Cancer Res Treat.
2018 Jan;50(1):71-87. 10.4143/crt.2017.013.
Downregulation of HuR Inhibits the Progression of Esophageal Cancer through Interleukin-18
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of General Surgery, The First People’s Hospital of Taicang City, Taicang Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China. wangyi_1966@126.com
- 2Department of Plastic Surgery, The Central Hospital of Zaozhuang Mining Group, Shandong Province, China.
- 3School of Radiation Medicine and Protection and Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Protection, Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou, China.
- 4Department of Radiation Oncology, Changzhou Cancer Hospital, Soochow University, Changzhou, China. tangyiting001@163.com
- KMID: 2403476
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2017.013
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of human antigen R (HuR) downregulation and the potential target genes of HuR on the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
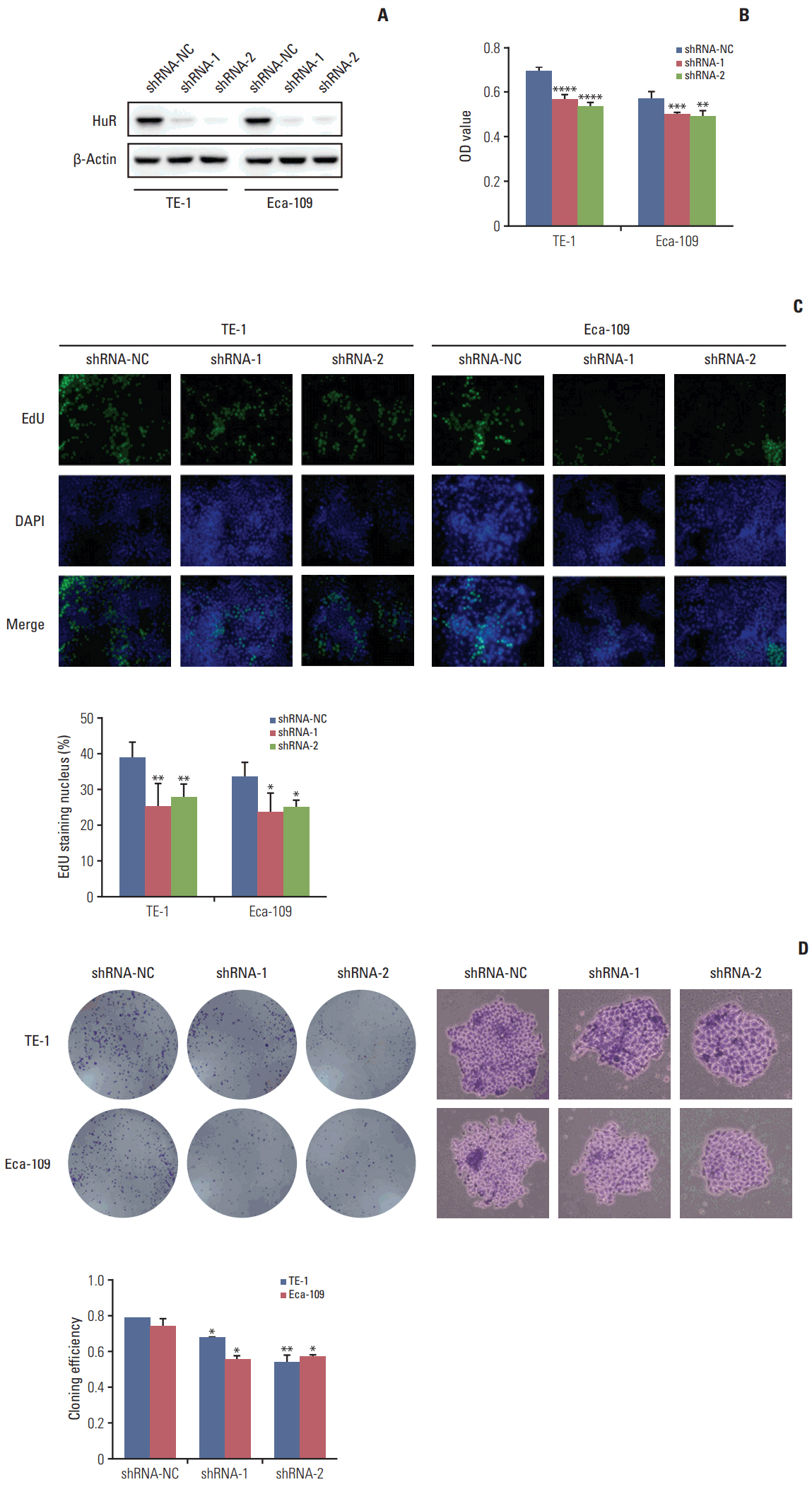
In this study, a proteomics assay was used to detect the expression of proteins after HuR downregulation, and a luciferase assay was used to detect the potential presence of a HuR binding site on the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of interleukin 18 (IL-18). In addition, colony formation assay, MTT, EdU incorporation assay, Western blot, flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, transwell invasion assay, and wound healing assay were used.
