Ann Lab Med.
2017 Nov;37(6):465-474. 10.3343/alm.2017.37.6.465.
Diagnostics and Prognostication of Myelodysplastic Syndromes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oncology and Hematology, Blood Transfusion Service, Policlinico Gemelli Foundation, Catholic University of Sacred Heart, Rome, Italy. gina.zini@unicatt.it
- KMID: 2425986
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2017.37.6.465
Abstract
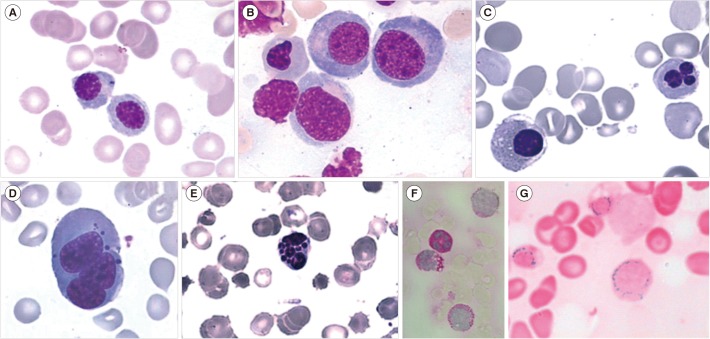
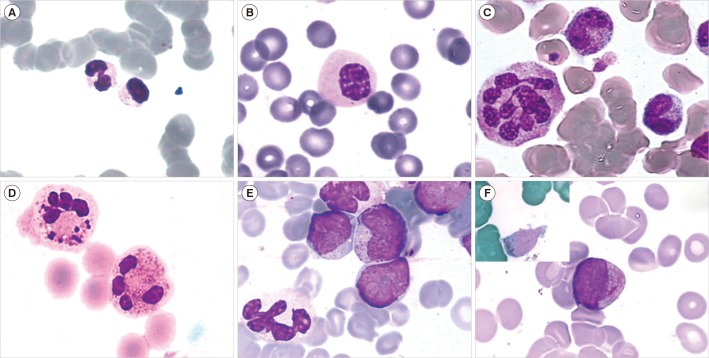
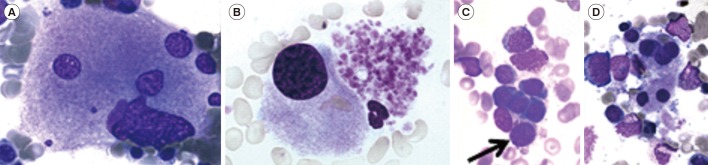
- MDS are a heterogeneous and complex group of clonal hematological neoplasms arising from a hematopoietic stem cell, and characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis, resulting in increased apoptosis in the bone marrow and peripheral cytopenia, which involves one or more lineages. Epigenetic changes are reported as "˜founder' mutations in the case of MDS. Its incidence in the general population has been reported as five new MDS diagnoses per 100,000 people. It affects men more frequently than it does women, and its incidence increases with age. The diagnostic classification, now in use, is the one of the World Health Organization, revised in August 2016. It recognizes six distinct entities in addition to a provisional entity of childhood. In most of the cases, diagnosis is based on the morphologic quantitative and qualitative evaluation of the peripheral blood and bone marrow using basic hematological techniques. Bone marrow biopsy and flow cytometric immunophenotyping also offer support for further diagnostic elucidation, while cytogenetics and molecular genetics are presently fully integrated into prognostication, treatment processes, and decision-making.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Myelodysplastic syndromes and overlap syndromes
Yoon Hwan Chang
Blood Res. 2021;56(S1):51-64. doi: 10.5045/br.2021.2021010.
