J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2016 Sep;23(3):197-205. 10.4184/jkss.2016.23.3.197.
Radiologic Findings of Pelvic Parameters Related to Sagittal Balance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. radbass@paran.com
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 2353912
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2016.23.3.197
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A literature review on the radiologic findings of pelvic parameters for treatment of spinal deformity
OBJECTIVES
This review examines sagittal spine alignment, pelvic parameters, and methods for assessing alignment, and examines the relationships among all of these parameters to understand spinal deformity. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Understanding the main pelvic and sagittal spinal parameters and recognizing their correlation is imperative in the diagnosis and treatment of various spinal disorders.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Review of the literature.
RESULTS
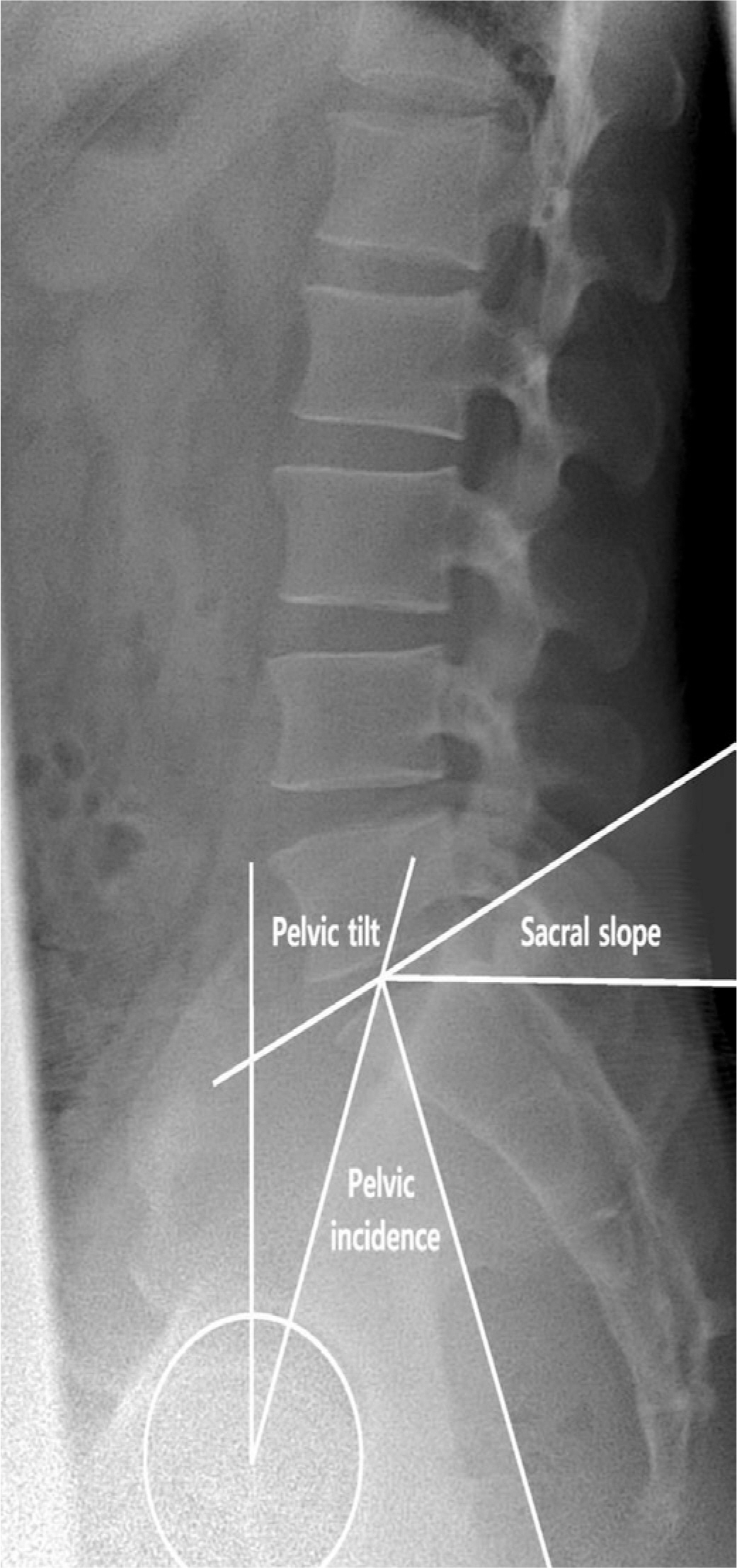
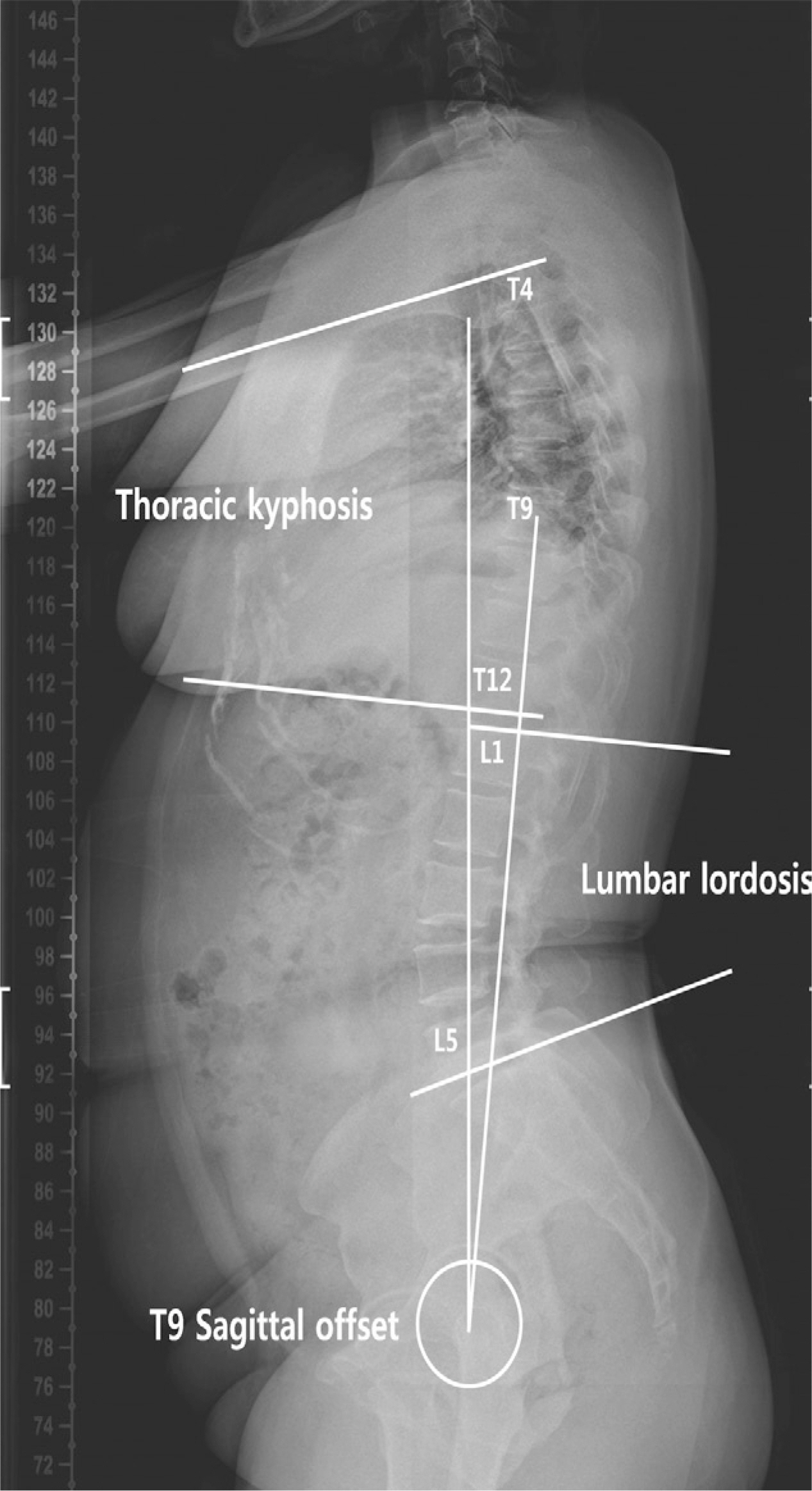
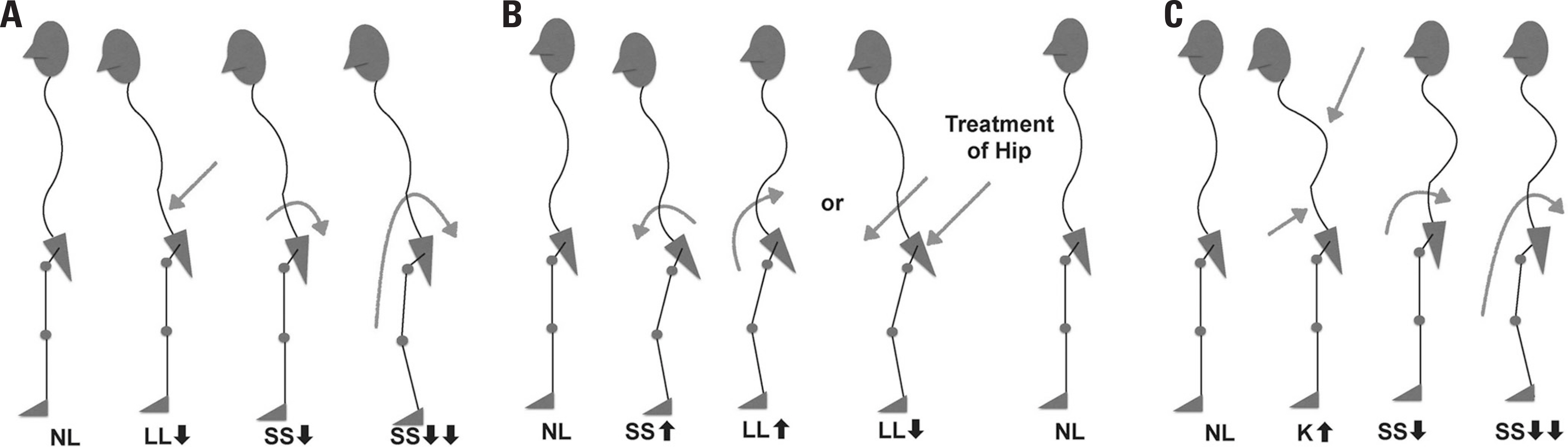