RESULTS
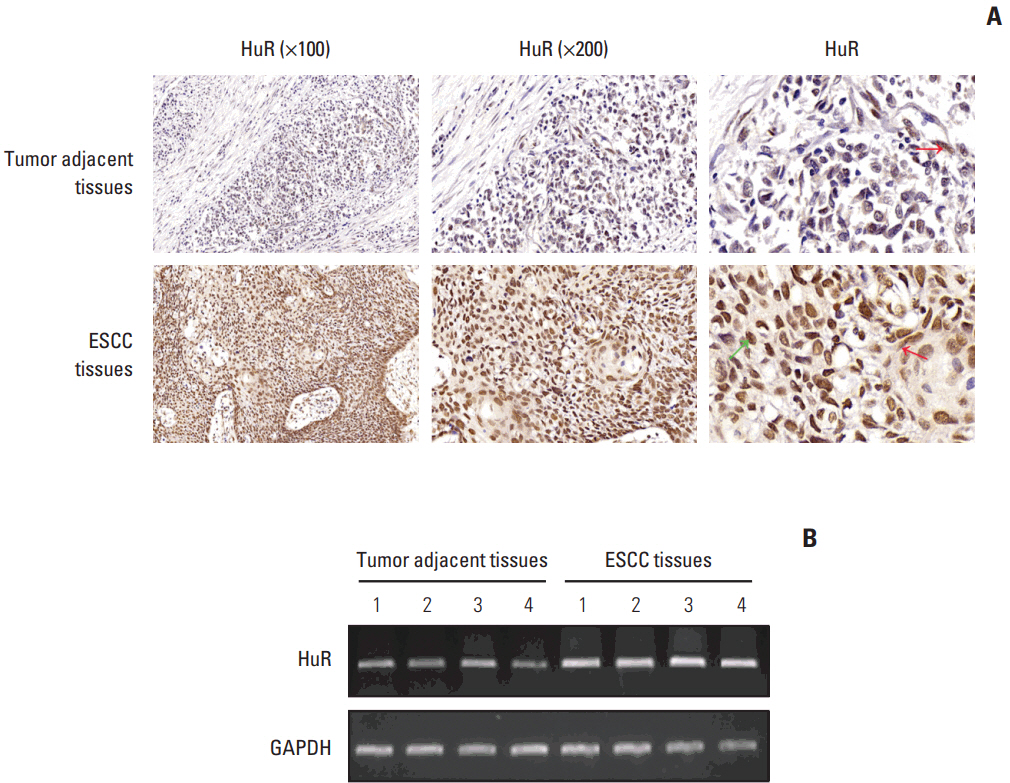
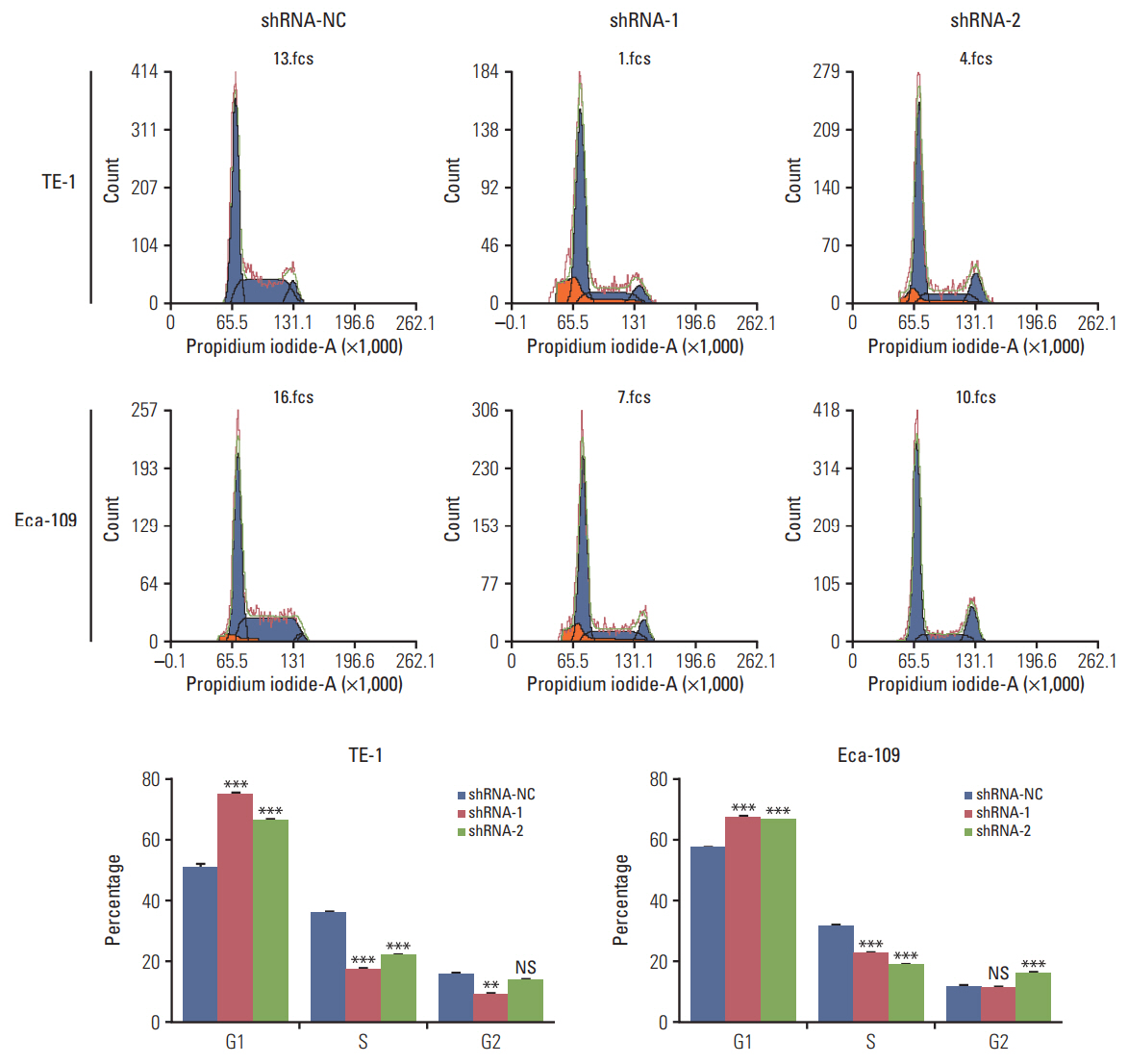
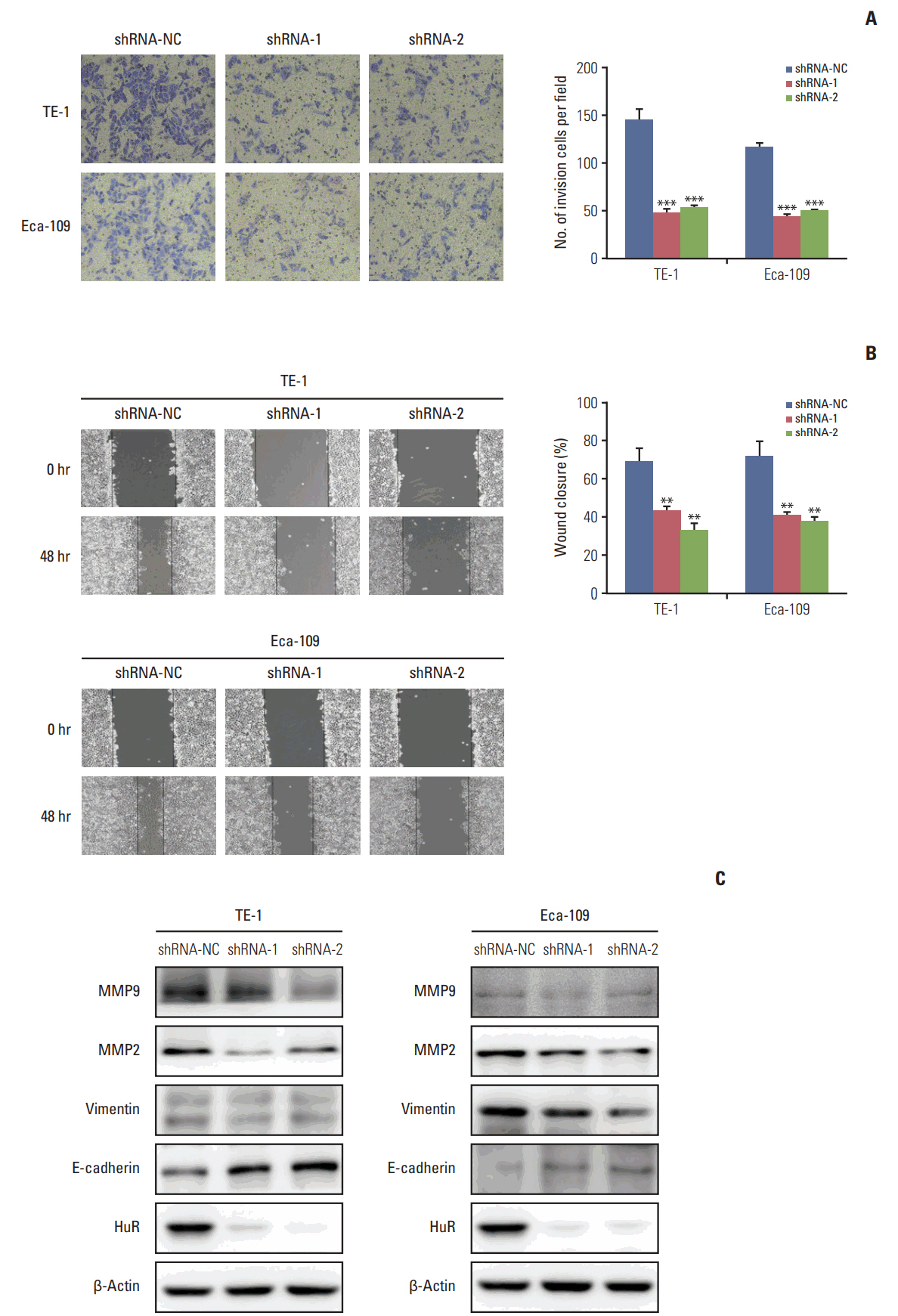
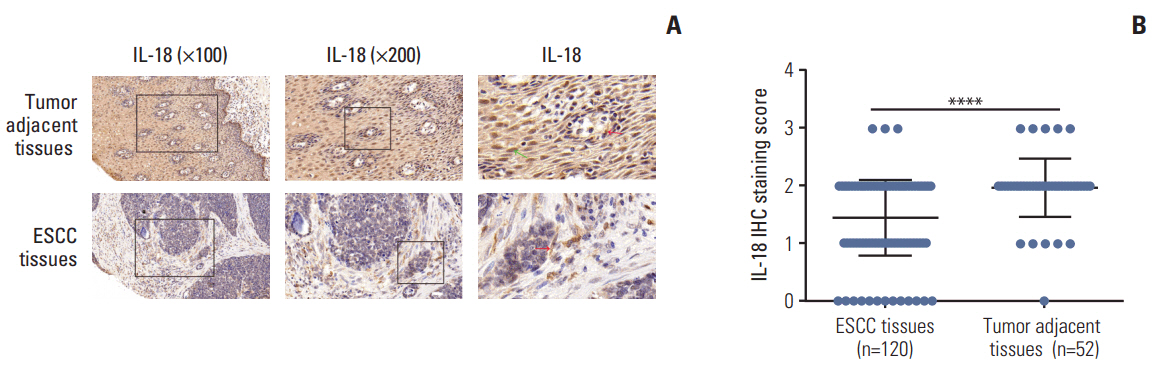
In the present study, we found that the expression of both HuR protein and mRNA levels were higher in tumor tissues than in the adjacent tissues. HuR downregulation significantly suppressed cell proliferation. In addition, the metastasis of esophageal cancer cells was inhibited, while the expression of E-cadherin was increased and the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2, MMP9, and vimentin was decreased after HuR knockdown. Moreover, silencing of HuR disturbed the cell cycle of ESCC cells mainly by inducing G1 arrest. Furthermore, proteomics analysis showed that downregulation of HuR in TE-1 cells resulted in 100 upregulated and 122 downregulated proteins, including IL-18 as a significantly upregulated protein. The expression of IL-18 was inversely regulated by HuR. IL-18 expression was decreased in ESCC tissues, and exogenous IL-18 significantly inhibited the proliferation and metastasis of ESCC cells. The 3'-UTR of IL-18 harbored a HuR binding site, as shown by an in vitro luciferase assay.
