J Vet Sci.
2016 Sep;17(3):315-321. 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.3.315.
Inhibitory effect of red ginseng acidic polysaccharide from Korean red ginseng on phagocytic activity and intracellular replication of Brucella abortus in RAW 264.7 cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju 52828, Korea. kimsuk@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Veterinary Paraclinical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, University of the Philippines Los Baños, Los Baños 4031, Philippines.
- 3Department of Veterinary Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41566, Korea.
- 4Institute of Agriculture and Life Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju 52828, Korea.
- KMID: 2413130
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2016.17.3.315
Abstract
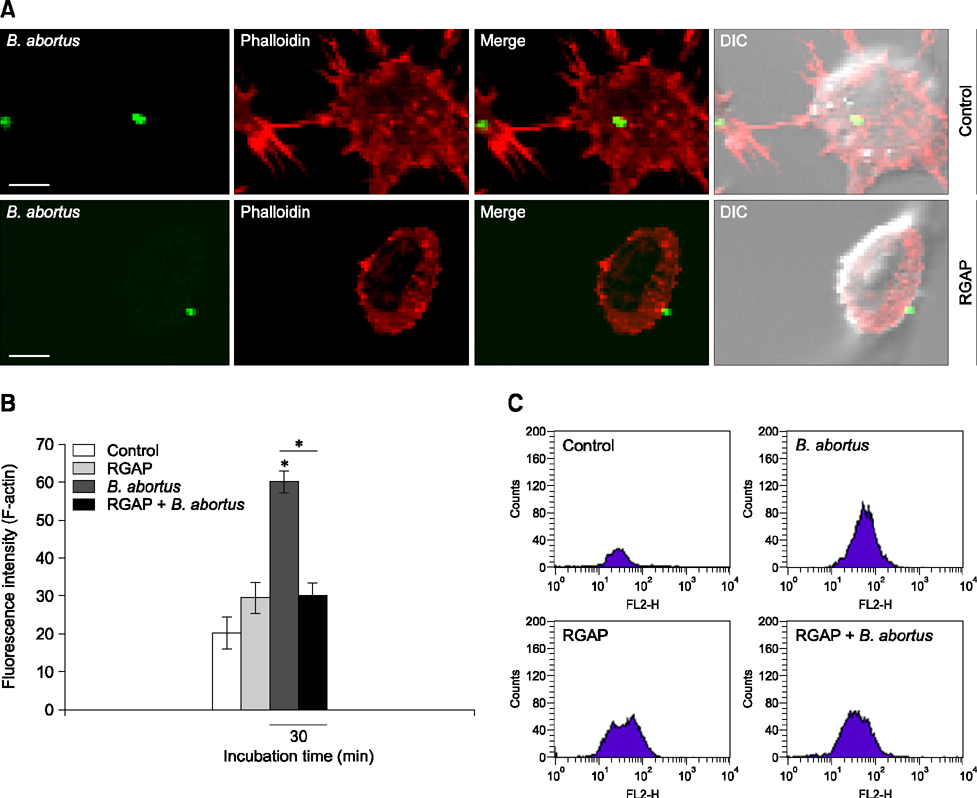
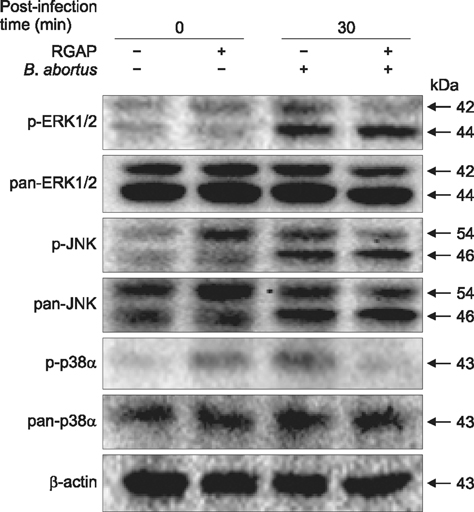
- Korean red ginseng (KRG) has long been used in traditional Korean and Oriental medicine. However, the anti-bacterial mechanism and therapeutic efficiency of KGR for intracellular Brucella infection are still unclear. In this study, the bactericidal activity of Korean red ginseng acidic polysaccharide (RGAP) on Brucella (B.) abortus and its cytotoxic effects on RAW 264.7 cells were evaluated. In addition, B. abortus internalization and intracellular replication in macrophages were investigated after RGAP treatment. RGAP-incubated cells displayed a marked reduction in the adherence, internalization and intracellular growth of B. abortus in macrophages. Furthermore, decreased F-actin fluorescence was observed relative to untreated B. abortus-infected cells. Western blot analysis of intracellular signaling proteins revealed reduced ERK, JNK and p38α phosphorylation levels in B. abortus-infected RGAP-treated cells compared to the control. Moreover, elevated co-localization of B. abortus-containing phagosomes with lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP-1) were observed in RGAP-treated cells compared with the control. Overall, the results of this study suggest that RGAP can disrupt phagocytic activity of B. abortus via suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) signaling proteins ERK, JNK and p38 levels and inhibit intracellular replication of B. abortus by enhancing phagolysosome fusion, which may provide an alternative control of brucellosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahn JY, Song JY, Yun YS, Jeong G, Choi IS. Protection of Staphylococcus aureus-infected septic mice by suppression of early acute inflammation and enhanced antimicrobial activity by ginsan. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2006; 46:187–197.