As spinal and pelvic parameters tend to have a strong correlation, it is essential to measure not only spinal parameters but also pelvic parameters in analyzing sagittal balance. Degenerative changes have the potential to greatly disrupt the normal curvature of the spine, leading to sagittal malalignment. Analysis of sagittal balance is crucial to optimizing the management of spinal diseases. Improvement in surgical outcomes may be achieved through better understanding of radiographic spino-pelvic parameters and their association with deformity.
CONCLUSIONS
Understanding spinal and pelvic parameters raises awareness of the relationship among alignment and balance, the soft tissue envelope, and compensatory mechanisms, which will, in turn, provide a more comprehensive understanding of the nature of spinal deformity and the modalities with which it is treated.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Hecquet J, et al. Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J. 1998; 7:99–103.
Article2. Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, et al. Adult spinal deformity— postoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tol-erate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine. 2010; 35:2224–31.3. Dubousset J, Challier V, Farcy J, et al. Spinal alignment versus spinal balance. Global spinal alignment: Principles, pathologies, and procedures book. 2014.4. Kumar M, Baklanov A, Chopin D. Correlation between sagittal plane changes and adjacent segment degeneration following lumbar spine fusion. Eur spine J. 2001; 10:314–9.
Article5. O'Brien M, Kuklo T, Blanke K, el al. Group SDS. Radiographic measurement manual. Medtronic Sofamor Danek: USA;2004.6. Duval-Beaupere G, Schmidt C, Cosson P. A Barycentre-metric study of the sagittal shape of spine and pelvis: the conditions required for an economic standing position. An-nals of biomedical engineering. 1992; 20:451–62.7. Mac-Thiong J-M, Berthonnaud É, Dimar JR, et al. Sagittal alignment of the spine and pelvis during growth. Spine. 2004; 29:1642–7.
Article8. Vaz G, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, et al. Sagittal mor-phology and equilibrium of pelvis and spine. Eur spine J. 2002; 11:80–7.
Article9. Barrey C, Jund Jm, Noseda O, et al. Sagittal balance of the pelvis-spine complex and lumbar degenerative diseases. A comparative study about 85 cases. Eur Spine J. 2007; 16:1459–67.