CONCLUSION
HuR plays an important role in the progression of esophageal carcinoma by targeting IL-18, which may be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of ESCC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Binding Sites
Blotting, Western
Cadherins
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell
Cell Cycle
Cell Proliferation
Down-Regulation*
ELAV-Like Protein 1
Esophageal Neoplasms*
Flow Cytometry
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
In Vitro Techniques
Interleukin-18*
Luciferases
Neoplasm Metastasis
Proteomics
RNA, Messenger
Vimentin
Wound Healing
Cadherins
ELAV-Like Protein 1
Interleukin-18
Luciferases
RNA, Messenger
Vimentin
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Wu C, Kraft P, Zhai K, Chang J, Wang Z, Li Y, et al. Genomewide association analyses of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese identify multiple susceptibility loci and gene-environment interactions. Nat Genet. 2012; 44:1090–7.
Article2. Chen M, Huang J, Zhu Z, Zhang J, Li K. Systematic review and meta-analysis of tumor biomarkers in predicting prognosis in esophageal cancer. BMC Cancer. 2013; 13:539.
Article3. Tong YS, Wang XW, Zhou XL, Liu ZH, Yang TX, Shi WH, et al. Identification of the long non-coding RNA POU3F3 in plasma as a novel biomarker for diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2015; 14:3.
Article4. Brennan CM, Steitz JA. HuR and mRNA stability. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001; 58:266–77.
Article5. Kundu P, Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Bhattacharyya SN, Filipowicz W. HuR protein attenuates miRNA-mediated repression by promoting miRISC dissociation from the target RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012; 40:5088–100.
Article6. Mrena J, Wiksten JP, Thiel A, Kokkola A, Pohjola L, Lundin J, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 is an independent prognostic factor in gastric cancer and its expression is regulated by the messenger RNA stability factor HuR. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:7362–8.
Article7. Denkert C, Koch I, von Keyserlingk N, Noske A, Niesporek S, Dietel M, et al. Expression of the ELAV-like protein HuR in human colon cancer: association with tumor stage and cyclooxygenase-2. Mod Pathol. 2006; 19:1261–9.
Article8. Heinonen M, Fagerholm R, Aaltonen K, Kilpivaara O, Aittomaki K, Blomqvist C, et al. Prognostic role of HuR in hereditary breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:6959–63.
Article9. Williams TK, Costantino CL, Bildzukewicz NA, Richards NG, Rittenhouse DW, Einstein L, et al. pp32 (ANP32A) expression inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth and induces gemcitabine resistance by disrupting HuR binding to mRNAs. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e15455.
Article10. Romeo C, Weber MC, Zarei M, DeCicco D, Chand SN, Lobo AD, et al. HuR contributes to TRAIL resistance by restricting death receptor 4 expression in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2016; 14:599–611.
Article11. Latorre E, Tebaldi T, Viero G, Sparta AM, Quattrone A, Provenzani A. Downregulation of HuR as a new mechanism of doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2012; 11:13.
Article12. Liu P, Gao Y, Huan J, Ge X, Tang Y, Shen W, et al. Upregulation of PAX2 promotes the metastasis of esophageal cancer through interleukin-5. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 35:740–54.
