Lab Anim Res.
2012 Jun;28(2):77-82. 10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.77.
Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) prevents the ischemic brain injury-induced decrease in parvalbumin expression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, College of Veterinary Medicine, Research Institute of Life Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. pokoh@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Life Science and Applied Life Science (Brain Korea 21), Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 1436697
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.77
Abstract
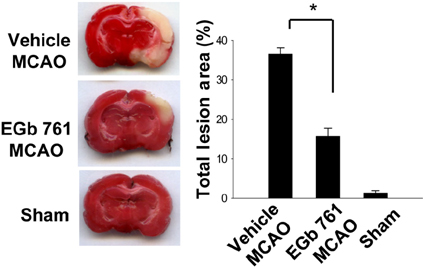
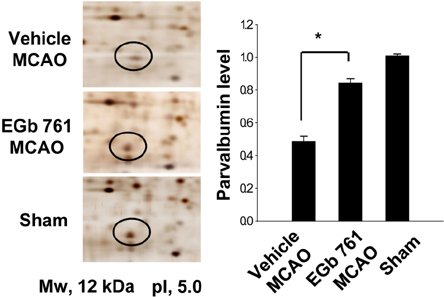
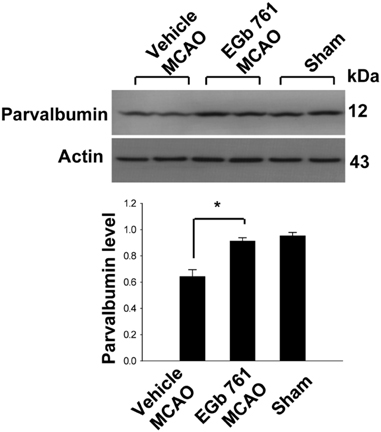
- Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) exerts a neuroprotective effect against ischemic brain injury through an anti-apoptotic mechanism. Parvalbumin is a calcium buffering protein that plays an important role in modulating intracellular calcium concentration and regulating apoptotic cell death. The aim of this study was to investigate whether EGb 761 affects parvalbumin expression in cerebral ischemic injury. Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with vehicle or EGb 761 (100 mg/kg) prior to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and cerebral cortex tissues were collected 24 h after MCAO. A proteomic approach revealed a reduction in parvalbumin expression in the vehicle-treated animals, whereas EGb 761 pretreatment attenuates the ischemic injury-induced decrease in parvalbumin expression. RT-PCR and Western blot analyses clearly confirmed the fact that EGb 761 prevents the injury-induced decrease in parvalbumin. Moreover, the results of immunohistochemical staining showed that the number of parvalbumin-positive cells was lower in vehicle-treated animals than in sham-operated animals, and EGb 761 averted this decrease. Thus, these results suggest that the maintenance of parvalbumin expression is associated with the neuroprotective function of EGb 761 against neuronal damage induced by ischemia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shah ZA, Nada SE, Dore S. Heme oxygenase 1, beneficial role in permanent ischemic stroke and in Gingko biloba (EGb 761) neuroprotection. Neuroscience. 2011. 180:248–255.2. Seif-El-Nasr M, El-Fattah AA. Lipid peroxide, phospholipids, glutathione levels and superoxide dismutase activity in rat brain after ischaemia: effect of ginkgo biloba extract. Pharmacol Res. 1995. 32(5):273–278.3. Calapai G, Crupi A, Firenzuoli F, Marciano MC, Squadrito F, Inferrera G, Parisi A, Rizzo A, Crisafulli C, Fiore A, Caputi AP. Neuroprotective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract in brain ischemia are mediated by inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis. Life Sci. 2000. 67(22):2673–2683.4. Maurer K, Ihl R, Dierks T, Frolich L. Clinical efficacy of Ginkgo biloba special extract EGb 761 in dementia of the Alzheimer type. J Psychiatr Res. 1997. 31(6):645–655.5. Oken BS, Storzbach DM, Kaye JA. The efficacy of Ginkgo biloba on cognitive function in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 1998. 55(11):1409–1415.6. Kotil K, Uyar R, Bilge T, Ton T, Kucukhuseyin C, Koldas M, Atay F. Investigation of the dose-dependent antivasospasmic effect of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Clin Neurosci. 2008. 15(12):1382–1386.7. Shi C, Zhao L, Zhu B, Li Q, Yew DT, Yao Z, Xu J. Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb761) and its constituents quercetin and ginkgolide B against beta-amyloid peptide-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2009. 181(1):115–123.8. Chard PS, Bleakman D, Christakos S, Fullmer CS, Miller RJ. Calcium buffering properties of calbindin D28k and parvalbumin in rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1993. 