J Korean Acad Nurs Adm.
2013 Jun;19(3):372-381.
Mediating Effects of Empowerment, Job Stress, and Organizational Commitment in Relation-oriented Nursing Organization Culture and Turnover Intention of Clinical Nurses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Operation Room, Jeju Hanmaeum Hospital, Korea. mika0221@hanmail.net
Abstract
- PURPOSE
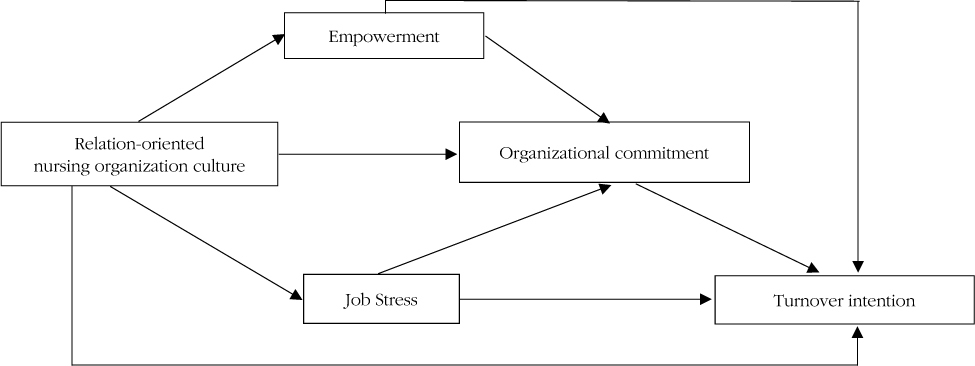
The purposes of this study were to analyze the mediating effects of empowerment, job stress, organizational commitment and relation-oriented nursing organization culture on turnover intention of clinical nurses.
METHODS
Participants selected for the final analysis were 382 nurses working in 4 general hospitals. Data were analyzed through descriptive statistics Pearson correlation analysis (SPSS/WIN 17.0), and Path analysis (AMOS 18.0).
RESULTS
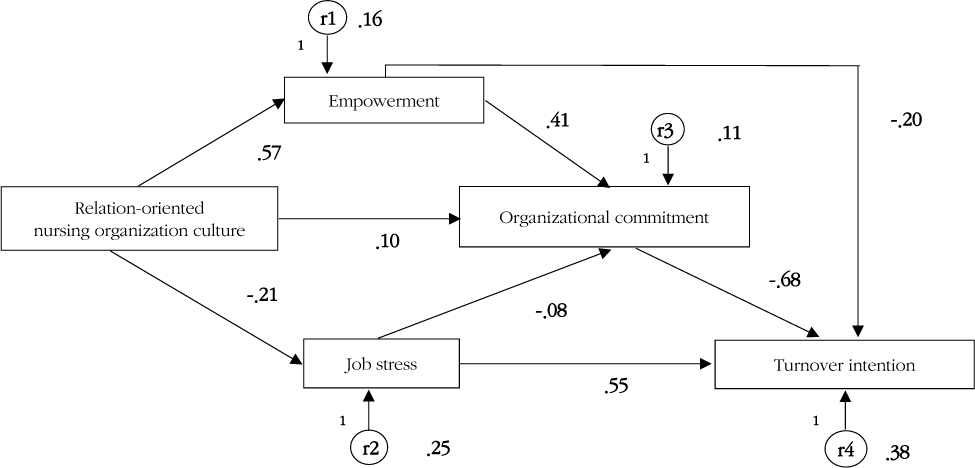
The study results are as follows: relation-oriented nursing organizational culture had no direct effect but had an indirect effect on nurses' turnover intention through empowerment, job stress, and organizational commitment, while job stress and organizational commitment had direct effects on turnover intention. The results also showed that empowerment had strong effect on organizational commitment, but job stress had very weak effect. Empowerment had an effect on turnover intention.
