Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2018 Mar;11(1):9-16. 10.21053/ceo.2017.00626.
The Protective Effect of Egb 761 Against 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Hearing Loss: The Role of Sirtuin 1
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. yhkiment@gmail.com
- KMID: 2407786
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2017.00626
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Local administration of 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP) to the inner ear induces sensorineural hearing loss. Several studies have shown the otoprotective effects of ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761. Moreover, EGb 761 has been reported to activate Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1). The present study was designed to investigate whether EGb 761 prevents 3-NP-induced sensorineural hearing loss and determine its effects on the expression of SIRT1.
METHODS
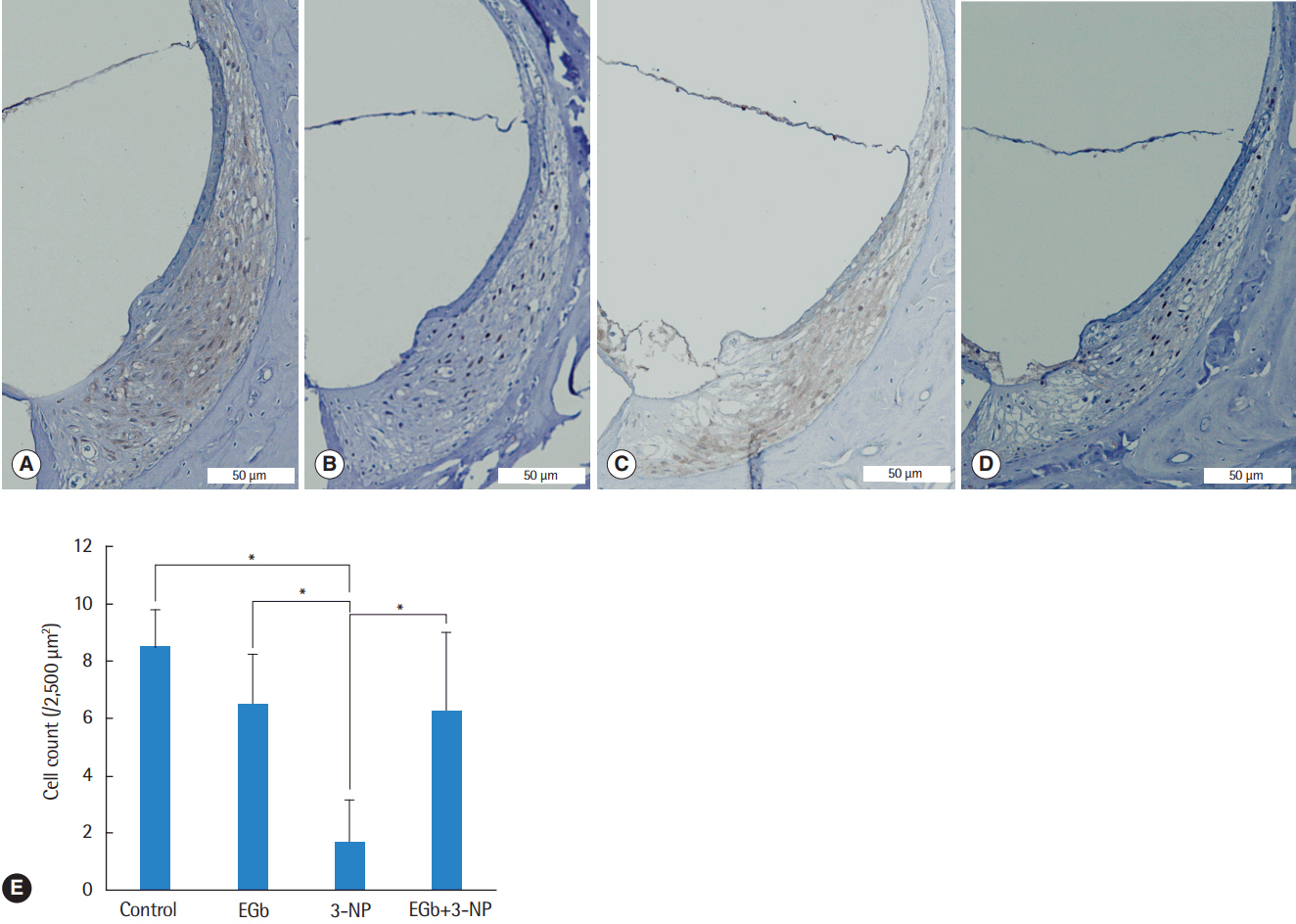
Sprague Dawley rats were divided into four experimental groups: control group receiving vehicle of 3-NP, EGb group receiving EGb 761, 3-NP group receiving 3-NP, and EGb+3-NP group receiving EGb 761 and 3-NP. EGb 761 was given orally for 5 days. The 3-NP solution was injected into the tympanum 3 days after the start of EGb 761 administration. The auditory brainstem response was recorded before and after the injection. At 4 weeks after the administration of 3-NP or vehicle of 3-NP, cochleae were harvested, and hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemistry for SIRT1 antibody were performed.