Reference
-
1. Itzykson R, Fenaux P. Epigenetics of myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia. 2014; 28:497–506. PMID: 24247656.2. Hahn CN, Chong CE, Carmichael CL, Wilkins EJ, Brautigan PJ, Li XC, et al. Heritable GATA2 mutations associated with familial myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet. 2011; 43:1012–1017. PMID: 21892162.3. Lewinsohn M, Brown AL, Weinel LM, Phung C, Rafidi G, Lee MK, et al. Novel germ line DDX41 mutations define families with a lower age of MDS/AML onset and lymphoid malignancies. Blood. 2016; 127:1017–1023. PMID: 26712909.4. Bannon SA, DiNardo CD. Hereditary predispositions to myelodysplastic syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17:838–849.5. Vardiman JW, Harris NL, Brunning RD. The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms. Blood. 2002; 100:2292–2302. PMID: 12239137.6. Bain BJ. The bone marrow aspirate of healthy subjects. Br J Haematol. 1996; 94:206–209. PMID: 8757536.7. Rollison DE, Howlader N, Smith MT, Strom SS, Merritt WD, Ries LA, et al. Epidemiology of myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myeloproliferative disorders in the United States, 2001-2004, using data from the NAACCR and SEER programs. Blood. 2008; 112:45–52. PMID: 18443215.8. Dinmohamed AG, Visser O, van Norden Y, Huijgens PC, Sonneveld P, van de Loosdrecht AA, et al. Trends in incidence, initial treatment and survival of myelodysplasticsyndromes: a population-based study of 5144 patients diagnosed in the Netherlands from 2001 to 2010. Eur J Cancer. 2014; 50:1004–1012. PMID: 24388662.9. Ma X. Epidemiology of myelodysplastic syndromes. Am J Med. 2012; 125(S7):S2–S5.10. Paydas S. Young age MDS: differences between Western and Eastern countries. Leuk Res. 2006; 30:362.11. Breccia M, Finsinger P, Loglisci G, Santopietro M, Salaroli A, Serrao A, et al. Prognostic features of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes aged <50 years: update of a single-institution experience. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012; 53:2439–2443. PMID: 22647078.12. Niemeyer CM, Baumann I. Myelodysplastic syndrome in children and adolescents. Semin Hematol. 2008; 45:60–70. PMID: 18179970.13. Liew E, Owen C. Familial myelodysplastic syndromes: a review of the literature. Haematologica. 2011; 96:1536–1542. PMID: 21606161.14. Bueso-Ramos CE, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Routbort MJ, Hanson CA. Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms. Am J Clin Pathol. 2015; 144:207–218. PMID: 26185306.15. Von Leube W. Rapid verlaufende schwere Anämie mit gleichzeitiger leukämischer Veränderung del Blutbildes. Klin Wochenschr. 1900; 37:85.16. Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, et al. Proposals for the classification of the acute leukaemias. French-American-British (FAB) cooperative group. Br J Haematol. 1976; 33:451–458. PMID: 188440.17. Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 1982; 51:189–199. PMID: 6952920.18. Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009; 114:937–951. PMID: 19357394.19. Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016; 127:2391–2405. PMID: 27069254.20. Malcovati L, Papaemmanuil E, Bowen DT, Boultwood J, Della Porta MG, Pascutto C, et al. Clinical significance of SF3B1 mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood. 2011; 118:6239–6246. PMID: 21998214.21. Greenberg PL, Stone RM, Al-Kali A, Barta SK, Bejar R, Bennett JM, et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes, Version 2.2017, NCCN Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2017; 15:60–87. PMID: 28040720.22. Lim EM, Cembrowski G, Cembrowski M, Clarke G. Race-specific WBC and neutrophil count reference intervals. Int J Lab Hematol. 