Article10. Mac-Thiong J-M, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud É, et al. Sagittal parameters of global spinal balance: normative values from a prospective cohort of seven hundred nine Caucasian asymptomatic adults. Spine. 2010; 35:E1193–8.11. Lamartina C, Zavatsky JM, Petruzzi M, et al. Novel con-cepts in the evaluation and treatment of high-dysplastic spondylolisthesis. European Spine Journal. 2009; 18:133–42.
Article12. Rajnics P, Templier A, Skalli W, et al. The association of sagittal spinal and pelvic parameters in asymptomatic per-sons and patients with isthmic spondylolisthesis. J. of spinal disorders & tech. 2002; 15:24–30.13. Labelle H, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud É, et al. Spondylolis-thesis, pelvic incidence, and spinopelvic balance: a correlation study. Spine. 2004; 29:2049–54.14. Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Noseda O, et al. The vertical pro-jection of the sum of the ground reactive forces of a standing patient is not the same as the C7 plumb line: a radiographic study of the sagittal alignment of 153 asymptomatic volunteers. Spine. 2006; 31:E320–5.15. Knight R, Jackson R, Killian J, et al. White paper on sagittal plane alignment. Scoliosis Research Society;2003.16. Guigui P, Levassor N, Rillardon L, et al. [Physiological value of pelvic and spinal parameters of sagital balance: analysis of 250 healthy volunteers]. Revue de chirurgie orthopedique et reparatrice de l'appareil moteur. 2003; 89:496–506.17. Morvan G, Mathieu P, Vuillemin V, et al. Standardized way for imaging of the sagittal spinal balance. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20:602–8.
Article18. Jackson RP, McManus AC. Radiographic Analysis of Sagittal Plane Alignment and Balance in Standing Volunteers and Patients with Low Back Pain Matched for Age, Sex, and Size: A Prospective Controlled Clinical Study. Spine. 1994; 19:1611–8.19. Gelb DE, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, et al. An analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in 100 asymptomatic middle and older aged volunteers. Spine. 1995; 20:1351–8.
Article20. Barrey C, Jund J, Noseda O, et al. Equilibre sagittal pelvi-rachidien et pathologies lombaires dé gé né ratives. Etude comparative apropos de. 2004; 100.21. Barrey C, Roussouly P, Le Huec J-C, et al. Compensatory mechanisms contributing to keep the sagittal balance of the spine. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22:834–41.
Article22. Mac-Thiong J-M, Transfeldt EE, Mehbod AA, et al. Can c7 plumbline and gravity line predict health related quality of life in adult scoliosis? Spine. 2009; 34:E519–27.
Article23. Glassman SD, Berven S, Bridwell K, et al. Correlation of radiographic parameters and clinical symptoms in adult scoliosis. Spine. 2005; 30:682–8.
Article24. Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Glassman SD, et al. Risk-benefit assessment of surgery for adult scoliosis: an analysis based on patient age. Spine. 2011; 36:817–24.25. Rose PS, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Role of pelvic incidence, thoracic kyphosis, and patient factors on sagittal plane correction following pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Spine. 2009; 34:785–91.
Article26. Legaye J. Analysis of the dynamic sagittal balance of the lumbo-pelvi-femoral complex. Biomechanics in applications. ISBN. 2011. 978–53.27. Takemitsu Y, Harada Y, Iwahara T, et al. Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis: Clinical, Radiological and Epidemiological Studies. Spine. 1988; 13:1317–26.28. Korovessis P, Dimas A, Iliopoulos P, et al. Correlative analysis of lateral vertebral radiographic variables and medical outcomes study short-form health survey: a comparative study in asymptomatic volunteers versus patients with low back pain. J. of spinal disorders & techniques. 2002; 15:384–90.29. Obeid I, Hauger O, Aunoble S, et al. Global analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in major deformities: correlation between lack of lumbar lordosis and flexion of the knee. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20:681–5.
Article30. Lafage V, Schwab F, Skalli W, et al. Standing balance and sagittal plane spinal deformity: analysis of spinopelvic and gravity line parameters. Spine. 2008; 33:1572–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spino-Pelvic Parameters in Adult Spinal Deformities
- Evaluation of Global Sagittal Balance in Koreans Adults
- Correlates of Bone Mineral Density and Sagittal Spinal Balance in the Aged
- Basic Pelvic Parameters Associated with Lumbar Degenerative Disease: Review Article
- Radiologic Measurement of Pelvic Sagittal Incidence and Lordosis in Young Korean Women