J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2017 Sep;24(3):169-175. 10.4184/jkss.2017.24.3.169.
Influence of Gonarthrosis on Sagittal Spinal Alignment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Korea. drortho@korea.com
- KMID: 2402830
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2017.24.3.169
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Research using radiographic findings.
OBJECTIVES
To compare spinopelvic parameters in detail between normal subjects and those who had bilateral gonarthrosis with or without spondylosis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: The relationship between knee joint flexion contracture and hypolordosis in the lumbar spine has been well established. However, spinopelvic parameters in subjects with gonarthrosis without flexion contracture have not been well described in the literature.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
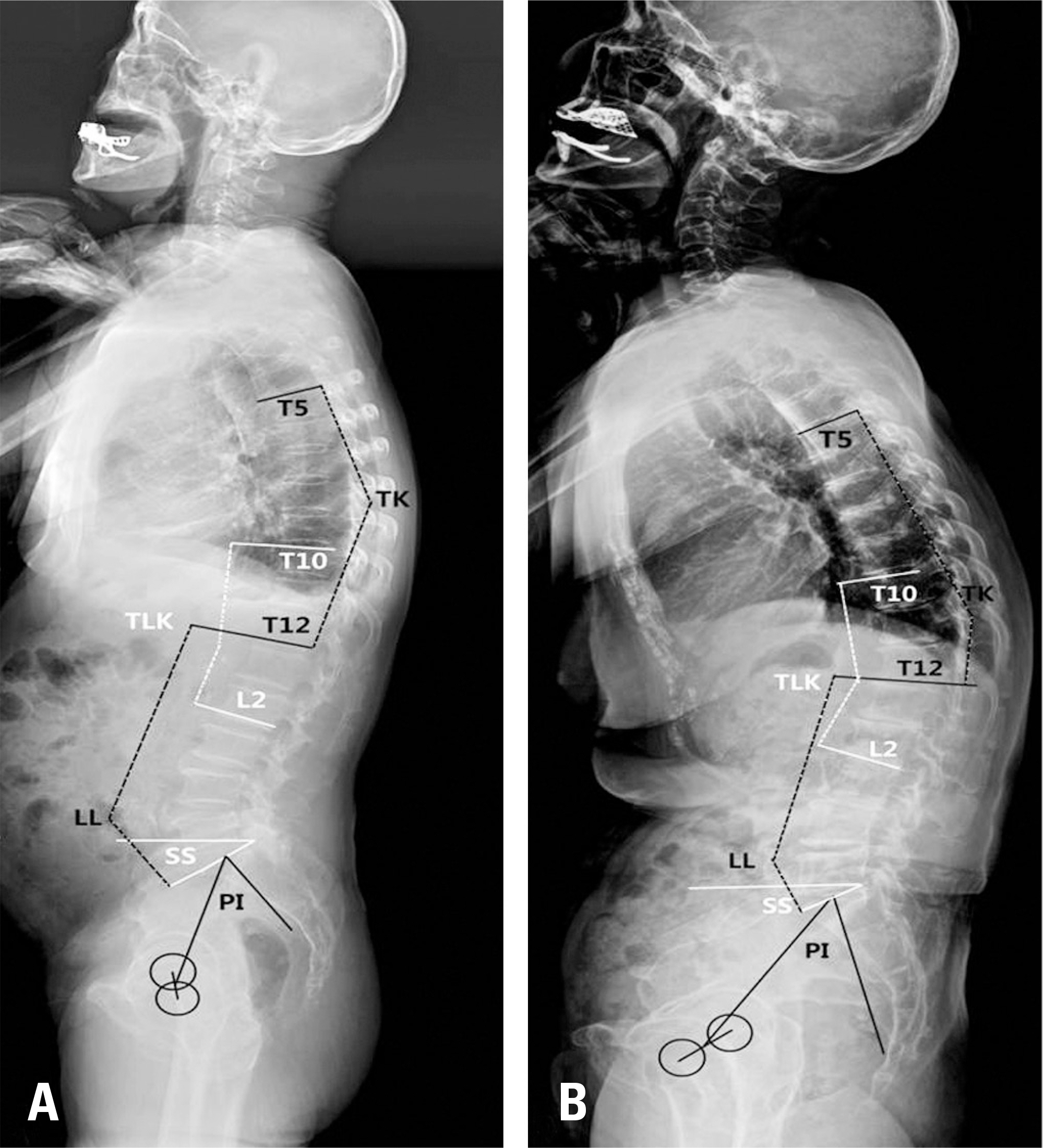
Fifty-seven male subjects in their 60s with bilateral gonarthrosis over Kellgren-Lawrence grade III were included. They were subdivided into the KS group (with spinal osteoarthritis, n=32) and the KN group (without spinal osteoarthritis, n=25). Normal asymptomatic subjects without disease in their back or leg were analyzed as the control group (NN; n=84). The following spinopelvic parameters were measured and compared; C7 plumbline (C7PL), thoracic kyphosis (TK), thoracolumbar kyphosis (TLK), lumbar lordosis (LL), sacral slope (SS), pelvic tilt (PT), and pelvic incidence (PI).
