J Korean Acad Nurs.
2018 Aug;48(4):432-442. 10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.432.
Effects of Group Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy on the Nurses' Job Stress, Burnout, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Youngnam Foreign Language College, Gyeongsan, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing · Institute for Health Science Research, Inje University, Busan, Korea. nurysh@inje.ac.kr
- KMID: 2424529
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.432
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to develop a Group REBT program with group counseling for nurses and test the effect of group counseling on their job stress, burnout, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention.
METHODS
A quasi-experimental study with nonequivalent control group design was employed to identify the effect of the Group REBT program on nurses' job stress, burnout, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention. Data were collected from 47 participants from two hospitals. The data from the experimental (n=23) and control (n=24) groups were analyzed from January 5 to April 3, 2015. The Group REBT program was conducted eight tmes in all, once a week, with each session lasting 180 minutes. The effect of experimental intervention was measured for each group using a series of structured questionnaires at each of the phases: Pre-intervention, post-intervention (immediately after intervention), and post-intervention (four weeks after intervention). Following this, the significance of the changes in the scores was tested.
RESULTS
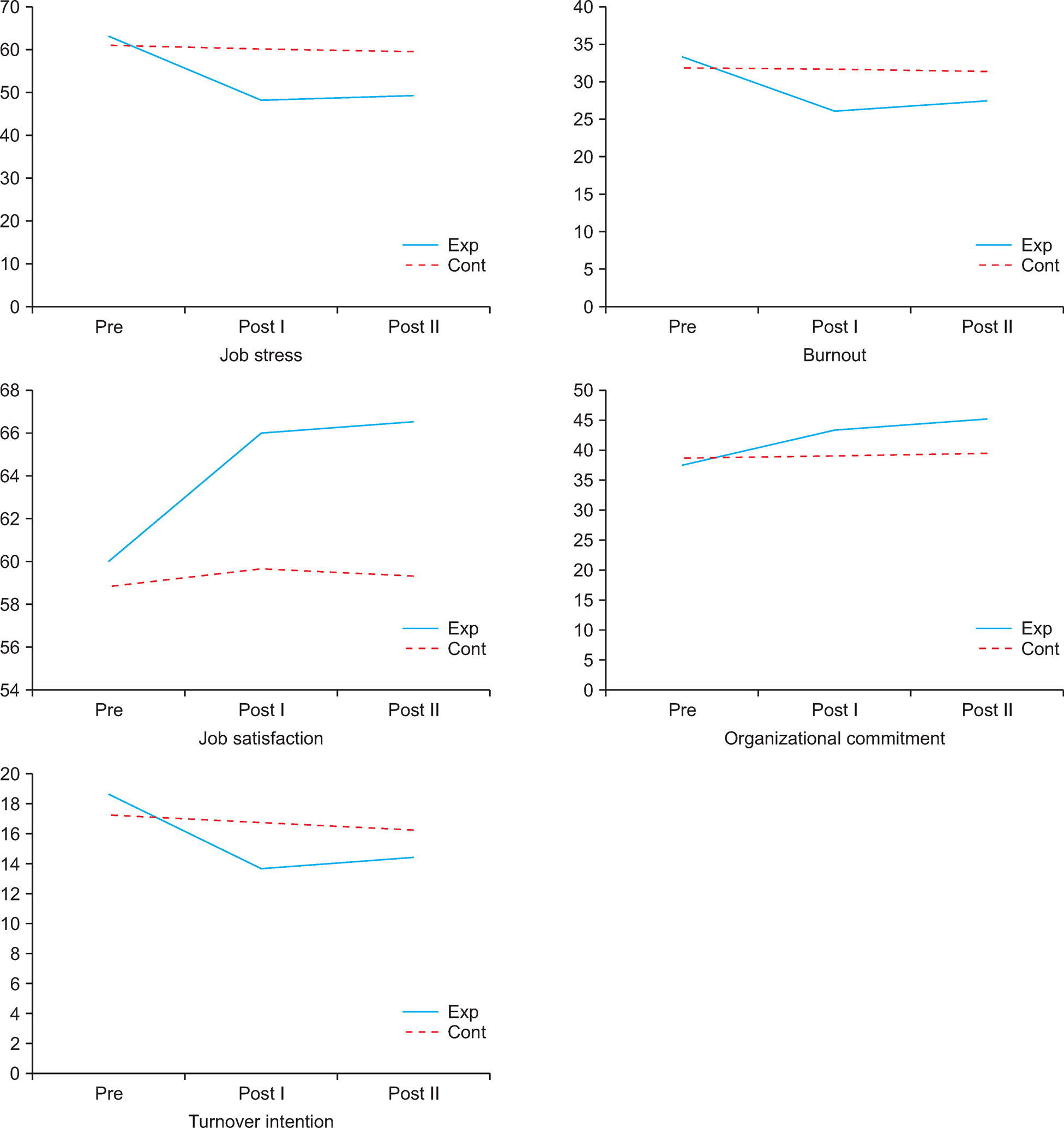
The scores of the experimental group, which received the Group REBT program, were compared with those of the control group; the hypotheses were supported in terms of job stress (F=8.85, p < .001), burnout (F=5.62, p=.022), job satisfaction (F=2.70, p=.042), organizational commitment (F=2.97, p=.048), and turnover intention (F=4.60, p=.012).