RESULTS
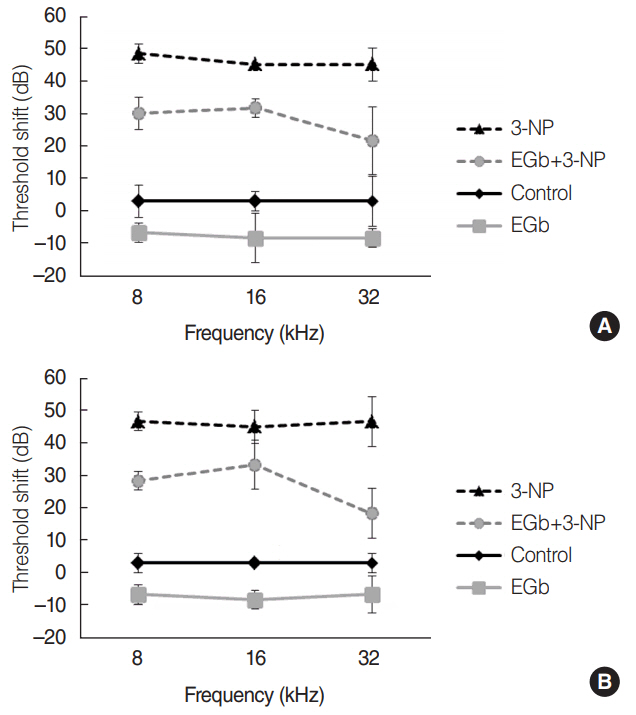
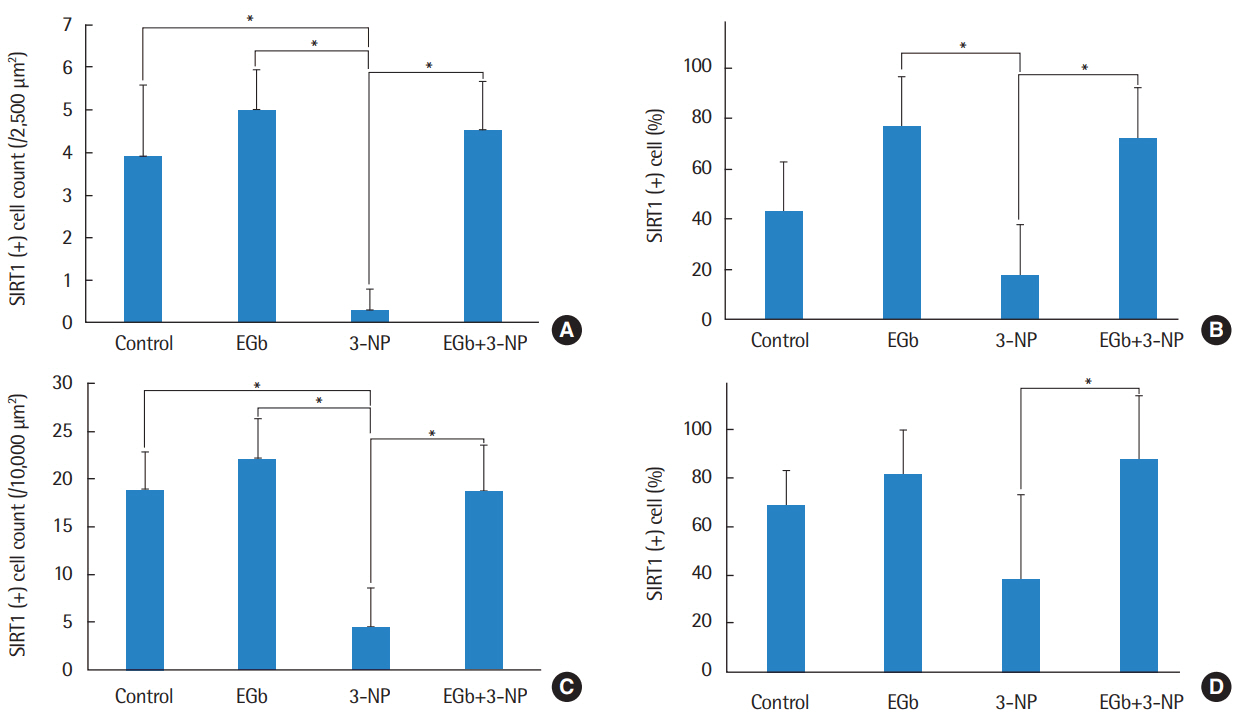
EGb+3-NP group showed significantly lower threshold shifts than 3-NP group. There was a significant preservation of type II fibrocytes and spiral ganglion cells in EGb+3-NP group than in 3-NP group. In EGb+3-NP group, there was a significantly greater number of SIRT1 immunopositive type II fibrocytes and spiral ganglion cells than in 3-NP group. Calculating the percentage of SIRT1 immunoreactive type II fibrocytes and spiral ganglion cells in viable type II fibrocytes and spiral ganglion cells, respectively, EGb+3-NP group showed significantly higher SIRT1 immunoreactive cells than 3-NP group.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that EGb 761 may prevent hearing loss induced by 3-NP in an acute ototoxic animal model, which appears to be related with SIRT1 expression.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cochlear Damage Caused by the Striking Noise of Titanium Head Golf Driver
Yong-Ho Park, Juyong Chung, Min Young Lee, Doh Young Lee, Young Ho Kim
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;12(1):18-26. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2017.01669.
Reference
-
1. Sone M, Hayashi H, Yamamoto H, Hoshino T, Mizushima T, Nakashima T. Upregulation of HSP by geranylgeranylacetone protects the cochlear lateral wall from endotoxin-induced inflammation. Hear Res. 2005; Jun. 204(1-2):140–6.
Article2. Yin HY, Ma XF, Liu F, Xia M, Xu AT. Protective effect of geranylgeranylacetone on cisplatin ototoxicity. Chemotherapy. 2009; 55(1):1–5.
Article3. Brouillet E. The 3-NP model of striatal neurodegeneration. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2014; Apr. 67:9481–14.