Article13. Zotti T, Scudiero I, Vito P, Stilo R. The emerging role of TRAF7 in tumor development. J Cell Physiol. 2017; 232:1233–8.
Article14. Ott CA, Linck L, Kremmer E, Meister G, Bosserhoff AK. Induction of exportin-5 expression during melanoma development supports the cellular behavior of human malignant melanoma cells. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:62292–304.
Article15. Carrascal MT, Mendoza L, Valcarcel M, Salado C, Egilegor E, Telleria N, et al. Interleukin-18 binding protein reduces b16 melanoma hepatic metastasis by neutralizing adhesiveness and growth factors of sinusoidal endothelium. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:491–7.16. Vidal-Vanaclocha F, Mendoza L, Telleria N, Salado C, Valcarcel M, Gallot N, et al. Clinical and experimental approaches to the pathophysiology of interleukin-18 in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006; 25:417–34.
Article17. Zhao J, Chen J, Lu B, Dong L, Wang H, Bi C, et al. TIP30 induces apoptosis under oxidative stress through stabilization of p53 messenger RNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2008; 68:4133–41.
Article18. Danilin S, Sourbier C, Thomas L, Rothhut S, Lindner V, Helwig JJ, et al. von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene-dependent mRNA stabilization of the survival factor parathyroid hormone-related protein in human renal cell carcinoma by the RNA-binding protein HuR. Carcinogenesis. 2009; 30:387–96.
Article19. Ge J, Chang N, Zhao Z, Tian L, Duan X, Yang L, et al. Essential roles of RNA-binding protein HuR in activation of hepatic stellate cells induced by transforming growth factor-beta1. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:22141.
Article20. Kotta-Loizou I, Vasilopoulos SN, Coutts RH, Theocharis S. Current evidence and future perspectives on HuR and breast cancer development, prognosis, and treatment. Neoplasia. 2016; 18:674–88.
Article21. Muralidharan R, Babu A, Amreddy N, Basalingappa K, Mehta M, Chen A, et al. Folate receptor-targeted nanoparticle delivery of HuR-RNAi suppresses lung cancer cell proliferation and migration. J Nanobiotechnology. 2016; 14:47.
Article22. Leijon H, Salmenkivi K, Heiskanen I, Hagstrom J, Louhimo J, Heikkila P, et al. HuR in pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas: overexpression in verified malignant tumors. APMIS. 2016; 124:757–63.23. Cha JD, Li S, Cha IH. Association between expression of embryonic lethal abnormal vision-like protein HuR and cyclooxygenase-2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2011; 33:627–37.
Article24. Yuan Z, Sanders AJ, Ye L, Jiang WG. HuR, a key post-transcriptional regulator, and its implication in progression of breast cancer. Histol Histopathol. 2010; 25:1331–40.25. Zhang W, Vreeland AC, Noy N. RNA-binding protein HuR regulates nuclear import of protein. J Cell Sci. 2016; 129:4025–33.26. Chu PC, Kulp SK, Chen CS. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor is suppressed through transcriptional repression and mRNA destabilization by a novel energy restriction-mimetic agent. Carcinogenesis. 2013; 34:2694–705.27. Li K, Wei L, Huang Y, Wu Y, Su M, Pang X, et al. Leptin promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion via IL-18 expression and secretion. Int J Oncol. 2016; 48:2479–87.
Article28. Markowitz GJ, Yang P, Fu J, Michelotti GA, Chen R, Sui J, et al. Inflammation-dependent IL18 signaling restricts hepatocellular carcinoma growth by enhancing the accumulation and activity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 2016; 76:2394–405.
Article29. Ko CY, Wang WL, Li CF, Jeng YM, Chu YY, Wang HY, et al. IL-18-induced interaction between IMP3 and HuR contributes to COX-2 mRNA stabilization in acute myeloid leukemia. J Leukoc Biol. 2016; 99:131–41.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Image-Enhanced Endoscopy for Early Identification of Esophageal Neoplasms
- Salvage Radiotherapy for Loco-regional Recurrence of Esophageal Cancer Following Surgery
- The effects of interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma on the expression of FcepsilonR II on B cells
- Esophageal Cancer Staging
- The Use of PET in Esophageal Cancer