CONCLUSION
The Group REBT program was shown to be an effective intervention that could reduce nurses' job stress and burnout and increase job satisfaction and organizational commitment. Therefore, the Group REBT program can be adopted by nursing organizations to strategically decrease nurses' turnover intention.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Moon SJ, Han SS. A predictive model on turnover intention of nurses in Korea. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2011; 41(5):633–641. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.5.633.
Article2. Mosadeghrad AM, Ferlie E, Rosenberg D. A study of relationship between job stress, quality of working life and turnover intention among hospital employees. Health Services Management Research. 2011; 24(4):170–181. https://doi.org/10.1258/hsmr.2011.011009.
Article3. AbuAlRub RF. Job stress, job performance, and social support among hospital nurses. Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 2004; 36(1):73–78.
Article4. Kim JH, Park SA. A study on the determinants of job stress responses of the staff nurses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2003; 9(2):217–232.5. Brewer EW, Clippard LF. Burnout and job satisfaction among student support services personnel. Human Resource Development Quarterly. 2002; 13(2):169–186. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrdq.1022.
Article6. Ohue T, Moriyama M, Nakaya T. Examination of a cognitive model of stress, burnout, and intention to resign for Japanese nurses. Japan Journal of Nursing Science. 2011; 8(1):76–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7924.2010.00161.x.
Article7. Ellis A. Changing rational-emotive therapy (RET) to rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT). Journal of Rational Emotive and Cognitive Behavior Therapy. 1995; 13(2):85–89.
Article8. Park KA, Back HS, Han JS. The effects of REBT group counseling on the job stress, positive affect, negative affect and self-esteem of nurses. Korea Journal of Counseling. 2007; 8(3):951–963.9. Baek HS, Yu SJ. Effects of REBT group counseling on self-efficacy and organizational effectiveness of nurses with high scores on dysfunctional attitude scale. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2005; 11(4):415–423.10. Kwon JO, Kim EY. Impact of unit-level nurse practice environment on nurse turnover intention in the small and medium sized hospitals. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2012; 18(4):414–423. https://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2012.18.4.414.
Article11. Kang KN. Factors influencing turnover intention of nurses in small-medium sized hospitals. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2012; 18(2):155–165. https://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2012.18.2.155.
Article12. Choi GH. The development and effect of an empowerment program for clinical nurses [dissertation]. Busan: Kosin University;2014. p. 1–110.13. Oh EY, Jung MS. Effects of a cognitive training program on cognitive function and activities of daily living in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2017; 47(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.1.
Article14. Kim CK, Lee SY, Lee YJ, Jeong JJ, Choi WY. Theory and practice of counseling. 2nd ed. Seoul: Hakjisa;2016. p. 13–337.15. Chang SJ, Koh SB, Kang D, Kim SA, Kang MG, Lee CG, et al. Developing an occupational stress scale for Korean employees. Korean Journal of Occupational and Environment Medicine. 2005; 17(4):297–317.
Article16. Demerouti E, Bakker AB, Vardakou I, Kantas A. The convergent validity of two burnout instruments: A multitrait-multimethod analysis. European Journal of Psychological Assessment. 2003; 19(1):12–23. https://doi.org/10.1027//1015-5759.19.1.12.17. Kim MY. A study on the relationship between job strain and burnout [master’s thesis]. Cheongju: Chungbuk National University;2004. p. 1–75.18. Slavitt DB, Stamps PL, Piedmont EB, Haase AM. Nurses’ satisfaction with their work situation. Nursing Research. 1978; 27(2):114–120.
Article19. Park HT. Transformational and transactional leadership styles of the nurse administrators and job satisfaction, organizational commitment in nursing service. The Journal of Nurses Aca- demic Society. 1997; 27(1):228–241. https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.228.
Article20. Mowday RT, Steers RM, Porter LW. The measurement of organizational commitment. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 1979; 14(2):224–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-8791(79)90072-1.
Article21. Kim KJ. An empirical study on the turnover making process model [master’s thesis]. Seoul: Korea University;1986. p. 1–100.22. Mobley WH. Employee turnover, causes, consequences and control. Reading (MA): Addison-Wesley;1982. p. 10–11.23. Kim JH. A meta-analysis of effects of job stress management interventions (SMIs). Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007; 37(4):529–539. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.4.529.24. Na BJ, Kim EJ. A study on the mediating and moderating effect of work-family conflict in the relationship among emotional labor, occupational stress, and turnover intention. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2016; 22(3):260–269. https://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2016.22.3.260.
Article25. Cho WS, You MS. Problems and prospects of nursing research on job stress in Korea. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2013; 19(1):63–75. https://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2013.19.1.63.
Article26. Han YH, Sohn IS, Park KO, Kang KH. The relationships between professionalism, job involvement, organizational commitment and turnover intention among clinical nurses. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2010; 16(2):17–31.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationships among Burnout, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention to Resign in Hospital Nurses
- Effects of Job Crafting, Burnout, and Job Satisfaction on Nurses' Turnover Intention: A Path Analysis
- Mediating Effects of Empowerment, Job Stress, and Organizational Commitment in Relation-oriented Nursing Organization Culture and Turnover Intention of Clinical Nurses
- Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention among Male Nurses
- A Structural Model of Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention: Focusing on Organizational Characteristics, Job Satisfaction, and Job Embeddedness