Article4. Khan A, Jamwal S, Bijjem KR, Prakash A, Kumar P. Neuroprotective effect of hemeoxygenase-1/glycogen synthase kinase-3β modulators in 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Neuroscience. 2015; Feb. 287:66–77.
Article5. Kumar P, Kumar P, Khan A, Deshmukh R, Lal Sharma P. Role of neurosteroids in experimental 3-nitropropionic acid induced neurotoxicity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014; Jan. 723:38–45.
Article6. Drew PD, Chavis JA. Inhibition of microglial cell activation by cortisol. Brain Res Bull. 2000; Jul. 52(5):391–6.
Article7. Longpre F, Garneau P, Christen Y, Ramassamy C. Protection by EGb 761 against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity: involvement of NF-kappaB, SIRT1, and MAPKs pathways and inhibition of amyloid fibril formation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006; Dec. 41(12):1781–94.8. Beal MF, Brouillet E, Jenkins BG, Ferrante RJ, Kowall NW, Miller JM, et al. Neurochemical and histologic characterization of striatal excitotoxic lesions produced by the mitochondrial toxin 3-nitropropionic acid. J Neurosci. 1993; Oct. 13(10):4181–92.
Article9. Hoya N, Okamoto Y, Kamiya K, Fujii M, Matsunaga T. A novel animal model of acute cochlear mitochondrial dysfunction. Neuroreport. 2004; Jul. 15(10):1597–600.
Article10. Fujinami Y, Mutai H, Kamiya K, Mizutari K, Fujii M, Matsunaga T. Enhanced expression of C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) precedes degeneration of fibrocytes in the lateral wall after acute cochlear mitochondrial dysfunction induced by 3-nitropropionic acid. Neurochem Int. 2010; Feb. 56(3):487–94.
