intact mouse liver. Cell Metab. 2007; 5:313–20.
Article18. Zang M, Zuccollo A, Hou X, Nagata D, Walsh K, Herscovitz H, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase is required for the lipid-lowering effect of metformin in insulin-resistant human HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:47898–905.
Article19. Liu YF, Paz K, Herschkovitz A, Alt A, Tennenbaum T, Sampson SR, et al. Insulin stimulates PKCzeta -mediated phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). A self-attenuated mechanism to negatively regulate the function of IRS proteins. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:14459–65.20. Ravichandran LV, Esposito DL, Chen J, Quon MJ. Protein kinase C-zeta phosphorylates insulin receptor substrate-1 and impairs its ability to activate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in response to insulin. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:3543–9.21. Bandyopadhyay G, Standaert ML, Sajan MP, Karnitz LM, Cong L, Quon MJ, et al. Dependence of insulin-stimulated glucose transporter 4 translocation on 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 and its target threonine-410 in the activation loop of protein kinase C-zeta. Mol Endocrinol. 1999; 13:1766–72.22. Leesnitzer LM, Parks DJ, Bledsoe RK, Cobb JE, Collins JL, Consler TG, et al. Functional consequences of cysteine modification in the ligand binding sites of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors by GW9662. Biochemistry. 2002; 41:6640–50.
Article23. Kintscher U. ONTARGET, TRANSCEND, and PRoFESS: new-onset diabetes, atrial fibrillation, and left ventricular hypertrophy. J Hypertens. 2009; 27:S36–9.
Article24. Cho H, Mu J, Kim JK, Thorvaldsen JL, Chu Q, Crenshaw EB 3rd, Kaestner KH, et al. Insulin resistance and a diabetes mellitus-like syndrome in mice lacking the protein kinase Akt2 (PKB beta). Science. 2001; 292:1728–31.
Article25. Cho H, Thorvaldsen JL, Chu Q, Feng F, Birnbaum MJ. Akt1/PKBalpha is required for normal growth but dispensable for maintenance of glucose homeostasis in mice. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:38349–52.26. Song KH, Park JH, Jo I, Park JY, Seo J, Kim SA, et al. Telmisartan attenuates hyperglycemia-exacerbated VCAM-1 expression and monocytes adhesion in TNFα-stimulated endothelial cells by inhibiting IKKβ expression. Vascul Pharmacol. 2016; 78:43–52.
Article27. Song KH, Bae SJ, Chang J, Park JH, Jo I, Cho KW, et al. Telmisartan mitigates hyperglycemia-induced vascular inflammation by increasing GSK3β-Ser(9) phosphorylation in endothelial cells and mouse aortas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017; 491:903–11.
Article28. Obermoser V, Urban ME, Murgueitio MS, Wolber G, Kintscher U, Gust R. New telmisartan-derived PPARγ agonists: impact of the 3D-binding mode on the pharmacological profile. Eur J Med Chem. 2016; 124:138–52.
Article29. Moeschel K, Beck A, Weigert C, Lammers R, Kalbacher H, Voelter W, et al. Protein kinase C-zeta-induced phosphorylation of Ser318 in insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) attenuates the interaction with the insulin receptor and the tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:25157–63.30. Smith DH, Matzek KM, Kempthorne-Rawson J. Dose response and safety of telmisartan in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. J Clin Pharmacol. 2000; 40:1380–90.31. Zhang P, Zhang Y, Chen X, Li R, Yin J, Zhong D. Pharmacokinetics of telmisartan in healthy Chinese subjects after oral administration of two dosage levels. Arzneimittelforschung. 2006; 56:569–73.
Article32. Cianchetti S, Del Fiorentino A, Colognato R, Di Stefano R, Franzoni F, Pedrinelli R. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties of telmisartan in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 2008; 198:22–8.
Article33. Nakano A, Hattori Y, Aoki C, Jojima T, Kasai K. Telmisartan inhibits cytokine-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation independently of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Hypertens Res. 2009; 32:765–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of naringenin and naringin on the glucose uptake and AMPK phosphorylation in high glucose treated HepG2 cells
- Rho-kinase and Insulin Signaling
- DA-1241, a Novel GPR119 Agonist, Improves Hyperglycaemia by Inhibiting Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Enhancing Insulin Secretion in Diabetic Mice
- The regulatory mechanism of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin in 3T3 L1 fibroblasts: phosphorylation-independent activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- Fimasartan Ameliorates Deteriorations in Glucose Metabolism in a High Glucose State by Regulating Skeletal Muscle and Liver Cells