Article2. Al-Mariri A, Saour G, Hamoud R. In vitro antibacterial effects of five volatile oil extracts against intramacrophage Brucella abortus 544. Iran J Med Sci. 2012; 37:119–125.3. Byeon SE, Lee J, Kim JH, Yang WS, Kwak YS, Kim SY, Choung ES, Rhee MH, Cho JY. Molecular mechanism of macrophage activation by red ginseng acidic polysaccharide from Korean red ginseng. Mediators Inflamm. 2012; 2012:732860.
Article4. Carvalho Neta AV, Mol JPS, Xavier MN, Paixão TA, Lage AP, Santos RL. Pathogenesis of bovine brucellosis. Vet J. 2010; 184:146–155.
Article5. Choi KT. Botanical characteristics, pharmacological effects and medicinal components of Korean Panax ginseng C A Meyer. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008; 29:1109–1118.
Article6. Gul ST, Khan A. Epidemiology and epizootology of brucellosis: a review. Pak Vet J. 2007; 27:145–151.7. Huynh KK, Eskelinen E, Scott CC, Malevanets A, Saftig P, Grinstein S. LAMP proteins are required for fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. EMBO J. 2007; 26:313–324.
Article8. Kang S, Min H. Ginseng, the 'immunity boost': the effects of Panax ginseng on immune system. J Ginseng Res. 2012; 36:354–368.
Article9. Kim DG, Simborio HLT, Reyes AWB, Min W, Lee HJ, Lee JJ, Kim S. The key roles of toll-like receptor (TLR) for intracellular survival of Brucella. J Prev Vet Med. 2013; 37:185–192.
Article10. Kwak YS, Kyung JS, Kim JS, Cho JY, Rhee MH. Anti-hyperlipidemic effects of red ginseng acidic polysaccharide from Korean red ginseng. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010; 33:468–472.
Article11. Lee JJ, Kim DH, Kim DG, Lee HJ, Min W, Rhee MH, Yun BS, Kim S. Phellinus baumii extract influences pathogenesis of Brucella abortus in phagocyte by disrupting the phagocytic and intracellular trafficking pathway. J Appl Microbiol. 2013; 114:329–338.
Article12. Lee JJ, Kim DH, Park SB, Lim JJ, Kim DG, Min WG, Lee HJ, Kim DK, Chang HH, Kim S. Redundant effects of ketamine on the pathogenesis and severity of Brucella abortus infection. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013; 36:71–81.
Article13. MacPhee DJ. Methodological considerations for improving Western blot analysis. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2010; 61:171–177.
Article14. Oliveira SC, de Almeida LA, Carvalho NB, Oliveira FS, Lacerda TLS. Update on the role of innate immune receptors during Brucella abortus infection. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012; 148:129–135.
Article15. Robertson GT, Roop RM Jr. The Brucella abortus host factor I (HF-I) protein contributes to stress resistance during stationary phase and is a major determinant of virulence in mice. Mol Microbiol. 1999; 34:690–700.
Article16. Song Z, Johansen HK, Faber V, Moser C, Kharazmi A, Rygaard J, Høiby N. Ginseng treatment reduces bacterial load and lung pathology in chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1997; 41:961–964.
Article17. Ullah RW, Shirazi JH, Abubakar M, Zahur AB, Latif A, Alam T. Genetic diversity, zoonotic risk and "One Health" initiative of bovine brucellosis. Res J Vet Pract. 2013; 1:5–9.18. Yoo DG, Kim MC, Park MK, Park KM, Quan FS, Song JM, Wee JJ, Wang BZ, Cho YK, Compas RW, Kang SM. Protective effect of ginseng polysaccharides on influenza viral infection. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e33678.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Different invasion efficiencies of Brucella abortus wild-type and mutantsin RAW 264.7 and THP-1 phagocytic cells and HeLa non-phagocytic cells
- Anti-oxidant and Hepatoprotective Effect of White Ginsengs in H2O2-Treated HepG2 Cells
- Red ginseng spa therapy identification and preferences: targeting Chinese and Japanese tourists
- A Case of Anaphylaxis Induced by Red Ginseng
- Leucocyte Chemotaxis with Korean Ginseng