2010; 32:590–597. PMID: 20236184.23. Goasguen JE, Bennett JM, Bain BJ, Brunning R, Vallespi MT, Tomonaga M, et al. Proposal for refining the definition of dysgranulopoiesis in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res. 2014; 38:447–453. PMID: 24439566.24. Mufti GJ, Bennett JM, Goasguen J, Bain BJ, Baumann I, Brunning R, et al. Diagnosis and classification of myelodysplastic syndrome: International Working Group on Morphology of myelodysplastic syndrome (IWGM-MDS) consensus proposals for the definition and enumeration of myeloblasts and ring sideroblasts. Haematologica. 2008; 93:1712–1717. PMID: 18838480.25. Goasguen JE, Bennett JM, Bain BJ, Vallespi T, Brunning R, Mufti GJ. Morphological evaluation of monocytes and their precursors. Haematologica. 2009; 94:994–997. PMID: 19535346.26. Bennett JM, Tuechler H, Aul C, Strupp C, Germing U. Dysplastic erythroid precursors in the myelodysplastic syndromes and the acute myeloid leukemias: Is there biologic significance? (How should blasts be counted?). Leuk Res. 2016; 47:63–69. PMID: 27258735.27. Zini G, d'Onofrio G. Epitaph for erythroleukemia. Haematologica. 2004; 89:ELT11. PMID: 15339700.28. Lai R, Arber DA, Brynes RK, Chan O, Chang KL. Untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia concurrent with or followed by acute myelogenous leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome. A report of five cases and review of the literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 1999; 111:373–378. PMID: 10078113.29. Al Mussaed E, Osman H, Elyamany G. Simultaneous existence of acute myeloid leukemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a case report. BMC Cancer. 2016; 16:739. PMID: 27643996.30. Bennett JM, Orazi A. Diagnostic criteria to distinguish hypocellular acute myeloid leukemia from hypocellular myelodysplastic syndromes and aplastic anemia: recommendations for a standardized approach. Haematologica. 2009; 94:264–268. PMID: 19144661.31. Goasguen JE, Bennett JM, Bain BJ, Brunning RD, Vallespí MT, Tomonaga M, et al. Quality control initiative on the evaluation of the dysmegakaryopoiesis in myeloid neoplasms: difficulties in the assessment of dysplasia. Leuk Res. 2016; 45:75–81. PMID: 27107657.32. Bartl R, Frisch B, Baumgart R. Morphologic classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS): combined utilization of bone marrow aspirates and trephine biopsies. Leuk Res. 1992; 16:15–33. PMID: 1732665.33. Orazi A. Histopathology in the diagnosis and classification of acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases. Pathobiology. 2007; 74:97–114. PMID: 17587881.34. Della Porta MG, Malcovati L, Boveri E, Travaglino E, Pietra D, Pascutto C, et al. Clinical relevance of bone marrow fibrosis and CD34-positive cell clusters in primary myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:754–762. PMID: 19103730.35. Charafeddine KM, Ibrahim GY, Mahfouz RA, Zaatari GS, Salem ZM. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia associated with myelodysplastic syndrome with ring sideroblasts. South Med J. 2010; 103:823–827. PMID: 20622728.36. van de Loosdrecht AA, Ireland R, Kern W, Della Porta MG, Alhan C, Balleisen JS, et al. Rationale for the clinical application of flow cytometry in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: position paper of an International Consortium and the European LeukemiaNet Working Group. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013; 54:472–475. PMID: 22916713.37. Haferlach T, Nagata Y, Grossmann V, Okuno Y, Bacher U, Nagae G, et al. Landscape of genetic lesions in 944 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia. 2014; 28:241–247. PMID: 24220272.38. Vila L, Charrin C, Archimbaud E, Treille-Ritouet D, Fraisse J, Felman P, et al. Correlations between cytogenetics and morphology in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blut. 1990; 60:223–227. PMID: 2337681.39. Gupta R, Soupir CP, Johri V, Hasserjian RP. Myelodysplastic syndrome with isolated deletion of chromosome 20q: an indolent disease with minimal morphologic dysplasia and frequent thrombocytopenic presentation. Br J Haematol. 