Article11. Fujioka M, Okamoto Y, Shinden S, Okano HJ, Okano H, Ogawa K, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cochlear mitochondrial respiratory chain induces secondary inflammation in the lateral wall: a potential therapeutic target for sensorineural hearing loss. PLoS One. 2014; Mar. 9(3):e90089.
Article12. Koo JW, Chang MY, Yun SC, Kim TS, Kong SK, Chung JW, et al. The efficacy and safety of systemic injection of Ginkgo biloba extract, EGb761, in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016; Sep. 273(9):2433–41.
Article13. Tziridis K, Korn S, Ahlf S, Schulze H. Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 against noise trauma-induced hearing loss and tinnitus development. Neural Plast. 2014; 2014:427298.14. Donmez G. The neurobiology of sirtuins and their role in neurodegeneration. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012; Sep. 33(9):494–501.
Article15. Yamakuchi M, Lowenstein CJ. MiR-34, SIRT1 and p53: the feedback loop. Cell Cycle. 2009; Mar. 8(5):712–5.
Article16. Yeung F, Hoberg JE, Ramsey CS, Keller MD, Jones DR, Frye RA, et al. Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J. 2004; Jun. 23(12):2369–80.17. Xiong H, Dai M, Ou Y, Pang J, Yang H, Huang Q, et al. SIRT1 expression in the cochlea and auditory cortex of a mouse model of age-related hearing loss. Exp Gerontol. 2014; Mar. 51:8–14.
Article18. Tian C, Kim YH, Kim YC, Park KT, Kim SW, Kim YJ, et al. Korean red ginseng ameliorates acute 3-nitropropionic acid-induced cochlear damage in mice. Neurotoxicology. 2013; Jan. 34:42–50.
Article19. Hequembourg S, Liberman MC. Spiral ligament pathology: a major aspect of age-related cochlear degeneration in C57BL/6 mice. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2001; Jun. 2(2):118–29.
Article20. Wang Y, Hirose K, Liberman MC. Dynamics of noise-induced cellular injury and repair in the mouse cochlea. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2002; Sep. 3(3):248–68.
Article21. Agarwal L, Pothier DD. Vasodilators and vasoactive substances for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009; Oct. (4):CD003422.
Article22. Birks J, Grimley Evans J. Ginkgo biloba for cognitive impairment and dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009; Jan. (1):CD003120.
Article23. Eckert A, Keil U, Scherping I, Hauptmann S, Muller WE. Stabilization of mitochondrial membrane potential and improvement of neuronal energy metabolism by Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005; Nov. 1056:474–85.
Article24. Mahdy HM, Tadros MG, Mohamed MR, Karim AM, Khalifa AE. The effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Neurochem Int. 2011; Nov. 59(6):770–8.
Article25. Nevado J, Sanz R, Sanchez-Rodriguez C, Garcia-Berrocal JR, Martin-Sanz E, Gonzalez-Garcia JA, et al. Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb761) protects against aging-related caspase-mediated apoptosis in rat cochlea. Acta Otolaryngol. 2010; Oct. 130(10):1101–12.
Article26. Park SY, Back SA, Kim HL, Kim DK, Yeo SW, Park SN. Renexin as a rescue regimen for noise-induced hearing loss. Noise Health. 2014; Sep-Oct. 16(72):257–64.
Article27. Xu O, Lu H, Li PQ, Zhang X, Lu Z. Effect of combination of Ginkgo leaf extract and deferoxamine in preventing and treating ototoxicity of cisplatin. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2004; Oct. 24(10):915–8.28. Xiong H, Pang J, Yang H, Dai M, Liu Y, Ou Y, et al. Activation of miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 signaling contributes to cochlear hair cell apoptosis: implications for age-related hearing loss. Neurobiol Aging. 2015; Apr. 36(4):1692–701.
Article29. Revollo JR, Li X. The ways and means that fine tune Sirt1 activity. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013; Mar. 38(3):160–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Ginkgo Biloba Extract on Experimentally Induced Hearing Loss by Noise
- Gingko biloba extract (EGb 761) attenuates ischemic brain injury-induced reduction in Ca2+ sensor protein hippocalcin
- An Effect of Ginkgo Extract on Salicylate Ototoxicity in Guinea Pigs
- Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) prevents the ischemic brain injury-induced decrease in parvalbumin expression
- Effect of Ginkgo Biloba Extract(EGb 761) on Apoptosis in Oral Cavity Cancer Cells