RESULTS
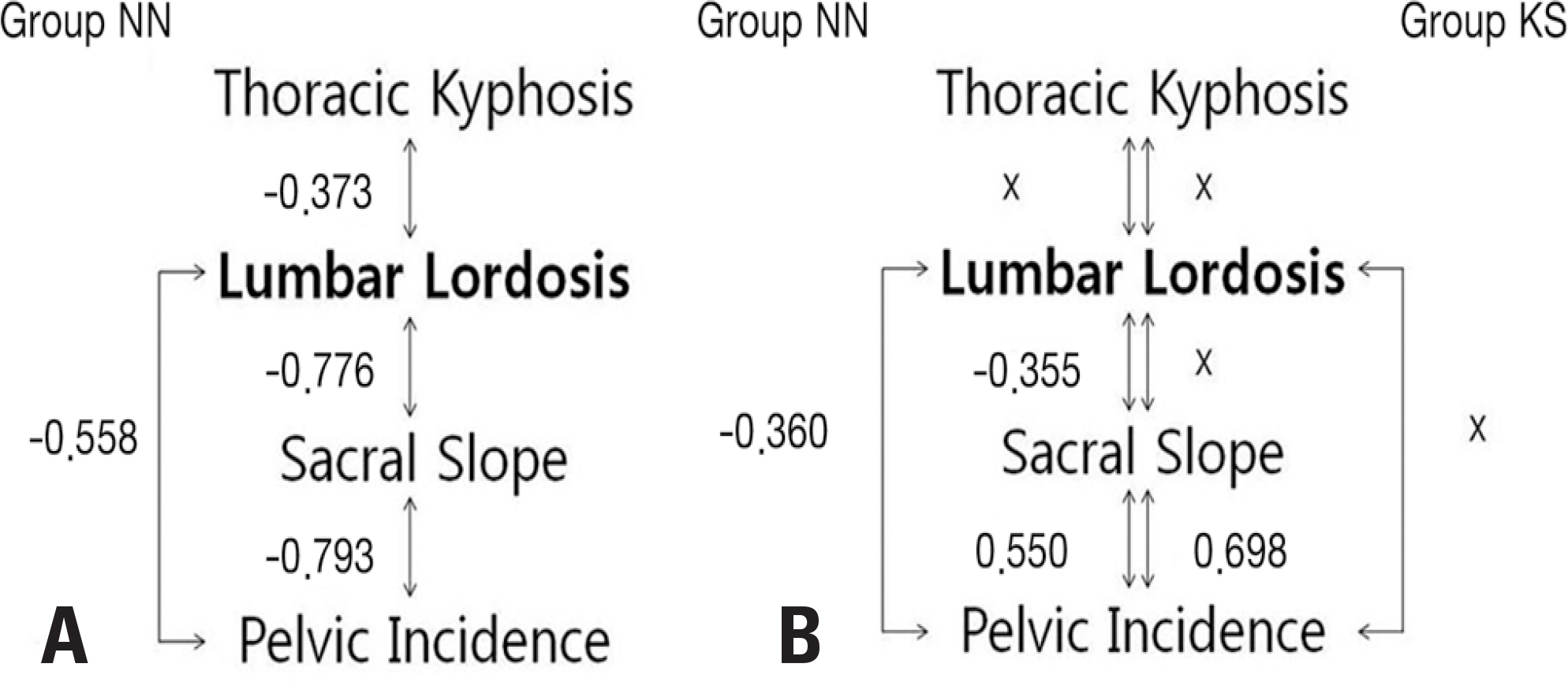
In the KS group, the C7PL was significantly anteriorly displaced compared to the KN group (1.7±4.5 cm vs. −0.6±2.9 cm, p=0.031) and the NN group (1.7±4.5 cm vs. −0.5±2.9 cm, p=0.014). TK in the KN group was significantly smaller than in the NN group (25.4±8.8° vs. 30.1±8.3°, p=0.041). The KS group had the smallest value of LL, while the NN group had the largest value of LL (−23.2±48.7° vs. −44.9±33.8° vs. −57.3±8.5°, p<0.001). No significant difference was observed in PI, SS, or PT among the 3 groups. A strong correlation was found between LL and SS in the NN group (R=−0.776, p<0.01), while this correlation was moderate in the KN group (R=−0.355, p<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
Overall balance was maintained in the subjects who had gonarthrosis without spinal osteoarthritis. Subjects with gonarthrosis showed less LL, especially if they had spinal osteoarthritis. Further studies are needed to characterize the differences in these pelvic parameters, and to evaluate changes in individuals with knee joint flexion contracture.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Murata Y, Takahashi K, Yamagata M, et al. The knee-spine syndrome. Association between lumbar lordosis and extension of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003; 85:95–9.2. Tsuji T, Matsuyama Y, Goto M, et al. Knee-spine syndrome: correlation between sacral inclination and patellofemoral joint pain. J Orthop Sci. 2002; 7:519–23.3. Chang CB, Park KW, Kang YG, et al. Coexisting lumbar spondylosis in patients undergoing TKA: how common and how serious? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472:710–7.