2007; 139:265–268. PMID: 17764468.40. Cargo CA, Rowbotham N, Evans PA, Barrans SL, Bowen DT, Crouch S, et al. Targeted sequencing identifies patients with preclinical MDS at high risk of disease progression. Blood. 2015; 126:2362–2365. PMID: 26392596.41. Malcovati L, Karimi M, Papaemmanuil E, Ambaglio I, Jädersten M, Jansson M, et al. SF3B1 mutation identifies a distinct subset of myelodysplastic syndrome with ring sideroblasts. Blood. 2015; 126:233–241. PMID: 25957392.42. Patnaik MM, Hanson CA, Sulai NH, Hodnefield JM, Knudson RA, Ketterling RP, et al. Prognostic irrelevance of ring sideroblast percentage in World Health Organization-defined myelodysplastic syndromes without excess blasts. Blood. 2012; 119:5674–5677. PMID: 22538853.43. Bejar R, Stevenson K, Abdel-Wahab O, Galili N, Nilsson B, Garcia-Manero G, et al. Clinical effect of point mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:2496–2506. PMID: 21714648.44. Ganguly BB, Kadam NN. Mutations of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS): an update. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2016; 769:47–62. PMID: 27543316.45. Steensma DP, Bejar R, Jaiswal S, Lindsley RC, Sekeres MA, Hasserjian RP, et al. Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential and its distinction from myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2015; 126:9–16. PMID: 25931582.46. Kwok B, Hall JM, Witte JS, Xu Y, Reddy P, Lin K, et al. MDS-associated somatic mutations and clonal hematopoiesis are common in idiopathic cytopenias of undetermined significance. Blood. 2015; 126:2355–2361. PMID: 26429975.47. Worsley A, Oscier DG, Stevens J, Darlow S, Figes A, Mufti GJ, et al. Prognostic features of chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia: a modified Bournemouth score gives the best prediction of survival. Br J Haematol. 1988; 68:17–21. PMID: 3422815.48. Goasguen JE, Garand R, Bizet M, Bremond JL, Gardais J, Callat MP, et al. Prognostic factors of myelodysplastic syndromes: a simplified 3-D scoring system. Leuk Res. 1990; 14:255–262. PMID: 2319806.49. Aul C, Gattermann N, Heyll A, Germing U, Derigs G, Schneider W. Primary myelodysplastic syndromes: analysis of prognostic factors in 235 patients and proposal for an improved scoring system. Leukemia. 1992; 6:52–59.50. Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997; 89:2079–2088. PMID: 9058730.51. Malcovati L, Porta MG, Pascutto C, Invernizzi R, Boni M, Travaglino E, et al. Prognostic factors and life expectancy in myelodysplastic syndromes classified according to WHO criteria: a basis for clinical decision making. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:7594–7603. PMID: 16186598.52. Malcovati L, Germing U, Kuendgen A, Della Porta MG, Pascutto C, Invernizzi R, et al. Time-dependent prognostic scoring system for predicting survival and leukemic evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:3503–3510. PMID: 17687155.53. Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, Sanz G, Garcia-Manero G, Solé F, et al. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2012; 120:2454–2465. PMID: 22740453.54. Kantarjian H, O'Brien S, Ravandi F, Cortes J, Shan J, Bennett JM, et al. Proposal for a new risk model in myelodysplastic syndrome that accounts for events not considered in the original International Prognostic Scoring System. Cancer. 2008; 113:1351–1361. PMID: 18618511.55. Garcia-Manero G, Shan J, Faderl S, Cortes J, Ravandi F, Borthakur G, et al. A prognostic score for patients with lower risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia. 2008; 22:538–543. PMID: 18079733.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Myelodysplastic syndromes and overlap syndromes
- Classifications and prognostic scoring systems in myelodysplastic syndrome
- Azathioprine-induced Myelodysplasia Mimicking Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- Copper deficiency mimicking myelodysplastic syndrome
- Sweet's Syndrome with Myelodysplastic Syndrome Progressing to Acute Myelogenous Leukemia