CONCLUSION
These results indicate that establishment of relation-oriented nursing organization culture is imperative if clinical nurses' turnover intention is to be decreased.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bae BR. Structural equation modeling with AMOS 19: Principles and practice. 2011. Seoul: CheongRam Publishing.2. Chandler GE. The relationship of nursing work environment to empowerment and powerlessness. 1986. Utah, Salt Lake: College of Nursing, University of Utah;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.3. Han SJ. A study on the relationship between nursing organizational culture and organizational performance. 2000. Seoul, Korea: Ewha Womans University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.4. Kanter RM. The change masters. 1983. New York: Basic Books.5. Kim DE. AMOS A to Z. 2008. Seoul: Hakhyunsa.6. Lee YJ, Kim KB. Experiences of nurse turnover. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2008. 38:248–257.7. Kim KJ. An empirical study on turnover decision process model. 1986. Seoul: Korea University Press.8. Kim MJ, Gu MO. The development of the stress measurement tool for staff nurses working in the hospital. J Nurs Acad Soc. 1984. 14(2):28–37.9. Kim MR. Influential factors on turnover intention of nurses: The effect of nurse organizational commitment and career commitment to turnover intention. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2007. 13:335–344.10. Kim MS, Han SJ, Kim SJ. The development of the nursing organization culture measurement tool. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2004. 10:175–184.11. Kim SI, Kim JA. A study on nursing unit culture, efficiency on nursing performance, job satisfaction and turnover intention. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 1997. 3(2):17–40.12. Kim SW, Jung HY. A review on assessment methods of fit for structural model. J Coll Educ Pusan Natl Univ. 1999. 38:179–196.13. Kim YJ. Field research on the nursing organizational culture in hospital setting. 2013. Seoul, Korea: Ewha Womans University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.14. Lee EJ, Han JY, Kim MY. Effects of the organizational culture on the job satisfaction and organization commitment. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2008. 14:5–12.15. Lee HK. Nurses' perceptions of job-related empowerment, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment. 2001. Seoul, Korea: Yonsei University;Unpublished master's thesis.16. Lee MH. Relationship between organizational commitment, job involvement, and role stress of clinical nurses. J Nurs Acad Soc. 1996. 26:467–482.17. Moon SJ. Structural model of nurses' intentions of changing workplaces. 2010. Seoul, Korea: Kyung Hee University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.18. Mowday RT, Steers RM, Porter LW. The measurement of organization commitment. J Vocat Behav. 1979. 14:224–247.19. Oh EH, Chung BY. The effect of empowerment on nursing performance, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover in hospital nurse's. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2011. 17:391–401.20. Park JS, Lee MS. The effect nursing organizational culture on job satisfaction and turnover intention in general hospital: The mediating effect of empowerment. Korean J Health Serv Manag. 2011. 5(3):1–11.21. Seong TJ, Si GJ. Research methodology. 2006. Seoul: Hakjisa.22. Shon KH. Relationship between organizational culture types and job satisfaction of nurses in general hospitals. Daehan J Bus. 2003. 41:2277–2294.23. Suh ID, Do JW. Mediating effect of organization identification on the relationship between organization culture, organization commitment and turnover intentions. J Hum Resour Manag Res. 2007. 14(2):77–97.24. Yang GM. Analysis of the relationship between the empowerment, the job-related individual characteristics and the work performance of nurses. 1999. Seoul, Korea: Kyung Hee University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.25. Yang YS. ICU new nurses's job stress, job satisfaction, organizational commitment and turnover intention. 2008. Seoul, Korea: Ewha Womans University;Unpublished master's thesis.26. Yoo SJ, Choi YH. Predictive factors influencing turnover intention of nurses in small and medium-sized hospitals in Daegu city. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2009. 15:16–25.27. Yoon JA, Lee HJ. Internal marking, job stress, organizational commitment and turnover intention in nursing organization. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2007. 13:293–301.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Organizational Culture, Self-Leadership and Empowerment on Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention in General Hospital Nurses
- Factors Affecting Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Person-environment Fit
- The Effect of Empowerment on Nursing Performance, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses
- Effect of Nursing Organizational culture, Organizational Silence, and Organizational Commitment on the Intention of Retention among Nurses: Applying the PROCESS Macro Model 6
- A Structural Model of Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention: Focusing on Organizational Characteristics, Job Satisfaction, and Job Embeddedness