472:341–357.9. Lee EJ, Chen HY, Wu TS, Chen TY, Ayoub IA, Maynard KI. Acute administration of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) affords neuroprotection against permanent and transient focal cerebral ischemia in Sprague-Dawley rats. J Neurosci Res. 2002. 68(5):636–645.10. Koh PO. ngko biloba extract (EGb 761) prevents increase of Bad-Bcl-XL interaction following cerebral ischemia. Am J Chin Med. 2009. 37(5):867–876.11. Van Den Bosch L, Schwaller B, Vleminckx V, Meijers B, Stork S, Ruehlicke T, Van Houtte E, Klaassen H, Celio MR, Missiaen L, Robberecht W, Berchtold MW. Protective effect of parvalbumin on excitotoxic motor neuron death. Exp Neurol. 2002. 174(2):150–161.12. Girard F, Meszar Z, Marti C, Davis FP, Celio M. Gene expression analysis in the parvalbumin-immunoreactive PV1 nucleus of the mouse lateral hypothalamus. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. 34(12):1934–1943.13. Starkov AA, Chinopoulos C, Fiskum G. Mitochondrial calcium and oxidative stress as mediators of ischemic brain injury. Cell Calcium. 2004. 36(3-4):257–264.14. Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989. 20(1):84–91.15. Koh PO. Identification of proteins differentially expressed in cerebral cortexes of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb761)-treated rats in a middle cerebral artery occlusion model--a proteomics approach. Am J Chin Med. 2011. 39(2):315–324.16. Bastianetto S, Ramassamy C, Dore S, Christen Y, Poirier J, Quirion R. The Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects hippocampal neurons against cell death induced by beta-amyloid. Eur J Neurosci. 2000. 12(6):1882–1890.17. Luo Y, Smith JV, Paramasivam V, Burdick A, Curry KJ, Buford JP, Khan I, Netzer WJ, Xu H, Butko P. Inhibition of amyloid-beta aggregation and caspase-3 activation by the Ginkgo biloba extract EGb761. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002. 99(19):12197–12202.18. Pierre S, Jamme I, Droy-Lefaix MT, Nouvelot A, Maixent JM. Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects Na,K-ATPase activity during cerebral ischemia in mice. Neuroreport. 1999. 10(1):47–51.19. Rojas P, Serrano-Garcia N, Medina-Campos ON, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Ogren SO, Rojas C. Antidepressant-like effect of a Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb761) in the mouse forced swimming test: role of oxidative stress. Neurochem Int. 2011. 59(5):628–636.20. Nitsch C, Scotti A, Sommacal A, Kalt G. GABAergic hippocampal neurons resistant to ischemia-induced neuronal death contain the Ca2(+)-binding protein parvalbumin. Neurosci Lett. 1989. 105(3):263–268.21. Hayashi T, Abe K. Ischemic neuronal cell death and organellae damage. Neurol Res. 2004. 26(8):827–834.22. Carafoli E. Intracellular calcium homeostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987. 56:395–433.23. Miller RJ. The control of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis. Prog Neurobiol. 1991. 37(3):255–285.24. Heizmann CW, Braun K. Changes in Ca(2+)-binding proteins in human neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci. 1992. 15(7):259–264.25. Siesjo BK. Historical overview. Calcium, ischemia, and death of brain cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988. 522:638–661.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gingko biloba extract (EGb 761) attenuates ischemic brain injury-induced reduction in Ca2+ sensor protein hippocalcin
- An experimental study on the effect of Ginkgo Biloba extract (EGb 761) on the healing process after weak crush injury
- Effect of Ginkgo Biloba Extract(EGb 761) on Apoptosis in Oral Cavity Cancer Cells
- The Protective Effect of Egb 761 Against 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Hearing Loss: The Role of Sirtuin 1
- Suppression of IL-1beta-induced MUC5AC Gene Expression by Ginkgo biloba Extract(EGb 761) in Human Airway Epithelial Cells