Article4. Roussouly P, Pinheiro-Franco JL. Biomechanical analysis of the spinopelvic organization and adaptation in pathology. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(Suppl):609–18.
Article5. Diebo BG, Ferrero E, Lafage R, et al. Recruitment of compensatory mechanisms in sagittal spinal malalignment is age and regional deformity dependent: a full-standing axis analysis of key radiographical parameters. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40:642–9.6. Obeid I, Hauger O, Aunoble S, et al. Global analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in major deformities: correlation between lack of lumbar lordosis and flexion of the knee. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(Suppl):681–5.
Article7. Tauchi R, Imagama S, Muramoto A, et al. Influence of spinal imbalance on knee osteoarthritis in community-living elderly adults. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2015; 77:329–37.8. Obeid I, Boissiere L, Yilgor C, et al. Global tilt: a single parameter incorporating spinal and pelvic sagittal parameters and least affected by patient positioning. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25:3644–9.
Article9. Wang WJ, Liu F, Zhu YW, et al. Sagittal alignment of the spine-pelvis-lower extremity axis in patients with severe knee osteoarthritis: A radiographic study. Bone Joint Res. 2016; 5:198–205.10. Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of os-teo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957; 16:494–502.
Article11. Wilke HJ, Rohlmann F, Neidlinger-Wilke C, et al. Validity and interobserver agreement of a new radiographic grading system for intervertebral disc degeneration: Part I. Lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2006; 15:720–30.
Article12. Kim YB, Kim YJ, Ahn YJ, et al. A comparative analysis of sagittal spinopelvic alignment between young and old men without localized disc degeneration. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23:1400–6.
Article13. Horton WC, Brown CW, Bridwell KH, et al. Is there an optimal patient stance for obtaining a lateral 36” radiograph? A critical comparison of three techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:427–33.14. Jenny JY, Barbe B. Small differences between anatomical and mechanical sagittal femur axes: a radiological and navigated study of 50 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012; 132:1053–7.
Article15. Gupta M, Henry JK, Schwab F, et al. Dedicated Spine Measurement Software (SMS) Quantifies Key Spino-Pelvic Parameters More Reliably Than Traditional PACS Tools. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 41:E22–7.16. Ferrero E, Liabaud B, Challier V, et al. Role of pelvic translation and lower-extremity compensation to maintain gravity line position in spinal deformity. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016; 24:436–46.
Article17. Kim YH, Dorj A, Han A, et al. Improvements in spinal alignment after high tibial osteotomy in patients with medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. Gait Posture. 2016; 48:131–6.
Article18. Lee CS, Park SJ, Chung SS, et al. The effect of simulated knee flexion on sagittal spinal alignment: novel interpretation of spinopelvic alignment. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22:1059–65.
Article19. Lazennec JY, Folinais D, Bendaya S, et al. The global alignment in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis: our experience using the EOS full-body images. Eur J Orthop Surg Trau-matol. 2016; 26:713–24.
Article20. Lowe T, Berven SH, Schwab FJ, et al. The SRS classification for adult spinal deformity: building on the King/Moe and Lenke classification systems. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31(Suppl):119–25.21. Stagnara P, De Mauroy JC, Dran G, et al. Reciprocal angulation of vertebral bodies in a sagittal plane: approach to references for the evaluation of kyphosis and lordosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1982; 7:335–42.
Article22. Korovessis PG, Stamatakis MV, Baikousis AG, et al. Reciprocal angulation of vertebral bodies in the sagittal plane in an asymptomatic Greek population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23:700–4.
Article23. Jang JS, Lee SH, Min JH, et al. Influence of lumbar lordosis restoration on thoracic curve and sagittal position in lumbar degenerative kyphosis patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:280–4.
Article24. Lee JH, Kim KT, Suk KS, et al. Analysis of spinopelvic parameters in lumbar degenerative kyphosis: correlation with spinal stenosis and spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:E1386–91.25. Le Huec J, Saddiki R, Franke J, et al. Equilibrium of the human body and the gravity line: the basics. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20:1–6.
Article26. Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Hecquet J, et al. Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J. 1998; 7:99–103.
Article27. Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G. Sagittal plane alignment of the spine and gravity: a radiological and clinical evaluation. Acta Orthop Belg. 2005; 71:213–20.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- From the Spinopelvic Parameters to Global Alignment and Proportion Scores in Adult Spinal Deformity
- Restoration of Sagittal Balance in Spinal Deformity Surgery
- Impact of appendicular and trunk skeletal muscle mass and back extensor strength on sagittal spinal alignment in Japanese women without vertebral fracture
- Cervical Sagittal Alignment: Literature Review and Future Directions
- Radiologic Findings of Pelvic Parameters Related to Sagittal Balance